 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gallium | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | (GAL-ee-əm) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | silvery blue | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight Ar°(Ga) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gallium in the periodic table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic number (Z) | 31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | group 13 (boron group) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Period | period 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Block | p-block | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrons per shell | 2, 8, 18, 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 302.9146 K (29.7646 °C, 85.5763 °F) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | 2673 K (2400 °C, 4352 °F)[2] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (near r.t.) | 5.91 g/cm3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| when liquid (at m.p.) | 6.095 g/cm3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | 5.59 kJ/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | 256 kJ/mol[2] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | 25.86 J/(mol·K) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vapor pressure
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | −5, −4, −3,[3] −2, −1, 0, +1, +2, +3[4] (an amphoteric oxide) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | Pauling scale: 1.81 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic radius | empirical: 135 pm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 122±3 pm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Van der Waals radius | 187 pm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Spectral lines of gallium | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural occurrence | primordial | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure | orthorhombic
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Speed of sound thin rod | 2740 m/s (at 20 °C) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal expansion | 18 µm/(m⋅K) (at 25 °C) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | 40.6 W/(m⋅K) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrical resistivity | 270 nΩ⋅m (at 20 °C) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic ordering | diamagnetic | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar magnetic susceptibility | −21.6×10−6 cm3/mol (at 290 K)[5] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Young’s modulus | 9.8 GPa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Poisson ratio | 0.47 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mohs hardness | 1.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brinell hardness | 56.8–68.7 MPa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 7440-55-3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Naming | after Gallia (Latin for: France), homeland of the discoverer | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prediction | Dmitri Mendeleev (1871) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery and first isolation | Lecoq de Boisbaudran (1875) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Main isotopes of gallium
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| references |
Gallium is a chemical element with the symbol Ga and atomic number 31. Discovered by French chemist Paul-Émile Lecoq de Boisbaudran in 1875,[6] Gallium is in group 13 of the periodic table and is similar to the other metals of the group (aluminium, indium, and thallium).
Elemental gallium is a soft, silvery metal in standard temperature and pressure. In its liquid state, it becomes silvery white. If too much force is applied, the gallium may fracture conchoidally. Since its discovery in 1875, gallium has widely been used to make alloys with low melting points. It is also used in semiconductors, as a dopant in semiconductor substrates.
The melting point of gallium is used as a temperature reference point. Gallium alloys are used in thermometers as a non-toxic and environmentally friendly alternative to mercury, and can withstand higher temperatures than mercury. An even lower melting point of −19 °C (−2 °F), well below the freezing point of water, is claimed for the alloy galinstan (62–95% gallium, 5–22% indium, and 0–16% tin by weight), but that may be the freezing point with the effect of supercooling.
Gallium does not occur as a free element in nature, but as gallium(III) compounds in trace amounts in zinc ores (such as sphalerite) and in bauxite. Elemental gallium is a liquid at temperatures greater than 29.76 °C (85.57 °F), and will melt in a person’s hands at normal human body temperature of 37.0 °C (98.6 °F).
Gallium is predominantly used in electronics. Gallium arsenide, the primary chemical compound of gallium in electronics, is used in microwave circuits, high-speed switching circuits, and infrared circuits. Semiconducting gallium nitride and indium gallium nitride produce blue and violet light-emitting diodes and diode lasers. Gallium is also used in the production of artificial gadolinium gallium garnet for jewelry. Gallium is considered a technology-critical element by the United States National Library of Medicine and Frontiers Media.[7][8]
Gallium has no known natural role in biology. Gallium(III) behaves in a similar manner to ferric salts in biological systems and has been used in some medical applications, including pharmaceuticals and radiopharmaceuticals.
Physical properties[edit]
Crystallization of gallium from the melt
Elemental gallium is not found in nature, but it is easily obtained by smelting. Very pure gallium is a silvery blue metal that fractures conchoidally like glass. Gallium liquid expands by 3.10% when it solidifies; therefore, it should not be stored in glass or metal containers because the container may rupture when the gallium changes state. Gallium shares the higher-density liquid state with a short list of other materials that includes water, silicon, germanium, bismuth, and plutonium.[9]
Gallium forms alloys with most metals. It readily diffuses into cracks or grain boundaries of some metals such as aluminium, aluminium–zinc alloys[10] and steel,[11] causing extreme loss of strength and ductility called liquid metal embrittlement.
The melting point of gallium, at 302.9146 K (29.7646 °C, 85.5763 °F), is just above room temperature, and is approximately the same as the average summer daytime temperatures in Earth’s mid-latitudes. This melting point (mp) is one of the formal temperature reference points in the International Temperature Scale of 1990 (ITS-90) established by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM).[12][13][14] The triple point of gallium, 302.9166 K (29.7666 °C, 85.5799 °F), is used by the US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in preference to the melting point.[15]
The melting point of gallium allows it to melt in the human hand, and then solidify if removed. The liquid metal has a strong tendency to supercool below its melting point/freezing point: Ga nanoparticles can be kept in the liquid state below 90 K.[16] Seeding with a crystal helps to initiate freezing. Gallium is one of the four non-radioactive metals (with caesium, rubidium, and mercury) that are known to be liquid at, or near, normal room temperature. Of the four, gallium is the only one that is neither highly reactive (as are rubidium and caesium) nor highly toxic (as is mercury) and can, therefore, be used in metal-in-glass high-temperature thermometers. It is also notable for having one of the largest liquid ranges for a metal, and for having (unlike mercury) a low vapor pressure at high temperatures. Gallium’s boiling point, 2673 K, is nearly nine times higher than its melting point on the absolute scale, the greatest ratio between melting point and boiling point of any element.[17] Unlike mercury, liquid gallium metal wets glass and skin, along with most other materials (with the exceptions of quartz, graphite, gallium(III) oxide[18] and PTFE),[19] making it mechanically more difficult to handle even though it is substantially less toxic and requires far fewer precautions than mercury. Gallium painted onto glass is a brilliant mirror.[19] For this reason as well as the metal contamination and freezing-expansion problems, samples of gallium metal are usually supplied in polyethylene packets within other containers.
| Property | a | b | c |
|---|---|---|---|
| α (~25 °C, μm/m) | 16 | 11 | 31 |
| ρ (29.7 °C, nΩ·m) | 543 | 174 | 81 |
| ρ (0 °C, nΩ·m) | 480 | 154 | 71.6 |
| ρ (77 K, nΩ·m) | 101 | 30.8 | 14.3 |
| ρ (4.2 K, pΩ·m) | 13.8 | 6.8 | 1.6 |
Gallium does not crystallize in any of the simple crystal structures. The stable phase under normal conditions is orthorhombic with 8 atoms in the conventional unit cell. Within a unit cell, each atom has only one nearest neighbor (at a distance of 244 pm). The remaining six unit cell neighbors are spaced 27, 30 and 39 pm farther away, and they are grouped in pairs with the same distance.[21] Many stable and metastable phases are found as function of temperature and pressure.[22]
The bonding between the two nearest neighbors is covalent; hence Ga2 dimers are seen as the fundamental building blocks of the crystal. This explains the low melting point relative to the neighbor elements, aluminium and indium. This structure is strikingly similar to that of iodine and may form because of interactions between the single 4p electrons of gallium atoms, further away from the nucleus than the 4s electrons and the [Ar]3d10 core. This phenomenon recurs with mercury with its «pseudo-noble-gas» [Xe]4f145d106s2 electron configuration, which is liquid at room temperature.[23] The 3d10 electrons do not shield the outer electrons very well from the nucleus and hence the first ionisation energy of gallium is greater than that of aluminium.[9] Ga2 dimers do not persist in the liquid state and liquid gallium exhibits a complex low-coordinated structure in which each gallium atom is surrounded by 10 others, rather than 11–12 neighbors typical of most liquid metals.[24][25]
The physical properties of gallium are highly anisotropic, i.e. have different values along the three major crystallographic axes a, b, and c (see table), producing a significant difference between the linear (α) and volume thermal expansion coefficients. The properties of gallium are strongly temperature-dependent, particularly near the melting point. For example, the coefficient of thermal expansion increases by several hundred percent upon melting.[20]
Isotopes[edit]
Gallium has 31 known isotopes, ranging in mass number from 56 to 86. Only two isotopes are stable and occur naturally, gallium-69 and gallium-71. Gallium-69 is more abundant: it makes up about 60.1% of natural gallium, while gallium-71 makes up the remaining 39.9%. All the other isotopes are radioactive, with gallium-67 being the longest-lived (half-life 3.261 days). Isotopes lighter than gallium-69 usually decay through beta plus decay (positron emission) or electron capture to isotopes of zinc, although the lightest few (mass numbers 56–59) decay through prompt proton emission. Isotopes heavier than gallium-71 decay through beta minus decay (electron emission), possibly with delayed neutron emission, to isotopes of germanium, while gallium-70 can decay through both beta minus decay and electron capture. Gallium-67 is unique among the light isotopes in having only electron capture as a decay mode, as its decay energy is not sufficient to allow positron emission.[26] Gallium-67 and gallium-68 (half-life 67.7 min) are both used in nuclear medicine.
Chemical properties[edit]
Gallium is found primarily in the +3 oxidation state. The +1 oxidation state is also found in some compounds, although it is less common than it is for gallium’s heavier congeners indium and thallium. For example, the very stable GaCl2 contains both gallium(I) and gallium(III) and can be formulated as GaIGaIIICl4; in contrast, the monochloride is unstable above 0 °C, disproportionating into elemental gallium and gallium(III) chloride. Compounds containing Ga–Ga bonds are true gallium(II) compounds, such as GaS (which can be formulated as Ga24+(S2−)2) and the dioxan complex Ga2Cl4(C4H8O2)2.[27]
Aqueous chemistry[edit]
Strong acids dissolve gallium, forming gallium(III) salts such as Ga(NO
3)
3 (gallium nitrate). Aqueous solutions of gallium(III) salts contain the hydrated gallium ion, [Ga(H
2O)
6]3+
.[28]: 1033 Gallium(III) hydroxide, Ga(OH)
3, may be precipitated from gallium(III) solutions by adding ammonia. Dehydrating Ga(OH)
3 at 100 °C produces gallium oxide hydroxide, GaO(OH).[29]: 140–141
Alkaline hydroxide solutions dissolve gallium, forming gallate salts (not to be confused with identically named gallic acid salts) containing the Ga(OH)−
4 anion.[30][28]: 1033 [31] Gallium hydroxide, which is amphoteric, also dissolves in alkali to form gallate salts.[29]: 141 Although earlier work suggested Ga(OH)3−
6 as another possible gallate anion,[32] it was not found in later work.[31]
Oxides and chalcogenides[edit]
Gallium reacts with the chalcogens only at relatively high temperatures. At room temperature, gallium metal is not reactive with air and water because it forms a passive, protective oxide layer. At higher temperatures, however, it reacts with atmospheric oxygen to form gallium(III) oxide, Ga
2O
3.[30] Reducing Ga
2O
3 with elemental gallium in vacuum at 500 °C to 700 °C yields the dark brown gallium(I) oxide, Ga
2O.[29]: 285 Ga
2O is a very strong reducing agent, capable of reducing H
2SO
4 to H
2S.[29]: 207 It disproportionates at 800 °C back to gallium and Ga
2O
3.[33]
Gallium(III) sulfide, Ga
2S
3, has 3 possible crystal modifications.[33]: 104 It can be made by the reaction of gallium with hydrogen sulfide (H
2S) at 950 °C.[29]: 162 Alternatively, Ga(OH)
3 can be used at 747 °C:[34]
- 2 Ga(OH)
3 + 3 H
2S → Ga
2S
3 + 6 H
2O
Reacting a mixture of alkali metal carbonates and Ga
2O
3 with H
2S leads to the formation of thiogallates containing the [Ga
2S
4]2−
anion. Strong acids decompose these salts, releasing H
2S in the process.[33]: 104–105 The mercury salt, HgGa
2S
4, can be used as a phosphor.[35]
Gallium also forms sulfides in lower oxidation states, such as gallium(II) sulfide and the green gallium(I) sulfide, the latter of which is produced from the former by heating to 1000 °C under a stream of nitrogen.[33]: 94
The other binary chalcogenides, Ga
2Se
3 and Ga
2Te
3, have the zincblende structure. They are all semiconductors but are easily hydrolysed and have limited utility.[33]: 104
Nitrides and pnictides[edit]


Gallium nitride (left) and gallium arsenide (right) wafers
Gallium reacts with ammonia at 1050 °C to form gallium nitride, GaN. Gallium also forms binary compounds with phosphorus, arsenic, and antimony: gallium phosphide (GaP), gallium arsenide (GaAs), and gallium antimonide (GaSb). These compounds have the same structure as ZnS, and have important semiconducting properties.[28]: 1034 GaP, GaAs, and GaSb can be synthesized by the direct reaction of gallium with elemental phosphorus, arsenic, or antimony.[33]: 99 They exhibit higher electrical conductivity than GaN.[33]: 101 GaP can also be synthesized by reacting Ga
2O with phosphorus at low temperatures.[36]
Gallium forms ternary nitrides; for example:[33]: 99
- Li
3Ga + N
2 → Li
3GaN
2
Similar compounds with phosphorus and arsenic are possible: Li
3GaP
2 and Li
3GaAs
2. These compounds are easily hydrolyzed by dilute acids and water.[33]: 101
Halides[edit]
Gallium(III) oxide reacts with fluorinating agents such as HF or F
2 to form gallium(III) fluoride, GaF
3. It is an ionic compound strongly insoluble in water. However, it dissolves in hydrofluoric acid, in which it forms an adduct with water, GaF
3·3H
2O. Attempting to dehydrate this adduct forms GaF
2OH·nH
2O. The adduct reacts with ammonia to form GaF
3·3NH
3, which can then be heated to form anhydrous GaF
3.[29]: 128–129
Gallium trichloride is formed by the reaction of gallium metal with chlorine gas.[30] Unlike the trifluoride, gallium(III) chloride exists as dimeric molecules, Ga
2Cl
6, with a melting point of 78 °C. Eqivalent compounds are formed with bromine and iodine, Ga
2Br
6 and Ga
2I
6.[29]: 133
Like the other group 13 trihalides, gallium(III) halides are Lewis acids, reacting as halide acceptors with alkali metal halides to form salts containing GaX−
4 anions, where X is a halogen. They also react with alkyl halides to form carbocations and GaX−
4.[29]: 136–137
When heated to a high temperature, gallium(III) halides react with elemental gallium to form the respective gallium(I) halides. For example, GaCl
3 reacts with Ga to form GaCl:
- 2 Ga + GaCl
3 ⇌ 3 GaCl (g)
At lower temperatures, the equilibrium shifts toward the left and GaCl disproportionates back to elemental gallium and GaCl
3. GaCl can also be produced by reacting Ga with HCl at 950 °C; the product can be condensed as a red solid.[28]: 1036
Gallium(I) compounds can be stabilized by forming adducts with Lewis acids. For example:
- GaCl + AlCl
3 → Ga+
[AlCl
4]−
The so-called «gallium(II) halides», GaX
2, are actually adducts of gallium(I) halides with the respective gallium(III) halides, having the structure Ga+
[GaX
4]−
. For example:[30][28]: 1036 [37]
- GaCl + GaCl
3 → Ga+
[GaCl
4]−
Hydrides[edit]
Like aluminium, gallium also forms a hydride, GaH
3, known as gallane, which may be produced by reacting lithium gallanate (LiGaH
4) with gallium(III) chloride at −30 °C:[28]: 1031
- 3 LiGaH
4 + GaCl
3 → 3 LiCl + 4 GaH
3
In the presence of dimethyl ether as solvent, GaH
3 polymerizes to (GaH
3)
n. If no solvent is used, the dimer Ga
2H
6 (digallane) is formed as a gas. Its structure is similar to diborane, having two hydrogen atoms bridging the two gallium centers,[28]: 1031 unlike α-AlH
3 in which aluminium has a coordination number of 6.[28]: 1008
Gallane is unstable above −10 °C, decomposing to elemental gallium and hydrogen.[38]
Organogallium compounds[edit]
Organogallium compounds are of similar reactivity to organoindium compounds, less reactive than organoaluminium compounds, but more reactive than organothallium compounds.[39] Alkylgalliums are monomeric. Lewis acidity decreases in the order Al > Ga > In and as a result organogallium compounds do not form bridged dimers as organoaluminium compounds do. Organogallium compounds are also less reactive than organoaluminium compounds. They do form stable peroxides.[40] These alkylgalliums are liquids at room temperature, having low melting points, and are quite mobile and flammable. Triphenylgallium is monomeric in solution, but its crystals form chain structures due to weak intermolecluar Ga···C interactions.[39]
Gallium trichloride is a common starting reagent for the formation of organogallium compounds, such as in carbogallation reactions.[41] Gallium trichloride reacts with lithium cyclopentadienide in diethyl ether to form the trigonal planar gallium cyclopentadienyl complex GaCp3. Gallium(I) forms complexes with arene ligands such as hexamethylbenzene. Because this ligand is quite bulky, the structure of the [Ga(η6-C6Me6)]+ is that of a half-sandwich. Less bulky ligands such as mesitylene allow two ligands to be attached to the central gallium atom in a bent sandwich structure. Benzene is even less bulky and allows the formation of dimers: an example is [Ga(η6-C6H6)2] [GaCl4]·3C6H6.[39]
History[edit]
Small gallium droplets fusing together
In 1871, the existence of gallium was first predicted by Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev, who named it «eka-aluminium» from its position in his periodic table. He also predicted several properties of eka-aluminium that correspond closely to the real properties of gallium, such as its density, melting point, oxide character, and bonding in chloride.[42]
-
Comparison between Mendeleev’s 1871 predictions and the known properties of gallium[43]
Property Mendeleev’s predictions Actual properties Atomic weight ~68 69.723 Density 5.9 g/cm3 5.904 g/cm3 Melting point Low 29.767 °C Formula of oxide M2O3 Ga2O3 Density of oxide 5.5 g/cm3 5.88 g/cm3 Nature of hydroxide amphoteric amphoteric
Mendeleev further predicted that eka-aluminium would be discovered by means of the spectroscope, and that metallic eka-aluminium would dissolve slowly in both acids and alkalis and would not react with air. He also predicted that M2O3 would dissolve in acids to give MX3 salts, that eka-aluminium salts would form basic salts, that eka-aluminium sulfate should form alums, and that anhydrous MCl3 should have a greater volatility than ZnCl2: all of these predictions turned out to be true.[43]
Gallium was discovered using spectroscopy by French chemist Paul Emile Lecoq de Boisbaudran in 1875 from its characteristic spectrum (two violet lines) in a sample of sphalerite.[44] Later that year, Lecoq obtained the free metal by electrolysis of the hydroxide in potassium hydroxide solution.[45]
He named the element «gallia», from Latin Gallia meaning Gaul, after his native land of France. It was later claimed that, in a multilingual pun of a kind favoured by men of science in the 19th century, he had also named gallium after himself: «Le coq» is French for «the rooster» and the Latin word for «rooster» is «gallus«. In an 1877 article, Lecoq denied this conjecture.[45]
Originally, de Boisbaudran determined the density of gallium as 4.7 g/cm3, the only property that failed to match Mendeleev’s predictions; Mendeleev then wrote to him and suggested that he should remeasure the density, and de Boisbaudran then obtained the correct value of 5.9 g/cm3, that Mendeleev had predicted exactly.[43]
From its discovery in 1875 until the era of semiconductors, the primary uses of gallium were high-temperature thermometrics and metal alloys with unusual properties of stability or ease of melting (some such being liquid at room temperature).
The development of gallium arsenide as a direct bandgap semiconductor in the 1960s ushered in the most important stage in the applications of gallium.[19] In 1978, the electronics industry used gallium to fabricate light emitting diodes, photovoltaics and semiconductors, while the metals business used it[46] to reduce the melting point of alloys.[47]
Occurrence[edit]
Gallium does not exist as a free element in the Earth’s crust, and the few high-content minerals, such as gallite (CuGaS2), are too rare to serve as a primary source.[48] The abundance in the Earth’s crust is approximately 16.9 ppm.[49] This is comparable to the crustal abundances of lead, cobalt, and niobium. Yet unlike these elements, gallium does not form its own ore deposits with concentrations of > 0.1 wt.% in ore. Rather it occurs at trace concentrations similar to the crustal value in zinc ores,[48][50] and at somewhat higher values (~ 50 ppm) in aluminium ores, from both of which it is extracted as a by-product. This lack of independent deposits is due to gallium’s geochemical behaviour, showing no strong enrichment in the processes relevant to the formation of most ore deposits.[48]
The United States Geological Survey (USGS) estimates that more than 1 million tons of gallium is contained in known reserves of bauxite and zinc ores.[51][52] Some coal flue dusts contain small quantities of gallium, typically less than 1% by weight.[53][54][55][56] However, these amounts are not extractable without mining of the host materials (see below). Thus, the availability of gallium is fundamentally determined by the rate at which bauxite, zinc ores (and coal) are extracted.
Production and availability[edit]

99.9999% (6N) gallium sealed in vacuum ampoule
Gallium is produced exclusively as a by-product during the processing of the ores of other metals. Its main source material is bauxite, the chief ore of aluminium, but minor amounts are also extracted from sulfidic zinc ores (sphalerite being the main host mineral).[57][58] In the past, certain coals were an important source.
During the processing of bauxite to alumina in the Bayer process, gallium accumulates in the sodium hydroxide liquor. From this it can be extracted by a variety of methods. The most recent is the use of ion-exchange resin.[57] Achievable extraction efficiencies critically depend on the original concentration in the feed bauxite. At a typical feed concentration of 50 ppm, about 15% of the contained gallium is extractable.[57] The remainder reports to the red mud and aluminium hydroxide streams. Gallium is removed from the ion-exchange resin in solution. Electrolysis then gives gallium metal. For semiconductor use, it is further purified with zone melting or single-crystal extraction from a melt (Czochralski process). Purities of 99.9999% are routinely achieved and commercially available.[59]

Its by-product status means that gallium production is constrained by the amount of bauxite, sulfidic zinc ores (and coal) extracted per year. Therefore, its availability needs to be discussed in terms of supply potential. The supply potential of a by-product is defined as that amount which is economically extractable from its host materials per year under current market conditions (i.e. technology and price).[60] Reserves and resources are not relevant for by-products, since they cannot be extracted independently from the main-products.[61] Recent estimates put the supply potential of gallium at a minimum of 2,100 t/yr from bauxite, 85 t/yr from sulfidic zinc ores, and potentially 590 t/yr from coal.[57] These figures are significantly greater than current production (375 t in 2016).[62] Thus, major future increases in the by-product production of gallium will be possible without significant increases in production costs or price. The average price for low-grade gallium was $120 per kilogram in 2016 and $135–140 per kilogram in 2017.[63]
In 2017, the world’s production of low-grade gallium was ca. 315 tons — an increase of 15% from 2016. China, Japan, South Korea, Russia, and Ukraine were the leading producers, while Germany ceased primary production of gallium in 2016. The yield of high-purity gallium was ca. 180 tons, mostly originating from China, Japan, Slovakia, UK and U.S. The 2017 world annual production capacity was estimated at 730 tons for low-grade and 320 tons for refined gallium.[63]
China produced ca. 250 tons of low-grade gallium in 2016 and ca. 300 tons in 2017. It also accounted for more than half of global LED production.[63]
Applications[edit]
Semiconductor applications dominate the commercial demand for gallium, accounting for 98% of the total. The next major application is for gadolinium gallium garnets.[64]
Semiconductors[edit]

Extremely high-purity (>99.9999%) gallium is commercially available to serve the semiconductor industry. Gallium arsenide (GaAs) and gallium nitride (GaN) used in electronic components represented about 98% of the gallium consumption in the United States in 2007. About 66% of semiconductor gallium is used in the U.S. in integrated circuits (mostly gallium arsenide), such as the manufacture of ultra-high-speed logic chips and MESFETs for low-noise microwave preamplifiers in cell phones. About 20% of this gallium is used in optoelectronics.[51]
Worldwide, gallium arsenide makes up 95% of the annual global gallium consumption.[59] It amounted to $7.5 billion in 2016, with 53% originating from cell phones, 27% from wireless communications, and the rest from automotive, consumer, fiber-optic, and military applications. The recent increase in GaAs consumption is mostly related to the emergence of 3G and 4G smartphones, which use 10 times more GaAs than older models.[63]
Gallium arsenide and gallium nitride can also be found in a variety of optoelectronic devices which had a market share of $15.3 billion in 2015 and $18.5 billion in 2016.[63] Aluminium gallium arsenide (AlGaAs) is used in high-power infrared laser diodes. The semiconductors gallium nitride and indium gallium nitride are used in blue and violet optoelectronic devices, mostly laser diodes and light-emitting diodes. For example, gallium nitride 405 nm diode lasers are used as a violet light source for higher-density Blu-ray Disc compact data disc drives.[65]
Other major application of gallium nitride are cable television transmission, commercial wireless infrastructure, power electronics, and satellites. The GaN radio frequency device market alone was estimated at $370 million in 2016 and $420 million in 2016.[63]
Multijunction photovoltaic cells, developed for satellite power applications, are made by molecular-beam epitaxy or metalorganic vapour-phase epitaxy of thin films of gallium arsenide, indium gallium phosphide, or indium gallium arsenide. The Mars Exploration Rovers and several satellites use triple-junction gallium arsenide on germanium cells.[66] Gallium is also a component in photovoltaic compounds (such as copper indium gallium selenium sulfide Cu(In,Ga)(Se,S)2) used in solar panels as a cost-efficient alternative to crystalline silicon.[67]
Galinstan and other alloys[edit]

Galinstan easily wetting a piece of ordinary glass

Gallium readily alloys with most metals, and is used as an ingredient in low-melting alloys. The nearly eutectic alloy of gallium, indium, and tin is a room temperature liquid used in medical thermometers. This alloy, with the trade-name Galinstan (with the «-stan» referring to the tin, stannum in Latin), has a low melting point of −19 °C (−2.2 °F).[68] It has been suggested that this family of alloys could also be used to cool computer chips in place of water, and is often used as a replacement for thermal paste in high-performance computing.[69][70] Gallium alloys have been evaluated as substitutes for mercury dental amalgams, but these materials have yet to see wide acceptance. Liquid alloys containing mostly gallium and indium have been found to precipitate gaseous CO2 into solid carbon and are being researched as potential methodologies for carbon capture and possibly carbon removal.[71][72]
Because gallium wets glass or porcelain, gallium can be used to create brilliant mirrors. When the wetting action of gallium-alloys is not desired (as in Galinstan glass thermometers), the glass must be protected with a transparent layer of gallium(III) oxide.[73]
The plutonium used in nuclear weapon pits is stabilized in the δ phase and made machinable by alloying with gallium.[74][75]
Biomedical applications[edit]
Although gallium has no natural function in biology, gallium ions interact with processes in the body in a manner similar to iron(III). Because these processes include inflammation, a marker for many disease states, several gallium salts are used (or are in development) as pharmaceuticals and radiopharmaceuticals in medicine. Interest in the anticancer properties of gallium emerged when it was discovered that 67Ga(III) citrate injected in tumor-bearing animals localized to sites of tumor. Clinical trials have shown gallium nitrate to have antineoplastic activity against non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma and urothelial cancers. A new generation of gallium-ligand complexes such as tris(8-quinolinolato)gallium(III) (KP46) and gallium maltolate has emerged.[76] Gallium nitrate (brand name Ganite) has been used as an intravenous pharmaceutical to treat hypercalcemia associated with tumor metastasis to bones. Gallium is thought to interfere with osteoclast function, and the therapy may be effective when other treatments have failed.[77] Gallium maltolate, an oral, highly absorbable form of gallium(III) ion, is an anti-proliferative to pathologically proliferating cells, particularly cancer cells and some bacteria that accept it in place of ferric iron (Fe3+). Researchers are conducting clinical and preclinical trials on this compound as a potential treatment for a number of cancers, infectious diseases, and inflammatory diseases.[78]
When gallium ions are mistakenly taken up in place of iron(III) by bacteria such as Pseudomonas, the ions interfere with respiration, and the bacteria die. This happens because iron is redox-active, allowing the transfer of electrons during respiration, while gallium is redox-inactive.[79][80]
A complex amine-phenol Ga(III) compound MR045 is selectively toxic to parasites resistant to chloroquine, a common drug against malaria. Both the Ga(III) complex and chloroquine act by inhibiting crystallization of hemozoin, a disposal product formed from the digestion of blood by the parasites.[81][82]
Radiogallium salts[edit]
Gallium-67 salts such as gallium citrate and gallium nitrate are used as radiopharmaceutical agents in the nuclear medicine imaging known as gallium scan. The radioactive isotope 67Ga is used, and the compound or salt of gallium is unimportant. The body handles Ga3+ in many ways as though it were Fe3+, and the ion is bound (and concentrates) in areas of inflammation, such as infection, and in areas of rapid cell division. This allows such sites to be imaged by nuclear scan techniques.[83]
Gallium-68, a positron emitter with a half-life of 68 min, is now used as a diagnostic radionuclide in PET-CT when linked to pharmaceutical preparations such as DOTATOC, a somatostatin analogue used for neuroendocrine tumors investigation, and DOTA-TATE, a newer one, used for neuroendocrine metastasis and lung neuroendocrine cancer, such as certain types of microcytoma. Gallium-68’s preparation as a pharmaceutical is chemical, and the radionuclide is extracted by elution from germanium-68, a synthetic radioisotope of germanium, in gallium-68 generators.[84]
Other uses[edit]
Neutrino detection: Gallium is used for neutrino detection. Possibly the largest amount of pure gallium ever collected in a single location is the Gallium-Germanium Neutrino Telescope used by the SAGE experiment at the Baksan Neutrino Observatory in Russia. This detector contains 55–57 tonnes (~9 cubic metres) of liquid gallium.[85] Another experiment was the GALLEX neutrino detector operated in the early 1990s in an Italian mountain tunnel. The detector contained 12.2 tons of watered gallium-71. Solar neutrinos caused a few atoms of 71Ga to become radioactive 71Ge, which were detected. This experiment showed that the solar neutrino flux is 40% less than theory predicted. This deficit was not explained until better solar neutrino detectors and theories were constructed (see SNO).[86]
Ion source: Gallium is also used as a liquid metal ion source for a focused ion beam. For example, a focused gallium-ion beam was used to create the world’s smallest book, Teeny Ted from Turnip Town.[87]
Lubricants: Gallium serves as an additive in glide wax for skis and other low-friction surface materials.[88]
Flexible electronics: Materials scientists speculate that the properties of gallium could make it suitable for the development of flexible and wearable devices.[89][90]
Hydrogen generation: Gallium disrupts the protective oxide layer on aluminium, allowing water to react with the aluminium in AlGa to produce hydrogen gas.[91]
Humor: A well-known practical joke among chemists is to fashion gallium spoons and use them to serve tea to unsuspecting guests, since gallium has a similar appearance to its lighter homolog aluminium. The spoons then melt in the hot tea.[92]
Gallium in the ocean[edit]
Advances in trace element testing have allowed scientists to discover traces of dissolved gallium in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans [93] In recent years, dissolved gallium concentrations have presented in the Beaufort Sea.[93][94] These reports reflect the possible profiles of the Pacific and Atlantic Ocean waters.[94] For the Pacific Oceans, typical dissolved gallium concentrations are between 4–6 pmol/kg at depths <~150 m. In comparison, for Atlantic waters 25–28 pmol/kg at depths >~350 m.[94]
Gallium has entered oceans mainly through aeolian input, but having gallium in our oceans can be used to resolve aluminium distribution in the oceans.[95] The reason for this is that gallium is geochemically similar to aluminium, just less reactive. Gallium also has a slightly larger surface water residence time than aluminium.[95] Gallium has a similar dissolved profile similar to that of aluminium, due to this gallium can be used as a tracer for aluminium.[95] Gallium can also be used as a tracer of aeolian inputs of iron.[96] Gallium is used as a tracer for iron in the northwest Pacific, south and central Atlantic Oceans.[96] For example, in the northwest Pacific, low gallium surface waters, in the subpolar region suggest that there is low dust input, which can subsequently explain the following high-nutrient, low-chlorophyll environmental behavior.[96]
Precautions[edit]
| Hazards | |
|---|---|
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |  |
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H290, H318 |
| Precautionary statements | P280, P305, P310, P338, P351[97] |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | [98]
1 0 0 |
Metallic gallium is not toxic. However, exposure to gallium halide complexes can result in acute toxicity.[99] The Ga3+ ion of soluble gallium salts tends to form the insoluble hydroxide when injected in large doses; precipitation of this hydroxide resulted in nephrotoxicity in animals. In lower doses, soluble gallium is tolerated well and does not accumulate as a poison, instead being excreted mostly through urine. Excretion of gallium occurs in two phases: the first phase has a biological half-life of 1 hour, while the second has a biological half-life of 25 hours.[83]
References[edit]
- ^ «Standard Atomic Weights: Gallium». CIAAW. 1987.
- ^ a b Zhang Y; Evans JRG; Zhang S (2011). «Corrected Values for Boiling Points and Enthalpies of Vaporization of Elements in Handbooks». J. Chem. Eng. Data. 56 (2): 328–337. doi:10.1021/je1011086.
- ^ Ga(−3) has been observed in LaGa, see Dürr, Ines; Bauer, Britta; Röhr, Caroline (2011). «Lanthan-Triel/Tetrel-ide La(Al,Ga)x(Si,Ge)1-x. Experimentelle und theoretische Studien zur Stabilität intermetallischer 1:1-Phasen» (PDF). Z. Naturforsch. (in German). 66b: 1107–1121.
- ^ Hofmann, Patrick (1997). Colture. Ein Programm zur interaktiven Visualisierung von Festkörperstrukturen sowie Synthese, Struktur und Eigenschaften von binären und ternären Alkali- und Erdalkalimetallgalliden (PDF) (Thesis) (in German). PhD Thesis, ETH Zurich. p. 72. doi:10.3929/ethz-a-001859893. hdl:20.500.11850/143357. ISBN 978-3728125972.
- ^ Weast, Robert (1984). CRC, Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. Boca Raton, Florida: Chemical Rubber Company Publishing. pp. E110. ISBN 0-8493-0464-4.
- ^ Scerri, Eric (2020). The Periodic Table: Its Story and Its Significance. Oxford University Press. p. 149. ISBN 978-0-19-091436-3.
- ^ Cobelo-García, A.; Filella, M.; Croot, P.; Frazzoli, C.; Du Laing, G.; Ospina-Alvarez, N.; Rauch, S.; Salaun, P.; Schäfer, J.; Zimmermann, S. (2015). «COST action TD1407: network on technology-critical elements (NOTICE)—from environmental processes to human health threats». Environmental Science and Pollution Research International. 22 (19): 15188–15194. doi:10.1007/s11356-015-5221-0. ISSN 0944-1344. PMC 4592495. PMID 26286804.
- ^ Romero-Freire, Ana; Santos-Echeandía, Juan; Neira, Patricia; Cobelo-García, Antonio (2019). «Less-Studied Technology-Critical Elements (Nb, Ta, Ga, In, Ge, Te) in the Marine Environment: Review on Their Concentrations in Water and Organisms». Frontiers in Marine Science. 6. doi:10.3389/fmars.2019.00532. ISSN 2296-7745.
- ^ a b Greenwood and Earnshaw, p. 222
- ^ Tsai, W. L; Hwu, Y.; Chen, C. H.; Chang, L. W.; Je, J. H.; Lin, H. M.; Margaritondo, G. (2003). «Grain boundary imaging, gallium diffusion and the fracture behavior of Al–Zn Alloy – An in situ study». Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B. 199: 457–463. Bibcode:2003NIMPB.199..457T. doi:10.1016/S0168-583X(02)01533-1.
- ^ Vigilante, G. N.; Trolano, E.; Mossey, C. (June 1999). «Liquid Metal Embrittlement of ASTM A723 Gun Steel by Indium and Gallium». Defense Technical Information Center. Retrieved 2009-07-07.
- ^ Preston–Thomas, H. (1990). «The International Temperature Scale of 1990 (ITS-90)» (PDF). Metrologia. 27 (1): 3–10. Bibcode:1990Metro..27….3P. doi:10.1088/0026-1394/27/1/002. S2CID 250785635. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2007-06-18.
- ^ «ITS-90 documents at Bureau International de Poids et Mesures».
- ^ Magnum, B. W.; Furukawa, G. T. (August 1990). «Guidelines for Realizing the International Temperature Scale of 1990 (ITS-90)» (PDF). National Institute of Standards and Technology. NIST TN 1265. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2003-07-04.
- ^ Strouse, Gregory F. (1999). «NIST realization of the gallium triple point». Proc. TEMPMEKO. 1999 (1): 147–152. Retrieved 2016-10-30.
- ^ Parravicini, G. B.; Stella, A.; Ghigna, P.; Spinolo, G.; Migliori, A.; d’Acapito, F.; Kofman, R. (2006). «Extreme undercooling (down to 90K) of liquid metal nanoparticles». Applied Physics Letters. 89 (3): 033123. Bibcode:2006ApPhL..89c3123P. doi:10.1063/1.2221395.
- ^ Greenwood and Earnshaw, p. 224
- ^ Chen, Ziyu; Lee, Jeong-Bong (2019). «Gallium Oxide Coated Flat Surface as Non-Wetting Surface for Actuation of Liquid Metal Droplets». 2019 IEEE 32nd International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS). pp. 1–4. doi:10.1109/memsys.2019.8870886. ISBN 978-1-7281-1610-5.
- ^ a b c Greenwood and Earnshaw, p. 221
- ^ a b Rosebury, Fred (1992). Handbook of Electron Tube and Vacuum Techniques. Springer. p. 26. ISBN 978-1-56396-121-2.
- ^ Bernascino, M.; et al. (1995). «Ab initio calculations of structural and electronic properties of gallium solid-state phases». Phys. Rev. B. 52 (14): 9988–9998. Bibcode:1995PhRvB..52.9988B. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.52.9988. PMID 9980044.
- ^ «Phase Diagrams of the Elements», David A. Young, UCRL-51902 «Prepared for the U.S. Energy Research & Development Administration under contract No. W-7405-Eng-48». (1975)
- ^ Greenwood and Earnshaw, p. 223
- ^ Yagafarov, O. F.; Katayama, Y.; Brazhkin, V. V.; Lyapin, A. G.; Saitoh, H. (November 7, 2012). «Energy dispersive x-ray diffraction and reverse Monte Carlo structural study of liquid gallium under pressure». Physical Review B. 86 (17): 174103. Bibcode:2012PhRvB..86q4103Y. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.86.174103 – via APS.
- ^ Drewitt, James W. E.; Turci, Francesco; Heinen, Benedict J.; Macleod, Simon G.; Qin, Fei; Kleppe, Annette K.; Lord, Oliver T. (April 9, 2020). «Structural Ordering in Liquid Gallium under Extreme Conditions». Physical Review Letters. 124 (14): 145501. Bibcode:2020PhRvL.124n5501D. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.124.145501. PMID 32338984. S2CID 216177238 – via DOI.org (Crossref).
- ^ Audi, Georges; Bersillon, Olivier; Blachot, Jean; Wapstra, Aaldert Hendrik (2003), «The NUBASE evaluation of nuclear and decay properties», Nuclear Physics A, 729: 3–128, Bibcode:2003NuPhA.729….3A, doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2003.11.001
- ^ Greenwood and Earnshaw, p. 240
- ^ a b c d e f g h Wiberg, Egon; Wiberg, Nils; Holleman, Arnold Frederick (2001). Inorganic chemistry. Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-12-352651-9.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Downs, Anthony John (1993). Chemistry of aluminium, gallium, indium, and thallium. Springer. ISBN 978-0-7514-0103-5.
- ^ a b c d Eagleson, Mary, ed. (1994). Concise encyclopedia chemistry. Walter de Gruyter. p. 438. ISBN 978-3-11-011451-5.
- ^ a b Sipos, P. L.; Megyes, T. N.; Berkesi, O. (2008). «The Structure of Gallium in Strongly Alkaline, Highly Concentrated Gallate Solutions—a Raman and 71
Ga
-NMR Spectroscopic Study». J Solution Chem. 37 (10): 1411–1418. doi:10.1007/s10953-008-9314-y. S2CID 95723025. - ^ Hampson, N. A. (1971). Harold Reginald Thirsk (ed.). Electrochemistry—Volume 3: Specialist periodical report. Great Britain: Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 71. ISBN 978-0-85186-027-5.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Greenwood, N. N. (1962). Harry Julius Emeléus; Alan G. Sharpe (eds.). Advances in inorganic chemistry and radiochemistry. Vol. 5. Academic Press. pp. 94–95. ISBN 978-0-12-023605-3.
- ^ Madelung, Otfried (2004). Semiconductors: data handbook (3rd ed.). Birkhäuser. pp. 276–277. ISBN 978-3-540-40488-0.
- ^ Krausbauer, L.; Nitsche, R.; Wild, P. (1965). «Mercury gallium sulfide, HgGa
2S
4, a new phosphor». Physica. 31 (1): 113–121. Bibcode:1965Phy….31..113K. doi:10.1016/0031-8914(65)90110-2. - ^ Michelle Davidson (2006). Inorganic Chemistry. Lotus Press. p. 90. ISBN 978-81-89093-39-6.
- ^ Arora, Amit (2005). Text Book Of Inorganic Chemistry. Discovery Publishing House. pp. 389–399. ISBN 978-81-8356-013-9.
- ^ Downs, Anthony J.; Pulham, Colin R. (1994). Sykes, A. G. (ed.). Advances in Inorganic Chemistry. Vol. 41. Academic Press. pp. 198–199. ISBN 978-0-12-023641-1.
- ^ a b c Greenwoood and Earnshaw, pp. 262–5
- ^ Uhl, W. and Halvagar, M. R.; et al. (2009). «Reducing Ga-H and Ga-C Bonds in Close Proximity to Oxidizing Peroxo Groups: Conflicting Properties in Single Molecules». Chemistry: A European Journal. 15 (42): 11298–11306. doi:10.1002/chem.200900746. PMID 19780106.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Amemiya, Ryo (2005). «GaCl3 in Organic Synthesis». European Journal of Organic Chemistry. 2005 (24): 5145–5150. doi:10.1002/ejoc.200500512.
- ^ Ball, Philip (2002). The Ingredients: A Guided Tour of the Elements. Oxford University Press. p. 105. ISBN 978-0-19-284100-1.
- ^ a b c Greenwood and Earnshaw, p. 217.
- ^ Lecoq de Boisbaudran, Paul Émile (1875). «Caractères chimiques et spectroscopiques d’un nouveau métal, le gallium, découvert dans une blende de la mine de Pierrefitte, vallée d’Argelès (Pyrénées)». Comptes Rendus Hebdomadaires des Séances de l’Académie des Sciences. 81: 493–495.
- ^ a b Weeks, Mary Elvira (1932). «The discovery of the elements. XIII. Some elements predicted by Mendeleeff». Journal of Chemical Education. 9 (9): 1605–1619. Bibcode:1932JChEd…9.1605W. doi:10.1021/ed009p1605.
- ^ Petkof, Benjamin (1978). «Gallium» (PDF). GPO. USGS Minerals Yearbook. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-06-02.
- ^ «An Overview of Gallium». AZoNetwork. 18 December 2001.
- ^ a b c Frenzel, Max (2016). «The distribution of gallium, germanium and indium in conventional and non-conventional resources – Implications for global availability (PDF Download Available)». ResearchGate. doi:10.13140/rg.2.2.20956.18564. Retrieved 2017-06-02.
- ^ Burton, J. D.; Culkin, F.; Riley, J. P. (2007). «The abundances of gallium and germanium in terrestrial materials». Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 16 (1): 151–180. Bibcode:1959GeCoA..16..151B. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(59)90052-3.
- ^ Frenzel, Max; Hirsch, Tamino; Gutzmer, Jens (July 2016). «Gallium, germanium, indium, and other trace and minor elements in sphalerite as a function of deposit type — A meta-analysis». Ore Geology Reviews. 76: 52–78. doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.12.017.
- ^ a b Kramer, Deborah A. «Mineral Commodity Summary 2006: Gallium» (PDF). United States Geological Survey. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2008-05-14. Retrieved 2008-11-20.
- ^ Kramer, Deborah A. «Mineral Yearbook 2006: Gallium» (PDF). United States Geological Survey. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2008-05-09. Retrieved 2008-11-20.
- ^ Xiao-quan, Shan; Wen, Wang & Bei, Wen (1992). «Determination of gallium in coal and coal fly ash by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry using slurry sampling and nickel chemical modification». Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry. 7 (5): 761. doi:10.1039/JA9920700761.
- ^ «Gallium in West Virginia Coals». West Virginia Geological and Economic Survey. 2002-03-02. Archived from the original on 11 March 2002.
- ^ Font, O; Querol, Xavier; Juan, Roberto; Casado, Raquel; Ruiz, Carmen R.; López-Soler, Ángel; Coca, Pilar; Peña, Francisco García (2007). «Recovery of gallium and vanadium from gasification fly ash». Journal of Hazardous Materials. 139 (3): 413–23. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.02.041. PMID 16600480.
- ^ Headlee, A. J. W. & Hunter, Richard G. (1953). «Elements in Coal Ash and Their Industrial Significance». Industrial and Engineering Chemistry. 45 (3): 548–551. doi:10.1021/ie50519a028.
- ^ a b c d Frenzel, Max; Ketris, Marina P.; Seifert, Thomas; Gutzmer, Jens (March 2016). «On the current and future availability of gallium». Resources Policy. 47: 38–50. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2015.11.005.
- ^ Frenzel, Max; Hirsch, Tamino; Gutzmer, Jens (2016). «Gallium, germanium, indium, and other trace and minor elements in sphalerite as a function of deposit type — A meta-analysis». Ore Geology Reviews. 76: 52–78. doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.12.017. ISSN 0169-1368.
- ^ a b Moskalyk, R. R. (2003). «Gallium: the backbone of the electronics industry». Minerals Engineering. 16 (10): 921–929. doi:10.1016/j.mineng.2003.08.003.
- ^ Frenzel, M; Tolosana-Delgado, R; Gutzmer, J (2015). «Assessing the supply potential of high-tech metals – A general method». Resources Policy. 46: 45–58. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2015.08.002.
- ^ Frenzel, Max; Mikolajczak, Claire; Reuter, Markus A.; Gutzmer, Jens (June 2017). «Quantifying the relative availability of high-tech by-product metals – The cases of gallium, germanium and indium». Resources Policy. 52: 327–335. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2017.04.008.
- ^ Gallium – In: USGS Mineral Commodity Summaries (PDF). United States Geological Survey. 2017. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-04-27.
- ^ a b c d e f Galium. USGS (2018)
- ^ Greber, J. F. (2012) «Gallium and Gallium Compounds» in Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, doi:10.1002/14356007.a12_163.
- ^ Coleman, James J.; Jagadish, Chennupati; Catrina Bryce, A. (2012-05-02). Advances in Semiconductor Lasers. pp. 150–151. ISBN 978-0-12-391066-0.
- ^ Crisp, D.; Pathare, A.; Ewell, R. C. (2004). «The performance of gallium arsenide/germanium solar cells at the Martian surface». Acta Astronautica. 54 (2): 83–101. Bibcode:2004AcAau..54…83C. doi:10.1016/S0094-5765(02)00287-4.
- ^ Alberts, V.; Titus J.; Birkmire R. W. (2003). «Material and device properties of single-phase Cu(In,Ga)(Se,S)2 alloys prepared by selenization/sulfurization of metallic alloys». Thin Solid Films. 451–452: 207–211. Bibcode:2004TSF…451..207A. doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2003.10.092.
- ^ Surmann, P; Zeyat, H (Nov 2005). «Voltammetric analysis using a self-renewable non-mercury electrode». Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry. 383 (6): 1009–13. doi:10.1007/s00216-005-0069-7. ISSN 1618-2642. PMID 16228199. S2CID 22732411.
- ^ Knight, Will (2005-05-05). «Hot chips chilled with liquid metal». Archived from the original on 2007-02-11. Retrieved 2008-11-20.
- ^ Martin, Yves. «High Performance Liquid Metal Thermal Interface for Large Volume Production» (PDF).
- ^ «Technology solidifies carbon dioxide — ASME». www.asme.org. Retrieved 2022-09-05.
- ^ «New way to turn carbon dioxide into coal could ‘rewind the emissions clock’«. www.science.org. Retrieved 2022-09-05.
- ^ United States. Office of Naval Research. Committee on the Basic Properties of Liquid Metals, U.S. Atomic Energy Commission (1954). Liquid-metals handbook. U.S. Govt. Print. Off. p. 128.
- ^ Sublette, Cary (2001-09-09). «Section 6.2.2.1». Nuclear Weapons FAQ. Retrieved 2008-01-24.
- ^ Besmann, Theodore M. (2005). «Thermochemical Behavior of Gallium in Weapons-Material-Derived Mixed-Oxide Light Water Reactor (LWR) Fuel». Journal of the American Ceramic Society. 81 (12): 3071–3076. doi:10.1111/j.1151-2916.1998.tb02740.x.
- ^ Chitambar, Christopher R. (2018). «Chapter 10. Gallium Complexes as Anticancer drugs». In Sigel, Astrid; Sigel, Helmut; Freisinger, Eva; Sigel, Roland K. O. (eds.). Metallo-Drugs: Development and Action of Anticancer Agents. Metal Ions in Life Sciences. Vol. 18. Berlin: de Gruyter GmbH. pp. 281–301. doi:10.1515/9783110470734-016. ISBN 9783110470734. PMID 29394029.
- ^ «gallium nitrate». Archived from the original on 2009-06-08. Retrieved 2009-07-07.
- ^ Bernstein, L. R.; Tanner, T.; Godfrey, C. & Noll, B. (2000). «Chemistry and Pharmacokinetics of Gallium Maltolate, a Compound With High Oral Gallium Bioavailability». Metal-Based Drugs. 7 (1): 33–47. doi:10.1155/MBD.2000.33. PMC 2365198. PMID 18475921.
- ^ «A Trojan-horse strategy selected to fight bacteria». INFOniac.com. 2007-03-16. Retrieved 2008-11-20.
- ^ Smith, Michael (2007-03-16). «Gallium May Have Antibiotic-Like Properties». MedPage Today. Retrieved 2008-11-20.
- ^ Goldberg D. E.; Sharma V.; Oksman A.; Gluzman I. Y.; Wellems T. E.; Piwnica-Worms D. (1997). «Probing the chloroquine resistance locus of Plasmodium falciparum with a novel class of multidentate metal(III) coordination complexes». J. Biol. Chem. 272 (10): 6567–72. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.10.6567. PMID 9045684. S2CID 3408513.
- ^ Biot, Christophe; Dive, Daniel (2010). «Bioorganometallic Chemistry and Malaria». Medicinal Organometallic Chemistry. Topics in Organometallic Chemistry. Vol. 32. p. 155. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-13185-1_7. ISBN 978-3-642-13184-4. S2CID 85940061.
- ^ a b Nordberg, Gunnar F.; Fowler, Bruce A.; Nordberg, Monica (7 August 2014). Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals (4th ed.). Academic Press. pp. 788–90. ISBN 978-0-12-397339-9.
- ^ Banerjee, Sangeeta Ray; Pomper, Martin G. (June 2013). «Clinical Applications of Gallium-68». Appl. Radiat. Isot. 76: 2–13. doi:10.1016/j.apradiso.2013.01.039. PMC 3664132. PMID 23522791.
- ^ «Russian American Gallium Experiment». 2001-10-19. Archived from the original on 2010-07-05. Retrieved 2009-06-24.
- ^ «Neutrino Detectors Experiments: GALLEX». 1999-06-26. Retrieved 2008-11-20.
- ^ «Nano lab produces world’s smallest book» Archived 2015-10-13 at the Wayback Machine. Simon Fraser University. 11 April 2007. Retrieved 31 January 2013.
- ^ US 5069803, Sugimura, Kentaro; Hasimoto, Shoji & Ono, Takayuki, «Use of a synthetic resin composition containing gallium particles in the glide surfacing material of skis and other applications», issued 1995
- ^ Kleiner, Kurt (3 May 2022). «Gallium: The liquid metal that could transform soft electronics». Knowable Magazine. doi:10.1146/knowable-050322-2. Retrieved 31 May 2022.
- ^ Tang, Shi-Yang; Tabor, Christopher; Kalantar-Zadeh, Kourosh; Dickey, Michael D. (26 July 2021). «Gallium Liquid Metal: The Devil’s Elixir». Annual Review of Materials Research. 51 (1): 381–408. Bibcode:2021AnRMS..51..381T. doi:10.1146/annurev-matsci-080819-125403. ISSN 1531-7331. S2CID 236566966. Retrieved 31 May 2022.
- ^ Amberchan, Gabriella; et al. (2022-02-14). «Aluminum Nanoparticles from a Ga–Al Composite for Water Splitting and Hydrogen Generation». ACS Applied Nano Materials. 5 (2): 2636–2643. doi:10.1021/acsanm.1c04331. ISSN 2574-0970.
- ^ Kean, Sam (2010). The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the Elements. Boston: Little, Brown and Company. ISBN 978-0-316-05164-4.
- ^ a b Orians, K. J.; Bruland, K. W. (April 1988). «Dissolved Gallium in the Open Ocean». Nature. 332 (21): 717–19. Bibcode:1988Natur.332..717O. doi:10.1038/332717a0. S2CID 4323435.
- ^ a b c McAlister, Jason A.; Orians, Kristin J. (20 December 2015). «Dissolved Gallium in the Beaufort Sea of the Western Arctic Ocean: A GEOTRACES cruise in the International Polar Year». Marine Chemistry. 177 (Part 1): 101–109. doi:10.1016/j.marchem.2015.05.007. Retrieved 29 August 2021 – via ScienceDirect.
- ^ a b c Shiller, A. M. (June 1998). «Dissolved Gallium in the Atlantic Ocean». Marine Chemistry. 61 (1): 87–99. doi:10.1016/S0304-4203(98)00009-7.
- ^ a b c Shiller, A. M.; Bairamadgi, G. R. (August 2006). «Dissolved Gallium in the northwest Pacific and the south and central Atlantic Oceans: Implications for aeolian Fe input and reconsideration of Profiles». Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems. 7 (8): n/a. Bibcode:2006GGG…..7.8M09S. doi:10.1029/2005GC001118. S2CID 129738391.
- ^ «Gallium 203319». Sigma Aldrich.
- ^ «MSDS – 203319». Sigma Aldrich.
- ^ Ivanoff, C. S.; Ivanoff, A. E.; Hottel, T. L. (February 2012). «Gallium poisoning: a rare case report». Food Chem. Toxicol. 50 (2): 212–5. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2011.10.041. PMID 22024274.
Bibliography[edit]
- Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
External links[edit]
- Gallium at The Periodic Table of Videos (University of Nottingham)
- Safety data sheet at acialloys.com
- High-resolution photographs of molten gallium, gallium crystals and gallium ingots under Creative Commons licence
- – textbook information regarding gallium
- Environmental effects of gallium
- [httpd://minerals.usgs.gov/minerals/pubs/commodity/gallium/460798.pdf Price development of gallium 1959–1998]
- Gallium: A Smart Metal United States Geological Survey
- Thermal conductivity
- Physical and thermodynamical properties of liquid gallium (doc pdf)
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gallium | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | (GAL-ee-əm) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | silvery blue | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight Ar°(Ga) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gallium in the periodic table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic number (Z) | 31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | group 13 (boron group) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Period | period 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Block | p-block | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrons per shell | 2, 8, 18, 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 302.9146 K (29.7646 °C, 85.5763 °F) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | 2673 K (2400 °C, 4352 °F)[2] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (near r.t.) | 5.91 g/cm3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| when liquid (at m.p.) | 6.095 g/cm3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | 5.59 kJ/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | 256 kJ/mol[2] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | 25.86 J/(mol·K) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vapor pressure
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | −5, −4, −3,[3] −2, −1, 0, +1, +2, +3[4] (an amphoteric oxide) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | Pauling scale: 1.81 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic radius | empirical: 135 pm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 122±3 pm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Van der Waals radius | 187 pm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Spectral lines of gallium | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural occurrence | primordial | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure | orthorhombic
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Speed of sound thin rod | 2740 m/s (at 20 °C) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal expansion | 18 µm/(m⋅K) (at 25 °C) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | 40.6 W/(m⋅K) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrical resistivity | 270 nΩ⋅m (at 20 °C) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic ordering | diamagnetic | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar magnetic susceptibility | −21.6×10−6 cm3/mol (at 290 K)[5] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Young’s modulus | 9.8 GPa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Poisson ratio | 0.47 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mohs hardness | 1.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brinell hardness | 56.8–68.7 MPa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 7440-55-3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Naming | after Gallia (Latin for: France), homeland of the discoverer | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prediction | Dmitri Mendeleev (1871) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery and first isolation | Lecoq de Boisbaudran (1875) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Main isotopes of gallium
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| references |
Gallium is a chemical element with the symbol Ga and atomic number 31. Discovered by French chemist Paul-Émile Lecoq de Boisbaudran in 1875,[6] Gallium is in group 13 of the periodic table and is similar to the other metals of the group (aluminium, indium, and thallium).
Elemental gallium is a soft, silvery metal in standard temperature and pressure. In its liquid state, it becomes silvery white. If too much force is applied, the gallium may fracture conchoidally. Since its discovery in 1875, gallium has widely been used to make alloys with low melting points. It is also used in semiconductors, as a dopant in semiconductor substrates.
The melting point of gallium is used as a temperature reference point. Gallium alloys are used in thermometers as a non-toxic and environmentally friendly alternative to mercury, and can withstand higher temperatures than mercury. An even lower melting point of −19 °C (−2 °F), well below the freezing point of water, is claimed for the alloy galinstan (62–95% gallium, 5–22% indium, and 0–16% tin by weight), but that may be the freezing point with the effect of supercooling.
Gallium does not occur as a free element in nature, but as gallium(III) compounds in trace amounts in zinc ores (such as sphalerite) and in bauxite. Elemental gallium is a liquid at temperatures greater than 29.76 °C (85.57 °F), and will melt in a person’s hands at normal human body temperature of 37.0 °C (98.6 °F).
Gallium is predominantly used in electronics. Gallium arsenide, the primary chemical compound of gallium in electronics, is used in microwave circuits, high-speed switching circuits, and infrared circuits. Semiconducting gallium nitride and indium gallium nitride produce blue and violet light-emitting diodes and diode lasers. Gallium is also used in the production of artificial gadolinium gallium garnet for jewelry. Gallium is considered a technology-critical element by the United States National Library of Medicine and Frontiers Media.[7][8]
Gallium has no known natural role in biology. Gallium(III) behaves in a similar manner to ferric salts in biological systems and has been used in some medical applications, including pharmaceuticals and radiopharmaceuticals.
Physical properties[edit]
Crystallization of gallium from the melt
Elemental gallium is not found in nature, but it is easily obtained by smelting. Very pure gallium is a silvery blue metal that fractures conchoidally like glass. Gallium liquid expands by 3.10% when it solidifies; therefore, it should not be stored in glass or metal containers because the container may rupture when the gallium changes state. Gallium shares the higher-density liquid state with a short list of other materials that includes water, silicon, germanium, bismuth, and plutonium.[9]
Gallium forms alloys with most metals. It readily diffuses into cracks or grain boundaries of some metals such as aluminium, aluminium–zinc alloys[10] and steel,[11] causing extreme loss of strength and ductility called liquid metal embrittlement.
The melting point of gallium, at 302.9146 K (29.7646 °C, 85.5763 °F), is just above room temperature, and is approximately the same as the average summer daytime temperatures in Earth’s mid-latitudes. This melting point (mp) is one of the formal temperature reference points in the International Temperature Scale of 1990 (ITS-90) established by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM).[12][13][14] The triple point of gallium, 302.9166 K (29.7666 °C, 85.5799 °F), is used by the US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in preference to the melting point.[15]
The melting point of gallium allows it to melt in the human hand, and then solidify if removed. The liquid metal has a strong tendency to supercool below its melting point/freezing point: Ga nanoparticles can be kept in the liquid state below 90 K.[16] Seeding with a crystal helps to initiate freezing. Gallium is one of the four non-radioactive metals (with caesium, rubidium, and mercury) that are known to be liquid at, or near, normal room temperature. Of the four, gallium is the only one that is neither highly reactive (as are rubidium and caesium) nor highly toxic (as is mercury) and can, therefore, be used in metal-in-glass high-temperature thermometers. It is also notable for having one of the largest liquid ranges for a metal, and for having (unlike mercury) a low vapor pressure at high temperatures. Gallium’s boiling point, 2673 K, is nearly nine times higher than its melting point on the absolute scale, the greatest ratio between melting point and boiling point of any element.[17] Unlike mercury, liquid gallium metal wets glass and skin, along with most other materials (with the exceptions of quartz, graphite, gallium(III) oxide[18] and PTFE),[19] making it mechanically more difficult to handle even though it is substantially less toxic and requires far fewer precautions than mercury. Gallium painted onto glass is a brilliant mirror.[19] For this reason as well as the metal contamination and freezing-expansion problems, samples of gallium metal are usually supplied in polyethylene packets within other containers.
| Property | a | b | c |
|---|---|---|---|
| α (~25 °C, μm/m) | 16 | 11 | 31 |
| ρ (29.7 °C, nΩ·m) | 543 | 174 | 81 |
| ρ (0 °C, nΩ·m) | 480 | 154 | 71.6 |
| ρ (77 K, nΩ·m) | 101 | 30.8 | 14.3 |
| ρ (4.2 K, pΩ·m) | 13.8 | 6.8 | 1.6 |
Gallium does not crystallize in any of the simple crystal structures. The stable phase under normal conditions is orthorhombic with 8 atoms in the conventional unit cell. Within a unit cell, each atom has only one nearest neighbor (at a distance of 244 pm). The remaining six unit cell neighbors are spaced 27, 30 and 39 pm farther away, and they are grouped in pairs with the same distance.[21] Many stable and metastable phases are found as function of temperature and pressure.[22]
The bonding between the two nearest neighbors is covalent; hence Ga2 dimers are seen as the fundamental building blocks of the crystal. This explains the low melting point relative to the neighbor elements, aluminium and indium. This structure is strikingly similar to that of iodine and may form because of interactions between the single 4p electrons of gallium atoms, further away from the nucleus than the 4s electrons and the [Ar]3d10 core. This phenomenon recurs with mercury with its «pseudo-noble-gas» [Xe]4f145d106s2 electron configuration, which is liquid at room temperature.[23] The 3d10 electrons do not shield the outer electrons very well from the nucleus and hence the first ionisation energy of gallium is greater than that of aluminium.[9] Ga2 dimers do not persist in the liquid state and liquid gallium exhibits a complex low-coordinated structure in which each gallium atom is surrounded by 10 others, rather than 11–12 neighbors typical of most liquid metals.[24][25]
The physical properties of gallium are highly anisotropic, i.e. have different values along the three major crystallographic axes a, b, and c (see table), producing a significant difference between the linear (α) and volume thermal expansion coefficients. The properties of gallium are strongly temperature-dependent, particularly near the melting point. For example, the coefficient of thermal expansion increases by several hundred percent upon melting.[20]
Isotopes[edit]
Gallium has 31 known isotopes, ranging in mass number from 56 to 86. Only two isotopes are stable and occur naturally, gallium-69 and gallium-71. Gallium-69 is more abundant: it makes up about 60.1% of natural gallium, while gallium-71 makes up the remaining 39.9%. All the other isotopes are radioactive, with gallium-67 being the longest-lived (half-life 3.261 days). Isotopes lighter than gallium-69 usually decay through beta plus decay (positron emission) or electron capture to isotopes of zinc, although the lightest few (mass numbers 56–59) decay through prompt proton emission. Isotopes heavier than gallium-71 decay through beta minus decay (electron emission), possibly with delayed neutron emission, to isotopes of germanium, while gallium-70 can decay through both beta minus decay and electron capture. Gallium-67 is unique among the light isotopes in having only electron capture as a decay mode, as its decay energy is not sufficient to allow positron emission.[26] Gallium-67 and gallium-68 (half-life 67.7 min) are both used in nuclear medicine.
Chemical properties[edit]
Gallium is found primarily in the +3 oxidation state. The +1 oxidation state is also found in some compounds, although it is less common than it is for gallium’s heavier congeners indium and thallium. For example, the very stable GaCl2 contains both gallium(I) and gallium(III) and can be formulated as GaIGaIIICl4; in contrast, the monochloride is unstable above 0 °C, disproportionating into elemental gallium and gallium(III) chloride. Compounds containing Ga–Ga bonds are true gallium(II) compounds, such as GaS (which can be formulated as Ga24+(S2−)2) and the dioxan complex Ga2Cl4(C4H8O2)2.[27]
Aqueous chemistry[edit]
Strong acids dissolve gallium, forming gallium(III) salts such as Ga(NO
3)
3 (gallium nitrate). Aqueous solutions of gallium(III) salts contain the hydrated gallium ion, [Ga(H
2O)
6]3+
.[28]: 1033 Gallium(III) hydroxide, Ga(OH)
3, may be precipitated from gallium(III) solutions by adding ammonia. Dehydrating Ga(OH)
3 at 100 °C produces gallium oxide hydroxide, GaO(OH).[29]: 140–141
Alkaline hydroxide solutions dissolve gallium, forming gallate salts (not to be confused with identically named gallic acid salts) containing the Ga(OH)−
4 anion.[30][28]: 1033 [31] Gallium hydroxide, which is amphoteric, also dissolves in alkali to form gallate salts.[29]: 141 Although earlier work suggested Ga(OH)3−
6 as another possible gallate anion,[32] it was not found in later work.[31]
Oxides and chalcogenides[edit]
Gallium reacts with the chalcogens only at relatively high temperatures. At room temperature, gallium metal is not reactive with air and water because it forms a passive, protective oxide layer. At higher temperatures, however, it reacts with atmospheric oxygen to form gallium(III) oxide, Ga
2O
3.[30] Reducing Ga
2O
3 with elemental gallium in vacuum at 500 °C to 700 °C yields the dark brown gallium(I) oxide, Ga
2O.[29]: 285 Ga
2O is a very strong reducing agent, capable of reducing H
2SO
4 to H
2S.[29]: 207 It disproportionates at 800 °C back to gallium and Ga
2O
3.[33]
Gallium(III) sulfide, Ga
2S
3, has 3 possible crystal modifications.[33]: 104 It can be made by the reaction of gallium with hydrogen sulfide (H
2S) at 950 °C.[29]: 162 Alternatively, Ga(OH)
3 can be used at 747 °C:[34]
- 2 Ga(OH)
3 + 3 H
2S → Ga
2S
3 + 6 H
2O
Reacting a mixture of alkali metal carbonates and Ga
2O
3 with H
2S leads to the formation of thiogallates containing the [Ga
2S
4]2−
anion. Strong acids decompose these salts, releasing H
2S in the process.[33]: 104–105 The mercury salt, HgGa
2S
4, can be used as a phosphor.[35]
Gallium also forms sulfides in lower oxidation states, such as gallium(II) sulfide and the green gallium(I) sulfide, the latter of which is produced from the former by heating to 1000 °C under a stream of nitrogen.[33]: 94
The other binary chalcogenides, Ga
2Se
3 and Ga
2Te
3, have the zincblende structure. They are all semiconductors but are easily hydrolysed and have limited utility.[33]: 104
Nitrides and pnictides[edit]


Gallium nitride (left) and gallium arsenide (right) wafers
Gallium reacts with ammonia at 1050 °C to form gallium nitride, GaN. Gallium also forms binary compounds with phosphorus, arsenic, and antimony: gallium phosphide (GaP), gallium arsenide (GaAs), and gallium antimonide (GaSb). These compounds have the same structure as ZnS, and have important semiconducting properties.[28]: 1034 GaP, GaAs, and GaSb can be synthesized by the direct reaction of gallium with elemental phosphorus, arsenic, or antimony.[33]: 99 They exhibit higher electrical conductivity than GaN.[33]: 101 GaP can also be synthesized by reacting Ga
2O with phosphorus at low temperatures.[36]
Gallium forms ternary nitrides; for example:[33]: 99
- Li
3Ga + N
2 → Li
3GaN
2
Similar compounds with phosphorus and arsenic are possible: Li
3GaP
2 and Li
3GaAs
2. These compounds are easily hydrolyzed by dilute acids and water.[33]: 101
Halides[edit]
Gallium(III) oxide reacts with fluorinating agents such as HF or F
2 to form gallium(III) fluoride, GaF
3. It is an ionic compound strongly insoluble in water. However, it dissolves in hydrofluoric acid, in which it forms an adduct with water, GaF
3·3H
2O. Attempting to dehydrate this adduct forms GaF
2OH·nH
2O. The adduct reacts with ammonia to form GaF
3·3NH
3, which can then be heated to form anhydrous GaF
3.[29]: 128–129
Gallium trichloride is formed by the reaction of gallium metal with chlorine gas.[30] Unlike the trifluoride, gallium(III) chloride exists as dimeric molecules, Ga
2Cl
6, with a melting point of 78 °C. Eqivalent compounds are formed with bromine and iodine, Ga
2Br
6 and Ga
2I
6.[29]: 133
Like the other group 13 trihalides, gallium(III) halides are Lewis acids, reacting as halide acceptors with alkali metal halides to form salts containing GaX−
4 anions, where X is a halogen. They also react with alkyl halides to form carbocations and GaX−
4.[29]: 136–137
When heated to a high temperature, gallium(III) halides react with elemental gallium to form the respective gallium(I) halides. For example, GaCl
3 reacts with Ga to form GaCl:
- 2 Ga + GaCl
3 ⇌ 3 GaCl (g)
At lower temperatures, the equilibrium shifts toward the left and GaCl disproportionates back to elemental gallium and GaCl
3. GaCl can also be produced by reacting Ga with HCl at 950 °C; the product can be condensed as a red solid.[28]: 1036
Gallium(I) compounds can be stabilized by forming adducts with Lewis acids. For example:
- GaCl + AlCl
3 → Ga+
[AlCl
4]−
The so-called «gallium(II) halides», GaX
2, are actually adducts of gallium(I) halides with the respective gallium(III) halides, having the structure Ga+
[GaX
4]−
. For example:[30][28]: 1036 [37]
- GaCl + GaCl
3 → Ga+
[GaCl
4]−
Hydrides[edit]
Like aluminium, gallium also forms a hydride, GaH
3, known as gallane, which may be produced by reacting lithium gallanate (LiGaH
4) with gallium(III) chloride at −30 °C:[28]: 1031
- 3 LiGaH
4 + GaCl
3 → 3 LiCl + 4 GaH
3
In the presence of dimethyl ether as solvent, GaH
3 polymerizes to (GaH
3)
n. If no solvent is used, the dimer Ga
2H
6 (digallane) is formed as a gas. Its structure is similar to diborane, having two hydrogen atoms bridging the two gallium centers,[28]: 1031 unlike α-AlH
3 in which aluminium has a coordination number of 6.[28]: 1008
Gallane is unstable above −10 °C, decomposing to elemental gallium and hydrogen.[38]
Organogallium compounds[edit]
Organogallium compounds are of similar reactivity to organoindium compounds, less reactive than organoaluminium compounds, but more reactive than organothallium compounds.[39] Alkylgalliums are monomeric. Lewis acidity decreases in the order Al > Ga > In and as a result organogallium compounds do not form bridged dimers as organoaluminium compounds do. Organogallium compounds are also less reactive than organoaluminium compounds. They do form stable peroxides.[40] These alkylgalliums are liquids at room temperature, having low melting points, and are quite mobile and flammable. Triphenylgallium is monomeric in solution, but its crystals form chain structures due to weak intermolecluar Ga···C interactions.[39]
Gallium trichloride is a common starting reagent for the formation of organogallium compounds, such as in carbogallation reactions.[41] Gallium trichloride reacts with lithium cyclopentadienide in diethyl ether to form the trigonal planar gallium cyclopentadienyl complex GaCp3. Gallium(I) forms complexes with arene ligands such as hexamethylbenzene. Because this ligand is quite bulky, the structure of the [Ga(η6-C6Me6)]+ is that of a half-sandwich. Less bulky ligands such as mesitylene allow two ligands to be attached to the central gallium atom in a bent sandwich structure. Benzene is even less bulky and allows the formation of dimers: an example is [Ga(η6-C6H6)2] [GaCl4]·3C6H6.[39]
History[edit]
Small gallium droplets fusing together
In 1871, the existence of gallium was first predicted by Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev, who named it «eka-aluminium» from its position in his periodic table. He also predicted several properties of eka-aluminium that correspond closely to the real properties of gallium, such as its density, melting point, oxide character, and bonding in chloride.[42]
-
Comparison between Mendeleev’s 1871 predictions and the known properties of gallium[43]
Property Mendeleev’s predictions Actual properties Atomic weight ~68 69.723 Density 5.9 g/cm3 5.904 g/cm3 Melting point Low 29.767 °C Formula of oxide M2O3 Ga2O3 Density of oxide 5.5 g/cm3 5.88 g/cm3 Nature of hydroxide amphoteric amphoteric
Mendeleev further predicted that eka-aluminium would be discovered by means of the spectroscope, and that metallic eka-aluminium would dissolve slowly in both acids and alkalis and would not react with air. He also predicted that M2O3 would dissolve in acids to give MX3 salts, that eka-aluminium salts would form basic salts, that eka-aluminium sulfate should form alums, and that anhydrous MCl3 should have a greater volatility than ZnCl2: all of these predictions turned out to be true.[43]
Gallium was discovered using spectroscopy by French chemist Paul Emile Lecoq de Boisbaudran in 1875 from its characteristic spectrum (two violet lines) in a sample of sphalerite.[44] Later that year, Lecoq obtained the free metal by electrolysis of the hydroxide in potassium hydroxide solution.[45]
He named the element «gallia», from Latin Gallia meaning Gaul, after his native land of France. It was later claimed that, in a multilingual pun of a kind favoured by men of science in the 19th century, he had also named gallium after himself: «Le coq» is French for «the rooster» and the Latin word for «rooster» is «gallus«. In an 1877 article, Lecoq denied this conjecture.[45]
Originally, de Boisbaudran determined the density of gallium as 4.7 g/cm3, the only property that failed to match Mendeleev’s predictions; Mendeleev then wrote to him and suggested that he should remeasure the density, and de Boisbaudran then obtained the correct value of 5.9 g/cm3, that Mendeleev had predicted exactly.[43]
From its discovery in 1875 until the era of semiconductors, the primary uses of gallium were high-temperature thermometrics and metal alloys with unusual properties of stability or ease of melting (some such being liquid at room temperature).
The development of gallium arsenide as a direct bandgap semiconductor in the 1960s ushered in the most important stage in the applications of gallium.[19] In 1978, the electronics industry used gallium to fabricate light emitting diodes, photovoltaics and semiconductors, while the metals business used it[46] to reduce the melting point of alloys.[47]
Occurrence[edit]
Gallium does not exist as a free element in the Earth’s crust, and the few high-content minerals, such as gallite (CuGaS2), are too rare to serve as a primary source.[48] The abundance in the Earth’s crust is approximately 16.9 ppm.[49] This is comparable to the crustal abundances of lead, cobalt, and niobium. Yet unlike these elements, gallium does not form its own ore deposits with concentrations of > 0.1 wt.% in ore. Rather it occurs at trace concentrations similar to the crustal value in zinc ores,[48][50] and at somewhat higher values (~ 50 ppm) in aluminium ores, from both of which it is extracted as a by-product. This lack of independent deposits is due to gallium’s geochemical behaviour, showing no strong enrichment in the processes relevant to the formation of most ore deposits.[48]
The United States Geological Survey (USGS) estimates that more than 1 million tons of gallium is contained in known reserves of bauxite and zinc ores.[51][52] Some coal flue dusts contain small quantities of gallium, typically less than 1% by weight.[53][54][55][56] However, these amounts are not extractable without mining of the host materials (see below). Thus, the availability of gallium is fundamentally determined by the rate at which bauxite, zinc ores (and coal) are extracted.
Production and availability[edit]

99.9999% (6N) gallium sealed in vacuum ampoule
Gallium is produced exclusively as a by-product during the processing of the ores of other metals. Its main source material is bauxite, the chief ore of aluminium, but minor amounts are also extracted from sulfidic zinc ores (sphalerite being the main host mineral).[57][58] In the past, certain coals were an important source.
During the processing of bauxite to alumina in the Bayer process, gallium accumulates in the sodium hydroxide liquor. From this it can be extracted by a variety of methods. The most recent is the use of ion-exchange resin.[57] Achievable extraction efficiencies critically depend on the original concentration in the feed bauxite. At a typical feed concentration of 50 ppm, about 15% of the contained gallium is extractable.[57] The remainder reports to the red mud and aluminium hydroxide streams. Gallium is removed from the ion-exchange resin in solution. Electrolysis then gives gallium metal. For semiconductor use, it is further purified with zone melting or single-crystal extraction from a melt (Czochralski process). Purities of 99.9999% are routinely achieved and commercially available.[59]

Its by-product status means that gallium production is constrained by the amount of bauxite, sulfidic zinc ores (and coal) extracted per year. Therefore, its availability needs to be discussed in terms of supply potential. The supply potential of a by-product is defined as that amount which is economically extractable from its host materials per year under current market conditions (i.e. technology and price).[60] Reserves and resources are not relevant for by-products, since they cannot be extracted independently from the main-products.[61] Recent estimates put the supply potential of gallium at a minimum of 2,100 t/yr from bauxite, 85 t/yr from sulfidic zinc ores, and potentially 590 t/yr from coal.[57] These figures are significantly greater than current production (375 t in 2016).[62] Thus, major future increases in the by-product production of gallium will be possible without significant increases in production costs or price. The average price for low-grade gallium was $120 per kilogram in 2016 and $135–140 per kilogram in 2017.[63]
In 2017, the world’s production of low-grade gallium was ca. 315 tons — an increase of 15% from 2016. China, Japan, South Korea, Russia, and Ukraine were the leading producers, while Germany ceased primary production of gallium in 2016. The yield of high-purity gallium was ca. 180 tons, mostly originating from China, Japan, Slovakia, UK and U.S. The 2017 world annual production capacity was estimated at 730 tons for low-grade and 320 tons for refined gallium.[63]
China produced ca. 250 tons of low-grade gallium in 2016 and ca. 300 tons in 2017. It also accounted for more than half of global LED production.[63]
Applications[edit]
Semiconductor applications dominate the commercial demand for gallium, accounting for 98% of the total. The next major application is for gadolinium gallium garnets.[64]
Semiconductors[edit]

Extremely high-purity (>99.9999%) gallium is commercially available to serve the semiconductor industry. Gallium arsenide (GaAs) and gallium nitride (GaN) used in electronic components represented about 98% of the gallium consumption in the United States in 2007. About 66% of semiconductor gallium is used in the U.S. in integrated circuits (mostly gallium arsenide), such as the manufacture of ultra-high-speed logic chips and MESFETs for low-noise microwave preamplifiers in cell phones. About 20% of this gallium is used in optoelectronics.[51]
Worldwide, gallium arsenide makes up 95% of the annual global gallium consumption.[59] It amounted to $7.5 billion in 2016, with 53% originating from cell phones, 27% from wireless communications, and the rest from automotive, consumer, fiber-optic, and military applications. The recent increase in GaAs consumption is mostly related to the emergence of 3G and 4G smartphones, which use 10 times more GaAs than older models.[63]
Gallium arsenide and gallium nitride can also be found in a variety of optoelectronic devices which had a market share of $15.3 billion in 2015 and $18.5 billion in 2016.[63] Aluminium gallium arsenide (AlGaAs) is used in high-power infrared laser diodes. The semiconductors gallium nitride and indium gallium nitride are used in blue and violet optoelectronic devices, mostly laser diodes and light-emitting diodes. For example, gallium nitride 405 nm diode lasers are used as a violet light source for higher-density Blu-ray Disc compact data disc drives.[65]
Other major application of gallium nitride are cable television transmission, commercial wireless infrastructure, power electronics, and satellites. The GaN radio frequency device market alone was estimated at $370 million in 2016 and $420 million in 2016.[63]
Multijunction photovoltaic cells, developed for satellite power applications, are made by molecular-beam epitaxy or metalorganic vapour-phase epitaxy of thin films of gallium arsenide, indium gallium phosphide, or indium gallium arsenide. The Mars Exploration Rovers and several satellites use triple-junction gallium arsenide on germanium cells.[66] Gallium is also a component in photovoltaic compounds (such as copper indium gallium selenium sulfide Cu(In,Ga)(Se,S)2) used in solar panels as a cost-efficient alternative to crystalline silicon.[67]
Galinstan and other alloys[edit]

Galinstan easily wetting a piece of ordinary glass

Gallium readily alloys with most metals, and is used as an ingredient in low-melting alloys. The nearly eutectic alloy of gallium, indium, and tin is a room temperature liquid used in medical thermometers. This alloy, with the trade-name Galinstan (with the «-stan» referring to the tin, stannum in Latin), has a low melting point of −19 °C (−2.2 °F).[68] It has been suggested that this family of alloys could also be used to cool computer chips in place of water, and is often used as a replacement for thermal paste in high-performance computing.[69][70] Gallium alloys have been evaluated as substitutes for mercury dental amalgams, but these materials have yet to see wide acceptance. Liquid alloys containing mostly gallium and indium have been found to precipitate gaseous CO2 into solid carbon and are being researched as potential methodologies for carbon capture and possibly carbon removal.[71][72]
Because gallium wets glass or porcelain, gallium can be used to create brilliant mirrors. When the wetting action of gallium-alloys is not desired (as in Galinstan glass thermometers), the glass must be protected with a transparent layer of gallium(III) oxide.[73]
The plutonium used in nuclear weapon pits is stabilized in the δ phase and made machinable by alloying with gallium.[74][75]
Biomedical applications[edit]
Although gallium has no natural function in biology, gallium ions interact with processes in the body in a manner similar to iron(III). Because these processes include inflammation, a marker for many disease states, several gallium salts are used (or are in development) as pharmaceuticals and radiopharmaceuticals in medicine. Interest in the anticancer properties of gallium emerged when it was discovered that 67Ga(III) citrate injected in tumor-bearing animals localized to sites of tumor. Clinical trials have shown gallium nitrate to have antineoplastic activity against non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma and urothelial cancers. A new generation of gallium-ligand complexes such as tris(8-quinolinolato)gallium(III) (KP46) and gallium maltolate has emerged.[76] Gallium nitrate (brand name Ganite) has been used as an intravenous pharmaceutical to treat hypercalcemia associated with tumor metastasis to bones. Gallium is thought to interfere with osteoclast function, and the therapy may be effective when other treatments have failed.[77] Gallium maltolate, an oral, highly absorbable form of gallium(III) ion, is an anti-proliferative to pathologically proliferating cells, particularly cancer cells and some bacteria that accept it in place of ferric iron (Fe3+). Researchers are conducting clinical and preclinical trials on this compound as a potential treatment for a number of cancers, infectious diseases, and inflammatory diseases.[78]
When gallium ions are mistakenly taken up in place of iron(III) by bacteria such as Pseudomonas, the ions interfere with respiration, and the bacteria die. This happens because iron is redox-active, allowing the transfer of electrons during respiration, while gallium is redox-inactive.[79][80]
A complex amine-phenol Ga(III) compound MR045 is selectively toxic to parasites resistant to chloroquine, a common drug against malaria. Both the Ga(III) complex and chloroquine act by inhibiting crystallization of hemozoin, a disposal product formed from the digestion of blood by the parasites.[81][82]
Radiogallium salts[edit]
Gallium-67 salts such as gallium citrate and gallium nitrate are used as radiopharmaceutical agents in the nuclear medicine imaging known as gallium scan. The radioactive isotope 67Ga is used, and the compound or salt of gallium is unimportant. The body handles Ga3+ in many ways as though it were Fe3+, and the ion is bound (and concentrates) in areas of inflammation, such as infection, and in areas of rapid cell division. This allows such sites to be imaged by nuclear scan techniques.[83]
Gallium-68, a positron emitter with a half-life of 68 min, is now used as a diagnostic radionuclide in PET-CT when linked to pharmaceutical preparations such as DOTATOC, a somatostatin analogue used for neuroendocrine tumors investigation, and DOTA-TATE, a newer one, used for neuroendocrine metastasis and lung neuroendocrine cancer, such as certain types of microcytoma. Gallium-68’s preparation as a pharmaceutical is chemical, and the radionuclide is extracted by elution from germanium-68, a synthetic radioisotope of germanium, in gallium-68 generators.[84]
Other uses[edit]
Neutrino detection: Gallium is used for neutrino detection. Possibly the largest amount of pure gallium ever collected in a single location is the Gallium-Germanium Neutrino Telescope used by the SAGE experiment at the Baksan Neutrino Observatory in Russia. This detector contains 55–57 tonnes (~9 cubic metres) of liquid gallium.[85] Another experiment was the GALLEX neutrino detector operated in the early 1990s in an Italian mountain tunnel. The detector contained 12.2 tons of watered gallium-71. Solar neutrinos caused a few atoms of 71Ga to become radioactive 71Ge, which were detected. This experiment showed that the solar neutrino flux is 40% less than theory predicted. This deficit was not explained until better solar neutrino detectors and theories were constructed (see SNO).[86]
Ion source: Gallium is also used as a liquid metal ion source for a focused ion beam. For example, a focused gallium-ion beam was used to create the world’s smallest book, Teeny Ted from Turnip Town.[87]
Lubricants: Gallium serves as an additive in glide wax for skis and other low-friction surface materials.[88]
Flexible electronics: Materials scientists speculate that the properties of gallium could make it suitable for the development of flexible and wearable devices.[89][90]
Hydrogen generation: Gallium disrupts the protective oxide layer on aluminium, allowing water to react with the aluminium in AlGa to produce hydrogen gas.[91]
Humor: A well-known practical joke among chemists is to fashion gallium spoons and use them to serve tea to unsuspecting guests, since gallium has a similar appearance to its lighter homolog aluminium. The spoons then melt in the hot tea.[92]
Gallium in the ocean[edit]
Advances in trace element testing have allowed scientists to discover traces of dissolved gallium in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans [93] In recent years, dissolved gallium concentrations have presented in the Beaufort Sea.[93][94] These reports reflect the possible profiles of the Pacific and Atlantic Ocean waters.[94] For the Pacific Oceans, typical dissolved gallium concentrations are between 4–6 pmol/kg at depths <~150 m. In comparison, for Atlantic waters 25–28 pmol/kg at depths >~350 m.[94]
Gallium has entered oceans mainly through aeolian input, but having gallium in our oceans can be used to resolve aluminium distribution in the oceans.[95] The reason for this is that gallium is geochemically similar to aluminium, just less reactive. Gallium also has a slightly larger surface water residence time than aluminium.[95] Gallium has a similar dissolved profile similar to that of aluminium, due to this gallium can be used as a tracer for aluminium.[95] Gallium can also be used as a tracer of aeolian inputs of iron.[96] Gallium is used as a tracer for iron in the northwest Pacific, south and central Atlantic Oceans.[96] For example, in the northwest Pacific, low gallium surface waters, in the subpolar region suggest that there is low dust input, which can subsequently explain the following high-nutrient, low-chlorophyll environmental behavior.[96]
Precautions[edit]
| Hazards | |
|---|---|
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |  |
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H290, H318 |
| Precautionary statements | P280, P305, P310, P338, P351[97] |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | [98]
1 0 0 |
Metallic gallium is not toxic. However, exposure to gallium halide complexes can result in acute toxicity.[99] The Ga3+ ion of soluble gallium salts tends to form the insoluble hydroxide when injected in large doses; precipitation of this hydroxide resulted in nephrotoxicity in animals. In lower doses, soluble gallium is tolerated well and does not accumulate as a poison, instead being excreted mostly through urine. Excretion of gallium occurs in two phases: the first phase has a biological half-life of 1 hour, while the second has a biological half-life of 25 hours.[83]
References[edit]
- ^ «Standard Atomic Weights: Gallium». CIAAW. 1987.
- ^ a b Zhang Y; Evans JRG; Zhang S (2011). «Corrected Values for Boiling Points and Enthalpies of Vaporization of Elements in Handbooks». J. Chem. Eng. Data. 56 (2): 328–337. doi:10.1021/je1011086.
- ^ Ga(−3) has been observed in LaGa, see Dürr, Ines; Bauer, Britta; Röhr, Caroline (2011). «Lanthan-Triel/Tetrel-ide La(Al,Ga)x(Si,Ge)1-x. Experimentelle und theoretische Studien zur Stabilität intermetallischer 1:1-Phasen» (PDF). Z. Naturforsch. (in German). 66b: 1107–1121.
- ^ Hofmann, Patrick (1997). Colture. Ein Programm zur interaktiven Visualisierung von Festkörperstrukturen sowie Synthese, Struktur und Eigenschaften von binären und ternären Alkali- und Erdalkalimetallgalliden (PDF) (Thesis) (in German). PhD Thesis, ETH Zurich. p. 72. doi:10.3929/ethz-a-001859893. hdl:20.500.11850/143357. ISBN 978-3728125972.
- ^ Weast, Robert (1984). CRC, Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. Boca Raton, Florida: Chemical Rubber Company Publishing. pp. E110. ISBN 0-8493-0464-4.
- ^ Scerri, Eric (2020). The Periodic Table: Its Story and Its Significance. Oxford University Press. p. 149. ISBN 978-0-19-091436-3.
- ^ Cobelo-García, A.; Filella, M.; Croot, P.; Frazzoli, C.; Du Laing, G.; Ospina-Alvarez, N.; Rauch, S.; Salaun, P.; Schäfer, J.; Zimmermann, S. (2015). «COST action TD1407: network on technology-critical elements (NOTICE)—from environmental processes to human health threats». Environmental Science and Pollution Research International. 22 (19): 15188–15194. doi:10.1007/s11356-015-5221-0. ISSN 0944-1344. PMC 4592495. PMID 26286804.
- ^ Romero-Freire, Ana; Santos-Echeandía, Juan; Neira, Patricia; Cobelo-García, Antonio (2019). «Less-Studied Technology-Critical Elements (Nb, Ta, Ga, In, Ge, Te) in the Marine Environment: Review on Their Concentrations in Water and Organisms». Frontiers in Marine Science. 6. doi:10.3389/fmars.2019.00532. ISSN 2296-7745.
- ^ a b Greenwood and Earnshaw, p. 222
- ^ Tsai, W. L; Hwu, Y.; Chen, C. H.; Chang, L. W.; Je, J. H.; Lin, H. M.; Margaritondo, G. (2003). «Grain boundary imaging, gallium diffusion and the fracture behavior of Al–Zn Alloy – An in situ study». Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B. 199: 457–463. Bibcode:2003NIMPB.199..457T. doi:10.1016/S0168-583X(02)01533-1.
- ^ Vigilante, G. N.; Trolano, E.; Mossey, C. (June 1999). «Liquid Metal Embrittlement of ASTM A723 Gun Steel by Indium and Gallium». Defense Technical Information Center. Retrieved 2009-07-07.
- ^ Preston–Thomas, H. (1990). «The International Temperature Scale of 1990 (ITS-90)» (PDF). Metrologia. 27 (1): 3–10. Bibcode:1990Metro..27….3P. doi:10.1088/0026-1394/27/1/002. S2CID 250785635. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2007-06-18.
- ^ «ITS-90 documents at Bureau International de Poids et Mesures».
- ^ Magnum, B. W.; Furukawa, G. T. (August 1990). «Guidelines for Realizing the International Temperature Scale of 1990 (ITS-90)» (PDF). National Institute of Standards and Technology. NIST TN 1265. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2003-07-04.
- ^ Strouse, Gregory F. (1999). «NIST realization of the gallium triple point». Proc. TEMPMEKO. 1999 (1): 147–152. Retrieved 2016-10-30.
- ^ Parravicini, G. B.; Stella, A.; Ghigna, P.; Spinolo, G.; Migliori, A.; d’Acapito, F.; Kofman, R. (2006). «Extreme undercooling (down to 90K) of liquid metal nanoparticles». Applied Physics Letters. 89 (3): 033123. Bibcode:2006ApPhL..89c3123P. doi:10.1063/1.2221395.
- ^ Greenwood and Earnshaw, p. 224
- ^ Chen, Ziyu; Lee, Jeong-Bong (2019). «Gallium Oxide Coated Flat Surface as Non-Wetting Surface for Actuation of Liquid Metal Droplets». 2019 IEEE 32nd International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS). pp. 1–4. doi:10.1109/memsys.2019.8870886. ISBN 978-1-7281-1610-5.
- ^ a b c Greenwood and Earnshaw, p. 221
- ^ a b Rosebury, Fred (1992). Handbook of Electron Tube and Vacuum Techniques. Springer. p. 26. ISBN 978-1-56396-121-2.
- ^ Bernascino, M.; et al. (1995). «Ab initio calculations of structural and electronic properties of gallium solid-state phases». Phys. Rev. B. 52 (14): 9988–9998. Bibcode:1995PhRvB..52.9988B. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.52.9988. PMID 9980044.
- ^ «Phase Diagrams of the Elements», David A. Young, UCRL-51902 «Prepared for the U.S. Energy Research & Development Administration under contract No. W-7405-Eng-48». (1975)
- ^ Greenwood and Earnshaw, p. 223
- ^ Yagafarov, O. F.; Katayama, Y.; Brazhkin, V. V.; Lyapin, A. G.; Saitoh, H. (November 7, 2012). «Energy dispersive x-ray diffraction and reverse Monte Carlo structural study of liquid gallium under pressure». Physical Review B. 86 (17): 174103. Bibcode:2012PhRvB..86q4103Y. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.86.174103 – via APS.
- ^ Drewitt, James W. E.; Turci, Francesco; Heinen, Benedict J.; Macleod, Simon G.; Qin, Fei; Kleppe, Annette K.; Lord, Oliver T. (April 9, 2020). «Structural Ordering in Liquid Gallium under Extreme Conditions». Physical Review Letters. 124 (14): 145501. Bibcode:2020PhRvL.124n5501D. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.124.145501. PMID 32338984. S2CID 216177238 – via DOI.org (Crossref).
- ^ Audi, Georges; Bersillon, Olivier; Blachot, Jean; Wapstra, Aaldert Hendrik (2003), «The NUBASE evaluation of nuclear and decay properties», Nuclear Physics A, 729: 3–128, Bibcode:2003NuPhA.729….3A, doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2003.11.001
- ^ Greenwood and Earnshaw, p. 240
- ^ a b c d e f g h Wiberg, Egon; Wiberg, Nils; Holleman, Arnold Frederick (2001). Inorganic chemistry. Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-12-352651-9.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Downs, Anthony John (1993). Chemistry of aluminium, gallium, indium, and thallium. Springer. ISBN 978-0-7514-0103-5.
- ^ a b c d Eagleson, Mary, ed. (1994). Concise encyclopedia chemistry. Walter de Gruyter. p. 438. ISBN 978-3-11-011451-5.
- ^ a b Sipos, P. L.; Megyes, T. N.; Berkesi, O. (2008). «The Structure of Gallium in Strongly Alkaline, Highly Concentrated Gallate Solutions—a Raman and 71
Ga
-NMR Spectroscopic Study». J Solution Chem. 37 (10): 1411–1418. doi:10.1007/s10953-008-9314-y. S2CID 95723025. - ^ Hampson, N. A. (1971). Harold Reginald Thirsk (ed.). Electrochemistry—Volume 3: Specialist periodical report. Great Britain: Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 71. ISBN 978-0-85186-027-5.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Greenwood, N. N. (1962). Harry Julius Emeléus; Alan G. Sharpe (eds.). Advances in inorganic chemistry and radiochemistry. Vol. 5. Academic Press. pp. 94–95. ISBN 978-0-12-023605-3.
- ^ Madelung, Otfried (2004). Semiconductors: data handbook (3rd ed.). Birkhäuser. pp. 276–277. ISBN 978-3-540-40488-0.
- ^ Krausbauer, L.; Nitsche, R.; Wild, P. (1965). «Mercury gallium sulfide, HgGa
2S
4, a new phosphor». Physica. 31 (1): 113–121. Bibcode:1965Phy….31..113K. doi:10.1016/0031-8914(65)90110-2. - ^ Michelle Davidson (2006). Inorganic Chemistry. Lotus Press. p. 90. ISBN 978-81-89093-39-6.
- ^ Arora, Amit (2005). Text Book Of Inorganic Chemistry. Discovery Publishing House. pp. 389–399. ISBN 978-81-8356-013-9.
- ^ Downs, Anthony J.; Pulham, Colin R. (1994). Sykes, A. G. (ed.). Advances in Inorganic Chemistry. Vol. 41. Academic Press. pp. 198–199. ISBN 978-0-12-023641-1.
- ^ a b c Greenwoood and Earnshaw, pp. 262–5
- ^ Uhl, W. and Halvagar, M. R.; et al. (2009). «Reducing Ga-H and Ga-C Bonds in Close Proximity to Oxidizing Peroxo Groups: Conflicting Properties in Single Molecules». Chemistry: A European Journal. 15 (42): 11298–11306. doi:10.1002/chem.200900746. PMID 19780106.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Amemiya, Ryo (2005). «GaCl3 in Organic Synthesis». European Journal of Organic Chemistry. 2005 (24): 5145–5150. doi:10.1002/ejoc.200500512.
- ^ Ball, Philip (2002). The Ingredients: A Guided Tour of the Elements. Oxford University Press. p. 105. ISBN 978-0-19-284100-1.
- ^ a b c Greenwood and Earnshaw, p. 217.
- ^ Lecoq de Boisbaudran, Paul Émile (1875). «Caractères chimiques et spectroscopiques d’un nouveau métal, le gallium, découvert dans une blende de la mine de Pierrefitte, vallée d’Argelès (Pyrénées)». Comptes Rendus Hebdomadaires des Séances de l’Académie des Sciences. 81: 493–495.
- ^ a b Weeks, Mary Elvira (1932). «The discovery of the elements. XIII. Some elements predicted by Mendeleeff». Journal of Chemical Education. 9 (9): 1605–1619. Bibcode:1932JChEd…9.1605W. doi:10.1021/ed009p1605.
- ^ Petkof, Benjamin (1978). «Gallium» (PDF). GPO. USGS Minerals Yearbook. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-06-02.
- ^ «An Overview of Gallium». AZoNetwork. 18 December 2001.
- ^ a b c Frenzel, Max (2016). «The distribution of gallium, germanium and indium in conventional and non-conventional resources – Implications for global availability (PDF Download Available)». ResearchGate. doi:10.13140/rg.2.2.20956.18564. Retrieved 2017-06-02.
- ^ Burton, J. D.; Culkin, F.; Riley, J. P. (2007). «The abundances of gallium and germanium in terrestrial materials». Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 16 (1): 151–180. Bibcode:1959GeCoA..16..151B. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(59)90052-3.
- ^ Frenzel, Max; Hirsch, Tamino; Gutzmer, Jens (July 2016). «Gallium, germanium, indium, and other trace and minor elements in sphalerite as a function of deposit type — A meta-analysis». Ore Geology Reviews. 76: 52–78. doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.12.017.
- ^ a b Kramer, Deborah A. «Mineral Commodity Summary 2006: Gallium» (PDF). United States Geological Survey. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2008-05-14. Retrieved 2008-11-20.
- ^ Kramer, Deborah A. «Mineral Yearbook 2006: Gallium» (PDF). United States Geological Survey. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2008-05-09. Retrieved 2008-11-20.
- ^ Xiao-quan, Shan; Wen, Wang & Bei, Wen (1992). «Determination of gallium in coal and coal fly ash by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry using slurry sampling and nickel chemical modification». Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry. 7 (5): 761. doi:10.1039/JA9920700761.
- ^ «Gallium in West Virginia Coals». West Virginia Geological and Economic Survey. 2002-03-02. Archived from the original on 11 March 2002.
- ^ Font, O; Querol, Xavier; Juan, Roberto; Casado, Raquel; Ruiz, Carmen R.; López-Soler, Ángel; Coca, Pilar; Peña, Francisco García (2007). «Recovery of gallium and vanadium from gasification fly ash». Journal of Hazardous Materials. 139 (3): 413–23. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.02.041. PMID 16600480.
- ^ Headlee, A. J. W. & Hunter, Richard G. (1953). «Elements in Coal Ash and Their Industrial Significance». Industrial and Engineering Chemistry. 45 (3): 548–551. doi:10.1021/ie50519a028.
- ^ a b c d Frenzel, Max; Ketris, Marina P.; Seifert, Thomas; Gutzmer, Jens (March 2016). «On the current and future availability of gallium». Resources Policy. 47: 38–50. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2015.11.005.
- ^ Frenzel, Max; Hirsch, Tamino; Gutzmer, Jens (2016). «Gallium, germanium, indium, and other trace and minor elements in sphalerite as a function of deposit type — A meta-analysis». Ore Geology Reviews. 76: 52–78. doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.12.017. ISSN 0169-1368.
- ^ a b Moskalyk, R. R. (2003). «Gallium: the backbone of the electronics industry». Minerals Engineering. 16 (10): 921–929. doi:10.1016/j.mineng.2003.08.003.
- ^ Frenzel, M; Tolosana-Delgado, R; Gutzmer, J (2015). «Assessing the supply potential of high-tech metals – A general method». Resources Policy. 46: 45–58. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2015.08.002.
- ^ Frenzel, Max; Mikolajczak, Claire; Reuter, Markus A.; Gutzmer, Jens (June 2017). «Quantifying the relative availability of high-tech by-product metals – The cases of gallium, germanium and indium». Resources Policy. 52: 327–335. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2017.04.008.
- ^ Gallium – In: USGS Mineral Commodity Summaries (PDF). United States Geological Survey. 2017. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-04-27.
- ^ a b c d e f Galium. USGS (2018)
- ^ Greber, J. F. (2012) «Gallium and Gallium Compounds» in Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, doi:10.1002/14356007.a12_163.
- ^ Coleman, James J.; Jagadish, Chennupati; Catrina Bryce, A. (2012-05-02). Advances in Semiconductor Lasers. pp. 150–151. ISBN 978-0-12-391066-0.
- ^ Crisp, D.; Pathare, A.; Ewell, R. C. (2004). «The performance of gallium arsenide/germanium solar cells at the Martian surface». Acta Astronautica. 54 (2): 83–101. Bibcode:2004AcAau..54…83C. doi:10.1016/S0094-5765(02)00287-4.
- ^ Alberts, V.; Titus J.; Birkmire R. W. (2003). «Material and device properties of single-phase Cu(In,Ga)(Se,S)2 alloys prepared by selenization/sulfurization of metallic alloys». Thin Solid Films. 451–452: 207–211. Bibcode:2004TSF…451..207A. doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2003.10.092.
- ^ Surmann, P; Zeyat, H (Nov 2005). «Voltammetric analysis using a self-renewable non-mercury electrode». Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry. 383 (6): 1009–13. doi:10.1007/s00216-005-0069-7. ISSN 1618-2642. PMID 16228199. S2CID 22732411.
- ^ Knight, Will (2005-05-05). «Hot chips chilled with liquid metal». Archived from the original on 2007-02-11. Retrieved 2008-11-20.
- ^ Martin, Yves. «High Performance Liquid Metal Thermal Interface for Large Volume Production» (PDF).
- ^ «Technology solidifies carbon dioxide — ASME». www.asme.org. Retrieved 2022-09-05.
- ^ «New way to turn carbon dioxide into coal could ‘rewind the emissions clock’«. www.science.org. Retrieved 2022-09-05.
- ^ United States. Office of Naval Research. Committee on the Basic Properties of Liquid Metals, U.S. Atomic Energy Commission (1954). Liquid-metals handbook. U.S. Govt. Print. Off. p. 128.
- ^ Sublette, Cary (2001-09-09). «Section 6.2.2.1». Nuclear Weapons FAQ. Retrieved 2008-01-24.
- ^ Besmann, Theodore M. (2005). «Thermochemical Behavior of Gallium in Weapons-Material-Derived Mixed-Oxide Light Water Reactor (LWR) Fuel». Journal of the American Ceramic Society. 81 (12): 3071–3076. doi:10.1111/j.1151-2916.1998.tb02740.x.
- ^ Chitambar, Christopher R. (2018). «Chapter 10. Gallium Complexes as Anticancer drugs». In Sigel, Astrid; Sigel, Helmut; Freisinger, Eva; Sigel, Roland K. O. (eds.). Metallo-Drugs: Development and Action of Anticancer Agents. Metal Ions in Life Sciences. Vol. 18. Berlin: de Gruyter GmbH. pp. 281–301. doi:10.1515/9783110470734-016. ISBN 9783110470734. PMID 29394029.
- ^ «gallium nitrate». Archived from the original on 2009-06-08. Retrieved 2009-07-07.
- ^ Bernstein, L. R.; Tanner, T.; Godfrey, C. & Noll, B. (2000). «Chemistry and Pharmacokinetics of Gallium Maltolate, a Compound With High Oral Gallium Bioavailability». Metal-Based Drugs. 7 (1): 33–47. doi:10.1155/MBD.2000.33. PMC 2365198. PMID 18475921.
- ^ «A Trojan-horse strategy selected to fight bacteria». INFOniac.com. 2007-03-16. Retrieved 2008-11-20.
- ^ Smith, Michael (2007-03-16). «Gallium May Have Antibiotic-Like Properties». MedPage Today. Retrieved 2008-11-20.
- ^ Goldberg D. E.; Sharma V.; Oksman A.; Gluzman I. Y.; Wellems T. E.; Piwnica-Worms D. (1997). «Probing the chloroquine resistance locus of Plasmodium falciparum with a novel class of multidentate metal(III) coordination complexes». J. Biol. Chem. 272 (10): 6567–72. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.10.6567. PMID 9045684. S2CID 3408513.
- ^ Biot, Christophe; Dive, Daniel (2010). «Bioorganometallic Chemistry and Malaria». Medicinal Organometallic Chemistry. Topics in Organometallic Chemistry. Vol. 32. p. 155. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-13185-1_7. ISBN 978-3-642-13184-4. S2CID 85940061.
- ^ a b Nordberg, Gunnar F.; Fowler, Bruce A.; Nordberg, Monica (7 August 2014). Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals (4th ed.). Academic Press. pp. 788–90. ISBN 978-0-12-397339-9.
- ^ Banerjee, Sangeeta Ray; Pomper, Martin G. (June 2013). «Clinical Applications of Gallium-68». Appl. Radiat. Isot. 76: 2–13. doi:10.1016/j.apradiso.2013.01.039. PMC 3664132. PMID 23522791.
- ^ «Russian American Gallium Experiment». 2001-10-19. Archived from the original on 2010-07-05. Retrieved 2009-06-24.
- ^ «Neutrino Detectors Experiments: GALLEX». 1999-06-26. Retrieved 2008-11-20.
- ^ «Nano lab produces world’s smallest book» Archived 2015-10-13 at the Wayback Machine. Simon Fraser University. 11 April 2007. Retrieved 31 January 2013.
- ^ US 5069803, Sugimura, Kentaro; Hasimoto, Shoji & Ono, Takayuki, «Use of a synthetic resin composition containing gallium particles in the glide surfacing material of skis and other applications», issued 1995
- ^ Kleiner, Kurt (3 May 2022). «Gallium: The liquid metal that could transform soft electronics». Knowable Magazine. doi:10.1146/knowable-050322-2. Retrieved 31 May 2022.
- ^ Tang, Shi-Yang; Tabor, Christopher; Kalantar-Zadeh, Kourosh; Dickey, Michael D. (26 July 2021). «Gallium Liquid Metal: The Devil’s Elixir». Annual Review of Materials Research. 51 (1): 381–408. Bibcode:2021AnRMS..51..381T. doi:10.1146/annurev-matsci-080819-125403. ISSN 1531-7331. S2CID 236566966. Retrieved 31 May 2022.
- ^ Amberchan, Gabriella; et al. (2022-02-14). «Aluminum Nanoparticles from a Ga–Al Composite for Water Splitting and Hydrogen Generation». ACS Applied Nano Materials. 5 (2): 2636–2643. doi:10.1021/acsanm.1c04331. ISSN 2574-0970.
- ^ Kean, Sam (2010). The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the Elements. Boston: Little, Brown and Company. ISBN 978-0-316-05164-4.
- ^ a b Orians, K. J.; Bruland, K. W. (April 1988). «Dissolved Gallium in the Open Ocean». Nature. 332 (21): 717–19. Bibcode:1988Natur.332..717O. doi:10.1038/332717a0. S2CID 4323435.
- ^ a b c McAlister, Jason A.; Orians, Kristin J. (20 December 2015). «Dissolved Gallium in the Beaufort Sea of the Western Arctic Ocean: A GEOTRACES cruise in the International Polar Year». Marine Chemistry. 177 (Part 1): 101–109. doi:10.1016/j.marchem.2015.05.007. Retrieved 29 August 2021 – via ScienceDirect.
- ^ a b c Shiller, A. M. (June 1998). «Dissolved Gallium in the Atlantic Ocean». Marine Chemistry. 61 (1): 87–99. doi:10.1016/S0304-4203(98)00009-7.
- ^ a b c Shiller, A. M.; Bairamadgi, G. R. (August 2006). «Dissolved Gallium in the northwest Pacific and the south and central Atlantic Oceans: Implications for aeolian Fe input and reconsideration of Profiles». Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems. 7 (8): n/a. Bibcode:2006GGG…..7.8M09S. doi:10.1029/2005GC001118. S2CID 129738391.
- ^ «Gallium 203319». Sigma Aldrich.
- ^ «MSDS – 203319». Sigma Aldrich.
- ^ Ivanoff, C. S.; Ivanoff, A. E.; Hottel, T. L. (February 2012). «Gallium poisoning: a rare case report». Food Chem. Toxicol. 50 (2): 212–5. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2011.10.041. PMID 22024274.
Bibliography[edit]
- Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
External links[edit]
- Gallium at The Periodic Table of Videos (University of Nottingham)
- Safety data sheet at acialloys.com
- High-resolution photographs of molten gallium, gallium crystals and gallium ingots under Creative Commons licence
- – textbook information regarding gallium
- Environmental effects of gallium
- [httpd://minerals.usgs.gov/minerals/pubs/commodity/gallium/460798.pdf Price development of gallium 1959–1998]
- Gallium: A Smart Metal United States Geological Survey
- Thermal conductivity
- Physical and thermodynamical properties of liquid gallium (doc pdf)
Галлий в таблице менделеева занимает 31 место, в 4 периоде.
| Символ | Ga |
| Номер | 31 |
| Атомный вес | 69.7230000 |
| Латинское название | Gallium |
| Русское название | Галлий |
Как самостоятельно построить электронную конфигурацию? Ответ здесь
Электронная схема галлия
Ga: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p1
Короткая запись:
Ga: [Ar]4s2 3d10 4p1
Одинаковую электронную конфигурацию имеют
атом галлия и
Ge+1, As+2, Br+4
Порядок заполнения оболочек атома галлия (Ga) электронами:
1s → 2s → 2p → 3s → 3p → 4s → 3d → 4p → 5s → 4d →
5p → 6s → 4f → 5d → 6p → 7s → 5f → 6d → 7p.
На подуровне ‘s’ может находиться до 2 электронов, на ‘s’ — до 6, на
‘d’ — до 10 и на ‘f’ до 14
Галлий имеет 31 электрон,
заполним электронные оболочки в описанном выше порядке:
2 электрона на 1s-подуровне
2 электрона на 2s-подуровне
6 электронов на 2p-подуровне
2 электрона на 3s-подуровне
6 электронов на 3p-подуровне
2 электрона на 4s-подуровне
10 электронов на 3d-подуровне
1 электрон на 4p-подуровне
Степень окисления галлия
Атомы галлия в соединениях имеют степени окисления 3, 2, 1.
Степень окисления — это условный заряд атома в соединении: связь в молекуле
между атомами основана на разделении электронов, таким образом, если у атома виртуально увеличивается
заряд, то степень окисления отрицательная (электроны несут отрицательный заряд), если заряд уменьшается,
то степень окисления положительная.
Ионы галлия
Валентность Ga
Атомы галлия в соединениях проявляют валентность III, II, I.
Валентность галлия характеризует способность атома Ga к образованию хмических связей.
Валентность следует из строения электронной оболочки атома, электроны, участвующие в образовании
химических соединений называются валентными электронами. Более обширное определение валентности это:
Число химических связей, которыми данный атом соединён с другими атомами
Валентность не имеет знака.
Квантовые числа Ga
Квантовые числа определяются последним электроном в конфигурации,
для атома Ga эти числа имеют значение N = 4, L = 1, Ml = -1, Ms = +½
Видео заполнения электронной конфигурации (gif):
Результат:

Энергия ионизации
Чем ближе электрон к центру атома — тем больше энергии необходимо, что бы его оторвать.
Энергия, затрачиваемая на отрыв электрона от атома называется энергией ионизации и обозначается Eo.
Если не указано иное, то энергия ионизации — это энергия отрыва первого электрона, также существуют энергии
ионизации для каждого последующего электрона.
Энергия ионизации Ga:
Eo = 579 кДж/моль
— Что такое ион читайте в статье.
Перейти к другим элементам таблицы менделеева
Где Ga в таблице менделеева?
Таблица Менделеева
Скачать таблицу менделеева в хорошем качестве
| |||
| Внешний вид простого вещества | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||
| Свойства атома | |||
| Имя, символ, номер | Галлий / Gallium (Ga), 31 | ||
| Атомная масса (молярная масса) | 69,723 а. е. м. (г/моль) | ||
| Электронная конфигурация | [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p1 | ||
| Радиус атома | 141 пм | ||
| Химические свойства | |||
| Ковалентный радиус | 126 пм | ||
| Радиус иона | (+3e) 62 (+1e) 81 пм | ||
| Электроотрицательность | 1,81 (шкала Полинга) | ||
| Электродный потенциал | 0 | ||
| Степени окисления | 3 | ||
| Энергия ионизации (первый электрон) | 578,7 (6,00) кДж/моль (эВ) | ||
| Термодинамические свойства простого вещества | |||
| Плотность (при н. у.) | 5,91 г/см³ | ||
| Температура плавления | 302,93 К (29,8 °C) | ||
| Температура кипения | 2 477 K | ||
| Теплота плавления | 5,59 кДж/моль | ||
| Теплота испарения | 270,3 кДж/моль | ||
| Молярная теплоёмкость | 26,07[1] Дж/(K·моль) | ||
| Молярный объём | 11,8 см³/моль | ||
| Кристаллическая решётка простого вещества | |||
| Структура решётки | орторомбическая | ||
| Параметры решётки | a=4,519 b=7,658 c=4,526 Å | ||
| Температура Дебая | 240 K | ||
| Прочие характеристики | |||
| Теплопроводность | (300 K) 28,1 Вт/(м·К) |
Га́ллий — элемент главной подгруппы третьей группы четвёртого периода периодической системы химических элементов Д. И. Менделеева, с атомным номером 31. Обозначается символом Ga (лат. Gallium). Относится к группе лёгких металлов. Простое вещество галлий (CAS-номер: 7440-55-3) — мягкий пластичный металл серебристо-белого (по другим данным светло-серого) цвета с синеватым оттенком.
Содержание
- 1 История
- 2 Происхождение названия
- 3 Нахождение в природе
- 3.1 Месторождения
- 4 Получение
- 5 Физические свойства
- 6 Химические свойства
- 7 Основные соединения
- 8 Применение
- 9 Биологическая роль и особенности обращения
- 10 Примечания
- 11 Литература
- 12 Ссылки
История
Существование галлия было научно предсказано Д. И. Менделеевым. При создании периодической системы химических элементов в 1869 г. он, основываясь на открытом им Периодическом законе, оставил вакантные места в третьей группе для неизвестных элементов — аналогов алюминия и кремния (экаалюминий и экасилиций). Менделеев, основываясь на свойствах соседних, хорошо изученных элементов, достаточно точно описал не только важнейшие физические и химические свойства, но и метод открытия — спектроскопия. В частности, в статье в «Журнале Русского химического общества» в 1871 г. Менделеев указал, что атомный вес экаалюминия близок к 68, удельный вес около 6 г/см3. В металлическом состоянии металл будет легкоплавок.
Вскоре галлий был открыт, выделен в виде простого вещества и изучен французским химиком Полем Эмилем Лекоком де Буабодраном. В 1875 году Лекок де Буабодран исследовал спектр цинковой обманки, привезенной из Пьеррфита (Пиренеи). В этом спектре им была обнаружена новая фиолетовая линия, свидетельствующая о присутствии в минерале неизвестного элемента. Выделение элемента было сопряжено с немалыми трудностями, поскольку содержание нового элемента в руде было меньше 0,1 %. В итоге Лекоку де Буабодрану удалось получить новый элемент в количестве менее 0,1 г и исследовать его. По свойствам новый элемент оказался сходен с цинком.
20 сентября 1875 г. на заседании Парижской академии наук было зачитано письмо Лекока де Буабодрана об открытии нового элемента и изучении его свойств. Бурный восторг вызвало сообщение о названии элемента в честь Франции. Менделеев, узнав об открытии из опубликованного доклада, обнаружил, что описание нового элемента почти в точности совпадает с описанием предсказанного им ранее экаалюминия. Об этом он отправил письмо Лекоку де Буабодрану, указав, что плотность нового металла определена неверно и должна быть 5,9-6,0 , а не 4,7 г/см3. Тщательная проверка показала правоту Менделеева, а сам Лекок де Буабодран писал по этому поводу:
Я думаю…, нет необходимости указывать на исключительное значение, которое имеет плотность нового элемента в отношении подтверждения теоретических взглядов Менделеева
— Цит. по [2]
Открытие галлия и последовавшие вскоре открытия германия и скандия укрепило позиции Периодического закона, ярко продемонстировав его прогностический потенциал. Менделеев называл Лекока де Буабодрана одним из «укрепителей периодического закона».
Происхождение названия
Поль Эмиль Лекок де Буабодран назвал элемент в честь своей родины Франции, по её латинскому названию — Галлия (Gallia).
Существует недокументированная легенда, что в названии элемента его первооткрыватель неявно увековечил и свою фамилию (Lecoq). Латинское название элемента (Gallium) созвучно gallus — «петух» (лат.). Примечательно, что именно петух le coq (франц.) является символом Франции.
Нахождение в природе
Среднее содержание галлия в земной коре 19 г/т. Галлий типичный рассеянный элемент, обладающий двойной геохимической природой. Ввиду близости его кристаллохимических свойств с главными породообразующими элементами (Al, Fe и др.) и широкой возможности изоморфизма с ними, галлий не образует больших скоплений, несмотря на значительную величину кларка. Выделяются следующие минералы с повышенным содержанием галлия: сфалерит (0 — 0,1 %), магнетит (0 — 0,003 %), касситерит (0 — 0,005 %), гранат (0 — 0,003 %), берилл (0 — 0,003 %), турмалин (0 — 0,01 %), сподумен (0,001 — 0,07 %), флогопит (0,001 — 0,005 %), биотит (0 — 0,1 %), мусковит (0 — 0,01 %), серицит (0 — 0,005 %), лепидолит (0,001 — 0,03 %), хлорит (0 — 0,001 %), полевые шпаты (0 — 0,01 %), нефелин (0 — 0,1 %), гекманит (0,01 — 0,07 %), натролит (0 — 0,1 %). Концентрация галлия в морской воде 3·10−5 мг/л[3].
Месторождения
Месторождения галлия известны в Юго-Западной Африке, России, странах СНГ[4].
Получение
Наиболее мощным потенциальным источником получения галлия служат растворы глинозёмного производства при переработке боксита и нефелина. Концентрация галлия в щелочном алюминатном растворе после разложения в процессе Байера: 100—150 мг/л, по способу спекания: 50—65 мг/л. По этим способам галлий отделяют от большей части алюминия карбонизацией, концентрируя в последней фракции осадка. Затем обогащённый осадок обрабатывают известью, галлий переходит в раствор, откуда черновой металл выделяется электролизом. Галлий можно получить с помощью переработки полиметаллических руд, угля. Загрязнённый галлий промывают водой, после этого фильтруют через пористые пластины и нагревают в вакууме для того, чтобы удалить летучие примеси. Для получения галлия высокой чистоты используют химический (реакции между солями), электрохимический (электролиз растворов) и физический (разложение) методы.
Физические свойства
Кристаллический галлий имеет несколько полиморфных модификаций, однако термодинамически устойчивой является только одна (I), имеющая орторомбическую (псевдотетрагональную) решётку с параметрами а = 4,5186 Å, b = 7,6570 Å, c = 4,5256 Å[1]. Другие модификации галлия (β, γ, δ, ε) кристаллизуются из переохлаждённого диспергированного металла и являются нестабильными. При повышенном давлении наблюдались ещё две полиморфные структуры галлия II и III, имеющие, соответственно, кубическую и тетрагональную решётки[1].
Плотность галлия в твёрдом состоянии при температуре T=20 °C равна 5,904 г/см³, жидкий галлий при T=29,8 °C имеет плотность 6,095 г/см³, то есть при затвердевании объём галлия увеличивается. Температура плавления галлия немного выше комнатной и равна Tпл.=29,8 °C, кипит галлий при Tкип.=2230 °C.
Одной из особенностей галлия является широкий температурный интервал существования жидкого состояния (от 30 и до 2230 °C), при этом он имеет низкое давление пара при температурах до 1100—1200 °C. Удельная теплоёмкость твёрдого галлия в температурном интервале T=0—24 °C равна 376,7 Дж/кг·К (0,09 кал/г·град.), в жидком состоянии при T=29—100 °C — 410 Дж/кг·К (0,098 кал/г·град).
Удельное электрическое сопротивление в твёрдом и жидком состоянии равны, соответственно, 53,4·10−6 ом·см (при T=0 °C) и 27,2·10−6 ом·см (при T=30 °C). Вязкость жидкого галлия при разных температурах равна 1,612 пуаз при T=98 °C и 0,578 пуаз при T=1100 °C. Поверхностное натяжение, измеренное при 30 °C в атмосфере водорода равно 0,735 н/м. Коэффициенты отражения для длин волн 4360 Å и 5890 Å составляют 75,6 % и 71,3 %, соответственно.
Природный галлий состоит из двух изотопов 69Ga (61,2 %) и 71Ga (38,8 %). Поперечное сечение захвата тепловых нейтронов равно для них 2,1·10−28 м² и 5,1·10−28 м², соответственно[1].
Химические свойства
Химические свойства галлия близки к свойствам алюминия. Оксидная плёнка, образующаяся на поверхности металла на воздухе, предохраняет галлий от дальнейшего окисления.
Галлий реагирует с горячей водой:
При реакции с перегретым паром (350 °C) образуется соединение GaOOH (гидрат оксида галлия или метагаллиевая кислота):
Галлий взаимодействует с минеральными кислотами с выделением водорода и образованием солей:
Продуктами реакции с щелочами и карбонатами калия и натрия являются гидроксогаллаты, содержащие ионы Ga(OH)4− и Ga(OH)63− :
Галлий реагирует с галогенами: реакция с хлором и фтором идёт при комнатной температуре, с бромом — уже при −35 °C (около 20 °C — с воспламенением), взаимодействие с иодом начинается при нагревании.
Галлий не взаимодействует с водородом, углеродом, азотом, кремнием и бором.
При высоких температурах галлий способен разрушать различные материалы и его действие сильнее расплава любого другого металла. Так, графит и вольфрам устойчивы к действию расплава галлия до 800 °C, алунд и оксид бериллия BeO — до 1000 °C, тантал, молибден и ниобий устойчивы до 400÷450 °C.
С большинством металлов галлий образует галлиды, исключением являются висмут, а также металлы подгрупп цинка, скандия, титана. Один из галлидов V3Ga имеет довольно высокую температуру перехода в сверхпроводящее состояние 16,8 K.
Галлий образует гидридогаллаты:
Устойчивость ионов падает в ряду BH4− → AlH4− → GaH4−. Ион BH4− устойчив в водном растворе, AlH4− и GaH4− быстро гидролизуются:
При растворении Ga(OH)3 и Ga2O3 в кислотах образуются аквакомплексы [Ga(H2O)6]3+, поэтому из водных растворов соли галлия выделяются в виде кристаллогидратов, например, хлорид галлия GaCl3*6H2O, галлийкалиевые квасцы KGa(SO4)2*12H2O. Аквакомплексы галлия в растворах бесцветны.
Основные соединения
- Ga2H6 — летучая жидкость, tпл −21,4 °C, tкип 139 °C. В эфирной суспензии с гидридом лития или таллия образует соединения LiGaH4 и TlGaH4. Образуется в результате обработки тетраметилдигаллана триэтиламином. Имеются банановые связи, как и в диборане
- Ga2O3 — белый или жёлтый порошок, tпл 1795 °C. Существует в виде двух модификаций. α-Ga2О3 — бесцветные тригональные кристаллы с плотностью 6,48 г/см³, малорастворимые в воде, растворимые в кислотах. β-Ga2О3 — бесцветные моноклинные кристаллы c плотностью 5,88 г/см³, малорастворимые в воде, кислотах и щёлочах. Получают нагреванием металлического галлия на воздухе при 260 °C или в атмосфере кислорода, или прокаливанием нитрата или сульфата галлия. ΔH°298(обр) −1089,10 кДж/моль; ΔG°298(обр) −998,24 кДж/моль; S°298 84,98 Дж/моль·K. Проявляют амфотерные свойства, хотя основные свойства, по сравнению с алюминием, усилены:
- Ga(OH)3 — выпадает в виде желеобразного осадка при обработке растворов солей трёхвалентного галлия гидроксидами и карбонатами щелочных металлов (pH 9,7). Растворяется в концентрированном аммиаке и концентрированном растворе карбоната аммония, при кипячении осаждается. Нагреванием гидроксид галлия можно перевести в GaOOH, затем в Ga2O3*H2O, и, наконец, в Ga2O3. Можно получить гидролизом солей трёхвалентного галлия.
- GaF3 — белый порошок. tпл >950 °C, tкип 1000 °C , плотность — 4,47 г/см³. Малорастворим в воде. Известен кристаллогидрат GaF3·3Н2O. Получают нагреванием оксида галлия в атмосфере фтора.
- GaCl3 — бесцветные гигроскопичные кристаллы. tпл 78 °C, tкип 215 °C, плотность — 2,47 г/см³. Хорошо растворим в воде. В водных растворах гидролизуется. Получают непосредственно из элементов. Применяется в качестве катализатора в органических синтезах.
- GaBr3 — бесцветные гигроскопичные кристаллы. tпл 122 °C, tкип 279 °C плотность — 3,69 г/см³. Растворяется в воде. В водных растворах гидролизуется. В аммиаке малорастворим. Получают непосредственно из элементов.
- GaI3 — гигроскопичные светло-жёлтые иглы. tпл 212 °C, tкип 346 °C, плотность — 4,15 г/см³. Гидролизуется тёплой водой. Получают непосредственно из элементов.
- Ga2S3 — жёлтые кристаллы или белый аморфный порошок с tпл 1250 °C и плотностью 3,65 г/см³. Взаимодействует с водой, при этом полностью гидролизуется. Получают взаимодействием галлия с серой или сероводородом.
- Ga2(SO4)3·18H2O — бесцветное, хорошо растворимое в воде вещество. Получается при взаимодействии галлия, его оксида и гидроксида с серной кислотой. С сульфатами щелочных металлов и аммония легко образует квасцы, например, KGa(SO4)2·12Н2О.
- Ga(NO3)3·8H2O — бесцветные, растворимые в воде и этаноле кристаллы. При нагревании разлагается с образованием оксида галлия (III). Получается действием азотной кислоты на гидроксид галлия.
Применение
Арсенид галлия GaAs — перспективный материал для полупроводниковой электроники.
Нитрид галлия используется в создании полупроводниковых лазеров и светодиодов синего и ультрафиолетового диапазона. Нитрид галлия обладает превосходными химическими и механическими свойствами, типичными для всех нитридных соединений.
Изотоп галлий-71 является важнейшим материалом для регистрации нейтрино и в связи с этим перед техникой стоит весьма актуальная задача выделения этого изотопа из природной смеси в целях повышения чувствительности детекторов нейтрино. Так как содержание 71Ga составляет в природной смеси изотопов около 39,9 %, то выделение чистого изотопа и использование его в качестве детектора нейтрино способно повысить чувствительность регистрации в 2,5 раза.
Галлий дорог, в 2005 году на мировом рынке тонна галлия стоила 1,2 млн долларов США, и в связи с высокой ценой и в то же время с большой потребностью в этом металле очень важно наладить его полное извлечение при алюминиевом производстве и переработке каменных углей на жидкое топливо.
Галлий имеет ряд сплавов, жидких при комнатной температуре, и один из его сплавов имеет температуру плавления 3 °C (эвтектика In-Ga-Sn), но с другой стороны галлий (сплавы в меньшей степени) весьма агрессивен к большинству конструкционных материалов (растрескивание и размывание сплавов при высокой температуре). Например, по отношению к алюминию и его сплавам галлий является мощным понизителем прочности, (см. адсорбционное понижение прочности, эффект Ребиндера). Это свойство галлия было ярчайше продемонстрировано и детально изучено П. А. Ребиндером и Е. Д. Щукиным при контакте алюминия с галлием или его эвтектическими сплавами (жидкометаллическое охрупчивание). Как теплоноситель галлий малоэффективен, а зачастую просто неприемлем.
Галлий — превосходный смазочный материал. На основе галлия и никеля, галлия и скандия созданы очень важные в практическом плане металлические клеи.
Металлическим галлием также заполняют кварцевые термометры (вместо ртути) для измерения высоких температур. Это связано с тем, что галлий имеет значительно более высокую температуру кипения по сравнению с ртутью.
Оксид галлия входит в состав ряда стратегически важных лазерных материалов группы гранатов — ГСГГ, ИАГ, ИСГГ и др.
Биологическая роль и особенности обращения
Не играет биологической роли.
Контакт кожи с галлием приводит к тому, что сверхмалые дисперсные частицы металла остаются на ней. Внешне это выглядит как серое пятно.
Клиническая картина острого отравления: кратковременное возбуждение, затем заторможенность, нарушение координации движений, адинамия, арефлексия, замедление дыхания, нарушение его ритма. На этом фоне наблюдается паралич нижних конечностей, далее — кома, смерть. Ингаляционное воздействие галлий-содержащего аэрозоля в концентрации 50 мг/м³ вызывает у человека поражение почек, равно как и внутривенное введение 10-25 мг/кг солей галлия. Отмечается протеинурия, азотемия, нарушение клиренса мочевины[5].
Из-за низкой температуры плавления слитки галлия рекомендуется транспортировать в пакетах из полиэтилена, который плохо смачивается жидким галлием.
Примечания
- ↑ 1 2 3 4 Химическая энциклопедия: в 5 тт. / Редкол.:Кнунянц И. Л. (гл. ред.). — Москва: Советская энциклопедия, 1988. — Т. 1. — С. 479. — 623 с. — 100 000 экз.
- ↑ Сулименко Л.М. Галлий / Популярная библиотека химических элементов. Т. 1. — М.: Наука, 1983. — С. 409
- ↑ J.P. Riley and Skirrow G. Chemical Oceanography V. I, 1965
- ↑ Галлий
- ↑ Новый справочник химика и технолога. Вредные вещества. Раздел 1. Неорганические соединения.
Литература
- Шека И. А, Чаус И. С, Мнтюрева Т. Т., Галлий, К., 1963;
- Еремин Н. И., Галлий, М., 1964;
- Рустамов П. Г., Халькогениды галлия, Баку, 1967;
- Дымов А. М., Савостин А. П., Аналитическая химия галлия, М., 1968;
- Иванова Р. В., Химия и технология галлия, М., 1973;
- Коган Б. И., Вершковская О. В., Славиковская И. М., Галлий. Геология, применение, экономика, М., 1973;
- Яценко С. П., Галлий. Взаимодействие с металлами, М., 1974;
- Процессы экстракции и сорбции в химической технологии галлия, Алма-Ата, 1985;
- Химия и технология редких и рассеянных элементов, под ред. К. А. Большакова, 2 изд., т. 1, М., 1976, с. 223-44;
- Федоров П. И., Мохосоев М. В.. Алексеев Ф. П., Химия галлия, индия и таллия, Новосиб., 1977. П. И. Федоров.
Ссылки
| Галлий на Викискладе? |
- Галлий на Webelements
- Галлий в Популярной библиотеке химических элементов
| Периодическая система химических элементов Д. И. Менделеева | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | |||||||||||||||
| 1 | H | He | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr | ||||||||||||||
| 5 | Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe | ||||||||||||||
| 6 | Cs | Ba | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| 7 | Fr | Ra | Ac | Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Uut | Fl | Uup | Lv | Uus | Uuo |
|
| |
|---|
| Eu, Sm, Li, Cs, Rb, K, Ra, Ba, Sr, Ca, Na, Ac, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Pm, Gd, Tb, Mg, Y, Dy, Am, Ho, Er, Tm, Lu, Sc, Pu, Th, Np, U, Hf, Be, Al, Ti, Zr, Yb, Mn, V, Nb, Pa, Cr, Zn, Ga, Fe, Cd, In, Tl, Co, Ni, Te, Mo, Sn, Pb, H2, W, Sb, Bi, Ge, Re, Cu, Tc, Te, Rh, Po, Hg, Ag, Pd, Os, Ir, Pt, Au Элементы расположены в порядке возрастания стандартного электродного потенциала. |
| Соединения галлия |
|---|
| Антимонид галлия (GaSb) • Арсенид галлия (GaAs) • Бромид галлия (GaBr3) • Гидроксид галлия (Ga(OH)3) • Гидроксо-ацетат галлия (Ga(CH3COO)2OH) • Дигаллан (Ga2H6) • Иодид галлия (GaI3) • Нитрат галлия (Ga(NO3)3) • Нитрид галлия (GaN) • Оксид галлия (Ga2O3) • Оксид галлия(I) (Ga2O) • Селенид галлия(II) (GaSe) • Селенид галлия(III) (Ga2Se3) • Сульфат галлия (Ga2(SO4)3) • Сульфид галлия(I) (Ga2S) • Сульфид галлия(II) (GaS) • Сульфид галлия(III) (Ga2S3) • Теллурид галлия(II) (GaTe) • Теллурид галлия(III) (Ga2Te3) • Тетраметилдигаллан (Ga2H2(CH3)4) • Триметилгаллий (Ga(CH3)3) • Трифенилгаллий (Ga(C6H5)3) • Триэтилгаллий (Ga(C2H5)3) • Фосфид галлия (GaP) • Фторид галлия (GaF3) • Хлорид галлия(II) (GaCl2) • Хлорид галлия (GaCl3) |




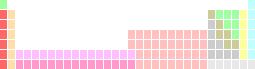




![mathsf{2Ga + 6H_2O + 2NaOH rightarrow 2Na[Ga(OH)_4] + 3H_2O}](https://dic.academic.ru/dic.nsf/ruwiki/3824f2cb28f9b7ee424f53473e712b3f.png)
![mathsf{4LiH + GaCl_3 rightarrow Li[GaH_4] + 3LiCl}](https://dic.academic.ru/dic.nsf/ruwiki/005c8393c89e75f9119673ecf818f597.png)
![mathsf{[GaH_4]^- + 4H_2O rightarrow Ga(OH)_3 + OH^- + 4H_2uparrow}](https://dic.academic.ru/dic.nsf/ruwiki/3ebc698a37c4b21498573eaab3be24e1.png)

![mathsf{Ga_2O_3 + 2NaOH +3H_2O rightarrow 2Na[Ga(OH)_4]}](https://dic.academic.ru/dic.nsf/ruwiki/d0047c0084b2582aec9558aa70c8e99e.png)
