Кто изобрел самый первый сенсорный телефон
Первая попытка создания сенсорного телефона была успешно реализована 20 лет назад. Времена меняются, новые технологии не стоят на месте, и сейчас сенсорные телефоны заняли твердую позицию на рынке сотовых.

Мы не представляем себе современной жизни без использования сотового телефона, он стал ее неотъемлемой частью. А ведь каких-то лет десять назад не каждый мог позволить себе приобрести сотовый, в основном он считался предметом роскоши.
В настоящее время индустрия мобильной техники динамично развивается, с каждым годом создаются все новые и новые модели. Однако настоящей революцией в этом стали сенсорные телефоны, которые завоевали широкую популярность среди пользователей и практически вытеснили из продаж обычные «кнопочные».
Мало кто это знает, но в действительности первый сенсорный телефон был изобретен в 1993 г. корпорацией IBM, большую часть своей деятельности посвятившей созданию компьютерной техники.
Эта компания была создана в далеком 1896 г. инженером Германом Холлеритом. Первоначально она имела название Tabulating Machine Company и занималась производством счетно-аналитических машин. В 1911 г. произошло слияние ТМС с компаниями Чарльза Флинта – International Time Recording Company и Computing Scale Corporation. В результате данного процесса образовалась корпорация Computing Tabulating Recording (CTR). В 1917 г. компания CTR вышла на рынки Канады под брендом International Business Machines (IBM), а в 1924 г. и американское подразделение сменило название.
Первый сенсорный телефон получил название IBM Simon. В те годы он казался высшим изобретением среди телефонов и произвел настоящий фурор, хотя весил более 0,5 кг и напоминал «кирпич», не имеющий ничего общего с современными легкими гаджетами. При всем том, что его сенсорный экран создавался для работы со стилусом, большую часть операций было возможно проводить пальцами.
Simon был укомплектован черно-белым экраном 160*293 и встроенным модемом. Аккумуляторная батарея была рассчитана на один час непрерывного разговора или на 8-12 часов нахождения в режиме ожидания. Кроме того, в конструкции телефона был предусмотрен специальный слот для дополнительной памяти.
Оперативная система представляла собой одну из версий DOS, которая была разработана компанией Datalight. Телефон имел 1 Мбайт оперативной памяти и 1 Мбайт для различных данных и приложений. В системе IBM Simon было предусмотрено получение факсов, электронной почты, он мог функционировать в качестве пейджера, а также запускал встроенные приложения.
Стоимость такого телефона была непомерно высокой – примерно 900 американских долларов при условии заключения договора с оператором на срок до двух лет или 1100 без этого условия. Несмотря на всю свою уникальность, гаджет часто выходил из строя и обширного распространения среди пользователей не получил. В итоге, компания IBM отказалась от затеи производства мобильных.
Источники:
- Самый первый сенсорный телефон в мире
- IBM Simon – первый в мире смартфон. Что внутри? / Блог компании IBM / Хабрахабр
- IBM: сто лет великой истории
Краткая история появления сенсорных экранов
Автор:
11 января 2019 12:33
Сегодня таким чудом, как сенсорный экран, который позволяет вводить информацию с помощью касаний, уже никого не удивишь. Подавляющее большинство современных смартфонов, планшетных ПК, электронных книг и других гаджетов оснащены подобной технологией. Какова же история появления сенсорного дисплея?

Источник:
Считается, что первое в мире сенсорное устройство появилось благодаря американскому преподавателю Сэмюэлу Хёрсту, которому приходилось вводить огромное количество данных с многочисленных лент самописцев. Это занятие отнимало много времени, было непроизводительным и требовало повышенной концентрации внимания, чтобы не допускать ошибок.
Для автоматизации процесса Хёрст стал разрабатывать сенсорный экран, по которому двигался самописец. Его творение, вышедшее в свет в 1971 году, получило название Elograph.

Источник:
В 1974 году образованная Сэмюэлом Хёрстом компания Elographics выпускает прозрачную сенсорную панель, а еще через несколько лет совместно с Siemens — первый телевизор с сенсорным дисплеем.

В 1983 году от компании Hewlett-Packard миру был представлен компьютер HP-150, который был оборудован сенсорным дисплеем, функционирующим по принципу инфракрасной сетки.

Источник:
Первым сотовым телефоном, имеющим сенсорный экран и выпущенным в 1998 году, стал Alcatel OneTouchCOM. Модель была оснащена небольшим монохромным дисплеем, однако это не помешало ей стать прообразом современного смартфона.

Источник:
Полноцветный дисплей с хорошим разрешением и поддержкой 4096 цветов был представлен компанией HTC в 2002 году. В модели Qtek с маркировкой 1010/02 XDA была использована резистивная технология.
Источник:
Благодаря компании Apple сенсорные дисплеи вышли на новый уровень. После выпуска iPhone в 2007 году устройства с сенсорными дисплеями завоевали невероятную популярность. К тому же, технология Multitouch значительно упростила процесс ввода информации.
Появление сенсорных дисплеев в жизни потребителей заметно упростило управление различного рода гаджетами, но вместе с тем принесло и некоторые неудобства, в первую очередь связанные с «хрупкостью» подобного типа экранов…
Источник:
Еще крутые истории!
Сенсорные телефоны получили широкое распространение. Потому сегодня ими вряд ли кого-то можно удивить. Тем не менее, далеко не каждому человеку известно, когда конкретно появился первый сенсорный телефон. Считается, что саму технологию придумал Сэмюэл Херст, которому требовалось вводить много информации с лент самописцев. Впоследствии этот принцип лег в основу инновационных телефонов, которыми сегодня пользуются люди во всем мире.
IBM Simon
Эту модель часто считают предшественником iPhone. Однако, по сути, она просто представляет собой первый тачфон. После этого девайса появилось много сенсорных устройств.
Сложно, сказать, кто конкретно изобрел первый IBM Simon. Это устройство было выпущено американской компанией IBM в сотрудничестве с телекоммуникационным брендом BellSouth. Впервые девайс был представлен в 1992 году, и тогда он казался чем-то нереальным. В 1994 году устройство поступило в продажу и стоило очень дорого. На тот момент его цена составляла 1090 долларов.
По сути, Simon представляет собой нечто среднее между карманным ПК и телефоном. Впоследствии такие девайсы получили название смартфонов. Также Simon можно было применять как факс и пейджер. В устройство входило много компонентов. Среди них стоит выделить адресную книгу, блокнот, перечень задач. Также устройство дополнялось календарем и калькулятором. В нем присутствовало несколько игр и клиент электронной почты.
Девайс отличался монохромным экраном, диагональ которого составляла 4,7 дюйма. При этом его разрешение было 160х293 пикселя. Физические клавиши на устройстве отсутствовали. Набрать номер или текст удавалось посредством виртуальной клавиатуры и стилуса.
В структуру Simon входил процессор, частота которого составляла 16 мегагерц, слот для карт, 1 мегабайт оперативной памяти. Для зарядки телефона использовалась специальная док-станция. Заряда аккумулятора хватало максимум на 8-12 часов работы в режиме ожидания и на 1 час разговоров и передачи информации. Но за дополнительную плату была возможность купить батарею большей емкости.
Стоит отметить, что новое устройство не получило широкого распространения. Многих потенциальных покупателей испугала высокая стоимость устройства. Девайс выпустили тиражом максимум 5000 экземпляров и вскоре забыли о нем. Тем не менее, устройство сыграло важную роль в технологическом развитии.
Sharp Personal Mobile Communicator MC-G1
Через 3 года после выхода IBM Simon в компании Sharp решили, что рынок созрел к новому девайсу. Результатом этого стал выпуск нового варианта телефона, оснащенного сенсорным дисплеем. Кто конкретно придумал устройство, сказать нельзя. Над созданием этого гаджета трудилась целая команда разработчиков.
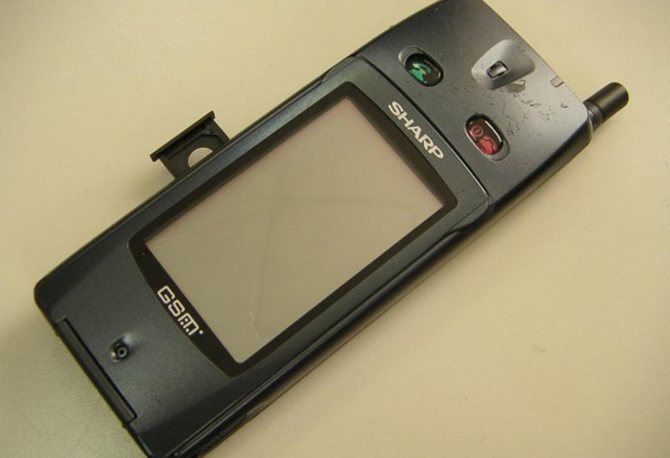

К сожалению, и это устройство не привлекло внимания потенциальных покупателей. Сегодня даже не сохранилось его фото в хорошем качестве. Полный список параметров тоже остался в секрете.
При этом доподлинно известно, что девайс комбинировал телефон и органайзер. С его помощью удавалось отправлять электронные письма, факсы, смс-сообщения. Также девайс оснащался инфракрасным портом. Стилус помогал выполнять рукописные заметки. Защита экрана обеспечивалась прозрачной пластиковой крышкой.
Ericsson R380
Это устройство стало первым мобильным телефоном, которое получило название смартфона. Кто конкретно создал его, установить невозможно. Как и над другими подобными гаджетами, над его разработкой трудилась целая команда специалистов.
В тот период устройство функционировало на новой операционной системе Symbian. В сложенном виде девайс работал, как обыкновенный моноблочный мобильный телефон. Чтобы трансформировать гаджет в смартфон, требовалось убрать клавиатуру, закрывающую сенсорный экран. И в закрытом виде устройством удавалось управлять посредством дисплея. При нажатии кнопок на цифровой клавиатуре они просто касались требуемого участка на дисплее.
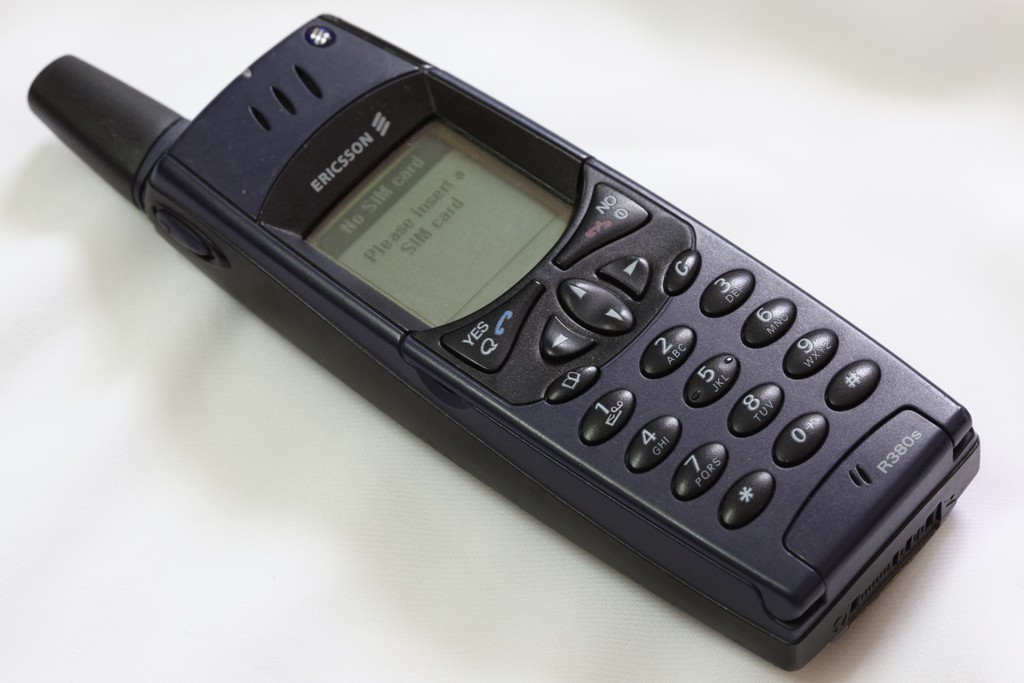

При этом модель Ericsson R380 характеризовалась важными минусами. Она имела довольно высокую стоимость. Помимо этого, несмотря на наличие Symbian, на устройство нельзя было ставить сторонние программы. Но это не помешало девайсу стать предшественником серии популярных смартфонов, среди которых стоит выделить весьма успешную модель Р800.
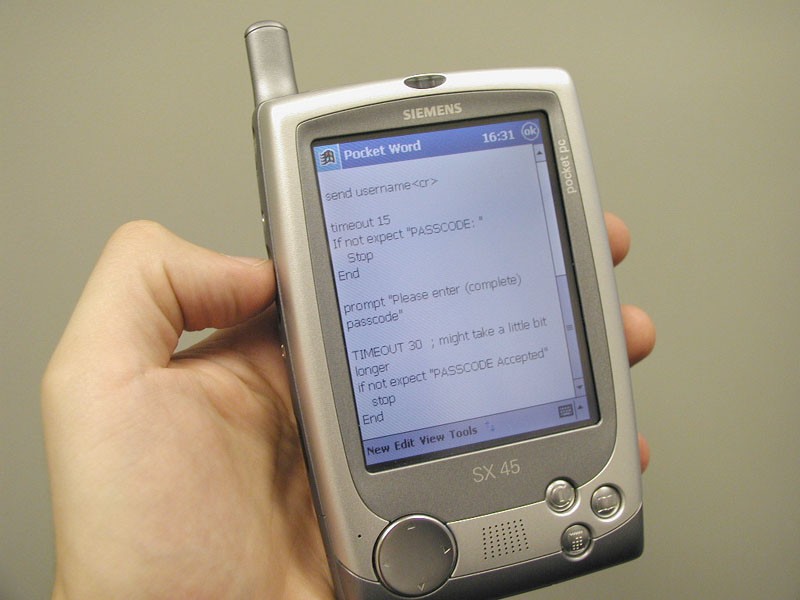
Siemens SX45
По мере развития технологий компания Siemens тоже решила включиться в гонку смартфонов. Однако на тот момент она не обладала своими собственными разработками. Это вынудило представителей бренда заключить договор Casio. Уже в имеющийся КПК Casio Cassiopea E125 установили GSM-модуль и несколько поменяли дизайн. В результате удалось создать один из первых смартфонов, который функционировал на основе операционной системы Microsoft Pocket PC 2000. Она стала предшественницей Windows Mobile.
Модель Siemens SX45 выпустили в 2001 году. Ее единственным минусом стало отсутствие микрофона. При этом динамик находился под дисплеем. Потому для разговора приходилось использовать гарнитуру.
Устройство обладало дисплеем размером 3,5 дюйма. При этом разрешение экрана составляло 240х320 точек. Также прибор отличался частотой 150 мегагерц и функцией поддержки карт памяти.

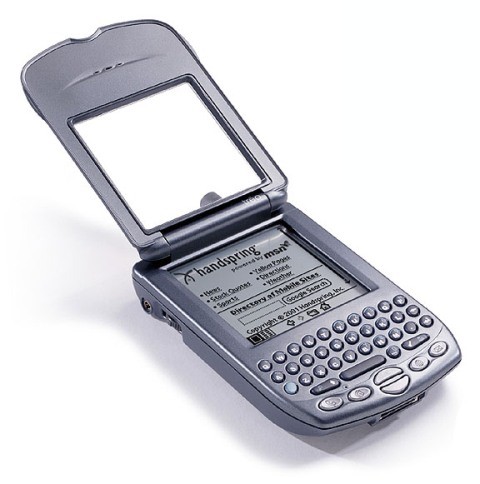
Palm Treo 180
Коммуникаторы, которые управлялись операционной системой Palm, стали появляться еще до Treo. Дело в том, что бренд активно продавал свою платформу другим компаниями. Однако именно Treo стала воплощением знаковой ОС, которая в настоящее время уже не используется.
Одним из первых смартфонов стала модель Treo 180. Вначале ее выпускал бренд Handspring. Но после объединения с Palm компания стала вызывать более стойкие ассоциации с линейкой Treo. Устройство оснащалось дисплеем с 16 оттенками серого цвета. Также оно имело крышку и физическую клавиатуру QWERTY.
Тогда же на рынок вышла модификация Treo 180g. Вместо клавиатуры она оснащалась полем, которое помогало распознавать рукописный текст и символы.

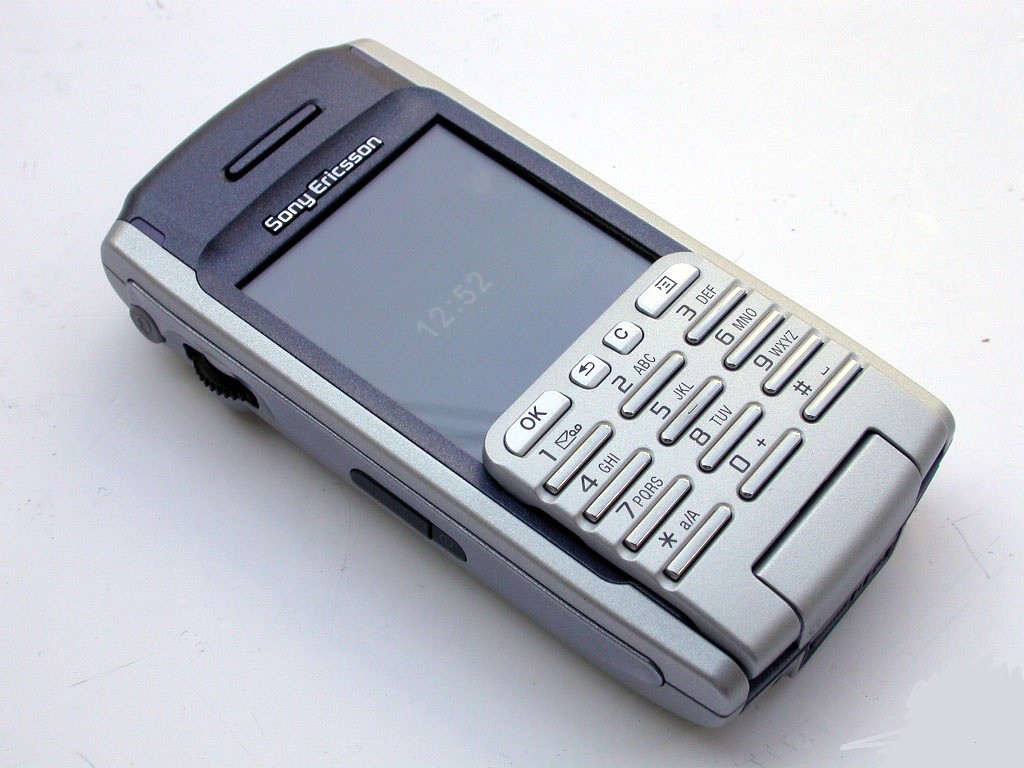
Sony Ericsson P900
Это устройство представляет собой первый вариант сенсорного коммуникатора на основе операционной системы Symbian, которая представляет собой платформу UIQ. Девайс имел экран 2,9 дюйма. Он отличался разрешением 208х320 пикселей, 16 мегабайтами памяти, процессором с частотой 156 мегагерц, Bluetooth и камерой 0,3 мегапикселя. Главной особенностью девайса была откидная крышка. В сложенном виде устройство представляло собой обыкновенный мобильный телефон.
В 2004 году появилась следующая модель Р910. Она не только оснащалась цифровой клавиатурой, но и QWERTY, которая также находилась на откидном блоке.

Philips 550/755/759
Это первый обычный телефон, который оснащался сенсорным экраном. В серии выпустили 3 устройства. Так, модели 755 и 759 отличались от 550 наличием инфракрасных портов и камер. При этом разница между устройствами касалась дизайна. 759 модель выглядела брутально, а 755 – стильно.
Сенсорный дисплей, прежде всего, использовался для отправки MMS. Стилус позволял рисовать изображения с нуля или заниматься редактированием фото. Также в комплекте присутствовала экранная клавиатура QWERTY. Однако она была мелкой и неудобной. Тем не менее, обзоры того времени отмечали, что использовать эту клавиатуру для набора текста было удобнее, чем обыкновенные кнопки.
В целом, устройство не стало особо успешным, поскольку его интерфейс был не особо хорошо приспособлен к сенсорному управлению. К тому же девайс отличался медленной работой. Эти телефоны стоили дороже, чем такие же устройства без тачскринов.

Neonode N1
В свое время это устройство стало настоящим прорывом в развитии технологий. В 2001-2002 годах небольшая шведская фирма Neonode первой предложила концепцию смартфона с удобным интерфейсом, управление которым можно было осуществлять исключительно при помощи пальцев. Это произошло в те времена, когда даже устройства со стилусами были новинкой.
Теоретически модель Neonode N1 могла стать прорывом вместо iPhone. Тем более, что она появилась на несколько лет раньше. Однако судьба распорядилась по-другому. Изначально в Neonode все время сдвигали сроки выпуска девайса.
После того, как устройство все-таки появилось в продаже, оно оказалось не самым удобным. Тем не менее, этот девайс по праву считается революционным. В нем использовался нестандартный метод реализации сенсорного управления. При этом по краям дисплея устанавливалось 17 инфракрасных датчиков. Они помогали телефону отслеживать место касания экрана. Безусловно, на тот момент добиться высокой точности не удалось. Однако, по крайней мере, устройство не требовало сильного давления, как при использовании резистивных дисплеев.
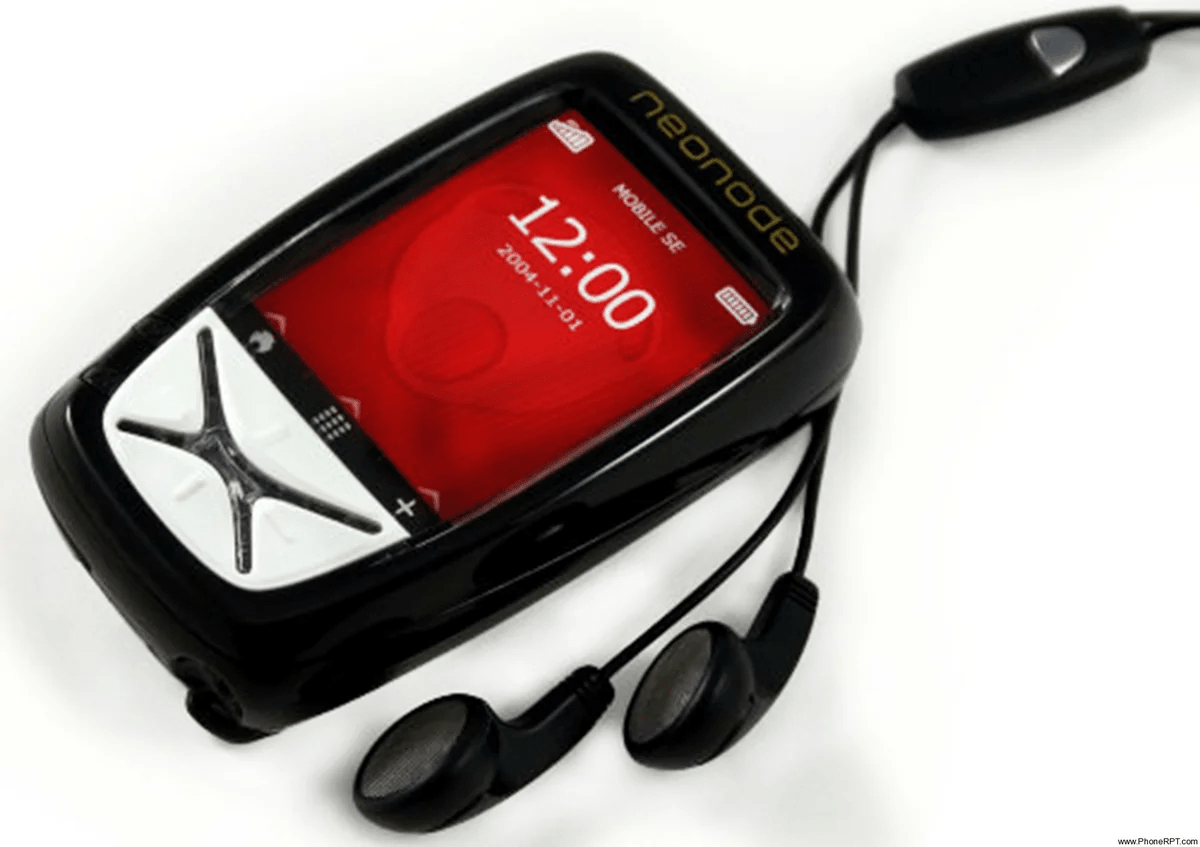

Характерной особенностью устройства стали его небольшие размеры. Оно было сопоставимо по габаритам с банковской картой. Однако и дисплей из-за этого был очень маленьким. Его размер не превышал 2,2 дюйма. Однако тогда эта особенность не подвергалась критике. В 2001-2002 годах смартфоны отличались огромными размерами. Дело в том, что операционная система Microsoft с ее небольшими деталями и шрифтами требовала больших дисплеев и стилуса. При этом ОС Symbian изначально вообще не сочеталась с тачскринами.
Еще одной характеристикой устройства стало жестовое управление. К примеру, вместо нажатия на «ок» требовалось провести пальцем слева направо. Для отмены это требовалось сделать в обратную сторону. В тот период ничего подобного не существовало.
При этом многих интересуют причины провала продаж. Их было несколько. Прежде всего, фирма Neonode слишком долго откладывала выпуск устройства. К тому же бренд все-таки не мог конкурировать с более известными компаниями. Также он испытывал трудности с каналами продаж. Телефон можно было заказать исключительно через Интернет. При этом продавался он только в европейских странах. На постсоветском пространстве предпринимались попытки наладить розничный сбыт, однако они провалились.
Девайс работал на основе Windows Compact Edition, которая представляла собой урезанный вариант настольной операционной системы с оболочкой от Neonode сверху. Поставить сторонние программы было невозможно. При этом набор встроенных приложений был весьма ограничен. Телефон не поддерживал MMS и запись видео. Он не имел почтового клиента и Bluetooth. При этом устройство стоило дорого.
В 2005 году появился улучшенный вариант Neonode N1m. Эта модель поддерживала много диапазонов GSM, оснащалась виброзвонком и камерой высокого разрешения. Также устройство имело новое ядро ОС Windows CE. Тем не менее, это не привело к заметному росту продаж.
Nokia 7710
Первый сенсорный телефон от Nokia функционировал на основе Symbian Series 90 и ориентировался на применение в горизонтальном развороте. Устройство дополнял дисплей размером 3,5 дюйма. При этом его разрешение составляло 640х320 пикселей. Телефон имел 90 мегабайт встроенной памяти и специальный слот для карт. Камера поддерживала запись видео.
Главным минусом устройства стало использование редкой платформы, в силу чего выбор программных продуктов для девайса был весьма скудным. При этом встроенный набор был весьма неплохим. Телефон оснащался полноценным органайзером и почтовым клиентом. В общем, интерфейс получился весьма неплохим, но отличался крайне медленной работой.

HTC Magician
Смартфон Qtek S100 компании HTC с 2005 года продавался под различными названиями. В Азии он назывался 2 Xda II Mini, а в Германии – O2 Xda mini. Также встречались такие названия, как Dopod 818, Vodafone VPA Compact и другие.
Девайс функционировал на основе Windows Mobile 2003. Он имел 64 мегабайта встроенной и такое же количество оперативной памяти. Также в комплект входил слот для карт SDIO/MMC, экран размером 2,8 дюйма, камера 1,3 мегапикселя. Плюсом устройства была сравнительно невысокая стоимость. Оно отличалось удобством и небольшими размерами.

ASUS P525
Эта модель обладала достаточно большим экраном. Его размер составлял 2,8 дюйма, а разрешение 240х320 пикселей. Также к отличительным особенностям устройства стоит отнести наличие QWERTY-клавиатуры, корпуса, оснащенного металлическими элементами, камеры 2 мегапикселя с автофокусом, 64 мегабайта оперативной памяти. Также девайс обеспечивал поддержку Wi-Fi и включал джойстик.
При этом изначально телефон сильно глючил. На нем исчезали сигналы, отменялись вызовы, выключался звук. Однако производитель постоянно выпускал все новые прошивки, которые помогли избавиться от проблем, и телефон стал удобнее.

Fujitsu Siemens Pocket LOOX T810
В 2000 годы появилась модель LOOX T810. Она поддерживала самые разные технологии – 3G, GPS, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi. Устройство имело камеру 2 мегапикселя, клавиатуру QWERTY и экран размером 2,4 дюйма. Телефон оснащался процессором с частотой 416 мегагерц и имел 128 мегабайт встроенной памяти и 64 мегабайта оперативной.
Sony Ericsson M600
Этот телефон отличался эффектным дизайном. Он оснащался дисплеем размером 2,6 дюйма и функционировал на основе Symbian UIQ. Работа девайса управлялась процессором Philips, частота которого составляла 208 мегагерц. Телефон имел 64 мегабайта памяти и слот для карт.
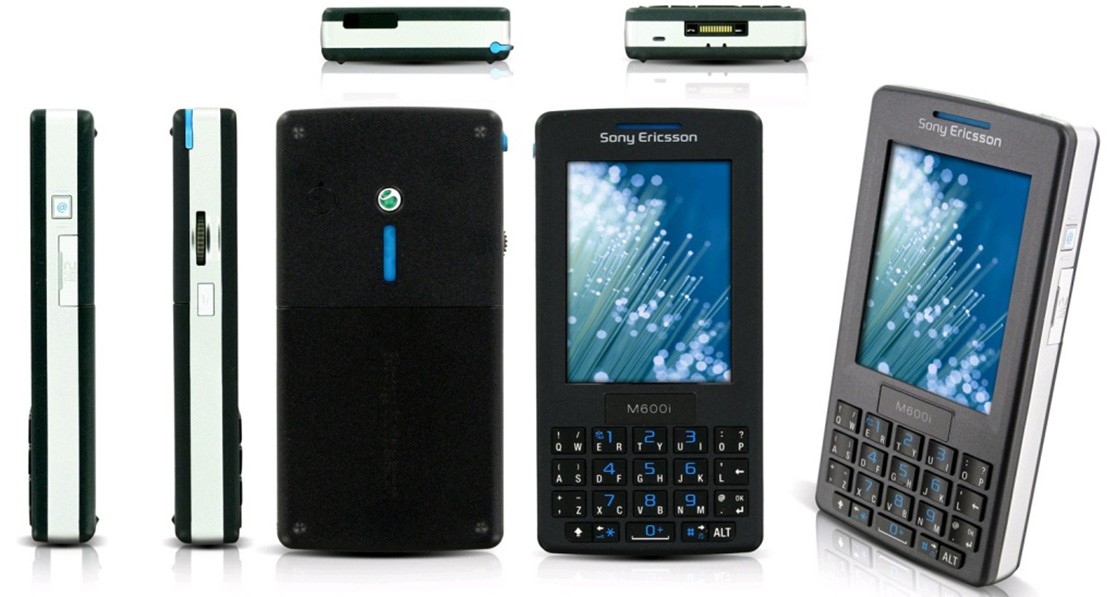

При этом камера у этой модели отсутствовала. Это было связано не с соображениями экономии, а с тем, что телефон предназначался для бизнеса. На множестве предприятий в тот период применение устройств с камерами было запрещено.
Toshiba Portege G900
В начале 2007 года появился продвинутый бизнес-коммуникатор Toshiba G900. Он функционировал на основе Windows Mobile 6 Professional, обеспечивал поддержку 3G, имел 128 мегабайт оперативной памяти и экран размером 3 дюйма. Для него было характерно достаточно высокое на тот момент разрешение 480х800. Также телефон оснащался выдвижной клавиатурой QWERTY и 2 камерами.
LG Prada
Эта модель стала первым мобильным телефоном, оснащенным сенсорным дисплеем емкостного типа. Это произошло в январе 2007 года, опередив на месяц знаменитую новинку компании Apple. Хотя Prada вышел первым, за 1,5 года LG сумела продать всего 1 миллион таких устройств, тогда как годовые объемы Apple превысили 6 миллионов iPhone.
Появление первого сенсорного телефона стало своего рода прорывом в развитии мобильных технологий. Такие устройства выпустили многие компании, однако все они отличались разной востребованностью среди потребителей.
Магнитный держатель для телефона в автомобиль
Сегодня, такое уникальное явление, как сенсорный экран мобильного устройства, позволяющий набирать информацию и развлекаться в различных приложениях только с помощью касаний, никого уже не удивляет. Рынок мобильной техники почти полностью перешел на современные тенденции с использованием данной технологии: персональные компьютеры, планшеты, девайсы, даже приставки — практически каждое устройство оснащено сенсорным дисплеем.
Однако, мало кто знает, когда и чего начиналось развитие мобильных технологий, как выглядели первые сенсорные устройства и какими техническими особенностями они обладали.

Смарт часы умные детские GPS
Содержание
- Развитие смартфонов
- Первый сенсорный телефон в мире
- Первый сенсорный телефон в России
- Кто придумал сенсорный телефон
- IBM Simon
- Первый смартфон с сенсорным экраном
Развитие смартфонов
Согласно некоторым данным, первый в мире девайс, реагирующий на касания по экрану, появился благодаря педагогу Сэмюэлю Хёрсту, который происходил родом из Америки. Его ежедневной работой являлось переписывание большого количества информации с многочисленных лент самописцев. Задача являлась монотонной и энергозатратной, отнимала много и времени и требовала максимальной концентрации внимания во избежание ошибок.
Чтобы автоматизировать процесс, преподаватель задумался над созданием сенсорного дисплея, по которому скользил измерительный прибор.
Изобретение Сэмюэля Хёрста, под названием Elograph увидело свет в 1971 году. Через три года, основанная американским педагогом компания Elographics презентует сенсорную консоль, а еще через пару лет, совместными усилиями с Siemens, выпускает первый полноэкранный сенсорный телевизор.
Wi-Fi роутер

Одним из первых девайсов с сенсорным тачпадом стал смартфон карманного размера — Alcatel OneTouchCOM, презентованный в 1998 году.
Аппарат имел небольшой монохромный экран, но это только подтолкнуло производителей использовать данную модель в качестве образца, и дало понимание, в каком направлении нужно развиваться.
Беспроводные наушники Air P SmartAIR

Качественный полноразмерный дисплей, отражающий все цвета с хорошим разрешением, был выпущен брендом НТС в начале 2000-х годов. Телефон получил название T-Mobile G1.
Магнитное беспроводное зарядное устройство

T-Mobile G1 — смартфон, выполненный в слайдерной конструкции, то есть его дисплей выдвигался, предоставляя пользователю доступ к раскладной клавиатурной панели. На тот момент никто даже не догадывался, что через некоторое время механику будет успешно заменена сенсорными тачпадами.
Сегодня технические параметры модели T-Mobile G1 кажутся смешными и несуразными, но тогда они являлись инновационными и уникальными:
Гидрогелевая пленка на заднюю крышку телефона
- дисплей диагональю 3,2 дюйма с доступным разрешением 320*480 пикселей;
- оперативная память составляла всего 192 мегабайта;
- процессор был выполнен с одним ядром на 528 ГГц.
Аппарат был разработан совместно с американским оператором T-Mobile и ориентирован на потребительский рынок Соединенных Штатов. На территории России смартфон поставлялся, как и первые изобретения iPhone, через интернет-магазин eBay.
Интересно! Модель Qtek, 1010/0 XDA, также презентованная компанией НТС, но несколько позже, была выполнена с использованием резистивного метода — фиксировались электрические сопротивления части системы в момент касания экрана пальцами.
Следующей презентацией, которая взорвала рынок мобильных устройств, стал выпуск первого iPhone в 2007 году. С тех пор сенсорные экраны стали пользоваться большим спросом среди пользователей.
Первым была модель iPhone 2G, которая позже была доработана и представлена в лучшей сборке по всему миру.
3D Увеличитель экрана телефона складной

Чем полезна технология мультитач, внедряемая на текущий момент в современные мобильные аппараты:
- возросло удобство пользования смартфонами, расширились функциональные возможности;
- ускорился процесс ввода данных.
Однако имеются и некоторые недостатки, выражающиеся в:
- хрупкости подобного типа дисплеев — царапины, трещины, все это отпечатывается на экране;
- высокой цене.
Apple Телефон
Первый сенсорный телефон в мире
Первым смартфоном с технологией мультитач, который имел сенсорный экран, считается модель IBM Simon. Ее конструкция была неудобной, форма была подобна кирпичу.

Интересно! В истории не отпечатались имена производителей, работающих над этой моделью. Фактом остается то, что аппарат был создан благодаря экспериментальной деятельности группы японских инженеров, работающих в компании Mitsubishi Electric.
Макролинза для телефона, объектив для телефона
Телефон был оснащен самыми примитивными функциями, которыми должен обладать каждый аппарат для связи — часы, книга номеров и калькулятор. Полноценная технология Multitouch здесь не была реализована — смартфон откликался лишь на касания экрана, осуществленные специальным стилусом.
Цена такого удовольствия на то время была достаточно высока — около 1000 долларов. Невзирая на первопроходство и инновационные внедрения, изобретение не было признано, а позже компания перестала производить мобильные аппараты.
Следующая информация о сенсорных телефонах встречалась в Японских источниках. В 1998 году предприятие Sharp презентовало смартфон с технологией сенсорного касания. Тогда и была презентована модель Alcatel OneTouchCOM. Однако и эти труды не получили должного признания, поэтому на некоторое время о подобного рода изобретениях все забыли.
3G/ 4G модем
Первый сенсорный телефон в России
Подавляющее большинство пользователей уверены, что первые сенсорные смартфоны, появившиеся на территории России, были презентованы компанией iPhone, что является большим заблуждением.
Такой тип телефонов, включающих в себя достаточные функциональные возможности как мобильного девайса, так и персонального компьютера, был предложен шведской компанией Ericsson еще в далеких нулевых годах.
Телефоны шведской компании Ericsson не получили тогда должного внимания и поддержки и ушли с российского рынка.
Следующим производителем, который презентовал сенсорные девайсы в России, стала финская компания Nokia классификации N.
Держатель для телефона для видео гибкий
Первый такой аппарат был разработан и презентован в 2006 году и носил название Nokia N73. Устройство, по сравнению с себе подобными, было оснащено достаточно большим количеством функциональных возможностей, хоть и было разработано на базе языка программирования Java.

На тот момент также выпускались сотовые мобильники, функционирующие на основе Windows. Они подобно изобретению Symbian, имели широкий спектр возможностей как коммуникативных, так и мультимедийных.
Внешний аккумулятор Power Bank
Кто придумал сенсорный телефон
Первым, кто придумал сенсорный смартфон, можно назвать Сэмюэля Херста, однако наиболее гармоничным, развитым и компактным стало устройство компании IBM.
Корпорация IBM, занимающаяся разработкой и производством компьютерной техники, выпустила в свет первый более-менее адекватный мобильник в 1993 году.
Интересно! Корпорация была основана американским инженером Германом Холлеритом в далеком 1896 году. Тогда она носила название Tabulating Machine Company, а главной ее задачей являлась разработка и выпуск счетно-аналитических приборов.
Стилус ручка GSMIN D13 для смартфона
IBM Simon
Первый сенсорный смартфон не был классифицирован, а получил примитивное и короткое название, созвучное именования корпорации — IBM Simon. Тогда он являлся чем-то невероятным, представленным на рынке техники, хотя вес его составлял более 500 граммов, а габариты были подобны кирпичу — ничего схожего с обычными гаджетами нынешнего времени.

Хоть модель IBM Simon и была рассчитана не для сенсорного управления, осуществляемого касаниями пальцев — на экране работали именно стилусом, аппарат все-таки отзывался на большинство касаний человеческих пальцев.
Смартфон TECNO POVA
Технические параметры мобильного аппарата были такими:
- черно-белый дисплей с допустимым разрешением 160*293 пикселя;
- встроенный модем, по которому осуществлялось соединение с другими устройствам;
- емкости аккумулятора хватало на 45-60 минут беспрерывного использования или на 12 часов, в случае если гаджет находился в выключенном состоянии;
- встроенной памяти на телефоне было всего 1 мегабайт;
- оригинальный и новый дизайн;
- имелся специальный разъем для установки карты памяти.
Операционная система Windows Mobile была рассчитана на получение различного рода электронных писем, на передачу голосовыми и письменными сообщениями, а также открывала уже имеющиеся в девайсе игры и приложения.
Стоил коммуникатор невероятного дорого — порядка 900 долларов, если заключался договор с оператором на несколько лет, если это условие не выполнялось, стоимость повышалась до 1100 долларов.
Невзирая на свое первопроходство, телефон часто ломался, происходили сбои в системе, поэтому должного признания среди публики он не получил, в результате чего корпорация IBM оставила идею изобретать детали и заниматься производством и продажей мобильных аппаратов.
Металлический складной держатель — кольцо для телефона
Первый смартфон с сенсорным экраном
На протяжении многих лет производители различных фирм пытались обуздать очень большие габариты создаваемых устройств и сделать их действительно карманными. Ведь те габариты смартфонов, которые были представлены на рынке техники вплоть до нулевых годов, невозможно было назвать приемлемыми для использования.
Уже в эпоху 90-х японские инженеры смогли соединить не самый практичный карманный персональный компьютер и телефон, дав ему название Sharp Personal Mobile Communicator MC-G1.
Подставка для телефона настольная
Новая модель Sharp Personal Mobile Communicator версии MC-G1 не была особо популярной, но стала первой в своем роде. Гаджет обладал широким спектром функциональных возможностей: использовался в роли звонилки, инструментов (калькулятор), развлечений (игры) и для передачи электронных писем.
Следующим, в 2000 году, вышел смартфон Ericsson R380, который набрал больше славы, благодаря профессиональному продвижению — реклама и расписанные преимущества модели были повсюду.

С тех пор мобильные телефоны стали набирать обороты в разработке и презентации на рынке техники. Среди множества однотипных, не совсем усовершенствованных аппаратов, выстрелило устройство Nokia 7710, презентованная в 2005 году.
Прозрачный чехол COMMO

Ее технические характеристики отличались следующими нововведениями:
- сенсорный экран с высоким разрешением;
- поддерживался офисный пакет MS Office;
- не было механической клавиатуры, она сменилась на сенсорную панель.
Так, мало-помалу, производители стали совершенствовать свои гаджеты, опираясь на ошибки и недоработки других компаний. Революция наступила с появлением на рынке смартфонов первого iPhone компании Apple, после чего появились и другие производители, создающие достойную продукцию, а до того времени люди довольствовались не самыми практичными и системно работающими телефонами Symbian.
Сетевое зарядное устройство COMMO

A user operating a touchscreen

A touchscreen or touch screen is the assembly of both an input (‘touch panel’) and output (‘display’) device. The touch panel is normally layered on the top of an electronic visual display of an information processing system. The display is often an LCD, AMOLED or OLED display while the system is usually used in a laptop, tablet, or smartphone. A user can give input or control the information processing system through simple or multi-touch gestures by touching the screen with a special stylus or one or more fingers.[1] Some touchscreens use ordinary or specially coated gloves to work while others may only work using a special stylus or pen. The user can use the touchscreen to react to what is displayed and, if the software allows, to control how it is displayed; for example, zooming to increase the text size.
The touchscreen enables the user to interact directly with what is displayed, rather than using a mouse, touchpad, or other such devices (other than a stylus, which is optional for most modern touchscreens).[2]
Touchscreens are common in devices such as game consoles, personal computers, electronic voting machines, and point-of-sale (POS) systems. They can also be attached to computers or, as terminals, to networks. They play a prominent role in the design of digital appliances such as personal digital assistants (PDAs) and some e-readers. Touchscreens are also important in educational settings such as classrooms or on college campuses.[3]
The popularity of smartphones, tablets, and many types of information appliances is driving the demand and acceptance of common touchscreens for portable and functional electronics. Touchscreens are found in the medical field, heavy industry, automated teller machines (ATMs), and kiosks such as museum displays or room automation, where keyboard and mouse systems do not allow a suitably intuitive, rapid, or accurate interaction by the user with the display’s content.
Historically, the touchscreen sensor and its accompanying controller-based firmware have been made available by a wide array of after-market system integrators, and not by display, chip, or motherboard manufacturers. Display manufacturers and chip manufacturers have acknowledged the trend toward acceptance of touchscreens as a user interface component and have begun to integrate touchscreens into the fundamental design of their products.
History[edit]

One predecessor of the modern touch screen includes stylus based systems. In 1946, a patent was filed by Philco Company for a stylus designed for sports telecasting which, when placed against an intermediate cathode ray tube display (CRT) would amplify and add to the original signal. Effectively, this was used for temporarily drawing arrows or circles onto a live television broadcast, as described in US 2487641A, Denk, William E, «Electronic pointer for television images», issued 1949-11-08. Later inventions built upon this system to free telewriting styli from their mechanical bindings. By transcribing what a user draws onto a computer, it could be saved for future use. See US 3089918A, Graham, Robert E, «Telewriting apparatus», issued 1963-05-14.
The first version of a touchscreen which operated independently of the light produced from the screen was patented by AT&T Corporation US 3016421A, Harmon, Leon D, «Electrographic transmitter», issued 1962-01-09. This touchscreen utilized a matrix of collimated lights shining orthogonally across the touch surface. When a beam is interrupted by a stylus, the photodetectors which no longer are receiving a signal can be used to determine where the interruption is. Later iterations of matrix based touchscreens built upon this by adding more emitters and detectors to improve resolution, pulsing emitters to improve optical signal to noise ratio, and a nonorthogonal matrix to remove shadow readings when using multi-touch.
The first finger driven touch screen was developed by Eric Johnson, of the Royal Radar Establishment located in Malvern, England, who described his work on capacitive touchscreens in a short article published in 1965[8][9] and then more fully—with photographs and diagrams—in an article published in 1967.[10] The application of touch technology for air traffic control was described in an article published in 1968.[11] Frank Beck and Bent Stumpe, engineers from CERN (European Organization for Nuclear Research), developed a transparent touchscreen in the early 1970s,[12] based on Stumpe’s work at a television factory in the early 1960s. Then manufactured by CERN, and shortly after by industry partners,[13] it was put to use in 1973.[14]
In the mid-1960s, another precursor of touchscreens, an ultrasonic-curtain-based pointing device in front of a terminal display, had been developed by a team around Rainer Mallebrein [de] at Telefunken Konstanz for an air traffic control system.[15] In 1970, this evolved into a device named «Touchinput-Einrichtung» («touch input facility») for the SIG 50 terminal utilizing a conductively coated glass screen in front of the display.[16][15] This was patented in 1971 and the patent was granted a couple of years later.[16][15] The same team had already invented and marketed the Rollkugel mouse RKS 100-86 for the SIG 100-86 a couple of years earlier.[16]
In 1972, a group at the University of Illinois filed for a patent on an optical touchscreen[17] that became a standard part of the Magnavox Plato IV Student Terminal and thousands were built for this purpose. These touchscreens had a crossed array of 16×16 infrared position sensors, each composed of an LED on one edge of the screen and a matched phototransistor on the other edge, all mounted in front of a monochrome plasma display panel. This arrangement could sense any fingertip-sized opaque object in close proximity to the screen. A similar touchscreen was used on the HP-150 starting in 1983. The HP 150 was one of the world’s earliest commercial touchscreen computers.[18] HP mounted their infrared transmitters and receivers around the bezel of a 9-inch Sony cathode ray tube (CRT).
In 1977, an American company, Elographics – in partnership with Siemens – began work on developing a transparent implementation of an existing opaque touchpad technology, U.S. patent No. 3,911,215, October 7, 1975, which had been developed by Elographics’ founder George Samuel Hurst.[19] The resulting resistive technology touch screen was first shown on the World’s Fair at Knoxville in 1982.[20]
In 1984, Fujitsu released a touch pad for the Micro 16 to accommodate the complexity of kanji characters, which were stored as tiled graphics.[21] In 1985, Sega released the Terebi Oekaki, also known as the Sega Graphic Board, for the SG-1000 video game console and SC-3000 home computer. It consisted of a plastic pen and a plastic board with a transparent window where pen presses are detected. It was used primarily with a drawing software application.[22] A graphic touch tablet was released for the Sega AI computer in 1986.[23][24]
Touch-sensitive control-display units (CDUs) were evaluated for commercial aircraft flight decks in the early 1980s. Initial research showed that a touch interface would reduce pilot workload as the crew could then select waypoints, functions and actions, rather than be «head down» typing latitudes, longitudes, and waypoint codes on a keyboard. An effective integration of this technology was aimed at helping flight crews maintain a high level of situational awareness of all major aspects of the vehicle operations including the flight path, the functioning of various aircraft systems, and moment-to-moment human interactions.[25]
In the early 1980s, General Motors tasked its Delco Electronics division with a project aimed at replacing an automobile’s non-essential functions (i.e. other than throttle, transmission, braking, and steering) from mechanical or electro-mechanical systems with solid state alternatives wherever possible. The finished device was dubbed the ECC for «Electronic Control Center», a digital computer and software control system hardwired to various peripheral sensors, servos, solenoids, antenna and a monochrome CRT touchscreen that functioned both as display and sole method of input.[26] The ECC replaced the traditional mechanical stereo, fan, heater and air conditioner controls and displays, and was capable of providing very detailed and specific information about the vehicle’s cumulative and current operating status in real time. The ECC was standard equipment on the 1985–1989 Buick Riviera and later the 1988–1989 Buick Reatta, but was unpopular with consumers—partly due to the technophobia of some traditional Buick customers, but mostly because of costly technical problems suffered by the ECC’s touchscreen which would render climate control or stereo operation impossible.[27]
Multi-touch technology began in 1982, when the University of Toronto’s Input Research Group developed the first human-input multi-touch system, using a frosted-glass panel with a camera placed behind the glass. In 1985, the University of Toronto group, including Bill Buxton, developed a multi-touch tablet that used capacitance rather than bulky camera-based optical sensing systems (see History of multi-touch).
The first commercially available graphical point-of-sale (POS) software was demonstrated on the 16-bit Atari 520ST color computer. It featured a color touchscreen widget-driven interface.[28] The ViewTouch[29] POS software was first shown by its developer, Gene Mosher, at the Atari Computer demonstration area of the Fall COMDEX expo in 1986.[30]
In 1987, Casio launched the Casio PB-1000 pocket computer with a touchscreen consisting of a 4×4 matrix, resulting in 16 touch areas in its small LCD graphic screen.
Touchscreens had a bad reputation of being imprecise until 1988. Most user-interface books would state that touchscreen selections were limited to targets larger than the average finger. At the time, selections were done in such a way that a target was selected as soon as the finger came over it, and the corresponding action was performed immediately. Errors were common, due to parallax or calibration problems, leading to user frustration. «Lift-off strategy»[31] was introduced by researchers at the University of Maryland Human–Computer Interaction Lab (HCIL). As users touch the screen, feedback is provided as to what will be selected: users can adjust the position of the finger, and the action takes place only when the finger is lifted off the screen. This allowed the selection of small targets, down to a single pixel on a 640×480 Video Graphics Array (VGA) screen (a standard of that time).
Sears et al. (1990)[32] gave a review of academic research on single and multi-touch human–computer interaction of the time, describing gestures such as rotating knobs, adjusting sliders, and swiping the screen to activate a switch (or a U-shaped gesture for a toggle switch). The HCIL team developed and studied small touchscreen keyboards (including a study that showed users could type at 25 wpm on a touchscreen keyboard), aiding their introduction on mobile devices. They also designed and implemented multi-touch gestures such as selecting a range of a line, connecting objects, and a «tap-click» gesture to select while maintaining location with another finger.
In 1990, HCIL demonstrated a touchscreen slider,[33] which was later cited as prior art in the lock screen patent litigation between Apple and other touchscreen mobile phone vendors (in relation to U.S. Patent 7,657,849).[34]
In 1991–1992, the Sun Star7 prototype PDA implemented a touchscreen with inertial scrolling.[35] In 1993, IBM released the IBM Simon the first touchscreen phone.
An early attempt at a handheld game console with touchscreen controls was Sega’s intended successor to the Game Gear, though the device was ultimately shelved and never released due to the expensive cost of touchscreen technology in the early 1990s.
The first mobile phone with a capacitive touchscreen was LG Prada released in May 2007 (which was before the first iPhone).[36] By 2009, touchscreen-enabled mobile phones were becoming trendy and quickly gaining popularity in both basic and advanced devices.[37][38] In Q4 2009 for the first time, a majority of smartphones (i.e. not all mobile phones) shipped with touchscreens over non-touch.[39]
Touchscreens would not be popularly used for video games until the release of the Nintendo DS in 2004.[40] Until recently,[when?] most consumer touchscreens could only sense one point of contact at a time, and few have had the capability to sense how hard one is touching. This has changed with the commercialization of multi-touch technology, and the Apple Watch being released with a force-sensitive display in April 2015.
In 2007, 93% of touchscreens shipped were resistive and only 4% were projected capacitance. In 2013, 3% of touchscreens shipped were resistive and 90% were projected capacitance.[41]
Technologies[edit]
There is a variety of touchscreen technologies with different methods of sensing touch.[32]
Resistive[edit]
A resistive touchscreen panel comprises several thin layers, the most important of which are two transparent electrically resistive layers facing each other with a thin gap between. The top layer (that which is touched) has a coating on the underside surface; just beneath it is a similar resistive layer on top of its substrate. One layer has conductive connections along its sides, the other along top and bottom. A voltage is applied to one layer and sensed by the other. When an object, such as a fingertip or stylus tip, presses down onto the outer surface, the two layers touch to become connected at that point.[42] The panel then behaves as a pair of voltage dividers, one axis at a time. By rapidly switching between each layer, the position of pressure on the screen can be detected.
Resistive touch is used in restaurants, factories and hospitals due to its high tolerance for liquids and contaminants. A major benefit of resistive-touch technology is its low cost. Additionally, as only sufficient pressure is necessary for the touch to be sensed, they may be used with gloves on, or by using anything rigid as a finger substitute. Disadvantages include the need to press down, and a risk of damage by sharp objects. Resistive touchscreens also suffer from poorer contrast, due to having additional reflections (i.e. glare) from the layers of material placed over the screen.[43] This is the type of touchscreen that was used by Nintendo in the DS family, the 3DS family, and the Wii U GamePad.[44]
Surface acoustic wave[edit]
Surface acoustic wave (SAW) technology uses ultrasonic waves that pass over the touchscreen panel. When the panel is touched, a portion of the wave is absorbed. The change in ultrasonic waves is processed by the controller to determine the position of the touch event. Surface acoustic wave touchscreen panels can be damaged by outside elements. Contaminants on the surface can also interfere with the functionality of the touchscreen.
SAW devices have a wide range of applications, including delay lines, filters, correlators and DC to DC converters.
Capacitive[edit]

Capacitive touchscreen of a mobile phone

The Casio TC500 Capacitive touch sensor watch from 1983, with angled light exposing the touch sensor pads and traces etched onto the top watch glass surface.
A capacitive touchscreen panel consists of an insulator, such as glass, coated with a transparent conductor, such as indium tin oxide (ITO).[45] As the human body is also an electrical conductor, touching the surface of the screen results in a distortion of the screen’s electrostatic field, measurable as a change in capacitance. Different technologies may be used to determine the location of the touch. The location is then sent to the controller for processing. Touchscreens that use silver instead of ITO exist, as ITO causes several environmental problems due to the use of indium.[46][47][48][49] The controller is typically a complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) chip, which in turn usually sends the signals to a CMOS digital signal processor (DSP) for processing.[50][51]
Unlike a resistive touchscreen, some capacitive touchscreens cannot be used to detect a finger through electrically insulating material, such as gloves. This disadvantage especially affects usability in consumer electronics, such as touch tablet PCs and capacitive smartphones in cold weather when people may be wearing gloves. It can be overcome with a special capacitive stylus, or a special-application glove with an embroidered patch of conductive thread allowing electrical contact with the user’s fingertip.
A low-quality switching-mode power supply unit with an accordingly unstable, noisy voltage may temporarily interfere with the precision, accuracy and sensitivity of capacitive touch screens.[52][53][54]
Some capacitive display manufacturers continue to develop thinner and more accurate touchscreens. Those for mobile devices are now being produced with ‘in-cell’ technology, such as in Samsung’s Super AMOLED screens, that eliminates a layer by building the capacitors inside the display itself. This type of touchscreen reduces the visible distance between the user’s finger and what the user is touching on the screen, reducing the thickness and weight of the display, which is desirable in smartphones.
A simple parallel-plate capacitor has two conductors separated by a dielectric layer. Most of the energy in this system is concentrated directly between the plates. Some of the energy spills over into the area outside the plates, and the electric field lines associated with this effect are called fringing fields. Part of the challenge of making a practical capacitive sensor is to design a set of printed circuit traces which direct fringing fields into an active sensing area accessible to a user. A parallel-plate capacitor is not a good choice for such a sensor pattern. Placing a finger near fringing electric fields adds conductive surface area to the capacitive system. The additional charge storage capacity added by the finger is known as finger capacitance, or CF. The capacitance of the sensor without a finger present is known as parasitic capacitance, or CP.
Surface capacitance[edit]
In this basic technology, only one side of the insulator is coated with a conductive layer. A small voltage is applied to the layer, resulting in a uniform electrostatic field. When a conductor, such as a human finger, touches the uncoated surface, a capacitor is dynamically formed. The sensor’s controller can determine the location of the touch indirectly from the change in the capacitance as measured from the four corners of the panel. As it has no moving parts, it is moderately durable but has limited resolution, is prone to false signals from parasitic capacitive coupling, and needs calibration during manufacture. It is therefore most often used in simple applications such as industrial controls and kiosks.[55]
Although some standard capacitance detection methods are projective, in the sense that they can be used to detect a finger through a non-conductive surface, they are very sensitive to fluctuations in temperature, which expand or contract the sensing plates, causing fluctuations in the capacitance of these plates.[56] These fluctuations result in a lot of background noise, so a strong finger signal is required for accurate detection. This limits applications to those where the finger directly touches the sensing element or is sensed through a relatively thin non-conductive surface.
Projected capacitance[edit]

Back side of a Multitouch Globe, based on projected capacitive touch (PCT) technology

8 x 8 projected capacitance touchscreen manufactured using 25 micron insulation coated copper wire embedded in a clear polyester film.

This diagram shows how eight inputs to a lattice touchscreen or keypad creates 28 unique intersections, as opposed to 16 intersections created using a standard x/y multiplexed touchscreen .
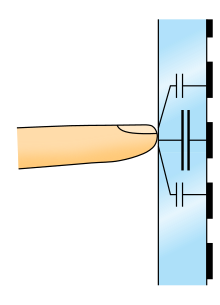
Schema of projected-capacitive touchscreen
Projected capacitive touch (PCT; also PCAP) technology is a variant of capacitive touch technology but where sensitivity to touch, accuracy, resolution and speed of touch have been greatly improved by the use of a simple form of
«Artificial Intelligence». This intelligent processing enables finger sensing to be projected, accurately and reliably, through very thick glass and even double glazing.[57]
Some modern PCT touch screens are composed of thousands of discrete keys,[58] but most PCT touch screens are made of an x/y matrix of rows and columns of conductive material, layered on sheets of glass.
This can be done either by etching a single conductive layer to form a grid pattern of electrodes, by etching two separate, perpendicular layers of conductive material with parallel lines or tracks to form a grid, or by forming an x/y grid of fine, insulation coated wires in a single layer . The number of fingers that can be detected simultaneously is determined by the number of cross-over points (x * y) . However, the number of cross-over points can be almost doubled by using a diagonal lattice layout, where, instead of x elements only ever crossing y elements, each conductive element crosses every other element .[59]
The conductive layer is often transparent, being made of Indium tin oxide (ITO), a transparent electrical conductor.
In some designs, voltage applied to this grid creates a uniform electrostatic field, which can be measured. When a conductive object, such as a finger, comes into contact with a PCT panel, it distorts the local electrostatic field at that point. This is measurable as a change in capacitance. If a finger bridges the gap between two of the «tracks», the charge field is further interrupted and detected by the controller. The capacitance can be changed and measured at every individual point on the grid. This system is able to accurately track touches.[60]
Due to the top layer of a PCT being glass, it is sturdier than less-expensive resistive touch technology.
Unlike traditional capacitive touch technology, it is possible for a PCT system to sense a passive stylus or gloved finger. However, moisture on the surface of the panel, high humidity, or collected dust can interfere with performance.
These environmental factors, however, are not a problem with ‘fine wire’ based touchscreens due to the fact that wire based touchscreens have a much lower ‘parasitic’ capacitance, and there is greater distance between neighbouring conductors.
There are two types of PCT: mutual capacitance and self-capacitance.
Mutual capacitance[edit]
This is a common PCT approach, which makes use of the fact that most conductive objects are able to hold a charge if they are very close together. In mutual capacitive sensors, a capacitor is inherently formed by the row trace and column trace at each intersection of the grid. A 16×14 array, for example, would have 224 independent capacitors. A voltage is applied to the rows or columns. Bringing a finger or conductive stylus close to the surface of the sensor changes the local electrostatic field, which in turn reduces the mutual capacitance. The capacitance change at every individual point on the grid can be measured to accurately determine the touch location by measuring the voltage in the other axis. Mutual capacitance allows multi-touch operation where multiple fingers, palms or styli can be accurately tracked at the same time.
Self-capacitance[edit]
Self-capacitance sensors can have the same X-Y grid as mutual capacitance sensors, but the columns and rows operate independently. With self-capacitance, the capacitive load of a finger is measured on each column or row electrode by a current meter, or the change in frequency of an RC oscillator.[61]
A finger may be detected anywhere along the whole length of a row.
If that finger is also detected by a column, then it can be assumed that the finger position is at the intersection of this row/column pair.
This allows for the speedy and accurate detection of a single finger, but it causes some ambiguity if more than one finger is to be detected.
[62]
Two fingers may have four possible detection positions, only two of which are true. However, by selectively de-sensitizing any touch-points in contention, conflicting results are easily eliminated.[63] This enables «Self Capacitance» to be used for multi-touch operation.
Alternatively, ambiguity can be avoided by applying a «de-sensitizing» signal to all but one of the columns .[63]
This leaves just a short section of any row sensitive to touch. By selecting a sequence of these sections along the row, it is possible to determine the accurate position of multiple fingers along that row. This process can then be repeated for all the other rows until the whole screen has been scanned.
Self-capacitive touch screen layers are used on mobile phones such as the Sony Xperia Sola,[64] the Samsung Galaxy S4, Galaxy Note 3, Galaxy S5, and Galaxy Alpha.
Self capacitance is far more sensitive than mutual capacitance and is mainly used for single touch, simple gesturing and proximity sensing where the finger does not even have to touch the glass surface.
Mutual capacitance is mainly used for multitouch applications.
[65]
Many touchscreen manufacturers use both self and mutual capacitance technologies in the same product, thereby combining their individual benefits.
[66]
Use of stylus on capacitive screens[edit]
Capacitive touchscreens do not necessarily need to be operated by a finger, but until recently the special styli required could be quite expensive to purchase. The cost of this technology has fallen greatly in recent years and capacitive styli are now widely available for a nominal charge, and often given away free with mobile accessories. These consist of an electrically conductive shaft with a soft conductive rubber tip, thereby resistively connecting the fingers to the tip of the stylus.
Infrared grid[edit]

Infrared sensors mounted around the display watch for a user’s touchscreen input on this PLATO V terminal in 1981. The monochromatic plasma display’s characteristic orange glow is illustrated.
An infrared touchscreen uses an array of X-Y infrared LED and photodetector pairs around the edges of the screen to detect a disruption in the pattern of LED beams. These LED beams cross each other in vertical and horizontal patterns. This helps the sensors pick up the exact location of the touch. A major benefit of such a system is that it can detect essentially any opaque object including a finger, gloved finger, stylus or pen. It is generally used in outdoor applications and POS systems that cannot rely on a conductor (such as a bare finger) to activate the touchscreen. Unlike capacitive touchscreens, infrared touchscreens do not require any patterning on the glass which increases durability and optical clarity of the overall system. Infrared touchscreens are sensitive to dirt and dust that can interfere with the infrared beams, and suffer from parallax in curved surfaces and accidental press when the user hovers a finger over the screen while searching for the item to be selected.
Infrared acrylic projection[edit]
A translucent acrylic sheet is used as a rear-projection screen to display information. The edges of the acrylic sheet are illuminated by infrared LEDs, and infrared cameras are focused on the back of the sheet. Objects placed on the sheet are detectable by the cameras. When the sheet is touched by the user, frustrated total internal reflection results in leakage of infrared light which peaks at the points of maximum pressure, indicating the user’s touch location. Microsoft’s PixelSense tablets use this technology.
Optical imaging[edit]
Optical touchscreens are a relatively modern development in touchscreen technology, in which two or more image sensors (such as CMOS sensors) are placed around the edges (mostly the corners) of the screen. Infrared backlights are placed in the sensor’s field of view on the opposite side of the screen. A touch blocks some lights from the sensors, and the location and size of the touching object can be calculated (see visual hull). This technology is growing in popularity due to its scalability, versatility, and affordability for larger touchscreens.
Dispersive signal technology[edit]
Introduced in 2002 by 3M, this system detects a touch by using sensors to measure the piezoelectricity in the glass. Complex algorithms interpret this information and provide the actual location of the touch.[67] The technology is unaffected by dust and other outside elements, including scratches. Since there is no need for additional elements on screen, it also claims to provide excellent optical clarity. Any object can be used to generate touch events, including gloved fingers. A downside is that after the initial touch, the system cannot detect a motionless finger. However, for the same reason, resting objects do not disrupt touch recognition.
Acoustic pulse recognition[edit]
The key to this technology is that a touch at any one position on the surface generates a sound wave in the substrate which then produces a unique combined signal as measured by three or more tiny transducers attached to the edges of the touchscreen. The digitized signal is compared to a list corresponding to every position on the surface, determining the touch location. A moving touch is tracked by rapid repetition of this process. Extraneous and ambient sounds are ignored since they do not match any stored sound profile. The technology differs from other sound-based technologies by using a simple look-up method rather than expensive signal-processing hardware. As with the dispersive signal technology system, a motionless finger cannot be detected after the initial touch. However, for the same reason, the touch recognition is not disrupted by any resting objects. The technology was created by SoundTouch Ltd in the early 2000s, as described by the patent family EP1852772, and introduced to the market by Tyco International’s Elo division in 2006 as Acoustic Pulse Recognition.[68] The touchscreen used by Elo is made of ordinary glass, giving good durability and optical clarity. The technology usually retains accuracy with scratches and dust on the screen. The technology is also well suited to displays that are physically larger.
Construction[edit]
| This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (September 2017) |
There are several principal ways to build a touchscreen. The key goals are to recognize one or more fingers touching a display, to interpret the command that this represents, and to communicate the command to the appropriate application.
In the resistive approach, which used to be the most popular technique, there are typically four layers:
- Top polyester-coated layer with a transparent metallic-conductive coating on the bottom.
- Adhesive spacer
- Glass layer coated with a transparent metallic-conductive coating on the top
- Adhesive layer on the backside of the glass for mounting.
When a user touches the surface, the system records the change in the electric current that flows through the display.
Dispersive-signal technology measures the piezoelectric effect—the voltage generated when mechanical force is applied to a material—that occurs chemically when a strengthened glass substrate is touched.
There are two infrared-based approaches. In one, an array of sensors detects a finger touching or almost touching the display, thereby interrupting infrared light beams projected over the screen. In the other, bottom-mounted infrared cameras record heat from screen touches.
In each case, the system determines the intended command based on the controls showing on the screen at the time and the location of the touch.
Development[edit]
The development of multi-touch screens facilitated the tracking of more than one finger on the screen; thus, operations that require more than one finger are possible. These devices also allow multiple users to interact with the touchscreen simultaneously.
With the growing use of touchscreens, the cost of touchscreen technology is routinely absorbed into the products that incorporate it and is nearly eliminated. Touchscreen technology has demonstrated reliability and is found in airplanes, automobiles, gaming consoles, machine control systems, appliances, and handheld display devices including cellphones; the touchscreen market for mobile devices was projected to produce US$5 billion by 2009.[69][needs update]
The ability to accurately point on the screen itself is also advancing with the emerging graphics tablet-screen hybrids. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) plays a major role in this innovation due its high piezoelectric properties, which allow the tablet to sense pressure, making such things as digital painting behave more like paper and pencil.[70]
TapSense, announced in October 2011, allows touchscreens to distinguish what part of the hand was used for input, such as the fingertip, knuckle and fingernail. This could be used in a variety of ways, for example, to copy and paste, to capitalize letters, to activate different drawing modes, etc.[71][72]
A real practical integration between television-images and the functions of a normal modern PC could be an innovation in the near future: for example «all-live-information» on the internet about a film or the actors on video, a list of other music during a normal video clip of a song or news about a person.
Ergonomics and usage[edit]
Touchscreen enable[edit]
For touchscreens to be effective input devices, users must be able to accurately select targets and avoid accidental selection of adjacent targets. The design of touchscreen interfaces should reflect technical capabilities of the system, ergonomics, cognitive psychology and human physiology.
Guidelines for touchscreen designs were first developed in the 2000s, based on early research and actual use of older systems, typically using infrared grids—which were highly dependent on the size of the user’s fingers. These guidelines are less relevant for the bulk of modern touch devices which use capacitive or resistive touch technology.[73][74]
From the mid-2000s, makers of operating systems for smartphones have promulgated standards, but these vary between manufacturers, and allow for significant variation in size based on technology changes, so are unsuitable from a human factors perspective.[75][76][77]
Much more important is the accuracy humans have in selecting targets with their finger or a pen stylus. The accuracy of user selection varies by position on the screen: users are most accurate at the center, less so at the left and right edges, and least accurate at the top edge and especially the bottom edge. The R95 accuracy (required radius for 95% target accuracy) varies from 7 mm (0.28 in) in the center to 12 mm (0.47 in) in the lower corners.[78][79][80][81][82] Users are subconsciously aware of this, and take more time to select targets which are smaller or at the edges or corners of the touchscreen.[83]
This user inaccuracy is a result of parallax, visual acuity and the speed of the feedback loop between the eyes and fingers. The precision of the human finger alone is much, much higher than this, so when assistive technologies are provided—such as on-screen magnifiers—users can move their finger (once in contact with the screen) with precision as small as 0.1 mm (0.004 in).[84][dubious – discuss]
Hand position, digit used and switching[edit]
Users of handheld and portable touchscreen devices hold them in a variety of ways, and routinely change their method of holding and selection to suit the position and type of input. There are four basic types of handheld interaction:
- Holding at least in part with both hands, tapping with a single thumb
- Holding with two hands and tapping with both thumbs
- Holding with one hand, tapping with the finger (or rarely, thumb) of another hand
- Holding the device in one hand, and tapping with the thumb from that same hand
Use rates vary widely. While two-thumb tapping is encountered rarely (1–3%) for many general interactions, it is used for 41% of typing interaction.[85]
In addition, devices are often placed on surfaces (desks or tables) and tablets especially are used in stands. The user may point, select or gesture in these cases with their finger or thumb, and vary use of these methods.[86]
Combined with haptics[edit]
Touchscreens are often used with haptic response systems. A common example of this technology is the vibratory feedback provided when a button on the touchscreen is tapped. Haptics are used to improve the user’s experience with touchscreens by providing simulated tactile feedback, and can be designed to react immediately, partly countering on-screen response latency. Research from the University of Glasgow (Brewster, Chohan, and Brown, 2007; and more recently Hogan) demonstrates that touchscreen users reduce input errors (by 20%), increase input speed (by 20%), and lower their cognitive load (by 40%) when touchscreens are combined with haptics or tactile feedback. On top of this, a study conducted in 2013 by Boston College explored the effects that touchscreens haptic stimulation had on triggering psychological ownership of a product. Their research concluded that a touchscreens ability to incorporate high amounts of haptic involvement resulted in customers feeling more endowment to the products they were designing or buying. The study also reported that consumers using a touchscreen were willing to accept a higher price point for the items they were purchasing.[87]
Customer service[edit]
Touchscreen technology has become integrated into many aspects of customer service industry in the 21st century.[88] The restaurant industry is a good example of touchscreen implementation into this domain. Chain restaurants such as Taco Bell,[89] Panera Bread, and McDonald’s offer touchscreens as an option when customers are ordering items off the menu.[90] While the addition of touchscreens is a development for this industry, customers may choose to bypass the touchscreen and order from a traditional cashier.[89] To take this a step further, a restaurant in Bangalore has attempted to completely automate the ordering process. Customers sit down to a table embedded with touchscreens and order off an extensive menu. Once the order is placed it is sent electronically to the kitchen.[91] These types of touchscreens fit under the Point of Sale (POS) systems mentioned in the lead section.
«Gorilla arm»[edit]
Extended use of gestural interfaces without the ability of the user to rest their arm is referred to as «gorilla arm».[92] It can result in fatigue, and even repetitive stress injury when routinely used in a work setting. Certain early pen-based interfaces required the operator to work in this position for much of the workday.[93] Allowing the user to rest their hand or arm on the input device or a frame around it is a solution for this in many contexts. This phenomenon is often cited as an example of movements to be minimized by proper ergonomic design.
Unsupported touchscreens are still fairly common in applications such as ATMs and data kiosks, but are not an issue as the typical user only engages for brief and widely spaced periods.[94]
Fingerprints[edit]

Touchscreens can suffer from the problem of fingerprints on the display. This can be mitigated by the use of materials with optical coatings designed to reduce the visible effects of fingerprint oils. Most modern smartphones have oleophobic coatings, which lessen the amount of oil residue. Another option is to install a matte-finish anti-glare screen protector, which creates a slightly roughened surface that does not easily retain smudges.
Glove touch[edit]
Touchscreens do not work most of the time when the user wears gloves. The thickness of the glove and the material they are made of play a significant role on that and the ability of a touchscreen to pick up a touch.
See also[edit]
- Dual-touchscreen
- Pen computing
- Energy harvesting
- Flexible keyboard
- Gestural interface
- Graphics tablet
- Light pen
- List of touch-solution manufacturers
- Lock screen
- Tablet computer
- Touch switch
- Touchscreen remote control
- Multi-touch
- Omnitouch
- Pointing device gesture
- Sensacell
- SixthSense
- Nintendo DS
References[edit]
- ^ Walker, Geoff (August 2012). «A review of technologies for sensing contact location on the surface of a display: Review of touch technologies». Journal of the Society for Information Display. 20 (8): 413–440. doi:10.1002/jsid.100. S2CID 40545665.
- ^ «What is a Touch Screen?». www.computerhope.com. Retrieved 2020-09-07.
- ^ Allvin, Rhian Evans (2014-09-01). «Technology in the Early Childhood Classroom». YC Young Children. 69 (4): 62. ISSN 1538-6619.
- ^ «The first capacitative touch screens at CERN». CERN Courrier. 31 March 2010. Archived from the original on 4 September 2010. Retrieved 2010-05-25.
- ^ Bent Stumpe (16 March 1977). «A new principle for x-y touch system» (PDF). CERN. Retrieved 2010-05-25.
- ^ Bent Stumpe (6 February 1978). «Experiments to find a manufacturing process for an x-y touch screen» (PDF). CERN. Retrieved 2010-05-25.
- ^ Beck, Frank; Stumpe, Bent (May 24, 1973). Two devices for operator interaction in the central control of the new CERN accelerator (Report). CERN. CERN-73-06. Retrieved 2017-09-14.
- ^ Johnson, E.A. (1965). «Touch Display — A novel input/output device for computers». Electronics Letters. 1 (8): 219–220. Bibcode:1965ElL…..1..219J. doi:10.1049/el:19650200.
- ^ «1965 — The Touchscreen». Malvern Radar and Technology History Society. 2016. Archived from the original on 31 January 2018. Retrieved 24 July 2017.
- ^ Johnson, E.A. (1967). «Touch Displays: A Programmed Man-Machine Interface». Ergonomics. 10 (2): 271–277. doi:10.1080/00140136708930868.
- ^ Orr, N.W.; Hopkins, V.D. (1968). «The Role of Touch Display in Air Traffic Control». The Controller. 7: 7–9.
- ^ Lowe, J. F. (18 November 1974). «Computer creates custom control panel». Design News: 54–55.
- ^ Stumpe, Bent; Sutton, Christine (1 June 2010). «CERN touch screen». Symmetry Magazine. A joint Fermilab/SLAC publication. Archived from the original on 2016-11-16. Retrieved 16 November 2016.
- ^ «Another of CERN’s many inventions! — CERN Document Server». CERN Document Server. Retrieved 29 July 2015.
- ^ a b c Mallebrein, Rainer (2018-02-18). «Oral History of Rainer Mallebrein» (PDF) (Interview). Interviewed by Steinbach, Günter. Singen am Hohentwiel, Germany: Computer History Museum. CHM Ref: X8517.2018. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-01-27. Retrieved 2021-08-23. (18 pages)
- ^ a b c Ebner, Susanne (2018-01-24). «Entwickler aus Singen über die Anfänge der Computermaus: «Wir waren der Zeit voraus»» [Singen-based developer about the advent of the computer mouse: «We were ahead of time»]. Leben und Wissen. Südkurier (in German). Konstanz, Germany: Südkurier GmbH. Archived from the original on 2021-03-02. Retrieved 2021-08-22.
- ^ F. Ebeling, R. Johnson, R. Goldhor, Infrared light beam x-y position encoder for display devices, US 3775560, granted November 27, 1973.
- ^ The H.P. Touch Computer (1983) Archived 2017-08-24 at the Wayback Machine. YouTube (2008-02-19). Retrieved on 2013-08-16.
- ^ USPTO. «DISCRIMINATING CONTACT SENSOR». Archived from the original on 19 May 2013. Retrieved 6 April 2013.
- ^ Emerson, Lewis (December 13, 2010). ««G. Samuel Hurst — the ‘Tom Edison’ of ORNL», December 14 2010″. G. Samuel Hurst — the ‘Tom Edison’ of ORNL. Retrieved 2010-12-13.[dead link]
- ^ Japanese PCs (1984) Archived 2017-07-07 at the Wayback Machine (12:21), Computer Chronicles
- ^ «Terebi Oekaki / Sega Graphic Board — Articles — SMS Power!». Archived from the original on 23 July 2015. Retrieved 29 July 2015.
- ^ «Software that takes games seriously». New Scientist. Reed Business Information. March 26, 1987. p. 34. Archived from the original on January 31, 2018 – via Google Books.
- ^ Technology Trends: 2nd Quarter 1986 Archived 2016-10-15 at the Wayback Machine, Japanese Semiconductor Industry Service — Volume II: Technology & Government
- ^ Biferno, M. A., Stanley, D. L. (1983). The Touch-Sensitive Control/Display Unit: A Promising Computer Interface. Technical Paper 831532, Aerospace Congress & Exposition, Long Beach, CA: Society of Automotive Engineers.
- ^ «1986, Electronics Developed for Lotus Active Suspension Technology — Generations of GM». History.gmheritagecenter.com. Archived from the original on 2013-06-17. Retrieved 2013-01-07.
- ^ Badal, Jaclyne (2008-06-23). «When Design Goes Bad». Online.wsj.com. Archived from the original on 2016-03-16. Retrieved 2013-01-07.
- ^ The ViewTouch restaurant system Archived 2009-09-09 at the Wayback Machine by Giselle Bisson
- ^ «The World Leader in GNU-Linux Restaurant POS Software». Viewtouch.com. Archived from the original on 2012-07-17. Retrieved 2013-01-07.
- ^ «File:Comdex 1986.png». Wikimedia Commons. 2012-09-11. Archived from the original on 2012-12-20. Retrieved 2013-01-07.
- ^ Potter, R.; Weldon, L.; Shneiderman, B. (1988). «Improving the accuracy of touch screens: an experimental evaluation of three strategies». Proceedings of the SIGCHI conference on Human factors in computing systems — CHI ’88. Proc. of the Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, CHI ’88. Washington, DC. pp. 27–32. doi:10.1145/57167.57171. ISBN 0201142376. Archived from the original on 2015-12-08.
- ^ a b Sears, Andrew; Plaisant, Catherine; Shneiderman, Ben (June 1990). «A new era for high-precision touchscreens». In Hartson, R.; Hix, D. (eds.). Advances in Human-Computer Interaction. Vol. 3. Ablex (1992). ISBN 978-0-89391-751-7. Archived from the original on October 9, 2014.
- ^ «1991 video of the HCIL touchscreen toggle switches (University of Maryland)». YouTube. Archived from the original on 13 March 2016. Retrieved 3 December 2015.
- ^ Apple touch-screen patent war comes to the UK (2011). Event occurs at 1:24 min in video. Archived from the original on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 3 December 2015.
- ^ Star7 Demo on YouTube. Retrieved on 2013-08-16.
- ^ «The LG KE850: touchable chocolate». Engadget.
- ^ «Touch Screen Market to Hit $9B by 2015». CBS News.
- ^ «Touch screen gamble: Which technology to use».
- ^ «Canalys — the leading global technology market analyst firm».
- ^ Travis Fahs (April 21, 2009). «IGN Presents the History of SEGA». IGN. p. 7. Archived from the original on February 4, 2012. Retrieved 2011-04-27.
- ^ «Short Course on Projected Capacitance» (PDF).
- ^ «What is touch screen? — Definition from WhatIs.com». WhatIs.com. Retrieved 2020-09-07.
- ^ Lancet, Yaara. (2012-07-19) What Are The Differences Between Capacitive & Resistive Touchscreens? Archived 2013-03-09 at the Wayback Machine. Makeuseof.com. Retrieved on 2013-08-16.
- ^ Vlad Savov. «Nintendo 3DS has resistive touchscreen for backwards compatibility, what’s the Wii U’s excuse?». Engadget. AOL. Archived from the original on 12 November 2015. Retrieved 29 July 2015.
- ^ Hong, Chan-Hwa; Shin, Jae-Heon; Ju, Byeong-Kwon; Kim, Kyung-Hyun; Park, Nae-Man; Kim, Bo-Sul; Cheong, Woo-Seok (1 November 2013). «Index-Matched Indium Tin Oxide Electrodes for Capacitive Touch Screen Panel Applications». Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology. 13 (11): 7756–7759. doi:10.1166/jnn.2013.7814. PMID 24245328. S2CID 24281861.
- ^ «Fujifilm reinforces the production facilities for its touch-panel sensor film «EXCLEAR»«. FUJIFILM Europe.
- ^ «Development of a Thin Double-sided Sensor Film «EXCLEAR» for Touch Panels via Silver Halide Photographic Technology» (PDF). www.fujifilm.com. Retrieved 2019-12-09.
- ^ «What’s behind your smartphone screen? This… |». fujifilm-innovation.tumblr.com.
- ^ «Environment: [Topics2] Development of Materials That Solve Environmental Issues EXCLEAR thin double-sided sensor film for touch panels | FUJIFILM Holdings». www.fujifilmholdings.com.
- ^ Kent, Joel (May 2010). «Touchscreen technology basics & a new development». CMOS Emerging Technologies Conference. CMOS Emerging Technologies Research. 6: 1–13. ISBN 9781927500057.
- ^ Ganapati, Priya (5 March 2010). «Finger Fail: Why Most Touchscreens Miss the Point». Wired. Archived from the original on 2014-05-11. Retrieved 9 November 2019.
- ^ Andi (2014-01-24). «How noise affects touch screens». West Florida Components. Retrieved 2020-10-24.
- ^ «Touch screens and charger noise |». epanorama.net. 2013-03-12.
- ^ «Aggressively combat noise in capacitive touch applications». EDN.com. 2013-04-08.
- ^ «Please Touch! Explore The Evolving World Of Touchscreen Technology». electronicdesign.com. Archived from the original on 2015-12-13. Retrieved 2009-09-02.
- ^ «formula for relationship between plate area and capacitance».
- ^ «Touch operated keyboard». Archived from the original on 2018-01-31. Retrieved 2018-01-30.
- ^ «Multipoint touchscreen».
- ^ «Espacenet — Original document». Worldwide.espacenet.com. 2017-04-26. Retrieved 2018-02-22.
- ^ Knowledge base: Multi-touch hardware Archived 2012-02-03 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «Use of RC oscillator in touchscreen».
- ^ «Ambiguity caused by multitouch in self capacitance touchscreens» (PDF).
- ^ a b «Multitouch using Self Capacitance».
- ^ «Self-capacitive touch described on official Sony Developers blog». Archived from the original on 2012-03-14. Retrieved 2012-03-14.
- ^ Du, Li (2016). «Comparison of self capacitance and mutual capacitance» (PDF). arXiv:1612.08227. doi:10.1017/S1743921315010388. S2CID 220453196.
- ^ «Hybrid self and mutual capacitance touch sensing controllers».
- ^ Beyers, Tim (2008-02-13). «Innovation Series: Touchscreen Technology». The Motley Fool. Archived from the original on 2009-03-24. Retrieved 2009-03-16.
- ^ «Acoustic Pulse Recognition Touchscreens» (PDF). Elo Touch Systems. 2006: 3. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2011-09-05. Retrieved 2011-09-27.
- ^ «Touch Screens in Mobile Devices to Deliver $5 Billion Next Year | Press Release». ABI Research. 2008-09-10. Archived from the original on 2011-07-07. Retrieved 2009-06-22.
- ^ «Insights Into PVDF Innovations». Fluorotherm. 17 August 2015. Archived from the original on 15 October 2016.
- ^ «New Screen Technology, TapSense, Can Distinguish Between Different Parts Of Your Hand». Archived from the original on October 20, 2011. Retrieved October 19, 2011.
- ^ «TapSense: Enhancing Finger Interaction on Touch Surfaces». Archived from the original on 11 January 2012. Retrieved 28 January 2012.
- ^ «ANSI/HFES 100-2007 Human Factors Engineering of Computer Workstations». Human Factors & Ergonomics Society. Santa Monica, CA. 2007.
- ^ «Ergonomic Requirements for Office Work with Visual Display Terminals (VDTs)–Part 9: Requirements for Non-keyboard Input Devices». International Organization for Standardization. Geneva, Switzerland. 2000.
- ^ «iOS Human Interface Guidelines». Apple. Archived from the original on 2014-08-26. Retrieved 2014-08-24.
- ^ «Metrics and Grids». Archived from the original on 2014-07-16. Retrieved 2014-08-24.
- ^ «Touch interactions for Windows». Microsoft. Archived from the original on 2014-08-26. Retrieved 2014-08-24.
- ^ Hoober, Steven (2013-02-18). «Common Misconceptions About Touch». UXmatters. Archived from the original on 2014-08-26. Retrieved 2014-08-24.
- ^ Hoober, Steven (2013-11-11). «Design for Fingers and Thumbs Instead of Touch». UXmatters. Archived from the original on 2014-08-26. Retrieved 2014-08-24.
- ^ Hoober, Steven; Shank, Patti; Boll, Susanne (2014). «Making mLearning Usable: How We Use Mobile Devices». Santa Rosa, CA.
- ^ Henze, Niels; Rukzio, Enrico; Boll, Susanne (2011). «100,000,000 Taps: Analysis and Improvement of Touch Performance in the Large». Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Human Computer Interaction with Mobile Devices and Services. New York.
- ^ Parhi, Pekka (2006). «Target Size Study for One-Handed Thumb Use on Small Touchscreen Devices». Proceedings of MobileHCI 2006. New York.
- ^ Lee, Seungyons; Zhai, Shumin (2009). «The Performance of Touch Screen Soft Buttons». Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. New York: 309. doi:10.1145/1518701.1518750. ISBN 9781605582467. S2CID 2468830.
- ^ Bérard, François (2012). «Measuring the Linear and Rotational User Precision in Touch Pointing». Proceedings of the 2012 ACM International Conference on Interactive Tabletops and Surfaces. New York: 183. doi:10.1145/2396636.2396664. ISBN 9781450312097. S2CID 15765730.
- ^ Hoober, Steven (2014-09-02). «Insights on Switching, Centering, and Gestures for Touchscreens». UXmatters. Archived from the original on 2014-09-06. Retrieved 2014-08-24.
- ^ Hoober, Steven (2013-02-18). «How Do Users Really Hold Mobile Devices?». UXmatters. Archived from the original on 2014-08-26. Retrieved 2014-08-24.
- ^ Brasel, S. Adam; Gips, James (2014). «Tablets, touchscreens, and touchpads: How varying touch interfaces trigger psychological ownership and endowment». Journal of Consumer Psychology. 24 (2): 226–233. doi:10.1016/j.jcps.2013.10.003.
- ^ Zhu, Ying; Meyer, Jeffrey (September 2017). «Getting in touch with your thinking style: How touchscreens influence purchase». Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services. 38: 51–58. doi:10.1016/j.jretconser.2017.05.006.
- ^ a b Hueter, Jackie; Swart, William (February 1998). «An Integrated Labor-Management System for Taco Bell». Interfaces. 28 (1): 75–91. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.565.3872. doi:10.1287/inte.28.1.75. S2CID 18514383.
- ^ Baker, Rosie (19 May 2011). «FOOD: McDonald’s explores digital touchscreens». Marketing Week: 4. Gale A264377887.
- ^ «A RESTAURANT THAT LETS GUESTS PLACE ORDERS VIA A TOUCHSCREEN TABLE (Touche is said to be the first touchscreen restaurant in India and fifth in the world)». India Business Insight. 31 August 2011. Gale A269135159.
- ^ «gorilla arm». Catb.org. Archived from the original on 2012-01-21. Retrieved 2012-01-04.
- ^ «Gesture Fatigue ruined light pens forever. Make sure it doesn’t ruin your gesture design». Gesture Design Blog. Archived from the original on 2015-02-13. Retrieved 2014-08-23.
- ^ David Pogue (January 3, 2013). «Why Touch Screens Will Not Take Over». Scientific American. 308 (1): 25. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0113-25. PMID 23342443.
Sources[edit]
- Shneiderman, B. (1991). «Touch screens now offer compelling uses». IEEE Software. 8 (2): 93–94, 107. doi:10.1109/52.73754. S2CID 14561929.
- Potter, R.; Weldon, L. & Shneiderman, B. (1988). An experimental evaluation of three strategies. Proc. CHI’88. Washington, DC: ACM Press. pp. 27–32.
- Sears, A.; Plaisant, C. & Shneiderman, B. (1992). «A new era for high precision touchscreens». In Hartson, R. & Hix, D. (eds.). Advances in Human-Computer Interaction. Vol. 3. Ablex, NJ. pp. 1–33.
External links[edit]

A user operating a touchscreen

A touchscreen or touch screen is the assembly of both an input (‘touch panel’) and output (‘display’) device. The touch panel is normally layered on the top of an electronic visual display of an information processing system. The display is often an LCD, AMOLED or OLED display while the system is usually used in a laptop, tablet, or smartphone. A user can give input or control the information processing system through simple or multi-touch gestures by touching the screen with a special stylus or one or more fingers.[1] Some touchscreens use ordinary or specially coated gloves to work while others may only work using a special stylus or pen. The user can use the touchscreen to react to what is displayed and, if the software allows, to control how it is displayed; for example, zooming to increase the text size.
The touchscreen enables the user to interact directly with what is displayed, rather than using a mouse, touchpad, or other such devices (other than a stylus, which is optional for most modern touchscreens).[2]
Touchscreens are common in devices such as game consoles, personal computers, electronic voting machines, and point-of-sale (POS) systems. They can also be attached to computers or, as terminals, to networks. They play a prominent role in the design of digital appliances such as personal digital assistants (PDAs) and some e-readers. Touchscreens are also important in educational settings such as classrooms or on college campuses.[3]
The popularity of smartphones, tablets, and many types of information appliances is driving the demand and acceptance of common touchscreens for portable and functional electronics. Touchscreens are found in the medical field, heavy industry, automated teller machines (ATMs), and kiosks such as museum displays or room automation, where keyboard and mouse systems do not allow a suitably intuitive, rapid, or accurate interaction by the user with the display’s content.
Historically, the touchscreen sensor and its accompanying controller-based firmware have been made available by a wide array of after-market system integrators, and not by display, chip, or motherboard manufacturers. Display manufacturers and chip manufacturers have acknowledged the trend toward acceptance of touchscreens as a user interface component and have begun to integrate touchscreens into the fundamental design of their products.
History[edit]

One predecessor of the modern touch screen includes stylus based systems. In 1946, a patent was filed by Philco Company for a stylus designed for sports telecasting which, when placed against an intermediate cathode ray tube display (CRT) would amplify and add to the original signal. Effectively, this was used for temporarily drawing arrows or circles onto a live television broadcast, as described in US 2487641A, Denk, William E, «Electronic pointer for television images», issued 1949-11-08. Later inventions built upon this system to free telewriting styli from their mechanical bindings. By transcribing what a user draws onto a computer, it could be saved for future use. See US 3089918A, Graham, Robert E, «Telewriting apparatus», issued 1963-05-14.
The first version of a touchscreen which operated independently of the light produced from the screen was patented by AT&T Corporation US 3016421A, Harmon, Leon D, «Electrographic transmitter», issued 1962-01-09. This touchscreen utilized a matrix of collimated lights shining orthogonally across the touch surface. When a beam is interrupted by a stylus, the photodetectors which no longer are receiving a signal can be used to determine where the interruption is. Later iterations of matrix based touchscreens built upon this by adding more emitters and detectors to improve resolution, pulsing emitters to improve optical signal to noise ratio, and a nonorthogonal matrix to remove shadow readings when using multi-touch.
The first finger driven touch screen was developed by Eric Johnson, of the Royal Radar Establishment located in Malvern, England, who described his work on capacitive touchscreens in a short article published in 1965[8][9] and then more fully—with photographs and diagrams—in an article published in 1967.[10] The application of touch technology for air traffic control was described in an article published in 1968.[11] Frank Beck and Bent Stumpe, engineers from CERN (European Organization for Nuclear Research), developed a transparent touchscreen in the early 1970s,[12] based on Stumpe’s work at a television factory in the early 1960s. Then manufactured by CERN, and shortly after by industry partners,[13] it was put to use in 1973.[14]
In the mid-1960s, another precursor of touchscreens, an ultrasonic-curtain-based pointing device in front of a terminal display, had been developed by a team around Rainer Mallebrein [de] at Telefunken Konstanz for an air traffic control system.[15] In 1970, this evolved into a device named «Touchinput-Einrichtung» («touch input facility») for the SIG 50 terminal utilizing a conductively coated glass screen in front of the display.[16][15] This was patented in 1971 and the patent was granted a couple of years later.[16][15] The same team had already invented and marketed the Rollkugel mouse RKS 100-86 for the SIG 100-86 a couple of years earlier.[16]
In 1972, a group at the University of Illinois filed for a patent on an optical touchscreen[17] that became a standard part of the Magnavox Plato IV Student Terminal and thousands were built for this purpose. These touchscreens had a crossed array of 16×16 infrared position sensors, each composed of an LED on one edge of the screen and a matched phototransistor on the other edge, all mounted in front of a monochrome plasma display panel. This arrangement could sense any fingertip-sized opaque object in close proximity to the screen. A similar touchscreen was used on the HP-150 starting in 1983. The HP 150 was one of the world’s earliest commercial touchscreen computers.[18] HP mounted their infrared transmitters and receivers around the bezel of a 9-inch Sony cathode ray tube (CRT).
In 1977, an American company, Elographics – in partnership with Siemens – began work on developing a transparent implementation of an existing opaque touchpad technology, U.S. patent No. 3,911,215, October 7, 1975, which had been developed by Elographics’ founder George Samuel Hurst.[19] The resulting resistive technology touch screen was first shown on the World’s Fair at Knoxville in 1982.[20]
In 1984, Fujitsu released a touch pad for the Micro 16 to accommodate the complexity of kanji characters, which were stored as tiled graphics.[21] In 1985, Sega released the Terebi Oekaki, also known as the Sega Graphic Board, for the SG-1000 video game console and SC-3000 home computer. It consisted of a plastic pen and a plastic board with a transparent window where pen presses are detected. It was used primarily with a drawing software application.[22] A graphic touch tablet was released for the Sega AI computer in 1986.[23][24]
Touch-sensitive control-display units (CDUs) were evaluated for commercial aircraft flight decks in the early 1980s. Initial research showed that a touch interface would reduce pilot workload as the crew could then select waypoints, functions and actions, rather than be «head down» typing latitudes, longitudes, and waypoint codes on a keyboard. An effective integration of this technology was aimed at helping flight crews maintain a high level of situational awareness of all major aspects of the vehicle operations including the flight path, the functioning of various aircraft systems, and moment-to-moment human interactions.[25]
In the early 1980s, General Motors tasked its Delco Electronics division with a project aimed at replacing an automobile’s non-essential functions (i.e. other than throttle, transmission, braking, and steering) from mechanical or electro-mechanical systems with solid state alternatives wherever possible. The finished device was dubbed the ECC for «Electronic Control Center», a digital computer and software control system hardwired to various peripheral sensors, servos, solenoids, antenna and a monochrome CRT touchscreen that functioned both as display and sole method of input.[26] The ECC replaced the traditional mechanical stereo, fan, heater and air conditioner controls and displays, and was capable of providing very detailed and specific information about the vehicle’s cumulative and current operating status in real time. The ECC was standard equipment on the 1985–1989 Buick Riviera and later the 1988–1989 Buick Reatta, but was unpopular with consumers—partly due to the technophobia of some traditional Buick customers, but mostly because of costly technical problems suffered by the ECC’s touchscreen which would render climate control or stereo operation impossible.[27]
Multi-touch technology began in 1982, when the University of Toronto’s Input Research Group developed the first human-input multi-touch system, using a frosted-glass panel with a camera placed behind the glass. In 1985, the University of Toronto group, including Bill Buxton, developed a multi-touch tablet that used capacitance rather than bulky camera-based optical sensing systems (see History of multi-touch).
The first commercially available graphical point-of-sale (POS) software was demonstrated on the 16-bit Atari 520ST color computer. It featured a color touchscreen widget-driven interface.[28] The ViewTouch[29] POS software was first shown by its developer, Gene Mosher, at the Atari Computer demonstration area of the Fall COMDEX expo in 1986.[30]
In 1987, Casio launched the Casio PB-1000 pocket computer with a touchscreen consisting of a 4×4 matrix, resulting in 16 touch areas in its small LCD graphic screen.
Touchscreens had a bad reputation of being imprecise until 1988. Most user-interface books would state that touchscreen selections were limited to targets larger than the average finger. At the time, selections were done in such a way that a target was selected as soon as the finger came over it, and the corresponding action was performed immediately. Errors were common, due to parallax or calibration problems, leading to user frustration. «Lift-off strategy»[31] was introduced by researchers at the University of Maryland Human–Computer Interaction Lab (HCIL). As users touch the screen, feedback is provided as to what will be selected: users can adjust the position of the finger, and the action takes place only when the finger is lifted off the screen. This allowed the selection of small targets, down to a single pixel on a 640×480 Video Graphics Array (VGA) screen (a standard of that time).
Sears et al. (1990)[32] gave a review of academic research on single and multi-touch human–computer interaction of the time, describing gestures such as rotating knobs, adjusting sliders, and swiping the screen to activate a switch (or a U-shaped gesture for a toggle switch). The HCIL team developed and studied small touchscreen keyboards (including a study that showed users could type at 25 wpm on a touchscreen keyboard), aiding their introduction on mobile devices. They also designed and implemented multi-touch gestures such as selecting a range of a line, connecting objects, and a «tap-click» gesture to select while maintaining location with another finger.
In 1990, HCIL demonstrated a touchscreen slider,[33] which was later cited as prior art in the lock screen patent litigation between Apple and other touchscreen mobile phone vendors (in relation to U.S. Patent 7,657,849).[34]
In 1991–1992, the Sun Star7 prototype PDA implemented a touchscreen with inertial scrolling.[35] In 1993, IBM released the IBM Simon the first touchscreen phone.
An early attempt at a handheld game console with touchscreen controls was Sega’s intended successor to the Game Gear, though the device was ultimately shelved and never released due to the expensive cost of touchscreen technology in the early 1990s.
The first mobile phone with a capacitive touchscreen was LG Prada released in May 2007 (which was before the first iPhone).[36] By 2009, touchscreen-enabled mobile phones were becoming trendy and quickly gaining popularity in both basic and advanced devices.[37][38] In Q4 2009 for the first time, a majority of smartphones (i.e. not all mobile phones) shipped with touchscreens over non-touch.[39]
Touchscreens would not be popularly used for video games until the release of the Nintendo DS in 2004.[40] Until recently,[when?] most consumer touchscreens could only sense one point of contact at a time, and few have had the capability to sense how hard one is touching. This has changed with the commercialization of multi-touch technology, and the Apple Watch being released with a force-sensitive display in April 2015.
In 2007, 93% of touchscreens shipped were resistive and only 4% were projected capacitance. In 2013, 3% of touchscreens shipped were resistive and 90% were projected capacitance.[41]
Technologies[edit]
There is a variety of touchscreen technologies with different methods of sensing touch.[32]
Resistive[edit]
A resistive touchscreen panel comprises several thin layers, the most important of which are two transparent electrically resistive layers facing each other with a thin gap between. The top layer (that which is touched) has a coating on the underside surface; just beneath it is a similar resistive layer on top of its substrate. One layer has conductive connections along its sides, the other along top and bottom. A voltage is applied to one layer and sensed by the other. When an object, such as a fingertip or stylus tip, presses down onto the outer surface, the two layers touch to become connected at that point.[42] The panel then behaves as a pair of voltage dividers, one axis at a time. By rapidly switching between each layer, the position of pressure on the screen can be detected.
Resistive touch is used in restaurants, factories and hospitals due to its high tolerance for liquids and contaminants. A major benefit of resistive-touch technology is its low cost. Additionally, as only sufficient pressure is necessary for the touch to be sensed, they may be used with gloves on, or by using anything rigid as a finger substitute. Disadvantages include the need to press down, and a risk of damage by sharp objects. Resistive touchscreens also suffer from poorer contrast, due to having additional reflections (i.e. glare) from the layers of material placed over the screen.[43] This is the type of touchscreen that was used by Nintendo in the DS family, the 3DS family, and the Wii U GamePad.[44]
Surface acoustic wave[edit]
Surface acoustic wave (SAW) technology uses ultrasonic waves that pass over the touchscreen panel. When the panel is touched, a portion of the wave is absorbed. The change in ultrasonic waves is processed by the controller to determine the position of the touch event. Surface acoustic wave touchscreen panels can be damaged by outside elements. Contaminants on the surface can also interfere with the functionality of the touchscreen.
SAW devices have a wide range of applications, including delay lines, filters, correlators and DC to DC converters.
Capacitive[edit]

Capacitive touchscreen of a mobile phone

The Casio TC500 Capacitive touch sensor watch from 1983, with angled light exposing the touch sensor pads and traces etched onto the top watch glass surface.
A capacitive touchscreen panel consists of an insulator, such as glass, coated with a transparent conductor, such as indium tin oxide (ITO).[45] As the human body is also an electrical conductor, touching the surface of the screen results in a distortion of the screen’s electrostatic field, measurable as a change in capacitance. Different technologies may be used to determine the location of the touch. The location is then sent to the controller for processing. Touchscreens that use silver instead of ITO exist, as ITO causes several environmental problems due to the use of indium.[46][47][48][49] The controller is typically a complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) chip, which in turn usually sends the signals to a CMOS digital signal processor (DSP) for processing.[50][51]
Unlike a resistive touchscreen, some capacitive touchscreens cannot be used to detect a finger through electrically insulating material, such as gloves. This disadvantage especially affects usability in consumer electronics, such as touch tablet PCs and capacitive smartphones in cold weather when people may be wearing gloves. It can be overcome with a special capacitive stylus, or a special-application glove with an embroidered patch of conductive thread allowing electrical contact with the user’s fingertip.
A low-quality switching-mode power supply unit with an accordingly unstable, noisy voltage may temporarily interfere with the precision, accuracy and sensitivity of capacitive touch screens.[52][53][54]
Some capacitive display manufacturers continue to develop thinner and more accurate touchscreens. Those for mobile devices are now being produced with ‘in-cell’ technology, such as in Samsung’s Super AMOLED screens, that eliminates a layer by building the capacitors inside the display itself. This type of touchscreen reduces the visible distance between the user’s finger and what the user is touching on the screen, reducing the thickness and weight of the display, which is desirable in smartphones.
A simple parallel-plate capacitor has two conductors separated by a dielectric layer. Most of the energy in this system is concentrated directly between the plates. Some of the energy spills over into the area outside the plates, and the electric field lines associated with this effect are called fringing fields. Part of the challenge of making a practical capacitive sensor is to design a set of printed circuit traces which direct fringing fields into an active sensing area accessible to a user. A parallel-plate capacitor is not a good choice for such a sensor pattern. Placing a finger near fringing electric fields adds conductive surface area to the capacitive system. The additional charge storage capacity added by the finger is known as finger capacitance, or CF. The capacitance of the sensor without a finger present is known as parasitic capacitance, or CP.
Surface capacitance[edit]
In this basic technology, only one side of the insulator is coated with a conductive layer. A small voltage is applied to the layer, resulting in a uniform electrostatic field. When a conductor, such as a human finger, touches the uncoated surface, a capacitor is dynamically formed. The sensor’s controller can determine the location of the touch indirectly from the change in the capacitance as measured from the four corners of the panel. As it has no moving parts, it is moderately durable but has limited resolution, is prone to false signals from parasitic capacitive coupling, and needs calibration during manufacture. It is therefore most often used in simple applications such as industrial controls and kiosks.[55]
Although some standard capacitance detection methods are projective, in the sense that they can be used to detect a finger through a non-conductive surface, they are very sensitive to fluctuations in temperature, which expand or contract the sensing plates, causing fluctuations in the capacitance of these plates.[56] These fluctuations result in a lot of background noise, so a strong finger signal is required for accurate detection. This limits applications to those where the finger directly touches the sensing element or is sensed through a relatively thin non-conductive surface.
Projected capacitance[edit]

Back side of a Multitouch Globe, based on projected capacitive touch (PCT) technology

8 x 8 projected capacitance touchscreen manufactured using 25 micron insulation coated copper wire embedded in a clear polyester film.

This diagram shows how eight inputs to a lattice touchscreen or keypad creates 28 unique intersections, as opposed to 16 intersections created using a standard x/y multiplexed touchscreen .

Schema of projected-capacitive touchscreen
Projected capacitive touch (PCT; also PCAP) technology is a variant of capacitive touch technology but where sensitivity to touch, accuracy, resolution and speed of touch have been greatly improved by the use of a simple form of
«Artificial Intelligence». This intelligent processing enables finger sensing to be projected, accurately and reliably, through very thick glass and even double glazing.[57]
Some modern PCT touch screens are composed of thousands of discrete keys,[58] but most PCT touch screens are made of an x/y matrix of rows and columns of conductive material, layered on sheets of glass.
This can be done either by etching a single conductive layer to form a grid pattern of electrodes, by etching two separate, perpendicular layers of conductive material with parallel lines or tracks to form a grid, or by forming an x/y grid of fine, insulation coated wires in a single layer . The number of fingers that can be detected simultaneously is determined by the number of cross-over points (x * y) . However, the number of cross-over points can be almost doubled by using a diagonal lattice layout, where, instead of x elements only ever crossing y elements, each conductive element crosses every other element .[59]
The conductive layer is often transparent, being made of Indium tin oxide (ITO), a transparent electrical conductor.
In some designs, voltage applied to this grid creates a uniform electrostatic field, which can be measured. When a conductive object, such as a finger, comes into contact with a PCT panel, it distorts the local electrostatic field at that point. This is measurable as a change in capacitance. If a finger bridges the gap between two of the «tracks», the charge field is further interrupted and detected by the controller. The capacitance can be changed and measured at every individual point on the grid. This system is able to accurately track touches.[60]
Due to the top layer of a PCT being glass, it is sturdier than less-expensive resistive touch technology.
Unlike traditional capacitive touch technology, it is possible for a PCT system to sense a passive stylus or gloved finger. However, moisture on the surface of the panel, high humidity, or collected dust can interfere with performance.
These environmental factors, however, are not a problem with ‘fine wire’ based touchscreens due to the fact that wire based touchscreens have a much lower ‘parasitic’ capacitance, and there is greater distance between neighbouring conductors.
There are two types of PCT: mutual capacitance and self-capacitance.
Mutual capacitance[edit]
This is a common PCT approach, which makes use of the fact that most conductive objects are able to hold a charge if they are very close together. In mutual capacitive sensors, a capacitor is inherently formed by the row trace and column trace at each intersection of the grid. A 16×14 array, for example, would have 224 independent capacitors. A voltage is applied to the rows or columns. Bringing a finger or conductive stylus close to the surface of the sensor changes the local electrostatic field, which in turn reduces the mutual capacitance. The capacitance change at every individual point on the grid can be measured to accurately determine the touch location by measuring the voltage in the other axis. Mutual capacitance allows multi-touch operation where multiple fingers, palms or styli can be accurately tracked at the same time.
Self-capacitance[edit]
Self-capacitance sensors can have the same X-Y grid as mutual capacitance sensors, but the columns and rows operate independently. With self-capacitance, the capacitive load of a finger is measured on each column or row electrode by a current meter, or the change in frequency of an RC oscillator.[61]
A finger may be detected anywhere along the whole length of a row.
If that finger is also detected by a column, then it can be assumed that the finger position is at the intersection of this row/column pair.
This allows for the speedy and accurate detection of a single finger, but it causes some ambiguity if more than one finger is to be detected.
[62]
Two fingers may have four possible detection positions, only two of which are true. However, by selectively de-sensitizing any touch-points in contention, conflicting results are easily eliminated.[63] This enables «Self Capacitance» to be used for multi-touch operation.
Alternatively, ambiguity can be avoided by applying a «de-sensitizing» signal to all but one of the columns .[63]
This leaves just a short section of any row sensitive to touch. By selecting a sequence of these sections along the row, it is possible to determine the accurate position of multiple fingers along that row. This process can then be repeated for all the other rows until the whole screen has been scanned.
Self-capacitive touch screen layers are used on mobile phones such as the Sony Xperia Sola,[64] the Samsung Galaxy S4, Galaxy Note 3, Galaxy S5, and Galaxy Alpha.
Self capacitance is far more sensitive than mutual capacitance and is mainly used for single touch, simple gesturing and proximity sensing where the finger does not even have to touch the glass surface.
Mutual capacitance is mainly used for multitouch applications.
[65]
Many touchscreen manufacturers use both self and mutual capacitance technologies in the same product, thereby combining their individual benefits.
[66]
Use of stylus on capacitive screens[edit]
Capacitive touchscreens do not necessarily need to be operated by a finger, but until recently the special styli required could be quite expensive to purchase. The cost of this technology has fallen greatly in recent years and capacitive styli are now widely available for a nominal charge, and often given away free with mobile accessories. These consist of an electrically conductive shaft with a soft conductive rubber tip, thereby resistively connecting the fingers to the tip of the stylus.
Infrared grid[edit]

Infrared sensors mounted around the display watch for a user’s touchscreen input on this PLATO V terminal in 1981. The monochromatic plasma display’s characteristic orange glow is illustrated.
An infrared touchscreen uses an array of X-Y infrared LED and photodetector pairs around the edges of the screen to detect a disruption in the pattern of LED beams. These LED beams cross each other in vertical and horizontal patterns. This helps the sensors pick up the exact location of the touch. A major benefit of such a system is that it can detect essentially any opaque object including a finger, gloved finger, stylus or pen. It is generally used in outdoor applications and POS systems that cannot rely on a conductor (such as a bare finger) to activate the touchscreen. Unlike capacitive touchscreens, infrared touchscreens do not require any patterning on the glass which increases durability and optical clarity of the overall system. Infrared touchscreens are sensitive to dirt and dust that can interfere with the infrared beams, and suffer from parallax in curved surfaces and accidental press when the user hovers a finger over the screen while searching for the item to be selected.
Infrared acrylic projection[edit]
A translucent acrylic sheet is used as a rear-projection screen to display information. The edges of the acrylic sheet are illuminated by infrared LEDs, and infrared cameras are focused on the back of the sheet. Objects placed on the sheet are detectable by the cameras. When the sheet is touched by the user, frustrated total internal reflection results in leakage of infrared light which peaks at the points of maximum pressure, indicating the user’s touch location. Microsoft’s PixelSense tablets use this technology.
Optical imaging[edit]
Optical touchscreens are a relatively modern development in touchscreen technology, in which two or more image sensors (such as CMOS sensors) are placed around the edges (mostly the corners) of the screen. Infrared backlights are placed in the sensor’s field of view on the opposite side of the screen. A touch blocks some lights from the sensors, and the location and size of the touching object can be calculated (see visual hull). This technology is growing in popularity due to its scalability, versatility, and affordability for larger touchscreens.
Dispersive signal technology[edit]
Introduced in 2002 by 3M, this system detects a touch by using sensors to measure the piezoelectricity in the glass. Complex algorithms interpret this information and provide the actual location of the touch.[67] The technology is unaffected by dust and other outside elements, including scratches. Since there is no need for additional elements on screen, it also claims to provide excellent optical clarity. Any object can be used to generate touch events, including gloved fingers. A downside is that after the initial touch, the system cannot detect a motionless finger. However, for the same reason, resting objects do not disrupt touch recognition.
Acoustic pulse recognition[edit]
The key to this technology is that a touch at any one position on the surface generates a sound wave in the substrate which then produces a unique combined signal as measured by three or more tiny transducers attached to the edges of the touchscreen. The digitized signal is compared to a list corresponding to every position on the surface, determining the touch location. A moving touch is tracked by rapid repetition of this process. Extraneous and ambient sounds are ignored since they do not match any stored sound profile. The technology differs from other sound-based technologies by using a simple look-up method rather than expensive signal-processing hardware. As with the dispersive signal technology system, a motionless finger cannot be detected after the initial touch. However, for the same reason, the touch recognition is not disrupted by any resting objects. The technology was created by SoundTouch Ltd in the early 2000s, as described by the patent family EP1852772, and introduced to the market by Tyco International’s Elo division in 2006 as Acoustic Pulse Recognition.[68] The touchscreen used by Elo is made of ordinary glass, giving good durability and optical clarity. The technology usually retains accuracy with scratches and dust on the screen. The technology is also well suited to displays that are physically larger.
Construction[edit]
| This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (September 2017) |
There are several principal ways to build a touchscreen. The key goals are to recognize one or more fingers touching a display, to interpret the command that this represents, and to communicate the command to the appropriate application.
In the resistive approach, which used to be the most popular technique, there are typically four layers:
- Top polyester-coated layer with a transparent metallic-conductive coating on the bottom.
- Adhesive spacer
- Glass layer coated with a transparent metallic-conductive coating on the top
- Adhesive layer on the backside of the glass for mounting.
When a user touches the surface, the system records the change in the electric current that flows through the display.
Dispersive-signal technology measures the piezoelectric effect—the voltage generated when mechanical force is applied to a material—that occurs chemically when a strengthened glass substrate is touched.
There are two infrared-based approaches. In one, an array of sensors detects a finger touching or almost touching the display, thereby interrupting infrared light beams projected over the screen. In the other, bottom-mounted infrared cameras record heat from screen touches.
In each case, the system determines the intended command based on the controls showing on the screen at the time and the location of the touch.
Development[edit]
The development of multi-touch screens facilitated the tracking of more than one finger on the screen; thus, operations that require more than one finger are possible. These devices also allow multiple users to interact with the touchscreen simultaneously.
With the growing use of touchscreens, the cost of touchscreen technology is routinely absorbed into the products that incorporate it and is nearly eliminated. Touchscreen technology has demonstrated reliability and is found in airplanes, automobiles, gaming consoles, machine control systems, appliances, and handheld display devices including cellphones; the touchscreen market for mobile devices was projected to produce US$5 billion by 2009.[69][needs update]
The ability to accurately point on the screen itself is also advancing with the emerging graphics tablet-screen hybrids. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) plays a major role in this innovation due its high piezoelectric properties, which allow the tablet to sense pressure, making such things as digital painting behave more like paper and pencil.[70]
TapSense, announced in October 2011, allows touchscreens to distinguish what part of the hand was used for input, such as the fingertip, knuckle and fingernail. This could be used in a variety of ways, for example, to copy and paste, to capitalize letters, to activate different drawing modes, etc.[71][72]
A real practical integration between television-images and the functions of a normal modern PC could be an innovation in the near future: for example «all-live-information» on the internet about a film or the actors on video, a list of other music during a normal video clip of a song or news about a person.
Ergonomics and usage[edit]
Touchscreen enable[edit]
For touchscreens to be effective input devices, users must be able to accurately select targets and avoid accidental selection of adjacent targets. The design of touchscreen interfaces should reflect technical capabilities of the system, ergonomics, cognitive psychology and human physiology.
Guidelines for touchscreen designs were first developed in the 2000s, based on early research and actual use of older systems, typically using infrared grids—which were highly dependent on the size of the user’s fingers. These guidelines are less relevant for the bulk of modern touch devices which use capacitive or resistive touch technology.[73][74]
From the mid-2000s, makers of operating systems for smartphones have promulgated standards, but these vary between manufacturers, and allow for significant variation in size based on technology changes, so are unsuitable from a human factors perspective.[75][76][77]
Much more important is the accuracy humans have in selecting targets with their finger or a pen stylus. The accuracy of user selection varies by position on the screen: users are most accurate at the center, less so at the left and right edges, and least accurate at the top edge and especially the bottom edge. The R95 accuracy (required radius for 95% target accuracy) varies from 7 mm (0.28 in) in the center to 12 mm (0.47 in) in the lower corners.[78][79][80][81][82] Users are subconsciously aware of this, and take more time to select targets which are smaller or at the edges or corners of the touchscreen.[83]
This user inaccuracy is a result of parallax, visual acuity and the speed of the feedback loop between the eyes and fingers. The precision of the human finger alone is much, much higher than this, so when assistive technologies are provided—such as on-screen magnifiers—users can move their finger (once in contact with the screen) with precision as small as 0.1 mm (0.004 in).[84][dubious – discuss]
Hand position, digit used and switching[edit]
Users of handheld and portable touchscreen devices hold them in a variety of ways, and routinely change their method of holding and selection to suit the position and type of input. There are four basic types of handheld interaction:
- Holding at least in part with both hands, tapping with a single thumb
- Holding with two hands and tapping with both thumbs
- Holding with one hand, tapping with the finger (or rarely, thumb) of another hand
- Holding the device in one hand, and tapping with the thumb from that same hand
Use rates vary widely. While two-thumb tapping is encountered rarely (1–3%) for many general interactions, it is used for 41% of typing interaction.[85]
In addition, devices are often placed on surfaces (desks or tables) and tablets especially are used in stands. The user may point, select or gesture in these cases with their finger or thumb, and vary use of these methods.[86]
Combined with haptics[edit]
Touchscreens are often used with haptic response systems. A common example of this technology is the vibratory feedback provided when a button on the touchscreen is tapped. Haptics are used to improve the user’s experience with touchscreens by providing simulated tactile feedback, and can be designed to react immediately, partly countering on-screen response latency. Research from the University of Glasgow (Brewster, Chohan, and Brown, 2007; and more recently Hogan) demonstrates that touchscreen users reduce input errors (by 20%), increase input speed (by 20%), and lower their cognitive load (by 40%) when touchscreens are combined with haptics or tactile feedback. On top of this, a study conducted in 2013 by Boston College explored the effects that touchscreens haptic stimulation had on triggering psychological ownership of a product. Their research concluded that a touchscreens ability to incorporate high amounts of haptic involvement resulted in customers feeling more endowment to the products they were designing or buying. The study also reported that consumers using a touchscreen were willing to accept a higher price point for the items they were purchasing.[87]
Customer service[edit]
Touchscreen technology has become integrated into many aspects of customer service industry in the 21st century.[88] The restaurant industry is a good example of touchscreen implementation into this domain. Chain restaurants such as Taco Bell,[89] Panera Bread, and McDonald’s offer touchscreens as an option when customers are ordering items off the menu.[90] While the addition of touchscreens is a development for this industry, customers may choose to bypass the touchscreen and order from a traditional cashier.[89] To take this a step further, a restaurant in Bangalore has attempted to completely automate the ordering process. Customers sit down to a table embedded with touchscreens and order off an extensive menu. Once the order is placed it is sent electronically to the kitchen.[91] These types of touchscreens fit under the Point of Sale (POS) systems mentioned in the lead section.
«Gorilla arm»[edit]
Extended use of gestural interfaces without the ability of the user to rest their arm is referred to as «gorilla arm».[92] It can result in fatigue, and even repetitive stress injury when routinely used in a work setting. Certain early pen-based interfaces required the operator to work in this position for much of the workday.[93] Allowing the user to rest their hand or arm on the input device or a frame around it is a solution for this in many contexts. This phenomenon is often cited as an example of movements to be minimized by proper ergonomic design.
Unsupported touchscreens are still fairly common in applications such as ATMs and data kiosks, but are not an issue as the typical user only engages for brief and widely spaced periods.[94]
Fingerprints[edit]

Touchscreens can suffer from the problem of fingerprints on the display. This can be mitigated by the use of materials with optical coatings designed to reduce the visible effects of fingerprint oils. Most modern smartphones have oleophobic coatings, which lessen the amount of oil residue. Another option is to install a matte-finish anti-glare screen protector, which creates a slightly roughened surface that does not easily retain smudges.
Glove touch[edit]
Touchscreens do not work most of the time when the user wears gloves. The thickness of the glove and the material they are made of play a significant role on that and the ability of a touchscreen to pick up a touch.
See also[edit]
- Dual-touchscreen
- Pen computing
- Energy harvesting
- Flexible keyboard
- Gestural interface
- Graphics tablet
- Light pen
- List of touch-solution manufacturers
- Lock screen
- Tablet computer
- Touch switch
- Touchscreen remote control
- Multi-touch
- Omnitouch
- Pointing device gesture
- Sensacell
- SixthSense
- Nintendo DS
References[edit]
- ^ Walker, Geoff (August 2012). «A review of technologies for sensing contact location on the surface of a display: Review of touch technologies». Journal of the Society for Information Display. 20 (8): 413–440. doi:10.1002/jsid.100. S2CID 40545665.
- ^ «What is a Touch Screen?». www.computerhope.com. Retrieved 2020-09-07.
- ^ Allvin, Rhian Evans (2014-09-01). «Technology in the Early Childhood Classroom». YC Young Children. 69 (4): 62. ISSN 1538-6619.
- ^ «The first capacitative touch screens at CERN». CERN Courrier. 31 March 2010. Archived from the original on 4 September 2010. Retrieved 2010-05-25.
- ^ Bent Stumpe (16 March 1977). «A new principle for x-y touch system» (PDF). CERN. Retrieved 2010-05-25.
- ^ Bent Stumpe (6 February 1978). «Experiments to find a manufacturing process for an x-y touch screen» (PDF). CERN. Retrieved 2010-05-25.
- ^ Beck, Frank; Stumpe, Bent (May 24, 1973). Two devices for operator interaction in the central control of the new CERN accelerator (Report). CERN. CERN-73-06. Retrieved 2017-09-14.
- ^ Johnson, E.A. (1965). «Touch Display — A novel input/output device for computers». Electronics Letters. 1 (8): 219–220. Bibcode:1965ElL…..1..219J. doi:10.1049/el:19650200.
- ^ «1965 — The Touchscreen». Malvern Radar and Technology History Society. 2016. Archived from the original on 31 January 2018. Retrieved 24 July 2017.
- ^ Johnson, E.A. (1967). «Touch Displays: A Programmed Man-Machine Interface». Ergonomics. 10 (2): 271–277. doi:10.1080/00140136708930868.
- ^ Orr, N.W.; Hopkins, V.D. (1968). «The Role of Touch Display in Air Traffic Control». The Controller. 7: 7–9.
- ^ Lowe, J. F. (18 November 1974). «Computer creates custom control panel». Design News: 54–55.
- ^ Stumpe, Bent; Sutton, Christine (1 June 2010). «CERN touch screen». Symmetry Magazine. A joint Fermilab/SLAC publication. Archived from the original on 2016-11-16. Retrieved 16 November 2016.
- ^ «Another of CERN’s many inventions! — CERN Document Server». CERN Document Server. Retrieved 29 July 2015.
- ^ a b c Mallebrein, Rainer (2018-02-18). «Oral History of Rainer Mallebrein» (PDF) (Interview). Interviewed by Steinbach, Günter. Singen am Hohentwiel, Germany: Computer History Museum. CHM Ref: X8517.2018. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-01-27. Retrieved 2021-08-23. (18 pages)
- ^ a b c Ebner, Susanne (2018-01-24). «Entwickler aus Singen über die Anfänge der Computermaus: «Wir waren der Zeit voraus»» [Singen-based developer about the advent of the computer mouse: «We were ahead of time»]. Leben und Wissen. Südkurier (in German). Konstanz, Germany: Südkurier GmbH. Archived from the original on 2021-03-02. Retrieved 2021-08-22.
- ^ F. Ebeling, R. Johnson, R. Goldhor, Infrared light beam x-y position encoder for display devices, US 3775560, granted November 27, 1973.
- ^ The H.P. Touch Computer (1983) Archived 2017-08-24 at the Wayback Machine. YouTube (2008-02-19). Retrieved on 2013-08-16.
- ^ USPTO. «DISCRIMINATING CONTACT SENSOR». Archived from the original on 19 May 2013. Retrieved 6 April 2013.
- ^ Emerson, Lewis (December 13, 2010). ««G. Samuel Hurst — the ‘Tom Edison’ of ORNL», December 14 2010″. G. Samuel Hurst — the ‘Tom Edison’ of ORNL. Retrieved 2010-12-13.[dead link]
- ^ Japanese PCs (1984) Archived 2017-07-07 at the Wayback Machine (12:21), Computer Chronicles
- ^ «Terebi Oekaki / Sega Graphic Board — Articles — SMS Power!». Archived from the original on 23 July 2015. Retrieved 29 July 2015.
- ^ «Software that takes games seriously». New Scientist. Reed Business Information. March 26, 1987. p. 34. Archived from the original on January 31, 2018 – via Google Books.
- ^ Technology Trends: 2nd Quarter 1986 Archived 2016-10-15 at the Wayback Machine, Japanese Semiconductor Industry Service — Volume II: Technology & Government
- ^ Biferno, M. A., Stanley, D. L. (1983). The Touch-Sensitive Control/Display Unit: A Promising Computer Interface. Technical Paper 831532, Aerospace Congress & Exposition, Long Beach, CA: Society of Automotive Engineers.
- ^ «1986, Electronics Developed for Lotus Active Suspension Technology — Generations of GM». History.gmheritagecenter.com. Archived from the original on 2013-06-17. Retrieved 2013-01-07.
- ^ Badal, Jaclyne (2008-06-23). «When Design Goes Bad». Online.wsj.com. Archived from the original on 2016-03-16. Retrieved 2013-01-07.
- ^ The ViewTouch restaurant system Archived 2009-09-09 at the Wayback Machine by Giselle Bisson
- ^ «The World Leader in GNU-Linux Restaurant POS Software». Viewtouch.com. Archived from the original on 2012-07-17. Retrieved 2013-01-07.
- ^ «File:Comdex 1986.png». Wikimedia Commons. 2012-09-11. Archived from the original on 2012-12-20. Retrieved 2013-01-07.
- ^ Potter, R.; Weldon, L.; Shneiderman, B. (1988). «Improving the accuracy of touch screens: an experimental evaluation of three strategies». Proceedings of the SIGCHI conference on Human factors in computing systems — CHI ’88. Proc. of the Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, CHI ’88. Washington, DC. pp. 27–32. doi:10.1145/57167.57171. ISBN 0201142376. Archived from the original on 2015-12-08.
- ^ a b Sears, Andrew; Plaisant, Catherine; Shneiderman, Ben (June 1990). «A new era for high-precision touchscreens». In Hartson, R.; Hix, D. (eds.). Advances in Human-Computer Interaction. Vol. 3. Ablex (1992). ISBN 978-0-89391-751-7. Archived from the original on October 9, 2014.
- ^ «1991 video of the HCIL touchscreen toggle switches (University of Maryland)». YouTube. Archived from the original on 13 March 2016. Retrieved 3 December 2015.
- ^ Apple touch-screen patent war comes to the UK (2011). Event occurs at 1:24 min in video. Archived from the original on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 3 December 2015.
- ^ Star7 Demo on YouTube. Retrieved on 2013-08-16.
- ^ «The LG KE850: touchable chocolate». Engadget.
- ^ «Touch Screen Market to Hit $9B by 2015». CBS News.
- ^ «Touch screen gamble: Which technology to use».
- ^ «Canalys — the leading global technology market analyst firm».
- ^ Travis Fahs (April 21, 2009). «IGN Presents the History of SEGA». IGN. p. 7. Archived from the original on February 4, 2012. Retrieved 2011-04-27.
- ^ «Short Course on Projected Capacitance» (PDF).
- ^ «What is touch screen? — Definition from WhatIs.com». WhatIs.com. Retrieved 2020-09-07.
- ^ Lancet, Yaara. (2012-07-19) What Are The Differences Between Capacitive & Resistive Touchscreens? Archived 2013-03-09 at the Wayback Machine. Makeuseof.com. Retrieved on 2013-08-16.
- ^ Vlad Savov. «Nintendo 3DS has resistive touchscreen for backwards compatibility, what’s the Wii U’s excuse?». Engadget. AOL. Archived from the original on 12 November 2015. Retrieved 29 July 2015.
- ^ Hong, Chan-Hwa; Shin, Jae-Heon; Ju, Byeong-Kwon; Kim, Kyung-Hyun; Park, Nae-Man; Kim, Bo-Sul; Cheong, Woo-Seok (1 November 2013). «Index-Matched Indium Tin Oxide Electrodes for Capacitive Touch Screen Panel Applications». Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology. 13 (11): 7756–7759. doi:10.1166/jnn.2013.7814. PMID 24245328. S2CID 24281861.
- ^ «Fujifilm reinforces the production facilities for its touch-panel sensor film «EXCLEAR»«. FUJIFILM Europe.
- ^ «Development of a Thin Double-sided Sensor Film «EXCLEAR» for Touch Panels via Silver Halide Photographic Technology» (PDF). www.fujifilm.com. Retrieved 2019-12-09.
- ^ «What’s behind your smartphone screen? This… |». fujifilm-innovation.tumblr.com.
- ^ «Environment: [Topics2] Development of Materials That Solve Environmental Issues EXCLEAR thin double-sided sensor film for touch panels | FUJIFILM Holdings». www.fujifilmholdings.com.
- ^ Kent, Joel (May 2010). «Touchscreen technology basics & a new development». CMOS Emerging Technologies Conference. CMOS Emerging Technologies Research. 6: 1–13. ISBN 9781927500057.
- ^ Ganapati, Priya (5 March 2010). «Finger Fail: Why Most Touchscreens Miss the Point». Wired. Archived from the original on 2014-05-11. Retrieved 9 November 2019.
- ^ Andi (2014-01-24). «How noise affects touch screens». West Florida Components. Retrieved 2020-10-24.
- ^ «Touch screens and charger noise |». epanorama.net. 2013-03-12.
- ^ «Aggressively combat noise in capacitive touch applications». EDN.com. 2013-04-08.
- ^ «Please Touch! Explore The Evolving World Of Touchscreen Technology». electronicdesign.com. Archived from the original on 2015-12-13. Retrieved 2009-09-02.
- ^ «formula for relationship between plate area and capacitance».
- ^ «Touch operated keyboard». Archived from the original on 2018-01-31. Retrieved 2018-01-30.
- ^ «Multipoint touchscreen».
- ^ «Espacenet — Original document». Worldwide.espacenet.com. 2017-04-26. Retrieved 2018-02-22.
- ^ Knowledge base: Multi-touch hardware Archived 2012-02-03 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «Use of RC oscillator in touchscreen».
- ^ «Ambiguity caused by multitouch in self capacitance touchscreens» (PDF).
- ^ a b «Multitouch using Self Capacitance».
- ^ «Self-capacitive touch described on official Sony Developers blog». Archived from the original on 2012-03-14. Retrieved 2012-03-14.
- ^ Du, Li (2016). «Comparison of self capacitance and mutual capacitance» (PDF). arXiv:1612.08227. doi:10.1017/S1743921315010388. S2CID 220453196.
- ^ «Hybrid self and mutual capacitance touch sensing controllers».
- ^ Beyers, Tim (2008-02-13). «Innovation Series: Touchscreen Technology». The Motley Fool. Archived from the original on 2009-03-24. Retrieved 2009-03-16.
- ^ «Acoustic Pulse Recognition Touchscreens» (PDF). Elo Touch Systems. 2006: 3. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2011-09-05. Retrieved 2011-09-27.
- ^ «Touch Screens in Mobile Devices to Deliver $5 Billion Next Year | Press Release». ABI Research. 2008-09-10. Archived from the original on 2011-07-07. Retrieved 2009-06-22.
- ^ «Insights Into PVDF Innovations». Fluorotherm. 17 August 2015. Archived from the original on 15 October 2016.
- ^ «New Screen Technology, TapSense, Can Distinguish Between Different Parts Of Your Hand». Archived from the original on October 20, 2011. Retrieved October 19, 2011.
- ^ «TapSense: Enhancing Finger Interaction on Touch Surfaces». Archived from the original on 11 January 2012. Retrieved 28 January 2012.
- ^ «ANSI/HFES 100-2007 Human Factors Engineering of Computer Workstations». Human Factors & Ergonomics Society. Santa Monica, CA. 2007.
- ^ «Ergonomic Requirements for Office Work with Visual Display Terminals (VDTs)–Part 9: Requirements for Non-keyboard Input Devices». International Organization for Standardization. Geneva, Switzerland. 2000.
- ^ «iOS Human Interface Guidelines». Apple. Archived from the original on 2014-08-26. Retrieved 2014-08-24.
- ^ «Metrics and Grids». Archived from the original on 2014-07-16. Retrieved 2014-08-24.
- ^ «Touch interactions for Windows». Microsoft. Archived from the original on 2014-08-26. Retrieved 2014-08-24.
- ^ Hoober, Steven (2013-02-18). «Common Misconceptions About Touch». UXmatters. Archived from the original on 2014-08-26. Retrieved 2014-08-24.
- ^ Hoober, Steven (2013-11-11). «Design for Fingers and Thumbs Instead of Touch». UXmatters. Archived from the original on 2014-08-26. Retrieved 2014-08-24.
- ^ Hoober, Steven; Shank, Patti; Boll, Susanne (2014). «Making mLearning Usable: How We Use Mobile Devices». Santa Rosa, CA.
- ^ Henze, Niels; Rukzio, Enrico; Boll, Susanne (2011). «100,000,000 Taps: Analysis and Improvement of Touch Performance in the Large». Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Human Computer Interaction with Mobile Devices and Services. New York.
- ^ Parhi, Pekka (2006). «Target Size Study for One-Handed Thumb Use on Small Touchscreen Devices». Proceedings of MobileHCI 2006. New York.
- ^ Lee, Seungyons; Zhai, Shumin (2009). «The Performance of Touch Screen Soft Buttons». Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. New York: 309. doi:10.1145/1518701.1518750. ISBN 9781605582467. S2CID 2468830.
- ^ Bérard, François (2012). «Measuring the Linear and Rotational User Precision in Touch Pointing». Proceedings of the 2012 ACM International Conference on Interactive Tabletops and Surfaces. New York: 183. doi:10.1145/2396636.2396664. ISBN 9781450312097. S2CID 15765730.
- ^ Hoober, Steven (2014-09-02). «Insights on Switching, Centering, and Gestures for Touchscreens». UXmatters. Archived from the original on 2014-09-06. Retrieved 2014-08-24.
- ^ Hoober, Steven (2013-02-18). «How Do Users Really Hold Mobile Devices?». UXmatters. Archived from the original on 2014-08-26. Retrieved 2014-08-24.
- ^ Brasel, S. Adam; Gips, James (2014). «Tablets, touchscreens, and touchpads: How varying touch interfaces trigger psychological ownership and endowment». Journal of Consumer Psychology. 24 (2): 226–233. doi:10.1016/j.jcps.2013.10.003.
- ^ Zhu, Ying; Meyer, Jeffrey (September 2017). «Getting in touch with your thinking style: How touchscreens influence purchase». Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services. 38: 51–58. doi:10.1016/j.jretconser.2017.05.006.
- ^ a b Hueter, Jackie; Swart, William (February 1998). «An Integrated Labor-Management System for Taco Bell». Interfaces. 28 (1): 75–91. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.565.3872. doi:10.1287/inte.28.1.75. S2CID 18514383.
- ^ Baker, Rosie (19 May 2011). «FOOD: McDonald’s explores digital touchscreens». Marketing Week: 4. Gale A264377887.
- ^ «A RESTAURANT THAT LETS GUESTS PLACE ORDERS VIA A TOUCHSCREEN TABLE (Touche is said to be the first touchscreen restaurant in India and fifth in the world)». India Business Insight. 31 August 2011. Gale A269135159.
- ^ «gorilla arm». Catb.org. Archived from the original on 2012-01-21. Retrieved 2012-01-04.
- ^ «Gesture Fatigue ruined light pens forever. Make sure it doesn’t ruin your gesture design». Gesture Design Blog. Archived from the original on 2015-02-13. Retrieved 2014-08-23.
- ^ David Pogue (January 3, 2013). «Why Touch Screens Will Not Take Over». Scientific American. 308 (1): 25. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0113-25. PMID 23342443.
Sources[edit]
- Shneiderman, B. (1991). «Touch screens now offer compelling uses». IEEE Software. 8 (2): 93–94, 107. doi:10.1109/52.73754. S2CID 14561929.
- Potter, R.; Weldon, L. & Shneiderman, B. (1988). An experimental evaluation of three strategies. Proc. CHI’88. Washington, DC: ACM Press. pp. 27–32.
- Sears, A.; Plaisant, C. & Shneiderman, B. (1992). «A new era for high precision touchscreens». In Hartson, R. & Hix, D. (eds.). Advances in Human-Computer Interaction. Vol. 3. Ablex, NJ. pp. 1–33.
