Сегодня рассмотрим пример настройки переадресации вызовов на Cisco Call Manager Express. Переадресация — это функция, которая позволяет переадресовать звонки с одного телефона на другой телефон. Пример настройки переадресации с номера 1080 на номер 1090:
Для SIP-телефонов:
voice register dn 8
number 1080
call-forward b2bua all 1090 ——— Переадресовать все звонки сразу на 1090 или можно включить на телефоне через soft-key
call-forward b2bua busy 1090 ——- Переадресовать все звонки, если линия занята
call-forward b2bua noan 1090 timout 15 — Переадресовать звонки, если не отвечает 15 сек.
call-forward b2bua unregistered 1090 — Переадресовать звонки, если телефон не зарегистр ирован.
Для SCCP-телефонов:
ephone-dn 8
number 1080
call-forward all 1090
call-forward busy 1090
call-forward b2bua noan 1090 timout 15
На этом пока всё. Хорошего всем дня!
Как настроить переадресацию звонков в ip-телефонии?
Обычно это делается при помощи виртуальной АТС. У 2 sip аккаунтов есть внутренний номер, например 101 и 102. на виртуальной АТС настраиваем перевод номера- решетка, например, или «0». Нажимаем этот символ, вирт. АТС понимает что один из номеров хочет сделать перевод, вызов ставится на ожидание, затем набираем номер другого sip аккаунта и туда он переходит.
В общем — пинайте поддержку дом.ру, но смысл один — у sip аккаунтов есть внутренний номер, нужно научиться на эти номера переводить звонки.
- Вконтакте
переадресация — это когда вы её включили один раз и все вызовы на ваш номер сразу будут уходить на номер назначения перевода. Типа, номер 100 включен переадресация на номер 200. Значит если позвонить на 100, то звонить сразу будет 200.
Вам нужен перевод. Что бы вы ответили и перевели вызов на второй свой номер. То есть вы на 100 ответили, сказали «але», а потом нажали пару кнопок и вызов будет передан на 200.
Какой телефонный аппарат вы используете? Дект трубка? Аналоговый панасоник? Напишите модель.
КАК ПЕРЕАДРЕСОВАТЬ НА СВОЙ ТЕЛЕФОН С ПОМОЩЬЮ IP-ТЕЛЕФОНА CISCO 7960 — ВОКРУГ-ДОМ — 2022
Видео: Cisco phone application: ETA запись разговора (Июнь 2022).
Переадресация звонков — это полезная функция телефона, которая позволяет вам принимать деловые звонки на отдельную трубку. IP-телефон Cisco 7960G — это служебный телефон, разработанный для работы в сети вашей компании. Если вы находитесь за пределами своего рабочего стола, вы можете настроить IP-телефон Cisco 7960G на переадресацию вызовов на ваш личный телефон, например, на сотовый или домашний номер. Используйте функциональную клавишу «CFwdAll» на IP-телефоне Cisco для настройки этого удобства.

Переадресация вызовов с вашего IP-телефона Cisco 7960 на ваш личный телефон.
Шаг 1
Нажмите функциональную клавишу «CFwdAll» под дисплеем Cisco IP Phone 7960G. Это кнопка, которая открывает опцию переадресации.
Шаг 2
Подождите, пока телефон подаст два звуковых сигнала.
Шаг 3
Введите целевой номер телефона. Это ваш личный номер телефона, например, сотовый или домашний стационарный телефон.
Шаг 4
Подождите, пока телефон Cisco подаст один звуковой сигнал. Ваш целевой номер будет показан внизу экрана. Вы также увидите мигающую стрелку в правом верхнем углу экрана, которая указывает, что ваши вызовы переадресовываются на номер, указанный ниже.
Как переадресовать телефон

Если вы ожидаете важного телефонного звонка у себя дома на своем стационарном телефоне, но вас там не будет, чтобы ответить на него, вы все равно сможете позвонить, переправив свой .
Как я могу переадресовать мои звонки на мобильный телефон T-Mobile?

Если вы заняты в течение нескольких часов или просто хотите отдохнуть от постоянного звонка вашего мобильного телефона, вы можете переадресовывать входящие звонки, чтобы перейти прямо на голосовую почту или на другой телефон .
Как переадресовать все входящие звонки на другой сотовый телефон

Многие профессионалы бизнеса имеют более одного номера мобильного телефона. Если вы это сделаете, то вам может быть удобно переадресовывать вызовы с одного устройства на другое. Вы можете переслать все, что я .
Основные операции с вызовами
IP-телефон Cisco 7961G/7961G-GE и 7941G/7941G-GE
29
Переадресация вызовов на другой номер
Функция переадресации всех вызовов позволяет перенаправлять все входящие вызовы
с IP-телефона Cisco на другой номер.
Примечание Введите номер для переадресации всех вызовов в точности так, как при наборе этого
номера с телефона на рабочем столе. В частности, при наличии кода доступа или кода
междугородной связи необходимо ввести эти коды.
Совет
• Вызовы могут переадресовываться на обычный аналоговый телефон или на другой
IP-телефон; однако системный администратор может ограничить переадресацию
вызовов, разрешив ее только на номера данной компании.
• Эту функцию необходимо настроить отдельно для каждой линии. Если вызов поступает
на линию, для которой переадресация вызовов не включена, воспроизводится обычный
звуковой сигнал вызова.
Если требуется…
Выполните следующие действия…
Настроить переадресацию
вызовов, поступающих на
основную линию
Нажмите =>все и введите номер телефона для переадресации.
Отменить переадресацию
вызовов, поступающих на
основную линию
Нажмите =>все.
Проверить включение
переадресации вызовов,
поступающих на основную
линию
Проверьте наличие над телефонным номером основной линии
следующего значка: .
Можно также проверить, отображается ли
в строке состояния внизу экрана номер адресата для переадресации
вызовов.
Настроить или отменить
переадресацию вызовов,
поступающих на
произвольную линию
Зарегистрируйтесь на web-страницах параметров пользователя,
выберите свое устройство, затем в главном меню выберите
Переадресация всех вызовов. Можно устанавливать и отменять
переадресацию вызовов для каждой линии телефона. Инструкции
по регистрации см. в разделе «Регистрация на web-страницах
параметров пользователя» на стр. 52.
При включенной переадресации вызовов для любой из линий,
кроме основной линии, на телефоне не отображается какого-либо
подтверждения переадресации вызовов. Для проверки включения
переадресации необходимо перейти на страницы параметров
пользователя.
Call Transfer and
Forward
Information About Call Transfer and Forward
Call
Forward
Call forward
feature diverts calls to a specified number under one or more of the following
conditions:
- All calls—When all-call
call forwarding is activated by a phone user, all incoming calls are diverted.
The target destination for diverted calls can be specified in the router
configuration or by the phone user with a soft key or feature access code. The
most recently entered destination is recognized by Cisco Unified CME,
regardless of how it was entered. - No answer—Incoming calls
are diverted when the extension does not answer before the timeout expires. The
target destination for diverted calls is specified in the router configuration. - Busy—Incoming calls are
diverted when the extension is busy and call waiting is not active. The target
destination for diverted calls is specified in the router configuration. - Night service—All incoming calls are
automatically diverted during night-service hours. The target destination for
diverted calls is specified in the router configuration.
A directory number
can have all four types of call forwarding defined at the same time with a
different forwarding destination defined for each type of call forwarding. If
more than one type of call forwarding is active at one time, the order for
evaluating the different types is as follows:
- Call forward night-service
- Call forward all
- Call forward busy and call forward
no-answer
H.450.3 capabilities
are enabled globally on the router by default, and can be disabled either
globally or for individual dial peers. You can configure incoming patterns for
using the H.450.3 standard. Calling-party numbers that do not match the
patterns defined with this command are forwarded using Cisco-proprietary call
forwarding for backward compatibility. For information about configuring
H.450.3 on a Cisco Unified CME system, see
Enable Call Forwarding for a Directory Number.
Selective Call
Forward
You can apply call
forward to a busy or no-answer directory number based on the number that is
dialed to reach the directory number: the primary number, the secondary number,
or either of those numbers expanded by a dial-plan pattern.
Cisco Unified CME
automatically creates one POTS dial peer for each ephone-dn when it is assigned
a primary number. If the ephone-dn is assigned a secondary number, it creates a
second POTS dial peer. If the
dialplan-pattern command is used to expand the
primary and secondary numbers for ephone-dns, it creates two more dial peers,
resulting in the creation of the following four dial peers for the ephone-dn:
-
A POTS dial peer
for the primary number -
A POTS dial peer
for the secondary number -
A POTS dial peer
for the primary number as expanded by the
dialplan-pattern command -
A POTS dial peer
for the secondary number as expanded by the
dialplan-pattern command
Call forwarding is
normally applied to all dial peers created for an ephone-dn. Selective call
forwarding allows you to apply call forwarding for busy or no-answer calls only
for the dial peers you have specified, based on the called number that was used
to route the call to the ephone-dn.
For example, the following commands set up a single ephone-dn (ephone-dn 5) with four dial peers:telephony-service dialplan-pattern 1 40855501.. extension-length 4 extension-pattern 50.. ephone-dn 5 number 5066 secondary 5067 In this example,
selective call forwarding can be applied so that calls are forwarded when:
-
callers dial the
primary number 5066. -
when callers
dial the secondary number 5067. -
when callers
dial the expanded numbers 4085550166 or 4085550167.
For configuration
information, see
Enable Call Forwarding for a Directory Number.
Call Forward
Unregistered
The Call Forward
Unregistered (CFU) feature allows you to forward a call to a different number
if the directory number (DN) is not associated with a phone or if the
associated phone is not registered to Cisco Unified CME. The CFU feature is
very useful for wireless phone users when the wireless phone is out of the
access point or phone shuts down automatically because of an automatic shutdown
feature. The service is not available and the call can be forwarded to the CFU
destination. Any unregistered or floating DN can be forwarded using the CFU
feature.
An unregistered DN
indicates that none of its associated phones are registered to the
Cisco Unified CME. A registered phone will become unregistered when the
Cisco Unified CME sends an unregistration request or responses to a phone’s
unregistration request. Cisco Unified CME sends an unregistration request under
the following circumstances:
- When the keepalive timer
expires. - When a user issues a reset or restart
command on the phone. - When an extension mobility (EM) user
logs into the phone. (All DNs configured under the logout-profile are
unregistered except for the shared ones that are associated with other
registered phones.) - When an EM user logs out of the phone.
(All DNs configured under the user-profile are unregistered except for the
shared ones that are associated with other registered phones.)
There is always a
gap between the time the phone loses its connection with Cisco Unified CME and
the time when Cisco Unified CME claims the phone is unregistered. The length of
the gap depends on the keepalive timer. Cisco Unified CME considers the phone
as registered and tries to associate DNs until the keepalive timer expires. You
can configure the expiration for the keepalive timer using the registrar server
expires max <seconds> min <seconds> command under sip in voice
service voip mode for SIP IP phones. For more information, see
Example for Configuring Keepalive Timer Expiration in SIP Phones.
Cisco Unified CME
8.6 supports the CFU feature on SIP IP phones using the call-forward b2bua
unregistered command under voice register dn tag. The CFU feature supports
overlap dialing and en-bloc dialing. A call to a floating DN is forwarded to
its CFU destination, if configured. Calls to a DN out of service point or
phones losing connection are not forwarded to a CFU number until the phone
becomes unregistered. For more information on configuring call-forward
unregistered, see
Example for Configuring Call Forward Unregistered for SIP IP Phones.
 Note | In earlier |
B2BUA Call Forward
for SIP Devices
Cisco Unified CME 3.4 an d later versions acts as both UA server
and UA client; that is, as a B2BUA. Calls into a SIP phone can be forwarded to
other SIP or SCCP devices (including Cisco Unity or Cisco Unity Express,
third-party voice mail systems, an auto attendant or an IVR system, such as
Cisco Unified IPCC and Cisco Unified IPCC Express). In addition, SCCP phones
can be forwarded to SIP phones.
Cisco Unity or other
voice-messaging systems connected by a SIP trunk or SIP user agent are able to
pass an MWI to a SIP phone when a call is forwarded. The SIP phone then
displays the MWI when indicated by the voice-messaging system.
The call-forward
busy response is triggered when a call is sent to a SIP phone using a VoIP dial
peer and a busy response is received back from the phone. SIP-to-SIP call
forwarding is invoked only if the phone is dialed directly. Call forwarding is
not invoked when the phone number is called through a sequential, longest-idle,
or peer hunt group.
You can configure
call forwarding for an individual directory number, or for every number on a
SIP phone. If the information is configured in both, the information under
voice register dn takes precedence over the information configured under voice
register pool.
For configuration
information, see
Configure SIP-to-SIP Phone Call Forwarding.
Call Forward All
Synchronization for SIP Phones
The Call Forward All
feature allows users to forward all incoming calls to a phone number that they
specify. This feature is supported on all SIP phones and can be provisioned
from either Cisco Unified CME or the individual SIP phone. Before
Cisco Unified CME 4.1, there was no method for exchanging the Call Forward All
configuration between Cisco Unified CME and the SIP phone. If Call Forward All
was enabled on the phone, the configuration in Cisco Unified CME was not
updated; conversely, the configuration in Cisco Unified CME was not sent to the
phone.
In Cisco Unified CME
4.1 and later, the following enhancements are supported for the
Cisco Unified IP Phone 7911G, 7941G, 7941GE, 7961G, 7961GE, 7970G, and 7971GE
to keep the configuration consistent between Cisco Unified CME and the SIP
phone:
- When Call Forward All is
configured on Cisco Unified CME with the
call-forward
b2bua all command, the configuration is sent to the phone which updates the
CfwdAll soft key to indicate that Call forward All is enabled. Because Call
Forward All is configured on a per line basis, the CfwdAll soft key is updated
only when Call Forward All is enabled for the primary line. - When a user enables Call Forward All
on a phone using the CfwdAll soft key, the uniform resource identifier (URI)
for the service (defined with the
call-feature-uri command) and the call forward number
(unless Call Forward All is disabled) is sent to Cisco Unified CME. It updates
its voice register pool and voice register dn configuration with the
call-forward
b2bua all command to be consistent with the phone configuration. - Call Forward All supports KPML so that
a user does not need to press the Dial or # key, or wait for the interdigit
timeout, to configure the Call Forward All number. Cisco Unified CME collects
the Call Forward All digits until it finds a match in the dial peers.
For configuration
information, see
Configure Call-Forwarding-All Softkey URI on SIP Phones.
Call Transfer
When you are connected to another party, call transfer allows you to
shift the connection of the other party to a different number. Call transfer
methods must inter-operate with systems in the other networks with which you
interface. Cisco CME 3.2 and later versions provide full call-transfer and
call-forwarding interoperability with call processing systems that support
H.450.2, H.450.3, and H.450.12 standards. For call processing systems that do
not support H.450 standards, Cisco CME 3.2 and later versions provide
VoIP-to-VoIP hairpin call routing.
Call transfers can be blind or consultative. A blind transfer is one in
which the transferring extension connects the caller to a destination extension
before ringback begins. A consultative transfer is one in which the
transferring party either connects the caller to a ringing phone (ringback
heard) or speaks with the third party before connecting the caller to the third
party.
You can configure blind or consultative transfer on a system-wide basis
or for individual extensions. For example, in a system that is set up for
consultative transfer, a specific extension with an auto-attendant that
automatically transfers incoming calls to specific extension numbers can be set
to use blind transfer, because auto-attendants do not use consultative
transfer.
Call Transfer
Blocking
Transfers to all
numbers except those on local phones are automatically blocked by default.
During configuration, you can allow transfers to nonlocal numbers. In
Cisco Unified CME 4.0 and later versions, you can prevent individual phones
from transferring calls to numbers that are globally enabled for transfer. This
ensures that individual phones do not incur toll charges by transferring calls
outside the Cisco Unified CME system. Call transfer blocking can be configured
for individual phones or configured as part of a template that is applied to a
set of phones.
Another way to
eliminate toll charges on call transfers is to limit the number of digits that
phone users can dial when transferring calls. For example, if you specify a
maximum of eight digits in the configuration, users who are transferring calls
can dial one digit for external access and seven digits more, which is
generally enough for a local number but not a long-distance number. In most
locations, this plan will limit transfers to nontoll destinations.
Long-distance calls, which typically require ten digits or more, will not be
allowed. This configuration is only necessary when global transfer to numbers
outside the Cisco Unified CME system has been enabled using the
transfer-pattern (telephony-service) command.
Transfers to numbers outside the Cisco Unified CME system are not permitted by
default.
For configuration
information, see
Configure Call Transfer Options for SCCP Phones.
Trunk-to-Trunk
Transfer Blocking for Toll Fraud Prevention on Cisco Unified SIP IP
Phones
In Cisco Unified CME
4.0 trunk-to-trunk transfer blocking for toll bypass fraud prevention is
supported on Cisco Unified Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP) IP phones.
In Cisco Unified CME
9.5, trunk-to-trunk transfer blocking for toll bypass fraud prevention is also
supported on Cisco Unified Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) IP phones.
In Cisco Unified CME
10.5, trunk-to-trunk conference blocking is also supported on Cisco Unified
Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP) and Cisco Unified Session Initiation
Protocol (SIP) IP phones.
Table 1
lists the transfer-blocking commands and the appropriate configuration modes
for Cisco Unified CME and Cisco Unified SRST.
| Commands | Cisco |
|---|---|
| transfer-pattern | telephony-service |
| transfer max-length | voice register pool or voice register template |
| transfer-pattern | voice register pool or voice register template |
| conference | telephony-service |
| conference max-length | ephone ephone-template voice register pool voice register template |
| conference-pattern | ephone ephone-template voice register pool voice register template |
 Note | The call transfer |
Transfer
Pattern
The
transfer-pattern command for Cisco Unified SCCP IP
phones is extended to Cisco Unified SIP IP phones.
transfer-pattern command specifies the directory
numbers for call transfer. The command can be configured up to 32 times using
the following command syntax:
transfer-pattern transfer-pattern [ blind]  Note | The |
With the
transfer-pattern command configured, only call
transfers to numbers that match the configured transfer pattern are allowed to
take place. With the transfer pattern configured, all or a subset of transfer
numbers can be dialed and the transfer to a remote party can be initiated.
 Note | In Cisco Unified |
The following are
examples of configurable transfer patterns:
-
.T—This
configuration allows call transfers to any destinations with one or more
digits, like 123, 877656, or 76548765. -
919……..—This
configuration only allows call transfers to remote numbers beginning with “919”
and followed by eight digits, like 91912345678. However, call transfers to
9191234 or 919123456789 are not allowed.
Backward Compatibility
To maintain backward compatibility, all call transfers from Cisco
Unified SIP IP phones to any number (local or over trunk) are allowed when no
transfer patterns are configured through the
transfer-pattern ,
transfer-pattern blocked , or
transfer max-length commands.
For Cisco Unified SCCP IP phones, call transfers over trunk continue to
be blocked when no transfer patterns are configured.
Dial Plans
Whatever dial plan is used for external calls, the same numbers should
be configured as specific numbers using the
transfer-pattern command.
If a dial plan requires “9” to be dialed before an external call is
made, then “9” should be a prefix of the transfer-pattern number. For example,
12345678 is an external number that requires “9” to be dialed before the
external call can be made so the transfer-pattern number should be 912345678.
 Note | In Cisco Unified CME 9.5 and later versions, once transfer patterns |
Transfer Max-Length
The
transfer max-length command is used to indicate
the maximum length of the number being dialed for a call transfer. When only a
specific number of digits are to be allowed during a call transfer, a value
between 3 and 16 is configured. When the number dialed exceeds the maximum
length configured, then the call transfer is blocked.
For example, the maximum length is configured as 5, then only call
transfers from Cisco Unified SIP IP phones up to a five-digit directory number
are allowed. All call transfers to directory numbers with more than five digits
are blocked.
 Note | If only transfer max length is configured and conference max-length |
Conference
Max-Length
Conference calls are allowed when:
-
both
conference transfer-pattern and
transfer-pattern commands are configured -
dialed digits match the configured transfer pattern
When conference
max-length command is configured, the Cisco Unified CME will allow the
conferences only if the dialed digits are within the max-length limit.
If configured, the
conference max-length command does not impact call transfers.
 Note | If both |
Conference-Pattern
Blocked
The
conference-pattern blocked command is used to prevent extensions on an ephone
or a voice register pool from initiating conferences.
summarizes the behavior of the
conference-pattern
blocked command in relation to
no conference-pattern
blocked ,
conference
max-length ,
no conference
max-length , and
transfer
max-length commands.
| conference | no conference max-length | |
|---|---|---|
| No | Allowing/Blocking of conference call depends on configured | Allowing/Blocking of conference call depends on configured |
| conference-pattern blocked | No |
| Max-length <= allowed max-length | Max-length > allowed max-length | |||
| Transfer | Conference | Transfer | Conference | |
| Transfer max-length + No Conference max-length (use transfer | Y | Y | N | N |
| No transfer max-length + Conference max-length (conference | Y | Y | Y | N |
| No transfer max-length + Conference max-length (conference | Y | Y | N | N |
| No transfer max-length + No conference max-length | All transfer and conference calls are allowed. |
Configure the
Maximum Number of Digits for a Conference Call
Before you begin
-
Cisco Unified
CME 10.5 or a later version. -
The conference
transfer-pattern command must be configured. -
The
transfer-pattern command must be configured.
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure
terminal - Enter one of the following commands:
- voice register pool pool-tag
- voice register template template-tag
- ephone phone-tag
- ephone template template-tag
- conference
max-length value - exit
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example: | Enables
|
| Step 2 | configure Example: | Enters global |
| Step 3 | Enter one of the following commands:
Example: | Enters voice register pool configuration mode and creates a pool configuration for a Cisco Unified SIP IP phone in Cisco Unified
or Enters voice register template configuration mode and defines a template of common parameters for Cisco Unified SIP IP phones.
or Enters ephone configuration mode.
|
| Step 4 | conference Example: | Allows the
|
| Step 5 | exit Example: | Exits voice |
Configure
Conference Blocking Options for Phones
To prevent
extensions from making conference calls to directory numbers that are otherwise
allowed globally.
Before you begin
-
Cisco Unified
CME 10.5 or a later version. -
The conference
transfer-pattern command must be configured. -
The
transfer-pattern command must be configured.
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure
terminal - Enter one of the following commands:
- voice register pool pool-tag or
- voice register template
template-tag - ephone
phone-tag - ephone template
template-tag - conference-pattern blocked
- exit
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example: | Enables
|
| Step 2 | configure Example: | Enters global |
| Step 3 | Enter one of the following commands:
Example: | Enters voice register pool configuration mode and creates a pool configuration for a Cisco Unified SIP IP phone in Cisco Unified
or Enters voice register template configuration mode and defines a template of common parameters for Cisco Unified SIP IP phones.
or Enters ephone configuration mode.
|
| Step 4 | conference-pattern blocked Example: | Blocks
|
| Step 5 | exit Example: | Exits voice |
Transfer-Pattern
Blocked
When the
transfer-pattern
blocked command is configured for a specific phone, no call
transfers are allowed from that phone over the trunk.
This feature forces
unconditional blocking of all call transfers from the specific phone to any
other non-local numbers (external calls from one trunk to another trunk). No
call transfers from this specific phone are possible even when a transfer
pattern matches the dialed digits for transfer.
Table 1
compares the behaviors of Cisco Unified SCCP and SIP IP phones for specific
configurations.
| Configuration | Cisco | Cisco | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No transfer | All | All | ||||
| Specific | Call | Call | ||||
| The | All
| All
|
Conference
Transfer-Pattern
When both the
transfer-pattern and
conference
transfer-pattern commands are configured and the dialed digits match the
configured transfer pattern, conference calls are allowed. However, when the
dialed digits do not match any of the configured transfer pattern, the
conference call is blocked.
For configuration
information, see
Specify Transfer Patterns for Trunk-to-Trunk Calls and Conferences for SIP
and
Conference-Pattern Blocked
and
Conference Max-Length.
For configuration
examples, see
Example for Configuring Conference Transfer Patterns,
Example for Configuring Maximum Length of Transfer Number,
Example for Configuring Transfer Patterns,
and
Example for Blocking All Call Transfers.
Call Transfer
Recall on SCCP Phones
The Call Transfer
Recall feature in Cisco Unified CME 4.3 and later versions returns a
transferred call to the phone that initiated the transfer if the destination is
busy or does not answer. After a phone user completes a transfer to a directory
number on a local phone, if the transfer-to party does not answer before the
configured recall timer expires, the call is directed back to the transferor
phone. The message “Transfer Recall From
xxxx” displays
on the transferor phone.
The transfer-to
directory number cannot have Call Forward Busy enabled, or it cannot be a hunt
group pilot number. If the transfer-to directory number has Call Forward No
Answer (CFNA) enabled, Cisco Unified CME recalls the call only if the
transfer-recall timeout is set to less than the CFNA timeout. If the
transfer-recall timeout is set to more than the CFNA timeout, the call is
forwarded to the CFNA target number after the transfer-to party does not
answer.
If the transferor
phone is busy, Cisco Unified CME attempts the recall again after the
transfer-recall timeout value expires. Cisco Unified CME attempts a recall up
to three times. If the transferor phone remains busy, the call is disconnected
after the third recall attempt.
The transferor phone
and transfer-to phone must be registered to the same Cisco Unified CME, however
the transferee phone can be remote.
For configuration
information, see
Enable Call Transfer and Forwarding on SCCP Phones at System-Level.
Call Transfer
Recall on SIP Phones
From Unified CME
11.6 onwards, Call Transfer Recall feature is supported on SIP phones. This
feature returns a transferred call to the phone that initiated the transfer if
the destination is busy or does not answer. After a phone user completes a
transfer to a directory number on a local SIP phone, and if the transfer-to
party does not answer before the configured recall timer expires, the call is
directed back to the transferor phone. The message «Transfer Recall From xxxx » displays on the
transferor phone.
The Call Transfer
Recall in SIP phones is achieved using the CLI
timeouts
transfer-recall command in voice register dn or voice register global
configuration modes.
The transfer-to
directory number cannot have Call Forward Busy enabled, or it cannot be a hunt
group pilot number. The transferor phone and transfer-to phone must be
registered to the same Cisco Unified CME, however the transferee phone can be
remote. If the transfer-to directory number has Call Forward No Answer (CFNA)
enabled, Cisco Unified CME recalls the call only if the transfer-recall timeout
is set to less than the CFNA timeout. If the transfer-recall timeout is set to
more than the CFNA timeout, the call is forwarded to the CFNA target number
after the transfer-to party does not answer. If the transfer-recall timeout is
equal to the CFNA timeout, the call is forwarded to the CFNA target number as
the CFNA timeout expires before the transfer-recall timeout.
When Call Forward
All is configured in Cisco Unified CME, the call is forwarded directly to call
forward target number irrespective of whether the phone is busy or idle. In
this scenario, transfer recall is not applicable after the call is forwarded.
If the transferor
phone is busy, Cisco Unified CME attempts the recall again after the
transfer-recall timeout value expires. Cisco Unified CME attempts a recall up
to three times. If the transferor phone remains busy, the call is disconnected
after the third recall attempt. Also, if the transferor phone is a shared line,
and if one of the phones is idle, the transfer recall is directed to the
transferor phone that is idle.
When Single Number
Reach (SNR) is configured in Cisco Unified CME, the desk IP Phone rings first.
If the desk IP Phone does not answer within the configured SNR timer expiry
value, the configured remote number (mobile) starts ringing while continuing to
ring the desk IP Phone. If both the extensions does not answer the call,
transfer recall is directed back to the transferor phone. Transfer recall does
not happen if the desk IP Phone or remote phone (mobile) is busy. Also,
transfer recall does not happen if one of the SNR extensions answers the call.
For configuration
information, see
Enable Call-Transfer Recall on SIP Phones at System-Level.
From Cisco Unified
CME release 11.6 onwards, call transfer recall feature supports mixed
deployment of SCCP and SIP phones. In a mixed deployment scenario, you can have
a SIP phone as transferor and with an SCCP phone being transfer-to or vice
versa.
In mixed mode, if
the transfer recall is performed with multiple SIP or SCCP transferors and a
single transfer-to SCCP phone, transfer recall display messages are displayed
on both the transferors. Here, transfer recall happens for all the calls when
the destination is busy or does not answer the call. In the case of single
transfer-to SIP phones, only the first phone call is recalled even if dual-line
is configured.
Consultative-Transfer Enhancements in Cisco Unified CME 4.3 and
Later Versions
Cisco Unified CME
4.3 modifies the digit-collection process for consultative call transfers.
After a phone user presses the Transfer soft key to make a consultative
transfer, a new consultative call leg is created and the Transfer soft key is
not displayed again until the dialed digits of the transfer-to number are
matched to a transfer pattern and the consultative call leg is in the alerting
state.
Transfer-to digits
dialed by the phone user are no longer buffered. The dialed digits, except the
call park FAC code, are collected on the seized consultative call-leg until the
digits match a pattern for consultative transfer, blind transfer, park-slot
transfer, park-slot transfer blocking, or PSTN transfer blocking. The existing
pattern matching process is unchanged, and you have the option of using this
new transfer digit-collection method or reverting to the former method.
Before Cisco Unified
CME 4.3, the consultative transfer feature collects dialed digits on the
original call leg until the digits either match a transfer pattern or blocking
pattern. When the transfer-to number is matched, and PSTN blocking is not
enabled, the original call is put on hold and an idle line or channel is seized
to send the dialed digits from the buffer.
The method of
matching a pattern for consultative transfer, blind transfer, park-slot
transfer, park-slot transfer blocking, PSTN transfer blocking, and after-hours
blocking remain the same. When the transfer-to number matches the pattern for a
blind transfer or park-slot transfer, Cisco Unified CME terminates the
consultative call leg and transfers the call.
After the
transfer-to digits are collected, if the transfer is not committed before the
transfer-timeout expires in 30 seconds, the consultation call leg is
disconnected.
These enhancements
are supported only if:
- The
transfer-system
full-consult command (default) is set in telephony-service
configuration mode. - The
transfer-mode
consult command (default) is set for the transferor’s directory
number (ephone-dn). - An idle line or channel is
available for seizing, digit collection, and dialing.
Cisco Unified CME 4.3 and later versions enable these transfer
enhancements by default.
To revert to the
digit-collection method used in previous versions of Cisco Unified CME, see
Enable Call Transfer and Forwarding on SCCP Phones at System-Level.
Consultative
Transfer With Direct Station Select
Direct Station
Select (DSS) is a feature that allows a multi-button phone user to transfer
calls to an idle monitored line by pressing the Transfer key and the
appropriate monitored line button. A monitored line is one that appears on two
phones; one phone can use the line to make and receive calls and the other
phone simply monitors whether the line is in use. For Cisco CME 3.2 and later
versions, consultative transfers can occur during Direct Station Select
(transferring calls to idle monitored lines).
If the person
sharing the monitored line does not want to accept the call, the person
announcing the call can reconnect to the incoming call by pressing the EndCall
soft key to terminate the announcement call and pressing the Resume soft key to
reconnect to the original caller.
Direct Station Select consultative transfer is enabled with the transfer-system full-consult dss command, which defines the call transfer method for all lines served by the router. The transfer-system full-consult dss command supports the keep-conference command. See Configure Hardware Conferencing.
H.450.2 and
H.450.3 Support
H.450.2 is a
standard protocol for exchanging call-transfer information across a network,
and H.450.3 is a standard protocol for exchanging call-forwarding information
across a network. Cisco CME 3.0 and later versions support the H.450.2
call-transfer standards and the H.450.3 call-forwarding standards that were
introduced in Cisco ITS V2.1. Using the H.450.2 and H.450.3 standards to manage
call transfer and forwarding in a VoIP network provides the following benefits:
- The final call path from
the transferred party to the transfer destination is optimal, with no
hairpinned routes or excessive use of resources.
-
Call parameters
(for example, codec) can be different for the different call legs. -
This solution is
scalable. -
There is no limit
to the number of times a call can be transferred.
Considerations for
using the H.450.2 and H.450.3 standards include the following:
-
Cisco IOS
Release 12.2(15)T or a later release is required on all voice gateways in the
network. -
Support of
H.450.2 and H.450.3 is required on all voice gateways in the network. H.450.2
and H.450.3 are used regardless of whether the transfer-to or forward-to target
is on the same Cisco Unified CME system as the transferring party or the
forwarding party, so the transferred party must also support H.450.2 and the
forwarded party must also support H.450.3. The exception is calls that can be
reoriginated through hairpin call routing or through the use of an H.450 tandem
gateway. -
Call forwarding
over SIP networks uses the
302 Moved
Temporarily SIP response, which works in a manner similar to the way in
which the H.450.3 standard is used for H.323 networks. To enable call
forwarding, you must specify a pattern that matches the calling-party numbers
of the calls that you want to be able to forward. -
Cisco Unified CME supports all SIP Refer method call transfer
scenarios, but you must ensure that call transfer is enabled using H.450.2
standards. -
H.450 standards
are not supported by Cisco Unified Communications Manager, Cisco BTS, or
Cisco PGW, although hairpin call routing or an H.450 tandem gateway can be set
up to handle calls to and from those types of systems.
The following series
of figures depicts a call being transferred using H.450.2 standards.
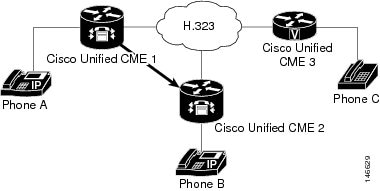
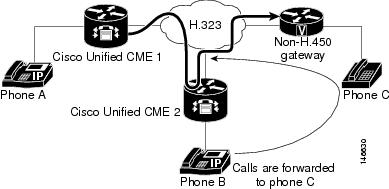
Call Transfer
Using H.450.2: A Calls B
shows A calling B.
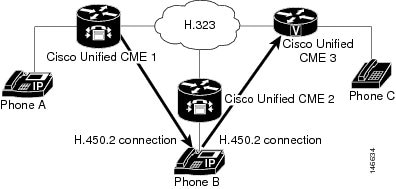
Call Transfer
Using H.450.2: B Consults with C
shows B consulting with C and putting A on hold.
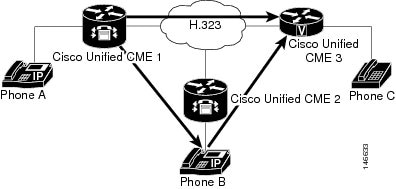
Call Transfer
Using H.450.2: B Transfers A to C
shows that B has connected A and C, and
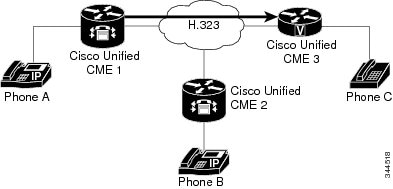
Call Transfer
Using H.450.2: A and C Are Connected
shows A and C directly connected, with B no longer involved in the call.
Using H.450.2: A Calls B
Using H.450.2: B Consults with C
Using H.450.2: B Transfers A to C
Using H.450.2: A and C Are Connected
Tips for Using
H.450 Standards
Use H.450 standards
when a network meets the following conditions:
-
The router that
you are configuring uses Cisco CME 3.0 or a later version, or Cisco ITS V2.1. -
For Cisco CME
3.0 or Cisco ITS V2.1 systems, all endpoints in the network must support
H.450.2 and H.450.3 standards. For Cisco CME 3.1 or later systems, if some of
the endpoints do not support H.450 standards (for example,
Cisco Unified Communications Manager, Cisco BTS, or Cisco PGW), you can use
hairpin call routing or an H.450 tandem gateway to handle transfers and
forwards with those endpoints. Also, either you must explicitly disable H.450.2
and H.450.3 on the dial peers that handle those calls or you must enable
H.450.12 capability to automatically detect the calls that support H.450.2 and
H.450.3 and those calls that do not.
Support for the
H.450.2 standard and the H.450.3 standard is enabled by default and can be
disabled globally or for individual dial peers. For configuration information,
see
Enable Call Transfer and Forwarding on SCCP Phones at System-Level.
Transfer Method
Recommendations by Cisco Unified CME Version
You must specify the
method to use for call transfers: H.450.2 standard signaling or Cisco
proprietary signaling, and whether transfers should be blind or allow
consultation.
Table 1
summarizes transfer method recommendations for all Cisco Unified CME versions.
| Cisco Unified CME Version | transfer-system Command Default | transfer-system Keyword to Use | Transfer |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4.0 and | full-consult | full-consult | Use H.450.2 full-blind or Optionally, Use H.450.7 |
| 3.0 to 3.3 | blind | full-consult | Use H.450.2 Optionally, |
| 2.1 | blind | blind or | Use the local-consult keyword. Optionally, |
| Earlier than | blind | blind | Use the local-consult keyword. |
H.450.12
Support
Cisco CME 3.1 and
later versions support the H.450.12 call capabilities standard, which provides
a means to advertise and dynamically discover H.450.2 and H.450.3 capabilities
in voice gateway endpoints on a call-by-call basis. When discovered, the calls
associated with non-H.450 endpoints can be directed to use non-H.450 methods
for transfer and forwarding, such as hairpin call routing or H.450 tandem
gateway.
When H.450.12 is
enabled, H.450.2 and H.450.3 services are disabled for call transfers and call
forwards unless a positive H.450.12 indication is received from all other VoIP
endpoints involved in the call. If a positive H.450.12 indication is received,
the router uses the H.450.2 standard for call transfers and the H.450.3
standard for call forwarding. If a positive H.450.12 indication is not
received, the router uses the alternative method that you have configured for
call transfers and forwards, either hairpin call routing or an H.450 tandem
gateway.
You can have either
of the following situations in your network:
- All gateway endpoints
support H.450.2 and H.450.3 standards. In this situation, no special
configuration is required because support for H.450.2 and H.450.3 standards is
enabled on the Cisco CME 3.1 or later router by default. H.450.12 capability is
disabled by default, but it is not required because all calls can use H.450.2
and H.450.3 standards. - Not all gateway endpoints
support H.450.2 and H.450.3 standards. Therefore, specify how non-H.450 calls
are to be handled by choosing one of the following options:- Enable the H.450.12 capability in
Cisco CME 3.1 and later to dynamically determine, on a call-by-call basis,
whether each call has H.450.2 and H.450.3 support. If H.450.12 is enabled and a
call is determined to have H.450 support, the call is transferred using H.450.2
standards or forwarded using H.450.3 standards. See
Enable H.450.12 Capabilities.Support for
the H.450.12 standard is disabled by default and can be enabled globally or for
individual dial peers.If the call
does not have H.450 support, it can be handled by a VoIP-to-VoIP connection
that you configure using dial peers and
Enable H.323-to-H.323 Connection Capabilities.
The connection can be used for hairpin call routing or routing to an H.450
tandem gateway. - Explicitly disable H.450.2 and H.450.3
capability on a global basis or by individual dial peer, which forces all calls
to be handled by a VoIP-to-VoIP connection that you configure using dial peers
and the
Enable H.323-to-H.323 Connection Capabilities.
This connection can be used for hairpin call routing or routing to an H.450
tandem gateway.
- Enable the H.450.12 capability in
Hairpin Call
Routing
Cisco CME 3.1 and
later supports hairpin call routing using a VoIP-to-VoIP connection to transfer
and forward calls that cannot use H.450 standards. When a call that originally
terminated on a voice gateway is transferred or forwarded by a phone or other
application attached to the gateway, the gateway reoriginates the call and
routes the call as appropriate, making a VoIP-to-VoIP, or hairpin, connection.
This approach avoids any protocol dependency on the far-end transferred-party
endpoint or transfer-destination endpoint. Hairpin routing of transferred and
forwarded calls also causes the generation of separate billing records for each
call leg, so that the transferred or forwarded call leg is typically billed to
the user who initiates the transfer or forward.
In Cisco CME 3.2 and
later versions, transcoding between G.711 and G.729 is supported when one leg
of a VoIP-to-VoIP hairpin call uses G.711 and the other leg uses G.729.
Hairpin call routing
provides the following benefits:
- Call transfer and
forwarding is provided to non-H.450 endpoints, such as
Cisco Unified Communications Manager, Cisco BTS, or Cisco PGW. - The network can also
contain Cisco CME 3.0 or Cisco ITS 2.1 systems.
Hairpin call routing
has the following disadvantages:
- End-to-end signaling and
media delay are increased significantly. - A single hairpinned call
uses as much WAN bandwidth as two directly connected calls.
VoIP-to-VoIP hairpin
connections can be made using dial peers if the
allow-connections
h323 to h323 command is enabled and at least one of the following is true:
- H.450.12 is used to detect
calls on which H.450.2 or H.450.3 is not supported by the remote system. - H.450.2 or H.450.3 is
explicitly disabled. - Cisco Unified CME automatically
detects that the remote system is a Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
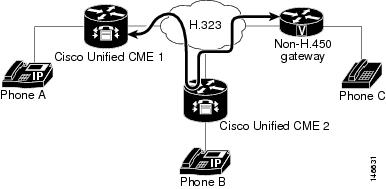
Hairpin with
H.323: A Calls B
shows a call that is made from A to B.
Hairpin with
H.323: Call is Forwarded to C
shows that B has forwarded all calls to C.
Hairpin with
H.323: A is Connected to C via B
shows that A and C are connected by an H.323 hairpin.
H.323: A Calls B

H.323: Call is Forwarded to C
H.323: A is Connected to C via B
Tips for Using
Hairpin Call Routing
Use hairpin call
routing when a network meets the following three conditions:
-
The router that
you are configuring uses Cisco CME 3.1 or a later version. -
Some or all
calls require VoIP-to-VoIP routing because they cannot use H.450 standards,
which can happen for any of the following reasons:-
H.450
capabilities have been explicitly disabled on the router. -
H.450
capabilities do not exist in the network. -
H.450
capabilities are supported on some endpoints and not supported on other
endpoints, including those handled by Cisco Unified Communications Manager,
Cisco BTS, and Cisco PGW. When some endpoints support H.450 and others do not,
you must enable H.450.12 capabilities on the router to detect which endpoints
are H.450-capable or designate some dial peers as H.450-capable. For more
information about enabling H.450.12 capabilities, see
Enable H.450.12 Capabilities.
-
-
No voice gateway
is available to act as an H.450 tandem gateway.
For information
about configuring Cisco Unified CME to forward calls using local hairpin
routing, see
Forward Calls Using Local Hairpin Routing.
Support for
VoIP-to-VoIP connections is disabled by default and can be enabled globally.
For configuration information, see
Enable H.323-to-H.323 Connection Capabilities.
Calling Number
Local
In a scenario where
calls are forwarded using local hairpin call routing, you can use the Calling
Number Local feature. Calling Number Local replaces a calling-party number and
name with the forwarding-party number and name (the local number and name). For
ephone-dns, the CLI command
calling-number
local is configured under telephony-service configuration to
enable the feature. For more information, see
Cisco Unified Communications
Manager Express Command Reference.
From Cisco Unified
CME Release 12.0 onwards, calling number local feature is supported for voice
register DNs as well. For voice register DNs, the CLI command
calling-number
local is configured in voice register global configuration mode.
For more information, see
Cisco Unified Communications
Manager Express Command Reference.
When the CLI
command
calling-number
local is enabled, the calling number is replaced with the
forwarding party’s number. If the forwarded number is over a trunk, toll
charges may be applied on the forwarding number.
H.450 Tandem
Gateways
H.450 tandem
gateways address the limitations of hairpin call routing using a manner similar
to hairpin call routing but without the double WAN link traversal created by
hairpin connections. An H.450 tandem gateway is an additional voice gateway
that serves as a “front-end” for a call processor that does not support the
H.450 standards, such as Cisco Unified Communications Manager, Cisco BTS
Softswitch (Cisco BTS), or Cisco PSTN Gateway (Cisco PGW). Transferred and
forwarded calls that are intended for non-H.450 endpoints are terminated
instead on the H.450 tandem gateway and reoriginated there for delivery to the
non-H.450 endpoints. The H.450 tandem gateway can also serve as a PSTN gateway.
An H.450 tandem
gateway is configured with a dial peer that points to the
Cisco Unified Communications Manager or other system for which the H.450 tandem
gateway is serving as a front end. The H.450 tandem voice gateway is also
configured with dial peers that point to all the Cisco Unified CME systems in
the private H.450 network. In this way, Cisco Unified CME and the
Cisco Unified Communications Manager are not directly linked to each other, but
are instead both linked to an H.450 tandem gateway that provides H.450 services
to the non-H.450 platform.
An H.450 tandem
gateway can also work as a PSTN gateway for remote Cisco Unified CME systems
and for Cisco Unified Communications Manager (or other non-H.450 system). Use
different inbound dial peers to separate
Cisco Unified Communications Manager-to-PSTN G.711 calls from tandem
gateway-to-Cisco Unified CME G.729 calls.
 Note | An H.450 tandem |
VoIP-to-VoIP
connections can be made for an H.450 tandem gateway if the
allow-connections
h323 to h323 command is enabled and one or more of the following is true:
-
H.450.12 is used
to dynamically detect calls on which H.450.2 or H.450.3 is not supported by the
remote VoIP system. -
H.450.2 or
H.450.3 is explicitly disabled. -
Cisco CME 3.1 or
later automatically detects that the remote system is a
Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
For Cisco CME 3.1
and earlier, the only type of VoIP-to-VoIP connection supported by
Cisco Unified CME is H.323-to-H.323. For Cisco CME 3.2 and later versions,
H.323-to-SIP connections are allowed only for Cisco Unified CME systems running
Cisco Unity Express.
H.450 Tandem
Gateway
shows a tandem voice gateway that is located between the central hub of the
network of a CPE-based Cisco CME 3.1 or later network and a
Cisco Unified Communications Manager network. This topology would work equally
well with a Cisco BTS or Cisco PGW in place of the
Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
In the network
topology in
H.450 Tandem
Gateway,
the following events occur (refer to the event numbers on the illustration):
-
A call is
generated from extension 4002 on phone 2, which is connected to a
Cisco Unified Communications Manager. The H.450 tandem gateway receives the
H.323 call and, acting as the H.323 endpoint, the H.450 tandem gateway handles
the call connection to a Cisco Unified IP phone in a CPE-based Cisco CME 3.1 or
later network. -
The call is
received by extension 1001 on phone 3, which is connected to Cisco Unified CME
1. Extension 1001 performs a consultation transfer to extension 2001 on phone
5, which is connected to Cisco Unified CME 2. -
When extension
1001 transfers the call, the H.450 tandem gateway receives an H.450.2 message
from extension 1001. -
The H.450 tandem
gateway terminates the call leg from extension 1001 and reoriginates a call leg
to extension 2001, which is connected to Cisco Unified CME 2. -
Extension 4002
is connected with extension 2001.
Gateway
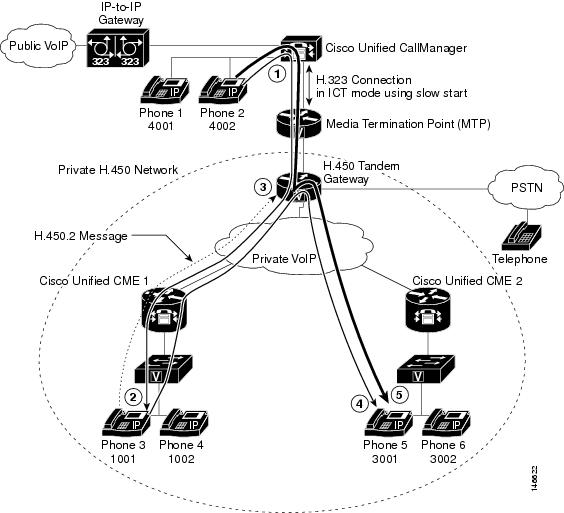
Tips for Using
H.450 Tandem Gateways
Use this procedure
when a network meets the following conditions:
-
The router that
you are configuring uses Cisco CME 3.1 or a later version. -
Some endpoints
in the network are not H.450-capable, including those handled by
Cisco Unified Communications Manager, Cisco BTS, and Cisco PGW.
Support for
VoIP-to-VoIP connections is disabled by default and can be enabled globally.
For more information, see
Enable H.323-to-H.323 Connection Capabilities.
Use dial peers to
set up an H.450 tandem gateway. See
Dial Peers.
Dial Peers
Dial peers describe
the virtual interfaces to or from which a call is established. All voice
technologies use dial peers to define the characteristics associated with a
call leg. Attributes applied to a call leg include specific quality of service
(QoS) features, compression/decompression (codec), voice activity detection
(VAD), and fax rate. Dial peers are also used to establish the routing paths in
your network, including special routing paths such as hairpins and H.450 tandem
gateways. Dial peer settings override the global settings for call forward and
call transfer.
Q Signaling
Supplementary Services
Q Signaling (QSIG)
is an intelligent inter-PBX signaling system widely adopted by PBX vendors. It
supports a range of basic services, generic functional procedures, and
supplementary services. Cisco Unified CME 4.0 introduces supplementary services
features that allow Cisco Unified CME phones to seamlessly interwork using QSIG
with phones connected to a PBX. One benefit is that IP phones can use a PBX
message center with proper MWI notifications.
Cisco Unified CME System with PBX
illustrates a topology for a Cisco Unified CME system with some phones under
the control of a PBX.
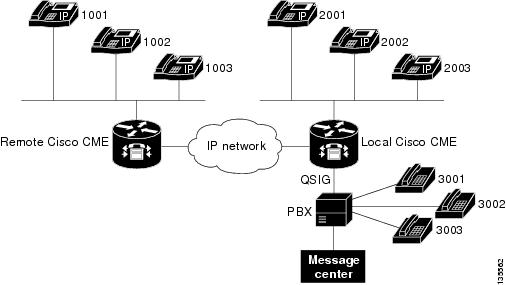
The following QSIG
supplementary service features are supported in Cisco Unified CME systems. They
follow the standards from the European Computer Manufacturers Association
(ECMA) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) on PRI and
BRI interfaces.
- Basic calls between IP
phones and PBX phones. - Calling Line/Name
identification (CLIP/CNIP) presented on an IP phone when called by a PBX phone;
in the reverse direction, such information is provided to the called endpoint. - Connected Line/Name identification
(COLP/CONP) information provided when a PBX phone calls an IP phone and is
connected; in the reverse direction, such information presented on an IP phone. - Call Forward using QSIG and H.450.3 to
support any combination of IP phone and PBX phone, including an IP phone in the
Cisco Unified CME system that is connected to a PBX or an IP phone in another
Cisco Unified CME system across an H.323 network. - Call forward to the PBX message center
according to the configured policy. The other two endpoints can be a mixture of
IP phone and PBX phones. - Hairpin call transfer, which
interworks with a PBX in transfer-by-join mode. Note that Cisco Unified CME
does not support the actual signaling specified for this transfer mode
(including the involved FACILITY message service APDUs) which are intended for
an informative purpose only and not for the transfer functionality itself. As a
transferrer (XOR) host, Cisco Unified CME simply hairpins two call legs to
create a connection; as a transferee (XEE) or transfer-to (XTO) host, it will
not be aware of a transfer that is taking place on an existing leg. As a
result, the final endpoint may not be updated with the accurate identity of its
peer. Both blind transfer and consult transfer are supported. - Message-waiting indicator (MWI)
activation or deactivation requests are processed from the PBX message center. - The PBX message center can be
interrogated for the MWI status of a particular ephone-dn. - A user can
retrieve voice messages from a PBX message center by making a normal call to
the message center access number.
For information
about enabling QSIG supplementary services, see
Enable H.450.7 and QSIG Supplementary Services at System-Level
and
Enable H.450.7 and QSIG Supplementary Services on a Dial Peer.
Disable SIP
Supplementary Services for Call Forward and Call Transfer
If a destination
gateway does not support supplementary services, you can disable REFER messages
for call transfers and the redirect responses for call forwarding from being
sent by Cisco Unified CME.
For configuration
information, see
Disable SIP Supplementary Services for Call Forward and Call Transfer.
Typical Network Scenarios for Call Transfer and Call
Forwarding
In a mixed network that involves two or more types of call agents or
call-control systems, there can be communication protocol discrepancies and
dependencies, and therefore the opportunity for interoperability errors. These
discrepancies show up most often when a call is being transferred or forwarded.
This section provides descriptions of the specific mixed-network scenarios you
might encounter when configuring a router running Cisco CME 3.1 or a later
version. Each of the following sections point to the configuration instructions
necessary to ensure call transfer and forwarding capabilities throughout the
network.
 Note | Cisco Communications Manager Express 3.2 (Cisco CME 3.2) and later |
Cisco CME 3.1 or
Later and Cisco IOS Gateways
In a network with
Cisco CME 3.1 or a later version and Cisco IOS gateways, all systems that might
participate in calls that involve call transfer and call forwarding are capable
of supporting the H.450.2, H.450.3, and H.450.12 standards. This is the
simplest environment for operating the Cisco CME 3.1 or later features.
Configuration for
this type of network consists of:
- Setting up call-transfer
and call-forwarding parameters for transfers and forwards that are initiated on
this router (H.450.2 and H.450.3 capabilities for transferred parties, transfer
destinations, forwarded parties, and forwarding destinations are enabled by
default). See
Enable Call Transfer and Forwarding on SCCP Phones at System-Level. - Enabling H.450.12 globally to detect
any calls on which H.450.2 and H.450.3 standards are not supported. Although
this step is optional, we recommend it. See
Enable H.450.12 Capabilities. - Optionally setting up VoIP-to-VoIP
connections (hairpin call routing or H.450 tandem gateway) to route calls that
do not support H.450.2 or H.450.3 standards. See
Enable H.323-to-H.323 Connection Capabilities. - Setting up dial peers to manage call
legs within the network.
Cisco CME 3.0 or
an Earlier Version and Cisco IOS Gateways
Before Cisco CME 3.1, H.450.2 and
H.450.3 standards are used for all calls by default and routers do not support
the H.450.12 standard.
Configuration for this type of network consists of:
-
Setting up call-transfer and
call-forwarding parameters for transfers and forwards that are initiated on
this router (H.450.2 and H.450.3 capabilities for transferred parties, transfer
destinations, forwarded parties, and forwarding destinations are enabled by
default). See
Enable Call Transfer and Forwarding on SCCP Phones at System-Level -
Enabling H.450.12 in advertise-only mode on Cisco CME 3.1 or later
systems. As each Cisco CME 3.0 system is upgraded to Cisco CME 3.1 or later,
enable H.450.12 in advertise-only mode. Note that no checking for H.450.2 or
H.450.3 support is done in advertise-only mode. When all Cisco CME 3.0 systems
in the network have been upgraded to Cisco CME 3.1 or later, remove the
advertise-only restriction. See
Enable H.450.12 Capabilities -
Optionally setting up VoIP-to-VoIP connections (hairpin call
routing or H.450 tandem gateway) to route calls that cannot use H.450.2 or
H.450.3 standards. See
Enable H.323-to-H.323 Connection Capabilities -
Setting up dial peers to manage call legs within the network.
Cisco CME 3.1 or
Later, Non-H.450 Gateways, and Cisco IOS Gateways
In a network with
Cisco CME 3.1 or later, non-H.450 gateways, and Cisco IOS gateways, the H.450.2
and H.450.3 services are provided only to calling endpoints that use H.450.12
to explicitly indicate that they are capable of H.450.2 and H.450.3 operations.
Because the Cisco BTS and Cisco PGW do not support the H.450.12 standard, calls
to and from these systems that involve call transfer or forwarding are handled
using H.323-to-H.323 hairpin call routing.
Configuration for
this type of network consists of:
- Setting up call-transfer
and call-forwarding parameters for transfers and forwards that are initiated on
this router (H.450.2 and H.450.3 capabilities for transferred parties, transfer
destinations, forwarded parties, and forwarding destinations are enabled by
default). Optionally disable H.450.2 and H.450.3 capabilities on dial peers
that point to non-H.450-capable systems such as
Cisco Unified Communications Manager, Cisco BTS, or Cisco PGW. See
Enable Call Transfer and Forwarding on SCCP Phones at System-Level. - Enabling H.450.12 to detect
any calls on which H.450.2 and H.450.3 standards are not supported, either
globally or for specific dial peers. See
Enable H.450.12 Capabilities. - Setting up VoIP-to-VoIP connections
(hairpin call routing or H.450 tandem gateway) to route calls that do not
support H.450.2 or H.450.3 standards. See
Enable H.323-to-H.323 Connection Capabilities. - Setting up dial peers to manage call
legs within the network.
 Note | If your network |
Cisco Unified CME,
Non-H.450 Gateways, and Cisco IOS Gateways
 Note | Cisco CME 3.0 and |
In a network that
contains a mix of Cisco Unified CME versions and at least one non-H.450
gateway, the simplest configuration approach is to globally disable all H.450.2
and H.450.3 services and force H.323-to-H.323 hairpin call routing for all
transferred and forwarded calls. In this case, you would enable H.450.12
detection capabilities globally. Alternatively, you could select to enable
H.450.12 capability for specific dial peers. In this case, you would not
configure H.450.12 capability globally; you would leave it in its default
disabled state.
Configuration for
this type of network consists of:
- Setting up call-transfer
and call-forwarding parameters for transfers and forwards that are initiated on
this router (H.450.2 and H.450.3 capabilities for transferred parties, transfer
destinations, forwarded parties, and forwarding destinations are enabled by
default). See
Enable Call Transfer and Forwarding on SCCP Phones at System-Level. - Enabling H.450.12 to detect
any calls on which H.450.2 and H.450.3 standards are not supported, either
globally or on specific dial peers. See
Enable H.450.12 Capabilities - Setting up VoIP-to-VoIP connections
(hairpin call routing or H.450 tandem gateway) to route all transferred and
forwarded calls. See
Enable H.323-to-H.323 Connection Capabilities. - Setting up dial peers to manage call
legs within the network.
 Note | If your network |
Cisco CME 3.1 or
Later, Cisco Unified Communications Manager, and Cisco IOS Gateways
In a network with Cisco CME 3.1 or
later, Cisco Unified Communications Manager, and Cisco IOS gateways, Cisco CME
3.1 and later versions support automatic detection of calls to and from Cisco
Unified Communications Manager using proprietary signaling elements that are
included with the standard H.323 message exchanges. The Cisco CME 3.1 or later
system uses these detection results to determine the H.450.2 and H.450.3
capabilities of calls rather than using H.450.12 supplementary services
capabilities exchange, which Cisco Unified Communications Manager does not
support. If a call is detected to be coming from or going to a Cisco Unified
Communications Manager endpoint, the call is treated as a non-H.450 call. All
other calls in this type of network are treated as though they support H.450
standards. Therefore, this type of network should contain only Cisco CME 3.1 or
later and Cisco Unified Communications Manager call-processing systems.
Configuration for this type of network consists of:
-
Setting up call-transfer and call-forwarding parameters for
transfers and forwards that are initiated on this router (H.450.2 and H.450.3
capabilities for transferred parties, transfer destinations, forwarded parties,
and forwarding destinations are enabled by default). See
Enable Call Transfer and Forwarding on SCCP Phones at System-Level -
Enabling H.450.12 to detect any calls on which H.450.2 and H.450.3
standards are not supported, either globally or on specific dial peers. See
Enable H.450.12 Capabilities -
Setting up VoIP-to-VoIP connections (hairpin call routing or H.450
tandem gateway) to route all transferred and forwarded calls that are detected
as being to or from Cisco Unified Communications Manager. SeeEnable H.323-to-H.323 Connection Capabilities -
Setting up specific parameters for Cisco Unified Communications
Manager. SeeEnable Cisco Unified Communications Manager to Interwork with Cisco Unified CME -
Setting up dial peers to manage call legs within the network.
Cisco CME 3.0 or
an Earlier Version, Cisco Unified Communications Manager, and Cisco IOS
Gateways
Calls between the
Cisco Unified Communications Manager and the older Cisco CME 3.0 or
Cisco ITS V2.1 networks need special consideration. Because Cisco CME 3.0 and
Cisco ITS V2.1 systems do not support automatic
Cisco Unified Communications Manager detection and also do not natively support
H.323-to-H.323 call routing, alternative arrangements are required for these
systems.
To configure call
transfer and forwarding on the Cisco CME 3.0 router, you can select from the
following three options:
- Use a Tcl script to handle call
transfer and forwarding by invoking Tcl-script-based H.323-to-H.323 hairpin
call routing (app-h450-transfer.2.0.0.9.tcl or a later version). Enable this
script on all VoIP dial peers and also under telephony-service mode, and set
the local-hairpin script parameter to 1. - Use a loopback-dn mechanism.
- Configure a
loopback call path using router physical voice ports.
All three options
force use of H.323-to-H.323 hairpin call routing for all calls regardless of
whether the call is from a Cisco Unified Communications Manager or other H.323
endpoint (including Cisco CME 3.1 or later).
Configure Call Transfer and Forwarding
Enable Call
Transfer and Forwarding on SCCP Phones at System-Level
To enable H.450
call transfers and forwards for transferring or forwarding parties; that is, to
allow transfers and forwards to be initiated from a Cisco Unified CME system,
perform the following steps.
 Note | H.450.2 and |
 Restriction |
Call-Transfer Recall
|
Before you begin
Cisco CME 3.0 or a
later version, or Cisco ITS V2.1.
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure
terminal - telephony-service
- transfer-system{ blind |
full-blind
|
full-consult [
dss ]
|
local-consult } - transfer-pattern
transfer-pattern
[ blind ] - call-forward
pattern
pattern - timeouts
transfer-recall
seconds
transfer-digit-collect
{ new-call
|
orig-call }- exit
- voice service
voip - supplementary-service
h450.2 - supplementary-service
h450.3 - exit
- dial-peer voice
tag voip - supplementary-service
h450.2 - supplementary-service
h450.3 - end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example: | Enables
| ||
| Step 2 | configure Example: | Enters global | ||
| Step 3 | telephony-service Example: | Enters | ||
| Step 4 | transfer-system{ blind | Example: | Specifies the
| ||
| Step 5 | transfer-pattern Example: | Allows
| ||
| Step 6 | call-forward Example: | Specifies
Calling-party numbers that do not match the patterns defined
| ||
| Step 7 | timeouts Example: | (Optional)
This command This command | ||
| Step 8 |
Example: | (Optional)
This command | ||
| Step 9 | exit Example: | Exits | ||
| Step 10 | voice service Example: | (Optional) | ||
| Step 11 | supplementary-service Example: | (Optional) Default is | ||
| Step 12 | supplementary-service Example: | (Optional) Default is | ||
| Step 13 | exit Example: | (Optional) | ||
| Step 14 | dial-peer voice Example: | (Optional) | ||
| Step 15 | supplementary-service Example: | (Optional) Default is
| ||
| Step 16 | supplementary-service Example: | (Optional) Default is
| ||
| Step 17 | end Example: | Returns to |
Enable
Call-Transfer Recall on SIP Phones at System-Level
To enable
call-transfer recalls to be initiated from a Cisco Unified CME system, perform
the following steps.
 Note |
|
Before you begin
Cisco Unified CME
11.6 or a later version.
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure
terminal - voice register global
- timeouts transfer-recall
seconds - exit
- voice service voip
- no supplementary-service sip refer
- end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example: | Enables
|
| Step 2 | configure Example: | Enters global |
| Step 3 | voice register global Example: | Enters voice |
| Step 4 | timeouts transfer-recall Example: | Enables
|
| Step 5 | exit Example: | Exits voice |
| Step 6 | voice service voip Example: | (Optional) |
| Step 7 | no supplementary-service sip refer Example: | Prevents the |
| Step 8 | end Example: | Returns to |
Enable Call
Forwarding for a Directory Number
To define the
conditions and target numbers for call forwarding for individual ephone-dns,
and set other restrictions for call forwarding, perform the following steps.
 Note | When defining |
 Restriction |
|
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure
terminal - telephony-service
- call-forward pattern
pattern - exit
- ephone-dn
dn-tag
[ dual-line ] - number
number
[ secondary
number ]
[ no-reg
[ both
|
primary ] ] - call-forward all
target-number - call-forward
busy
target-number
[ primary
|
secondary ]
[ dialplan-pattern ] - call-forward
noan
target-number
timeout
seconds
[ primary
|
secondary ]
[ dialplan-pattern ] - call-forward
night-service
target-number - call-forward
max-length
length - no forward
local-calls - end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example: | Enables
| ||
| Step 2 | configure Example: | Enters global | ||
| Step 3 | telephony-service Example: | Enters | ||
| Step 4 | call-forward pattern Example: | Specifies the
| ||
| Step 5 | exit Example: | Exits | ||
| Step 6 | ephone-dn Example: | Enters
| ||
| Step 7 | number Example: | Configures a | ||
| Step 8 | call-forward all Example: | Forwards all
| ||
| Step 9 | call-forward Example: | Forwards | ||
| Step 10 | call-forward Example: | Forwards | ||
| Step 11 | call-forward Example: | Automatically forwards incoming calls to the specified number
| ||
| Step 12 | call-forward Example: | (Optional)
| ||
| Step 13 | no forward Example: | (Optional)
| ||
| Step 14 | end Example: | Returns to |
Call Transfer for
a Directory Number
To enable call
transfer for a specific directory number, perform the following steps. This
procedure overrides the global setting for blind or consultative transfer for
individual directory numbers.
Before you begin
Call transfer must
be enabled globally. See
Enable Call Transfer and Forwarding on SCCP Phones at System-Level.
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure
terminal - ephone-dn
dn-tag
[ dual-line ] - transfer-mode
{ blind
|
consult } - timeouts transfer-recall
seconds - end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example: | Enables
|
| Step 2 | configure Example: | Enters global |
| Step 3 | ephone-dn Example: | Enters
|
| Step 4 | transfer-mode Example: | Specifies the type of call transfer for an individual directory number using the H.450.2 standard, allowing you to override
|
| Step 5 | timeouts transfer-recall Example: | (Optional)
|
| Step 6 | end Example: | Returns to |
Configure Call
Transfer Options for SCCP Phones
To specify a
maximum number of digits for transfer destinations or block transfers to
external destinations by individual phones, perform the following steps.
Before you begin
-
Transfers made
to speed-dial numbers are not blocked when the
transfer-pattern blocked command is used. -
Transfers made
using speed-dial are not blocked by the
after-hours
block pattern command.
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure
terminal - ephone-template
template-tag - transfer-pattern blocked
- transfer max-length
digit-length - exit
- ephone
phone-tag - ephone-template
template-tag - restart
- end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example: | Enables
| ||
| Step 2 | configure Example: | Enters global | ||
| Step 3 | ephone-template Example: | Enters
| ||
| Step 4 | transfer-pattern blocked Example: | (Optional)
| ||
| Step 5 | transfer max-length Example: | (Optional)
| ||
| Step 6 | exit Example: | Exits | ||
| Step 7 | ephone Example: | Enters ephone | ||
| Step 8 | ephone-template Example: | Applies a
| ||
| Step 9 | restart Example: | Performs a Repeat Step 6 | ||
| Step 10 | end Example: | Exits to |
Verify Call
Transfer for SCCP Phones
Procedure
| Step 1 | Use the Example: |
| Step 2 | If you have Example: |
| Step 3 | Use the |
Specify Transfer Patterns for Trunk-to-Trunk Calls and Conferences for
SIP
 Restriction | Call transfer and conference restrictions apply when transfers or |
Before you begin
Cisco Unified CME 9.5 or a later version.
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure
terminal - telephony-service
- transfer-pattern
transfer-pattern - exit
- Enter one of the following commands:
- voice register pool pool-tag
- voice register template template-tag
- ephone phone tag
- ephone-template template-tag
- transfer max-length
max-length - exit
- telephony-service
- conference transfer-pattern
- end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example: | Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
| Step 2 | configure Example: | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | telephony-service Example: | Enters telephony-service configuration mode for configuring Cisco |
| Step 4 | transfer-pattern Example: | Allows the transfer of calls from Cisco IP phones to specified
|
| Step 5 | exit Example: | Exits telephony-service configuration mode and enters global |
| Step 6 | Enter one of the following commands:
Example: | Enters voice register pool configuration mode and creates a pool configuration for a Cisco Unified SIP IP phone in Cisco Unified
or Enters voice register template configuration mode and defines a template of common parameters for Cisco Unified SIP IP phones.
or Enters ephone configuration mode.
|
| Step 7 | transfer max-length Example: | (Optional) Specifies the maximum length of the transfer number.
|
| Step 8 | exit Example: | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 9 | telephony-service Example: | Enters telephony-service configuration mode for configuring Cisco |
| Step 10 | conference transfer-pattern Example: | Enables a Cisco Unified CME system to apply transfer patterns to a |
| Step 11 | end Example: | Exits telephony-service configuration mode and enters privileged |
Conference
Max-Length
Conference calls are allowed when:
-
both
conference transfer-pattern and
transfer-pattern commands are configured -
dialed digits match the configured transfer pattern
When conference
max-length command is configured, the Cisco Unified CME will allow the
conferences only if the dialed digits are within the max-length limit.
If configured, the
conference max-length command does not impact call transfers.
 Note | If both |
Block
Trunk-to-Trunk Call Transfers for SIP
To block call
transfers to external destinations, perform the following steps.
 Restriction | Call transfer |
Before you begin
Cisco Unified CME
9.5 or a later version.
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure
terminal - Enter one of the following commands:
- voice register pool pool-tag
- voice register template template-tag
- transfer-pattern blocked
- end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example: | Enables
|
| Step 2 | configure Example: | Enters global |
| Step 3 | Enter one of the following commands:
Example: | Enters voice register pool configuration mode and creates a pool configuration for a Cisco Unified SIP IP phone in Cisco Unified
Enters voice register template configuration mode and defines a template of common parameters for Cisco Unified SIP IP phones.
|
| Step 4 | transfer-pattern blocked Example: | Blocks all |
| Step 5 | end Example: | Exits voice |
Enable H.450.12 Capabilities
To enable H.450.12 capabilities globally or by individual dial peer
when not all gateway endpoints in your network support H.450.2 and H.450.3
standards, perform the following steps. H.450.12 capabilities are disabled by
default to minimize the risk of compatibility issues with other types of H.323
systems. Settings for individual dial peers override the global setting.
 Restriction | Cisco CME 3.0 and earlier versions do not support H.450.12. |
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure
terminal - voice service voip
- supplementary-service h450.12
[ advertise-only ] - exit
- dial-peer voice
tag
voip - supplementary-service h450.12
- end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example: | Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
| Step 2 | configure Example: | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | voice service voip Example: | (Optional) Enters voice service configuration mode to establish |
| Step 4 | supplementary-service h450.12 Example: | (Optional) Enables H.450.12 supplementary services capabilities
This command is also used in dial-peer configuration mode to |
| Step 5 | exit Example: | (Optional) Exits voice-service configuration mode. |
| Step 6 | dial-peer voice Example: | (Optional) Enters dial-peer configuration mode. |
| Step 7 | supplementary-service h450.12 Example: | (Optional) Enables H.450.12 supplementary services capabilities This command is also used in voice-service configuration mode to
|
| Step 8 | end Example: | Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
Enable
H.323-to-H.323 Connection Capabilities
Vo IP-to-VoIP c
onnections permit the termination and reorigination of transferred and
forwarded calls over the VoIP network. VoIP-to-VoIP connections are used for
hairpin call routing and for H.450 tandem gateways. The only type of
VoIP-to-VoIP connection that is supported by Cisco CME 3.1 or a later version
is H.323-to-H.323 connection.
VoIP-to-VoIP
connections are disabled on the router by default, and they must be explicitly
enabled to make use of hairpin call routing or an H.450 tandem gateway. In
addition, you must configure a mechanism to direct transferred or forwarded
calls to the hairpin or the H.450 tandem gateway, using one of the following
methods:
- Enable H.450.12
capabilities globally or on the routes that your transfers and forwards take.
See
Enable H.450.12 Capabilities. - Explicitly disable H.450.2
and H.450.3 capabilities globally or on the routes that your transfers and
forwards take. See
Enable Call Transfer and Forwarding on SCCP Phones at System-Level.
 Restriction |
|
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure
terminal - voice service voip
- allow-connections h323 to h323
- end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example: | Enables
|
| Step 2 | configure Example: | Enters global |
| Step 3 | voice service voip Example: | Enters voice |
| Step 4 | allow-connections h323 to h323 Example: | Enables |
| Step 5 | end Example: | Returns to |
Forward Calls
Using Local Hairpin Routing
When
Cisco Unified CME is used to forward calls that originate on phones that do not
support the H.450.3 standard such as Cisco Unified Communications Manager
phones, local hairpin routing must be used to forward the calls. For calling
parties whose numbers match the pattern specified, the system automatically
detects whether H.450.3 is supported and uses the appropriate method to forward
calls.
To enable hairpin
routing, you must denote the originating and terminating legs of the hairpin.
To forward calls to Cisco Unity Express, connections must be allowed to a SIP
trunk.
Optionally, you
can disable the use of H.450.3 but this is not required because the system
automatically detects calls on which H.450.3 is not supported and local hairpin
routing is required when the calling-party numbers match the pattern specified.
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure
terminal - telephony-service
- call-forward pattern
pattern - calling-number local
- exit
- voice service voip
- allow connections
from-type
to
to-type - supplementary-service h450.3
- end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example: | Enables
| ||
| Step 2 | configure Example: | Enters global | ||
| Step 3 | telephony-service Example: | Enters | ||
| Step 4 | call-forward pattern Example: | Specifies the
| ||
| Step 5 | calling-number local Example: | (Optional)
| ||
| Step 6 | exit Example: | Exits | ||
| Step 7 | voice service voip Example: | Enters | ||
| Step 8 | allow connections Example: | Allows
| ||
| Step 9 | supplementary-service h450.3 Example: | (Optional)
| ||
| Step 10 | end Example: | Exits to |
Enable H.450.7 and
QSIG Supplementary Services at System-Level
To enable H.4350.7
capabilities and QSIG supplementary services on all dial peers, perform the
following steps.
 Restriction |
|
Before you begin
Cisco Unified CME
4.0 or a later version.
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure terminal
- voice service voip
- supplementary-service h450.7
- qsig decode
- exit
- voice service pots
- supplementary-service qsig call-forward
- end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example: | Enables
|
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example: | Enters global |
| Step 3 | voice service voip Example: | Enters VoIP |
| Step 4 | supplementary-service h450.7 Example: | Enables |
| Step 5 | qsig decode Example: | Enables |
| Step 6 | exit Example: | Exits VoIP |
| Step 7 | voice service pots Example: | Enters POTS |
| Step 8 | supplementary-service qsig call-forward Example: | Enables QSIG |
| Step 9 | end Example: | Exits to |
Enable H.450.7 and
QSIG Supplementary Services on a Dial Peer
To enable H.4350.7
capabilities and QSIG supplementary services on an individual dial peer,
perform the following steps.
 Restriction |
|
Before you begin
Cisco Unified CME
4.0 or a later version.
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure terminal
- voice service voip
- qsig decode
- exit
- dial-peer voice
tag
voip - supplementary-service h450.7
- exit
- dial-peer voice
tag
pots - supplementary-service qsig call-forward
- end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example: | Enables
|
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example: | Enters global |
| Step 3 | voice service voip Example: | Enters VoIP |
| Step 4 | qsig decode Example: | Enables |
| Step 5 | exit Example: | Exits VoIP |
| Step 6 | dial-peer voice Example: | Enters |
| Step 7 | supplementary-service h450.7 Example: | Enables |
| Step 8 | exit Example: | Exits |
| Step 9 | dial-peer voice Example: | Enters |
| Step 10 | supplementary-service qsig call-forward Example: | Enables QSIG |
| Step 11 | end Example: | Exits to |
Disable SIP
Supplementary Services for Call Forward and Call Transfer
To disable REFER
messages for call transfers or redirect responses for call forwarding from
being sent to the destination by Cisco Unified CME, perform the following
steps. You can disable these supplementary features if the destination gateway
does not support them.
 Restriction |
|
Before you begin
Cisco Unified CME
4.1 or a later version.
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure
terminal - Enter one of the following commands:
- voice service voip
- dial-peer voice tag
voip - no supplementary-service sip
moved-temporarily - no supplementary-service sip
refer - end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example: | Enables
|
| Step 2 | configure Example: | Enters global |
| Step 3 | Enter one of the following commands:
Example: | Enters voice-service configuration mode to set global parameters for VoIP features. or Enters dial peer configuration mode to set parameters for a specific dial peer. |
| Step 4 | no supplementary-service sip Example: | Disables SIP Sending |
| Step 5 | no supplementary-service sip Example: | Disables SIP Sending REFER |
| Step 6 | end Example: | Exits to |
Enable Interworking with Cisco Unified Communications Manager
If Cisco CME 3.1 or
later and Cisco Unified Communications Manager are used in the same network,
some additional configuration is necessary, as described in the following
sections:
-
Configure Cisco CME 3.1 or Later to Interwork with Cisco Unified Communications Manager
-
Enable Cisco Unified Communications Manager to Interwork with Cisco Unified CME
-
Troubleshooting Call Transfer and Forward Configuration
Network with
Cisco Unified CME and Cisco Unified Communications Manager
shows a network containing Cisco Unified CME and Cisco Unified Communications
Manager systems.
Cisco Unified CME and Cisco Unified Communications Manager

Prerequisites
-
Cisco Unified CME must be configured to forward calls using local hairpin routing. For configuration information, see Forward Calls Using Local Hairpin Routing.
Configure
Cisco CME 3.1 or Later to Interwork with Cisco Unified Communications
Manager
All of the
commands in this section are optional because they are set by default to work
with Cisco Unified Communications Manager. They are included here only to
explain how to implement optional capabilities or return non default settings
to their defaults.
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure
terminal - voice service voip
- h323
- telephony-service ccm-compatible
- h225 h245-address on-connect
- exit
- supplementary-service h225-notify cid-update
- exit
- voice class h323
tag - telephony-service
ccm-compatible - h225 h245-address
on-connect - exit
- dial-peer
voice
tag
voip - supplementary-service
h225-notify cid-update - voice-class
h323
tag - end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example: | Enables
|
| Step 2 | configure Example: | Enters global |
| Step 3 | voice service voip Example: | Enters |
| Step 4 | h323 Example: | Enters H.323 |
| Step 5 | telephony-service ccm-compatible Example: | (Optional)
|
| Step 6 | h225 h245-address on-connect Example: | (Optional)
|
| Step 7 | exit Example: | Exits H.323 |
| Step 8 | supplementary-service h225-notify cid-update Example: | (Optional)
This command
|
| Step 9 | exit Example: | Exits |
| Step 10 | voice class h323 Example: | (Optional) |
| Step 11 | telephony-service Example: | (Optional)
|
| Step 12 | h225 h245-address Example: | (Optional)
|
| Step 13 | exit Example: | Exits |
| Step 14 | dial-peer Example: | (Optional) |
| Step 15 | supplementary-service Example: | (Optional)
|
| Step 16 | voice-class Example: | (Optional) |
| Step 17 | end Example: | Exits to |
What to do next
Set up Cisco Unified Communications Manager using the configuration
procedure in the
Enable Cisco Unified Communications Manager to Interwork with Cisco Unified CME.
Enable
Cisco Unified Communications Manager to Interwork with
Cisco Unified CME
To enable
Cisco Unified Communications Manager to interwork with Cisco CME 3.1 or a later
version, perform the following steps in addition to the normal
Cisco Unified Communications Manager configuration.
Procedure
| Step 1 | Set
|
| Step 2 | Configure |
| Step 3 | Ensure that |
| Step 4 | Set up dial |
Troubleshooting
Call Transfer and Forward Configuration
Procedure
| Step 1 | If you |
| Step 2 | Use the |
| Step 3 | For calls that |
| Step 4 | Use the If you are not |
Configure
SIP-to-SIP Phone Call Forwarding
To configure
SIP-to-SIP call forwarding using a back-to-back user agent (B2BUA) which allows
call forwarding on any dial peer, perform the following steps.
 Restriction |
|
Before you begin
-
Cisco CME 3.4
or a later version. -
Connections
between specific types of endpoints in a Cisco IP-to-IP gateway must be
configured by using the
allow-connections
command. For configuration information, see
Enable Calls in Your VoIP Network.
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure terminal
- voice register dn
dn-tag - call-forward b2bua all
directory-
number - call-forward b2bua busy
directory-
number - call-forward b2bua mailbox
directory-
number - call-forward b2bua night-service
directory- number - call-forward b2bua noan
directory- number
timeout seconds - call-forward b2bua unreachable
directory-
number - end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example: | Enables
|
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example: | Enters global |
| Step 3 | voice register dn Example: | Enters voice |
| Step 4 | call-forward b2bua all Example: | Enables call
|
| Step 5 | call-forward b2bua busy Example: | Enables call
|
| Step 6 | call-forward b2bua mailbox Example: | Enables call
|
| Step 7 | call-forward b2bua night-service Example: | Enables call forwarding for a SIP back-to-back user agent so that
|
| Step 8 | call-forward b2bua noan Example: | Enables call
|
| Step 9 | call-forward b2bua unreachable Example: | (Optional)
|
| Step 10 | end Example: | Exits to |
Configure Call Forward Unregistered for SIP IP Phones
Before you begin
-
Cisco Unified CME 8.6 or a later version.
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure
terminal - voice register dn
tag - call-forward b2bua unregistered
directory-number - end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example: | Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
| Step 2 | configure Example: | Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | voice register dn Example: | Enters voice register dn mode to define a directory number for a |
| Step 4 | call-forward b2bua unregistered Example: | Enables call forwarding for a SIP back-to-back user agent so that |
| Step 5 | end Example: | Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
Troubleshooting
Tips for Call Forward Unregistered
-
Use the
show dial-peer voice summary command to
check whether a CFU dial peer is created or removed. -
Enable
deb voice reg event ,
deb voice reg state , and
deb voice reg error commands to trace the
creation and deletion of the CFU dial peer. -
Enable
deb voice reg event ,
deb voip ccapi inout ,
deb voip app callsetup ,
deb voip app core ,
deb voip app state , and
deb voip app error commands to trace the
call flow for CFU.
Configure
Keepalive Timer Expiration in SIP Phones
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure
terminal - voice service voip
- sip
- registrar server
[ expires
[ max
seconds ]
[ min
seconds ] ] - end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example: | Enables
|
| Step 2 | configure Example: | Enters global |
| Step 3 | voice service voip Example: | Enters |
| Step 4 | sip Example: | Enters SIP |
| Step 5 | registrar server Example: | Enables SIP
|
| Step 6 | end Example: | Returns to |
Configure
Call-Forwarding-All Softkey URI on SIP Phones
To specify the
uniform resource identifier (URI) for the call forward all (CfwdAll) softkey on
supported SIP phones, perform the following steps. This URI and the call
forward number is sent to Cisco Unified CME when a user enables Call Forward
All on a SIP phone.
 Restriction |
|
Before you begin
- Cisco Unified CME 4.1 or a
later version. - The
mode cme
command must be enabled in Cisco Unified CME. - Call Forward All must be
enabled on the directory number. For information, see
Configure SIP-to-SIP Phone Call Forwarding.
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure
terminal - voice register global
- call-feature-uri cfwdall
service-uri - end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example: | Enables
|
| Step 2 | configure Example: | Enters global |
| Step 3 | voice register global Example: | Enters voice |
| Step 4 | call-feature-uri cfwdall Example: | Specifies the |
| Step 5 | end Example: | Exits to |
Specify Number of
3XX Responses To be Handled on SIP Phones
To specify how
many subsequent 3XX responses an originating SIP phone can handle for a single
call when the terminating side is a forwarding party which does not use B2BUA,
perform the following steps.
Before you begin
-
Cisco CME 3.4
or a later version. -
The
mode cme
command must be enabled
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure terminal
- voice register global
- phone-redirect-limit
number - end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example: | Enables
|
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example: | Enters global |
| Step 3 | voice register global Example: | Enters voice |
| Step 4 | phone-redirect-limit Example: | Changes the
|
| Step 5 | end Example: | Exits to |
Configure Call
Transfer on SIP Phones
To create and
apply a template to enable call transfer softkeys on an individual SIP phone in
Cisco Unified CME, perform the following steps.
 Restriction |
|
Before you begin
Cisco CME 3.4 or a
later version.
SUMMARY STEPS
- enable
- configure terminal
- voice register template
template-tag - transfer-attended
- transfer-blind
- exit
- voice register pool
pool-tag - template
template-tag - end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example: | Enables
|
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example: | Enters global |
| Step 3 | voice register template Example: | Enters voice
|
| Step 4 | transfer-attended Example: | Enable a soft |
| Step 5 | transfer-blind Example: | Enable a soft |
| Step 6 | exit Example: | Exits |
| Step 7 | voice register pool Example: | Enters voice |
| Step 8 | template Example: | Applies a
|
| Step 9 | end Example: | Exits to |
Configuration Examples for Call Transfer and Forwarding
Example for Configuring H.450.2 and H.450.3 Support
The following example sets all transfers and forwards that are
initiated by a Cisco CME 3.0 or later system to use the H.450 standards,
globally enables H.450.2 and H.450.3 capabilities, and disables those
capabilities for dial peer 37. The
supplementary-service commands under voice-service configuration
mode are not necessary because these values are the default, but they are shown
here for illustration.
telephony-servicetransfer-system full-consulttransfer-pattern .Tcall-forward pattern .T!voice service voipsupplementary-service h450.2 supplementary-service h450.3 !dial-peer voice 37 voipdestination-pattern 555....session target ipv4:10.5.6.7 no supplementary-service h450.2 no supplementary-service h450.3 Example for Configuring Basic Call Forwarding
The following example sets up forwarding for extension 2777 to
extension 2513 on all calls, busy, and no answer. During night service hours,
calls are forwarded to a different number, extension 2879.
ephone-dn 20 number 2777 call-forward all 2513 call-forward busy 2513 call-forward noan 2513 timeout 45 call-forward night-service 2879Example for Configuring Call Forwarding Blocked for Local
Calls
In the following example, extension 2555 is configured to not forward
local calls that are internal to the Cisco Unified CME system. Extension 2222
dials extension 2555. If 2555 is busy, the caller hears a busy tone. If 2555
does not answer, the caller hears ringback. The internal call is not forwarded.
ephone-dn 25 number 2555 no forward local-calls call-forward busy 2244 call-forward noan 2244 timeout 45Example for
Configuring Transfer Patterns
The following
example shows how to configure transfer patterns beginning with 1234:
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# telephony-service
Router(config-telephony)# transfer-pattern 1234
Example for
Configuring Maximum Length of Transfer Number
The following
example shows how to configure the maximum length of the transfer number under
voice register pool 1. Because the maximum length is configured as 5, only call
transfers to Cisco Unified SIP IP phones with a five-digit directory number are
allowed. All call transfers to directory numbers with more than five digits are
blocked.
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# voice register pool 1
Router(config-register-pool)# transfer max-length 5
The following
example shows how to configure the maximum length of the transfer number for a
set of phones under voice register template 2:
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# voice register template 2
Router(config-register-temp)# transfer max-length 10
Example for Configuring Conference Transfer Patterns
The following example configures transfer patterns that allow
conference calls:
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)# telephony-service
Router(config-telephony)# transfer-pattern 1357
Router(config-telephony)# transfer-pattern 222 ....
Router(config-telephony)# conference transfer-pattern
Example for
Blocking All Call Transfers
The following
example shows how to block all call transfers for voice register pool 5:
Router(config)# voice register pool 5
Router(config-register-pool)# transfer-pattern ?
blocked global transfer pattern not allowed
Router(config-register-pool)# transfer-pattern blocked The following
example shows how to block all call transfers for a set of Cisco Unified SIP IP
phones defined by voice register template 9:
Router(config)# voice register template 9
Router(config-register-temp)# transfer-pattern ?
blocked global transfer pattern not allowed
Router(config-register-temp)# transfer-pattern blocked Example for Configuring Selective Call Forwarding
The following example sets call forwarding on busy and no answer for
ephone-dn 38 only for its primary number, 2777. Callers who dial 2778 will hear
a busy signal if the ephone-dn is busy or ringback if there is no answer.
ephone-dn 38number 2777 secondary 2778call-forward busy 3000 primarycall-forward noan 3000 primary timeout 45Example for Configuring Call Transfer
The following example limits transfers from ephone 6, extension 2977,
to numbers containing a maximum of 8 digits.
telephony-serviceload 7910 P00403020214load 7960-7940 P00305000600load 7914 S00103020002load 7905 CP7905040000SCCP040701Aload 7912 CP7912040000SCCP040701Amax-ephones 100max-dn 500ip source-address 10.104.8.205 port 2000max-redirect 20system message XYZ Inc.create cnf-files version-stamp 7960 Jul 13 2004 03:39:28voicemail 7189max-conferences 8 gain -6moh music-on-hold.auweb admin system name admin1 password admin1dn-webedit time-webedit transfer-system full-consulttransfer-pattern 91..........transfer-pattern 92......transfer-pattern 93......transfer-pattern 94......transfer-pattern 95......transfer-pattern 96......transfer-pattern 97......transfer-pattern 98......transfer-pattern 99......secondary-dialtone 9fac standardephone-template 2transfer max-length 8ephone-dn 4number 2977ephone 6button 1:4ephone-template 2Example for
Configuring Call Transfer Recall for SCCP Phones
The following
example shows that transfer recall is enabled globally. After 60 seconds an
unanswered call is forwarded back to the phone that initiated the transfer
(transferor).
telephony-service max-ephones 100 max-dn 240 timeouts transfer-recall 60 max-conferences 8 gain -6 transfer-system full-consultThe following
example shows that transfer recall is enabled for extension 1030 (ephone-dn
103), which is assigned to ephone 3. If extension 1030 forwards a call and the
transfer-to party does not answer, after 60 seconds the unanswered call is sent
back to extension 1030 (transferor). The
timeouts
transfer-recall command can also be set in an ephone-dn template and
applied to one or more directory numbers.
ephone-dn 103number 1030name Smith, Johntimeouts transfer-recall 60!ephone 3mac-address 002D.264E.54FAtype 7962button 1:103Example for
Configuring Call-Transfer Recall for SIP Phones
The following
example shows that transfer recall is enabled globally. After 20 seconds, an
unanswered call is forwarded back to the phone that initiated the transfer
(transferor).
voice register global
mode cme
source-address 8.39.17.29 port 5060
timeouts transfer-recall 20
max-dn 100
max-pool 100
tftp-path flash:
create profile sync 0342574150542703
keepalive 140
auto-register The following
example shows that transfer recall is enabled for extension 111 (voice register
dn 1). If extension 111 forwards a call to voice register dn 2 and the
transfer-to party does not answer, after 20 seconds the unanswered call is sent
back to extension 1111 (transferor).
voice register dn 1
timeouts transfer-recall 20
number 111
voice register dn 2
number 222Example for Enabling H.450.12 Capabilities
The following example globally disables H.450.12 capabilities and then
enables them only on dial peer 24.
voice service voipno supplementary-service h450.12!dial-peer voice 24 voipdestination-pattern 555....session target ipv4:10.5.6.7 supplementary-service h450.12Example for Enabling H.450.7 and QSIG Supplementary Services
The following example implements QSIG supplementary services on
extension 74367 and globally enables H.450.7 supplementary services and QSIG
call-forwarding supplementary services.
telephony-servicevoicemail 74398transfer-system full-consultephone-dn 25number 74367mwi qsigcall-forward all 74000voice service voipsupplementary-service h450.7voice service potssupplementary-service qsig call-forwardExample for
Configuring Cisco Unified CME and Cisco Unified Communications Manager in Same
Network
The following
example shows a running configuration for a Cisco CME 3.1 or later router that
has a Cisco Unified Communications Manager in its network.
Router# show running-config version 12.3service timestamps debug datetime msecservice timestamps log datetime msecno service password-encryption!hostname Router!enable password pswd!aaa new-model!!aaa session-id commonno ip subnet-zero!ip dhcp pool phone1 host 172.24.82.3 255.255.255.0 client-identifier 0100.07eb.4629.9e default-router 172.24.82.2 option 150 ip 172.24.82.2!ip dhcp pool phone2 host 172.24.82.4 255.255.255.0 client-identifier 0100.0b5f.f932.58 default-router 172.24.82.2 option 150 ip 172.24.82.2!ip cefno ip domain lookupno mpls ldp logging neighbor-changesno ftp-server write-enable!voice service voip allow-connections h323 to h323!voice class codec 1 codec preference 1 g711ulaw!no voice hpi capture bufferno voice hpi capture destination!interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 172.24.82.2 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto h323-gateway voip interface h323-gateway voip bind srcaddr 172.24.82.2!ip classlessip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.24.82.1ip route 192.168.254.254 255.255.255.255 172.24.82.1!ip http server!tftp-server flash:P00303020700.bin!voice-port 1/0/0!voice-port 1/0/1!dial-peer cor custom!dial-peer voice 1001 voip description points-to-CCM destination-pattern 1.T voice-class codec 1 session target ipv4:172.26.82.10!dial-peer voice 1002 voip description points to router destination-pattern 4... voice-class codec 1 session target ipv4:172.25.82.2!dial-peer voice 1 pots destination-pattern 3000 port 1/0/0!dial-peer voice 1003 voip destination-pattern 26.. session target ipv4:10.22.22.38!!telephony-service load 7960-7940 P00303020700 max-ephones 48 max-dn 15 ip source-address 172.24.82.2 port 2000 create cnf-files version-stamp Jan 01 2002 00:00:00 keepalive 10 max-conferences 4 moh minuet.au transfer-system full-consult transfer-pattern ....!ephone-dn 1 number 3001 name abcde-1 call-forward busy 4001!ephone-dn 2 number 3002 name abcde-2!ephone-dn 3 number 3003 name abcde-3!ephone-dn 4 number 3004 name abcde-4!ephone 1 mac-address 0003.EB27.289E button 1:1 2:2!ephone 2 mac-address 000D.39F9.3A58 button 1:3 2:4!line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 logging synchronousline aux 0line vty 0 4 password pswd!endExample for Configuring H.450 Tandem Gateway Working with
Cisco Unified CME and Cisco Unified Communications Manager
The following example shows a sample configuration for a Cisco CME 3.1
or later system that is linked to an H.450 tandem gateway that serves as a
proxy for Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
Router# show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration : 1938 bytes!version 12.3service timestamps debug datetime msecservice timestamps log datetime msecno service password-encryption!hostname Router!boot-start-markerboot-end-marker!enable password pswd!aaa new-model!aaa session-id commonno ip subnet-zero!ip cefno ip domain lookupno ftp-server write-enableno scripting tcl initno scripting tcl encdir!voice call send-alert!voice service voip allow-connections h323 to h323 supplementary-service h450.12 h323!voice class codec 1codec preference 1 g711ulawcodec preference 2 g729r8codec preference 3 g729br8!interface FastEthernet0/0ip address 172.27.82.2 255.255.255.0duplex autospeed autoh323-gateway voip interfaceh323-gateway voip h323-id host24!ip classlessip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.26.82.1ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.27.82.1ip http server!dial-peer cor custom!dial-peer voice 1001 voipdescription points-to-CCM destination-pattern 4...session target ipv4:172.24.89.150!dial-peer voice 1002 voipdescription points to CCME1destination-pattern 28..session target ipv4:172.24.22.38!dial-peer voice 1003 voipdescription points to CCME3destination-pattern 9... session target ipv4:192.168.1.29!dial-peer voice 1004 voipdescription points to CCME2destination-pattern 29..session target ipv4:172.24.22.42!line con 0exec-timeout 0 0logging synchronousline aux 0line vty 0 4password pswd!endExample for Configuring Call Forward to Cisco Unity Express
The following example enables the ability to forward calls that
originate from Cisco Unified Communications Manager phones and are routed
through a Cisco Unified CME system to a Cisco Unity Express extension. Call
forwarding is enabled for all calling parties, H.450.3 is disabled, and
connections are allowed to SIP endpoints.
telephony-service call-forward pattern .T voice service voip no supplementary-service h450.3 allow connections from h323 to sipExample for Configuring Call Forward Unregistered for SIP IP
Phones
The following example shows CFU configured for voice register dn 20:
!!!voice service voip allow-connections sip to sip sip registrar server expires max 250 min 75!!voice register global mode cme source-address 10.100.109.10 port 5060 bandwidth video tias-modifier 256 negotiate end-to-end max-dn 200 max-pool 42 url directory http://1.4.212.11/localdirectory create profile sync 0004625832149157!voice register dn 20 number 10 call-forward b2bua unregistered 2345!voice register pool 1 number 1 dn 20 id mac 1111.1111.1111 camera video!voice register pool 2id mac 0009.A3D4.1234Example for Configuring Keepalive Timer Expiration in SIP
Phones
The following example shows the minimum and maximum registrar server
expiration time for SIP phones:
Router#show run!!!!!!voice service voipallow-connections sip to sipsipregistrar server expires max 250 min 75!!voice register globalmode cmesource-address 10.100.109.10 port 5060bandwidth video tias-modifier 256 negotiate end-to-endmax-dn 200Where to Go
Next
If you are finished
modifying the configuration, generate a new configuration file and restart the
phones. See
Generate Configuration Files for Phones.
Softkeys
To block the
function of the call-forward-all or transfer softkey without removing the key
display or to remove the softkey from one or more phones, see
Customize Softkeys.
Feature
Access Codes (FACs)
Phone users can
activate and deactivate a phone’s call-forward-all setting by using a feature
access code (FAC) instead of a soft key on the phone if standard or custom FACs
have been enabled for your system. The following are the standard FACs for call
forward all:
-
callfwd all —Call forward all calls. Standard FAC
is **1 plus an optional target extension. -
callfwd cancel —Cancel call forward all calls.
Standard FAC is **2.
For more information
about FACs, see
Feature Access Codes.
Night
Service
Calls can be
automatically forwarded during night service hours, but you must define the
night-service periods, which are the dates or days and hours during which night
service will be active. For instance, you may want to designate night service
periods that include every weeknight between 5 p.m. and 8 a.m. and all day
every Saturday and Sunday. For more information, see
Configure Call Coverage Features.
Feature
Information for Call Transfer and Forwarding
The following table
provides release information about the feature or features described in this
module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for
a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise,
subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature
Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image
support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to
www.cisco.com/go/cfn.
An account on Cisco.com is not required.
| Feature | Cisco Unified CME Version | Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Calling Number Local | 12.0 | Introduced support to configure Calling Number Local feature for |
| Call | 11.6 | Call |
| Trunk-to-Trunk Transfer Blocking for Toll Fraud Prevention on | 9.5 | Introduced |
| Call | 4.1 |
|
| 4.0 |
| |
| 3.4 | Calls into | |
| 3.1 |
| |
| 3.0 |
| |
| 2.1 | Call | |
| 1.0 | Call | |
| Call | 8.6 | The Call |
| Call | 4.3 |
|
| 4.1 |
| |
| 4.0 |
| |
| 3.4 | Support | |
| 3.2 |
| |
| 3.1 | Support
| |
| 3.0 | Local | |
| 2.1 | Consultative transfer using the ITU-T H.450.2 standard was | |
| 1.0 | Call |
