| Alexander Graham Bell | |
|---|---|
 Bell c. 1917 | |
| Born | Alexander Bell March 3, 1847 Edinburgh, Scotland |
| Died | August 2, 1922 (aged 75) Beinn Bhreagh, Nova Scotia, Canada |
| Citizenship | United Kingdom (1847–1922) British-subject in Canada (1870–1882) United States (1882–1922) |
| Alma mater |
|
| Occupations |
|
| Known for | Invention of the telephone b Cofounding of AT&T |
| Spouse | Mabel Gardiner Hubbard (m. 1877) |
| Children | 4 |
| Parents |
|
| Relatives |
|
| Awards |
|
| Re-identified in 2013, Bell made this wax-disc recording of his voice in 1885. | |
| Signature | |
| Notes | |
|
Alexander Graham Bell (, born Alexander Bell; March 3, 1847 – August 2, 1922)[4] was a Scottish-born[N 1] inventor, scientist and engineer who is credited with patenting the first practical telephone. He also co-founded the American Telephone and Telegraph Company (AT&T) in 1885.[7]
Bell’s father, grandfather, and brother had all been associated with work on elocution and speech, and both his mother and wife were deaf; profoundly influencing Bell’s life’s work.[8] His research on hearing and speech further led him to experiment with hearing devices which eventually culminated in Bell being awarded the first U.S. patent for the telephone, on March 7, 1876.[N 2] Bell considered his invention an intrusion on his real work as a scientist and refused to have a telephone in his study.[9][N 3]
Many other inventions marked Bell’s later life, including groundbreaking work in optical telecommunications, hydrofoils, and aeronautics. Bell also had a strong influence on the National Geographic Society[11] and its magazine while serving as the second president from January 7, 1898, until 1903.
Beyond his work in engineering, Bell had a deep interest in the emerging science of heredity.[12]
Early life
Bell was born in Edinburgh, Scotland, on March 3, 1847.[13] The family home was at South Charlotte Street, and has a stone inscription marking it as Bell’s birthplace. He had two brothers: Melville James Bell (1845–1870) and Edward Charles Bell (1848–1867), both of whom would die of tuberculosis.[14] His father was Alexander Melville Bell, a phonetician, and his mother was Eliza Grace Bell (née Symonds).[15] Born as just «Alexander Bell», at age 10, he made a plea to his father to have a middle name like his two brothers.[16][N 4] For his 11th birthday, his father acquiesced and allowed him to adopt the name «Graham», chosen out of respect for Alexander Graham, a Canadian being treated by his father who had become a family friend.[17] To close relatives and friends he remained «Aleck».[18] Bell and his siblings attended a Presbyterian Church in their youth.[19]
First invention
As a child, Bell displayed a curiosity about his world; he gathered botanical specimens and ran experiments at an early age. His best friend was Ben Herdman, a neighbour whose family operated a flour mill. At the age of 12, Bell built a homemade device that combined rotating paddles with sets of nail brushes, creating a simple dehusking machine that was put into operation at the mill and used steadily for a number of years.[20] In return, Ben’s father John Herdman gave both boys the run of a small workshop in which to «invent».[20]
From his early years, Bell showed a sensitive nature and a talent for art, poetry, and music that was encouraged by his mother. With no formal training, he mastered the piano and became the family’s pianist.[21] Despite being normally quiet and introspective, he revelled in mimicry and «voice tricks» akin to ventriloquism that continually entertained family guests during their occasional visits.[21] Bell was also deeply affected by his mother’s gradual deafness (she began to lose her hearing when he was 12), and learned a manual finger language so he could sit at her side and tap out silently the conversations swirling around the family parlour.[22] He also developed a technique of speaking in clear, modulated tones directly into his mother’s forehead wherein she would hear him with reasonable clarity.[23] Bell’s preoccupation with his mother’s deafness led him to study acoustics.
His family was long associated with the teaching of elocution: his grandfather, Alexander Bell, in London, his uncle in Dublin, and his father, in Edinburgh, were all elocutionists. His father published a variety of works on the subject, several of which are still well known, especially his The Standard Elocutionist (1860),[21] which appeared in Edinburgh in 1868. The Standard Elocutionist appeared in 168 British editions and sold over a quarter of a million copies in the United States alone. In this treatise, his father explains his methods of how to instruct deaf-mutes (as they were then known) to articulate words and read other people’s lip movements to decipher meaning. Bell’s father taught him and his brothers not only to write Visible Speech but to identify any symbol and its accompanying sound.[24] Bell became so proficient that he became a part of his father’s public demonstrations and astounded audiences with his abilities. He could decipher Visible Speech representing virtually every language, including Latin, Scottish Gaelic, and even Sanskrit, accurately reciting written tracts without any prior knowledge of their pronunciation.[24]
Education
As a young child, Bell, like his brothers, received his early schooling at home from his father. At an early age, he was enrolled at the Royal High School, Edinburgh, Scotland, which he left at the age of 15, having completed only the first four forms.[25] His school record was undistinguished, marked by absenteeism and lacklustre grades. His main interest remained in the sciences, especially biology, while he treated other school subjects with indifference, to the dismay of his father.[26] Upon leaving school, Bell travelled to London to live with his grandfather, Alexander Bell, on Harrington Square. During the year he spent with his grandfather, a love of learning was born, with long hours spent in serious discussion and study. The elder Bell took great efforts to have his young pupil learn to speak clearly and with conviction, the attributes that his pupil would need to become a teacher himself.[27] At the age of 16, Bell secured a position as a «pupil-teacher» of elocution and music, in Weston House Academy at Elgin, Moray, Scotland. Although he was enrolled as a student in Latin and Greek, he instructed classes himself in return for board and £10 per session.[28] The following year, he attended the University of Edinburgh, joining his older brother Melville who had enrolled there the previous year. In 1868, not long before he departed for Canada with his family, Bell completed his matriculation exams and was accepted for admission to University College London.[29][failed verification]
First experiments with sound
His father encouraged Bell’s interest in speech and, in 1863, took his sons to see a unique automaton developed by Sir Charles Wheatstone based on the earlier work of Baron Wolfgang von Kempelen.[30] The rudimentary «mechanical man» simulated a human voice. Bell was fascinated by the machine and after he obtained a copy of von Kempelen’s book, published in German, and had laboriously translated it, he and his older brother Melville built their own automaton head. Their father, highly interested in their project, offered to pay for any supplies and spurred the boys on with the enticement of a «big prize» if they were successful.[30] While his brother constructed the throat and larynx, Bell tackled the more difficult task of recreating a realistic skull. His efforts resulted in a remarkably lifelike head that could «speak», albeit only a few words.[30] The boys would carefully adjust the «lips» and when a bellows forced air through the windpipe, a very recognizable Mama ensued, to the delight of neighbours who came to see the Bell invention.[31]
Intrigued by the results of the automaton, Bell continued to experiment with a live subject, the family’s Skye Terrier, Trouve.[32] After he taught it to growl continuously, Bell would reach into its mouth and manipulate the dog’s lips and vocal cords to produce a crude-sounding «Ow ah oo ga ma ma». With little convincing, visitors believed his dog could articulate «How are you, grandmama?[33]» Indicative of his playful nature, his experiments convinced onlookers that they saw a «talking dog».[34] These initial forays into experimentation with sound led Bell to undertake his first serious work on the transmission of sound, using tuning forks to explore resonance.
At age 19, Bell wrote a report on his work and sent it to philologist Alexander Ellis, a colleague of his father.[34] Ellis immediately wrote back indicating that the experiments were similar to existing work in Germany, and also lent Bell a copy of Hermann von Helmholtz’s work, The Sensations of Tone as a Physiological Basis for the Theory of Music.[35]
Dismayed to find that groundbreaking work had already been undertaken by Helmholtz who had conveyed vowel sounds by means of a similar tuning fork «contraption», Bell pored over the German scientist’s book. Working from his own erroneous mistranslation of a French edition,[36] Bell fortuitously then made a deduction that would be the underpinning of all his future work on transmitting sound, reporting: «Without knowing much about the subject, it seemed to me that if vowel sounds could be produced by electrical means, so could consonants, so could articulate speech.» He also later remarked: «I thought that Helmholtz had done it … and that my failure was due only to my ignorance of electricity. It was a valuable blunder … If I had been able to read German in those days, I might never have commenced my experiments!»[37][38][39][N 5]
Family tragedy
In 1865, when the Bell family moved to London,[40] Bell returned to Weston House as an assistant master and, in his spare hours, continued experiments on sound using a minimum of laboratory equipment. Bell concentrated on experimenting with electricity to convey sound and later installed a telegraph wire from his room in Somerset College to that of a friend.[41] Throughout late 1867, his health faltered mainly through exhaustion. His younger brother, Edward «Ted,» was similarly affected by tuberculosis. While Bell recovered (by then referring to himself in correspondence as «A. G. Bell») and served the next year as an instructor at Somerset College, Bath, England, his brother’s condition deteriorated. Edward would never recover. Upon his brother’s death, Bell returned home in 1867. His older brother Melville had married and moved out. With aspirations to obtain a degree at University College London, Bell considered his next years as preparation for the degree examinations, devoting his spare time at his family’s residence to studying.
Helping his father in Visible Speech demonstrations and lectures brought Bell to Susanna E. Hull’s private school for the deaf in South Kensington, London. His first two pupils were deaf-mute girls who made remarkable progress under his tutelage. While his older brother seemed to achieve success on many fronts including opening his own elocution school, applying for a patent on an invention, and starting a family, Bell continued as a teacher. However, in May 1870, Melville died from complications due to tuberculosis, causing a family crisis. His father had also experienced a debilitating illness earlier in life and had been restored to health by a convalescence in Newfoundland. Bell’s parents embarked upon a long-planned move when they realized that their remaining son was also sickly. Acting decisively, Alexander Melville Bell asked Bell to arrange for the sale of all the family property,[42][N 6] conclude all of his brother’s affairs (Bell took over his last student, curing a pronounced lisp),[43] and join his father and mother in setting out for the «New World». Reluctantly, Bell also had to conclude a relationship with Marie Eccleston, who, as he had surmised, was not prepared to leave England with him.[44]
Canada
In 1870, 23-year-old Bell travelled with his parents and his brother’s widow, Caroline Margaret Ottaway,[45] to Paris, Ontario,[46] to stay with Thomas Henderson, a Baptist minister and family friend.[47] The Bell family soon purchased a farm of 10.5 acres (42,000 m2) at Tutelo Heights (now called Tutela Heights), near Brantford, Ontario. The property consisted of an orchard, large farmhouse, stable, pigsty, hen-house, and a carriage house, which bordered the Grand River.[48][N 7]
At the homestead, Bell set up his own workshop in the converted carriage house near to what he called his «dreaming place»,[50] a large hollow nestled in trees at the back of the property above the river.[51] Despite his frail condition upon arriving in Canada, Bell found the climate and environs to his liking, and rapidly improved.[52][N 8] He continued his interest in the study of the human voice and when he discovered the Six Nations Reserve across the river at Onondaga, he learned the Mohawk language and translated its unwritten vocabulary into Visible Speech symbols. For his work, Bell was awarded the title of Honorary Chief and participated in a ceremony where he donned a Mohawk headdress and danced traditional dances.[53][N 9]
After setting up his workshop, Bell continued experiments based on Helmholtz’s work with electricity and sound.[54] He also modified a melodeon (a type of pump organ) so that it could transmit its music electrically over a distance.[55] Once the family was settled in, both Bell and his father made plans to establish a teaching practice and in 1871, he accompanied his father to Montreal, where Melville was offered a position to teach his System of Visible Speech.
Work with the deaf

Bell, top right, providing pedagogical instruction to teachers at the Boston School for Deaf Mutes, 1871. Throughout his life, he referred to himself as «a teacher of the deaf».
Bell’s father was invited by Sarah Fuller, principal of the Boston School for Deaf Mutes (later to become the public Horace Mann School for the Deaf)[56] to introduce the Visible Speech System by providing training for Fuller’s instructors, but he declined the post in favour of his son. Travelling to Boston in April 1871, Bell proved successful in training the school’s instructors.[57] He was subsequently asked to repeat the programme at the American Asylum for Deaf-mutes in Hartford, Connecticut, and the Clarke School for the Deaf in Northampton, Massachusetts.
Returning home to Brantford after six months abroad, Bell continued his experiments with his «harmonic telegraph».[58][N 10] The basic concept behind his device was that messages could be sent through a single wire if each message was transmitted at a different pitch, but work on both the transmitter and receiver was needed.[59]
Unsure of his future, he contemplated returning to London to complete his studies, but decided to return to Boston as a teacher.[60] His father helped him set up his private practice by contacting Gardiner Greene Hubbard, the president of the Clarke School for the Deaf for a recommendation. Teaching his father’s system, in October 1872, Alexander Bell opened his «School of Vocal Physiology and Mechanics of Speech» in Boston, which attracted a large number of deaf pupils, with his first class numbering 30 students.[61][62] While he was working as a private tutor, one of his pupils was Helen Keller, who came to him as a young child unable to see, hear, or speak. She was later to say that Bell dedicated his life to the penetration of that «inhuman silence which separates and estranges».[63] In 1893, Keller performed the sod-breaking ceremony for the construction of Bell’s new Volta Bureau, dedicated to «the increase and diffusion of knowledge relating to the deaf».[64][65]
Throughout his lifetime, Bell sought to integrate the deaf and hard of hearing with the hearing world. Bell encouraged speech therapy and lip reading over sign language. He outlined this in a 1898 paper[66] detailing his belief that with resources and effort, the deaf could be taught to read lips and speak (known as oralism)[67] thus enabling their integration within the wider society.[68] Bell has been criticised by members of the Deaf community for supporting ideas that could cause the closure of dozens of deaf schools, and what some consider eugenicist ideas.[69] Bell did not support a ban on deaf people marrying each other, an idea articulated by the National Association of the Deaf (United States).[70] Although, in his memoir Memoir upon the Formation of a Deaf Variety of the Human Race, Bell observed that if deaf people tended to marry other deaf people, this could result in the emergence of a «deaf race».[71] Ultimately, in 1880, the Second International Congress on Education of the Deaf passed a resolution preferring the teaching of oral communication rather than signing in schools.
Continuing experimentation
In 1872, Bell became professor of Vocal Physiology and Elocution at the Boston University School of Oratory. During this period, he alternated between Boston and Brantford, spending summers in his Canadian home. At Boston University, Bell was «swept up» by the excitement engendered by the many scientists and inventors residing in the city. He continued his research in sound and endeavored to find a way to transmit musical notes and articulate speech, but although absorbed by his experiments, he found it difficult to devote enough time to experimentation. While days and evenings were occupied by his teaching and private classes, Bell began to stay awake late into the night, running experiment after experiment in rented facilities at his boarding house. Keeping «night owl» hours, he worried that his work would be discovered and took great pains to lock up his notebooks and laboratory equipment. Bell had a specially made table where he could place his notes and equipment inside a locking cover.[72] Worse still, his health deteriorated as he had severe headaches.[59] Returning to Boston in fall 1873, Bell made a far-reaching decision to concentrate on his experiments in sound.
Deciding to give up his lucrative private Boston practice, Bell retained only two students, six-year-old «Georgie» Sanders, deaf from birth, and 15-year-old Mabel Hubbard. Each pupil would play an important role in the next developments. George’s father, Thomas Sanders, a wealthy businessman, offered Bell a place to stay in nearby Salem with Georgie’s grandmother, complete with a room to «experiment». Although the offer was made by George’s mother and followed the year-long arrangement in 1872 where her son and his nurse had moved to quarters next to Bell’s boarding house, it was clear that Mr. Sanders was backing the proposal. The arrangement was for teacher and student to continue their work together, with free room and board thrown in.[73] Mabel was a bright, attractive girl who was ten years Bell’s junior but became the object of his affection. Having lost her hearing after a near-fatal bout of scarlet fever close to her fifth birthday,[74][75][N 11] she had learned to read lips but her father, Gardiner Greene Hubbard, Bell’s benefactor and personal friend, wanted her to work directly with her teacher.[76]
The telephone
| External audio |
|---|
By 1874, Bell’s initial work on the harmonic telegraph had entered a formative stage, with progress made both at his new Boston «laboratory» (a rented facility) and at his family home in Canada a big success.[N 12] While working that summer in Brantford, Bell experimented with a «phonautograph», a pen-like machine that could draw shapes of sound waves on smoked glass by tracing their vibrations. Bell thought it might be possible to generate undulating electrical currents that corresponded to sound waves.[78] Bell also thought that multiple metal reeds tuned to different frequencies like a harp would be able to convert the undulating currents back into sound. But he had no working model to demonstrate the feasibility of these ideas.[79]
In 1874, telegraph message traffic was rapidly expanding and in the words of Western Union President William Orton, had become «the nervous system of commerce». Orton had contracted with inventors Thomas Edison and Elisha Gray to find a way to send multiple telegraph messages on each telegraph line to avoid the great cost of constructing new lines.[80] When Bell mentioned to Gardiner Hubbard and Thomas Sanders that he was working on a method of sending multiple tones on a telegraph wire using a multi-reed device, the two wealthy patrons began to financially support Bell’s experiments.[81] Patent matters would be handled by Hubbard’s patent attorney, Anthony Pollok.[82]
In March 1875, Bell and Pollok visited the scientist Joseph Henry, who was then director of the Smithsonian Institution, and asked Henry’s advice on the electrical multi-reed apparatus that Bell hoped would transmit the human voice by telegraph. Henry replied that Bell had «the germ of a great invention». When Bell said that he did not have the necessary knowledge, Henry replied, «Get it!» That declaration greatly encouraged Bell to keep trying, even though he did not have the equipment needed to continue his experiments, nor the ability to create a working model of his ideas. However, a chance meeting in 1874 between Bell and Thomas A. Watson, an experienced electrical designer and mechanic at the electrical machine shop of Charles Williams, changed all that.
With financial support from Sanders and Hubbard, Bell hired Thomas Watson as his assistant,[N 13] and the two of them experimented with acoustic telegraphy. On June 2, 1875, Watson accidentally plucked one of the reeds and Bell, at the receiving end of the wire, heard the overtones of the reed; overtones that would be necessary for transmitting speech. That demonstrated to Bell that only one reed or armature was necessary, not multiple reeds. This led to the «gallows» sound-powered telephone, which could transmit indistinct, voice-like sounds, but not clear speech.
The race to the patent office
In 1875, Bell developed an acoustic telegraph and drew up a patent application for it. Since he had agreed to share U.S. profits with his investors Gardiner Hubbard and Thomas Sanders, Bell requested that an associate in Ontario, George Brown, attempt to patent it in Britain, instructing his lawyers to apply for a patent in the U.S. only after they received word from Britain (Britain would issue patents only for discoveries not previously patented elsewhere).[84]

Alexander Graham Bell’s telephone patent[85] drawing, March 7, 1876
Meanwhile, Elisha Gray was also experimenting with acoustic telegraphy and thought of a way to transmit speech using a water transmitter. On February 14, 1876, Gray filed a caveat with the U.S. Patent Office for a telephone design that used a water transmitter. That same morning, Bell’s lawyer filed Bell’s application with the patent office. There is considerable debate about who arrived first and Gray later challenged the primacy of Bell’s patent. Bell was in Boston on February 14 and did not arrive in Washington until February 26.[citation needed]

The master telephone patent, 174465, March 7, 1876
Bell’s patent 174,465, was issued to Bell on March 7, 1876, by the U.S. Patent Office. Bell’s patent covered «the method of, and apparatus for, transmitting vocal or other sounds telegraphically … by causing electrical undulations, similar in form to the vibrations of the air accompanying the said vocal or other sound»[86][N 14] Bell returned to Boston the same day and the next day resumed work, drawing in his notebook a diagram similar to that in Gray’s patent caveat.[citation needed]
On March 10, 1876, three days after his patent was issued, Bell succeeded in getting his telephone to work, using a liquid transmitter similar to Gray’s design. Vibration of the diaphragm caused a needle to vibrate in the water, varying the electrical resistance in the circuit. When Bell spoke the sentence «Mr. Watson—Come here—I want to see you» into the liquid transmitter,[87] Watson, listening at the receiving end in an adjoining room, heard the words clearly.[88]
Although Bell was, and still is, accused of stealing the telephone from Gray,[89] Bell used Gray’s water transmitter design only after Bell’s patent had been granted, and only as a proof of concept scientific experiment,[90] to prove to his own satisfaction that intelligible «articulate speech» (Bell’s words) could be electrically transmitted.[91] After March 1876, Bell focused on improving the electromagnetic telephone and never used Gray’s liquid transmitter in public demonstrations or commercial use.[92]
The question of priority for the variable resistance feature of the telephone was raised by the examiner before he approved Bell’s patent application. He told Bell that his claim for the variable resistance feature was also described in Gray’s caveat. Bell pointed to a variable resistance device in his previous application in which he described a cup of mercury, not water. He had filed the mercury application at the patent office a year earlier on February 25, 1875, long before Elisha Gray described the water device. In addition, Gray abandoned his caveat, and because he did not contest Bell’s priority, the examiner approved Bell’s patent on March 3, 1876. Gray had reinvented the variable resistance telephone, but Bell was the first to write down the idea and the first to test it in a telephone.[93]
The patent examiner, Zenas Fisk Wilber, later stated in an affidavit that he was an alcoholic who was much in debt to Bell’s lawyer, Marcellus Bailey, with whom he had served in the Civil War. He claimed he showed Gray’s patent caveat to Bailey. Wilber also claimed (after Bell arrived in Washington D.C. from Boston) that he showed Gray’s caveat to Bell and that Bell paid him $100 (equivalent to $2,500 in 2021). Bell claimed they discussed the patent only in general terms, although in a letter to Gray, Bell admitted that he learned some of the technical details. Bell denied in an affidavit that he ever gave Wilber any money.[94]
Later developments

On March 10, 1876, Bell used «the instrument» in Boston to call Thomas Watson who was in another room but out of earshot. He said, «Mr. Watson, come here – I want to see you» and Watson soon appeared at his side.[95]
Continuing his experiments in Brantford, Bell brought home a working model of his telephone. On August 3, 1876, from the telegraph office in Brantford, Ontario, Bell sent a tentative telegram to the village of Mount Pleasant four miles (six kilometres) distant, indicating that he was ready. He made a telephone call via telegraph wires and faint voices were heard replying. The following night, he amazed guests as well as his family with a call between the Bell Homestead and the office of the Dominion Telegraph Company in Brantford along an improvised wire strung up along telegraph lines and fences, and laid through a tunnel. This time, guests at the household distinctly heard people in Brantford reading and singing. The third test on August 10, 1876, was made via the telegraph line between Brantford and Paris, Ontario, eight miles (thirteen kilometres) distant. This test was said by many sources to be the «world’s first long-distance call».[96][97] The final test certainly proved that the telephone could work over long distances, at least as a one-way call.
[98]
The first two-way (reciprocal) conversation over a line occurred between Cambridge and Boston (roughly 2.5 miles) on October 9, 1876.[99] During that conversation, Bell was on Kilby Street in Boston and Watson was at the offices of the Walworth Manufacturing Company.[100]

Bell at the opening of the long-distance line from New York to Chicago in 1892
Bell and his partners, Hubbard and Sanders, offered to sell the patent outright to Western Union for $100,000, equal to $2,544,688 today. The president of Western Union balked, countering that the telephone was nothing but a toy. Two years later, he told colleagues that if he could get the patent for $25 million (equal to $701,982,759 today), he would consider it a bargain. By then, the Bell company no longer wanted to sell the patent.[101] Bell’s investors would become millionaires while he fared well from residuals and at one point had assets of nearly one million dollars.[102]
Bell began a series of public demonstrations and lectures to introduce the new invention to the scientific community as well as the general public. A short time later, his demonstration of an early telephone prototype at the 1876 Centennial Exposition in Philadelphia brought the telephone to international attention.[103] Influential visitors to the exhibition included Emperor Pedro II of Brazil. One of the judges at the Exhibition, Sir William Thomson (later, Lord Kelvin), a renowned Scottish scientist, described the telephone as «the greatest by far of all the marvels of the electric telegraph».[104]
On January 14, 1878, at Osborne House, on the Isle of Wight, Bell demonstrated the device to Queen Victoria,[105] placing calls to Cowes, Southampton and London. These were the first publicly witnessed long-distance telephone calls in the UK. The queen considered the process to be «quite extraordinary» although the sound was «rather faint».[106] She later asked to buy the equipment that was used, but Bell offered to make «a set of telephones» specifically for her.[107][108]
The Bell Telephone Company was created in 1877, and by 1886, more than 150,000 people in the U.S. owned telephones. Bell Company engineers made numerous other improvements to the telephone, which emerged as one of the most successful products ever. In 1879, the Bell company acquired Edison’s patents for the carbon microphone from Western Union. This made the telephone practical for longer distances, and it was no longer necessary to shout to be heard at the receiving telephone.[citation needed]
Emperor Pedro II of Brazil was the first person to buy stock in Bell’s company, the Bell Telephone Company. One of the first telephones in a private residence was installed in his palace in Petrópolis, his summer retreat forty miles (sixty-four kilometres) from Rio de Janeiro.[109]
In January 1915, Bell made the first ceremonial transcontinental telephone call. Calling from the AT&T head office at 15 Dey Street in New York City, Bell was heard by Thomas Watson at 333 Grant Avenue in San Francisco. The New York Times reported:
On October 9, 1876, Alexander Graham Bell and Thomas A. Watson talked by telephone to each other over a two-mile wire stretched between Cambridge and Boston. It was the first wire conversation ever held. Yesterday afternoon [on January 25, 1915], the same two men talked by telephone to each other over a 3,400-mile wire between New York and San Francisco. Dr. Bell, the veteran inventor of the telephone, was in New York, and Mr. Watson, his former associate, was on the other side of the continent.[110]
Competitors
As is sometimes common in scientific discoveries, simultaneous developments can occur, as evidenced by a number of inventors who were at work on the telephone.[111] Over a period of 18 years, the Bell Telephone Company faced 587 court challenges to its patents, including five that went to the U.S. Supreme Court,[112] but none was successful in establishing priority over the original Bell patent[113][114] and the Bell Telephone Company never lost a case that had proceeded to a final trial stage.[113] Bell’s laboratory notes and family letters were the key to establishing a long lineage to his experiments.[113] The Bell company lawyers successfully fought off myriad lawsuits generated initially around the challenges by Elisha Gray and Amos Dolbear. In personal correspondence to Bell, both Gray and Dolbear had acknowledged his prior work, which considerably weakened their later claims.[115]
On January 13, 1887, the U.S. Government moved to annul the patent issued to Bell on the grounds of fraud and misrepresentation. After a series of decisions and reversals, the Bell company won a decision in the Supreme Court, though a couple of the original claims from the lower court cases were left undecided.[116][117] By the time that the trial wound its way through nine years of legal battles, the U.S. prosecuting attorney had died and the two Bell patents (No. 174,465 dated March 7, 1876, and No. 186,787 dated January 30, 1877) were no longer in effect, although the presiding judges agreed to continue the proceedings due to the case’s importance as a precedent. With a change in administration and charges of conflict of interest (on both sides) arising from the original trial, the US Attorney General dropped the lawsuit on November 30, 1897, leaving several issues undecided on the merits.[118]
During a deposition filed for the 1887 trial, Italian inventor Antonio Meucci also claimed to have created the first working model of a telephone in Italy in 1834. In 1886, in the first of three cases in which he was involved,[N 15] Meucci took the stand as a witness in the hope of establishing his invention’s priority. Meucci’s testimony in this case was disputed due to a lack of material evidence for his inventions, as his working models were purportedly lost at the laboratory of American District Telegraph (ADT) of New York, which was later incorporated as a subsidiary of Western Union in 1901.[119][120] Meucci’s work, like many other inventors of the period, was based on earlier acoustic principles and despite evidence of earlier experiments, the final case involving Meucci was eventually dropped upon Meucci’s death.[121] However, due to the efforts of Congressman Vito Fossella, the U.S. House of Representatives on June 11, 2002, stated that Meucci’s «work in the invention of the telephone should be acknowledged».[122][123][124] This did not put an end to the still-contentious issue.[125] Some modern scholars do not agree with the claims that Bell’s work on the telephone was influenced by Meucci’s inventions.[126][N 16]
The value of the Bell patent was acknowledged throughout the world, and patent applications were made in most major countries, but when Bell delayed the German patent application, the electrical firm of Siemens & Halske set up a rival manufacturer of Bell telephones under their own patent. The Siemens company produced near-identical copies of the Bell telephone without having to pay royalties.[127] The establishment of the International Bell Telephone Company in Brussels, Belgium in 1880, as well as a series of agreements in other countries eventually consolidated a global telephone operation. The strain put on Bell by his constant appearances in court, necessitated by the legal battles, eventually resulted in his resignation from the company.[128][N 17]
Family life


The Brodhead–Bell mansion, the Bell family residence in Washington, D.C., from 1882 to 1889[129]
On July 11, 1877, a few days after the Bell Telephone Company was established, Bell married Mabel Hubbard (1857–1923) at the Hubbard estate in Cambridge, Massachusetts. His wedding present to his bride was to turn over 1,487 of his 1,497 shares in the newly formed Bell Telephone Company.[130] Shortly thereafter, the newlyweds embarked on a year-long honeymoon in Europe. During that excursion, Bell took a handmade model of his telephone with him, making it a «working holiday». The courtship had begun years earlier; however, Bell waited until he was more financially secure before marrying. Although the telephone appeared to be an «instant» success, it was not initially a profitable venture and Bell’s main sources of income were from lectures until after 1897.[131] One unusual request exacted by his fiancée was that he use «Alec» rather than the family’s earlier familiar name of «Aleck». From 1876, he would sign his name «Alec Bell».[132][133] They had four children:
- Elsie May Bell (1878–1964) who married Gilbert Hovey Grosvenor of National Geographic fame.[134][135]
- Marian Hubbard Bell (1880–1962) who was referred to as «Daisy». Married David Fairchild.[136][137][N 18]
- Two sons who died in infancy (Edward in 1881 and Robert in 1883).
The Bell family home was in Cambridge, Massachusetts, until 1880 when Bell’s father-in-law bought a house in Washington, D.C.; in 1882 he bought a home in the same city for Bell’s family, so they could be with him while he attended to the numerous court cases involving patent disputes.[140]
Bell was a British subject throughout his early life in Scotland and later in Canada until 1882 when he became a naturalized citizen of the United States. In 1915, he characterized his status as: «I am not one of those hyphenated Americans who claim allegiance to two countries.»[141][page needed][142] Despite this declaration, Bell has been proudly claimed as a «native son» by all three countries he resided in: the United States, Canada, and the United Kingdom.[143]
By 1885, a new summer retreat was contemplated. That summer, the Bells had a vacation on Cape Breton Island in Nova Scotia, spending time at the small village of Baddeck.[144] Returning in 1886, Bell started building an estate on a point across from Baddeck, overlooking Bras d’Or Lake.[145] By 1889, a large house, christened The Lodge was completed and two years later, a larger complex of buildings, including a new laboratory,[146] were begun that the Bells would name Beinn Bhreagh (Gaelic: Beautiful Mountain) after Bell’s ancestral Scottish highlands.[147][N 19] Bell also built the Bell Boatyard on the estate, employing up to 40 people building experimental craft as well as wartime lifeboats and workboats for the Royal Canadian Navy and pleasure craft for the Bell family. He was an enthusiastic boater, and Bell and his family sailed or rowed a long series of vessels on Bras d’Or Lake, ordering additional vessels from the H.W. Embree and Sons boatyard in Port Hawkesbury, Nova Scotia. In his final, and some of his most productive years, Bell split his residency between Washington, D.C., where he and his family initially resided for most of the year, and Beinn Bhreagh, where they spent increasing amounts of time.[148]
Until the end of his life, Bell and his family would alternate between the two homes, but Beinn Bhreagh would, over the next 30 years, become more than a summer home as Bell became so absorbed in his experiments that his annual stays lengthened. Both Mabel and Bell became immersed in the Baddeck community and were accepted by the villagers as «their own».[146][N 20] The Bells were still in residence at Beinn Bhreagh when the Halifax Explosion occurred on December 6, 1917. Mabel and Bell mobilized the community to help victims in Halifax.[149]
Later inventions

Alexander Graham Bell in his later years
Although Alexander Graham Bell is most often associated with the invention of the telephone, his interests were extremely varied. According to one of his biographers, Charlotte Gray, Bell’s work ranged «unfettered across the scientific landscape» and he often went to bed voraciously reading the Encyclopædia Britannica, scouring it for new areas of interest.[150] The range of Bell’s inventive genius is represented only in part by the 18 patents granted in his name alone and the 12 he shared with his collaborators. These included 14 for the telephone and telegraph, four for the photophone, one for the phonograph, five for aerial vehicles, four for «hydroairplanes», and two for selenium cells. Bell’s inventions spanned a wide range of interests and included a metal jacket to assist in breathing, the audiometer to detect minor hearing problems, a device to locate icebergs, investigations on how to separate salt from seawater, and work on finding alternative fuels.[citation needed]
Bell worked extensively in medical research and invented techniques for teaching speech to the deaf. During his Volta Laboratory period, Bell and his associates considered impressing a magnetic field on a record as a means of reproducing sound. Although the trio briefly experimented with the concept, they could not develop a workable prototype. They abandoned the idea, never realizing they had glimpsed a basic principle which would one day find its application in the tape recorder, the hard disc and floppy disc drive, and other magnetic media.[citation needed]
Bell’s own home used a primitive form of air conditioning, in which fans blew currents of air across great blocks of ice. He also anticipated modern concerns with fuel shortages and industrial pollution. Methane gas, he reasoned, could be produced from the waste of farms and factories. At his Canadian estate in Nova Scotia, he experimented with composting toilets and devices to capture water from the atmosphere. In a magazine interview published shortly before his death, he reflected on the possibility of using solar panels to heat houses.[citation needed]
Photophone

Bell and his assistant Charles Sumner Tainter jointly invented a wireless telephone, named a photophone, which allowed for the transmission of both sounds and normal human conversations on a beam of light.[151][152] Both men later became full associates in the Volta Laboratory Association.
On June 21, 1880, Bell’s assistant transmitted a wireless voice telephone message a considerable distance, from the roof of the Franklin School in Washington, D.C., to Bell at the window of his laboratory, some 700 feet (213 m) away, 19 years before the first voice radio transmissions.[153][154][155][156]
Bell believed the photophone’s principles were his life’s «greatest achievement», telling a reporter shortly before his death that the photophone was «the greatest invention [I have] ever made, greater than the telephone».[157] The photophone was a precursor to the fiber-optic communication systems which achieved popular worldwide usage in the 1980s.[158][159] Its master patent was issued in December 1880, many decades before the photophone’s principles came into popular use.
Metal detector
Bell’s voice, from a Volta Laboratory recording in 1885. Restored by the Smithsonian in 2013.
Bell is also credited with developing one of the early versions of a metal detector through the use of an induction balance, after the shooting of U.S. President James A. Garfield in 1881. According to some accounts, the metal detector worked flawlessly in tests but did not find Guiteau’s bullet, partly because the metal bed frame on which the President was lying disturbed the instrument, resulting in static.[160] Garfield’s surgeons, led by self-appointed chief physician Doctor Willard Bliss, were skeptical of the device, and ignored Bell’s requests to move the President to a bed not fitted with metal springs.[160] Alternatively, although Bell had detected a slight sound on his first test, the bullet may have been lodged too deeply to be detected by the crude apparatus.[160]
Bell’s own detailed account, presented to the American Association for the Advancement of Science in 1882, differs in several particulars from most of the many and varied versions now in circulation, by concluding that extraneous metal was not to blame for failure to locate the bullet. Perplexed by the peculiar results he had obtained during an examination of Garfield, Bell «proceeded to the Executive Mansion the next morning … to ascertain from the surgeons whether they were perfectly sure that all metal had been removed from the neighborhood of the bed. It was then recollected that underneath the horse-hair mattress on which the President lay was another mattress composed of steel wires. Upon obtaining a duplicate, the mattress was found to consist of a sort of net of woven steel wires, with large meshes. The extent of the [area that produced a response from the detector] having been so small, as compared with the area of the bed, it seemed reasonable to conclude that the steel mattress had produced no detrimental effect.» In a footnote, Bell adds, «The death of President Garfield and the subsequent post-mortem examination, however, proved that the bullet was at too great a distance from the surface to have affected our apparatus.»[161]
Hydrofoils
Main article: HD-4

Bell’s HD-4 on a test run ca. 1919
The March 1906 Scientific American article by American pioneer William E. Meacham explained the basic principle of hydrofoils and hydroplanes. Bell considered the invention of the hydroplane as a very significant achievement. Based on information gained from that article, he began to sketch concepts of what is now called a hydrofoil boat. Bell and assistant Frederick W. «Casey» Baldwin began hydrofoil experimentation in the summer of 1908 as a possible aid to airplane takeoff from water. Baldwin studied the work of the Italian inventor Enrico Forlanini and began testing models. This led him and Bell to the development of practical hydrofoil watercraft.
During his world tour of 1910–11, Bell and Baldwin met with Forlanini in France. They had rides in the Forlanini hydrofoil boat over Lake Maggiore. Baldwin described it as being as smooth as flying. On returning to Baddeck, a number of initial concepts were built as experimental models, including the Dhonnas Beag (Scottish Gaelic for ‘little devil’), the first self-propelled Bell-Baldwin hydrofoil.[162] The experimental boats were essentially proof-of-concept prototypes that culminated in the more substantial HD-4, powered by Renault engines. A top speed of 54 miles per hour (87 km/h) was achieved, with the hydrofoil exhibiting rapid acceleration, good stability, and steering, along with the ability to take waves without difficulty.[163] In 1913, Dr. Bell hired Walter Pinaud, a Sydney yacht designer and builder as well as the proprietor of Pinaud’s Yacht Yard in Westmount, Nova Scotia, to work on the pontoons of the HD-4. Pinaud soon took over the boatyard at Bell Laboratories on Beinn Bhreagh, Bell’s estate near Baddeck, Nova Scotia. Pinaud’s experience in boatbuilding enabled him to make useful design changes to the HD-4. After the First World War, work began again on the HD-4. Bell’s report to the U.S. Navy permitted him to obtain two 350-horsepower (260-kilowatt) engines in July 1919. On September 9, 1919, the HD-4 set a world marine speed record of 70.86 miles per hour (114.04 kilometres per hour),[164] a record which stood for ten years.
Aeronautics

In 1891, Bell had begun experiments to develop motor-powered heavier-than-air aircraft. The AEA was first formed as Bell shared the vision to fly with his wife, who advised him to seek «young» help as Bell was at the age of 60.
In 1898, Bell experimented with tetrahedral box kites and wings constructed of multiple compound tetrahedral kites covered in maroon silk.[N 21] The tetrahedral wings were named Cygnet I, II, and III, and were flown both unmanned and manned (Cygnet I crashed during a flight carrying Selfridge) in the period from 1907 to 1912. Some of Bell’s kites are on display at the Alexander Graham Bell National Historic Site.[166]
Bell was a supporter of aerospace engineering research through the Aerial Experiment Association (AEA), officially formed at Baddeck, Nova Scotia, in October 1907 at the suggestion of his wife Mabel and with her financial support after the sale of some of her real estate.[167] The AEA was headed by Bell and the founding members were four young men: American Glenn H. Curtiss, a motorcycle manufacturer at the time and who held the title «world’s fastest man», having ridden his self-constructed motor bicycle around in the shortest time, and who was later awarded the Scientific American Trophy for the first official one-kilometre flight in the Western hemisphere, and who later became a world-renowned airplane manufacturer; Lieutenant Thomas Selfridge, an official observer from the U.S. Federal government and one of the few people in the army who believed that aviation was the future; Frederick W. Baldwin, the first Canadian and first British subject to pilot a public flight in Hammondsport, New York; and J. A. D. McCurdy–Baldwin and McCurdy being new engineering graduates from the University of Toronto.[168]
The AEA’s work progressed to heavier-than-air machines, applying their knowledge of kites to gliders. Moving to Hammondsport, the group then designed and built the Red Wing, framed in bamboo and covered in red silk and powered by a small air-cooled engine.[169] On March 12, 1908, over Keuka Lake, the biplane lifted off on the first public flight in North America.[N 22][N 23] The innovations that were incorporated into this design included a cockpit enclosure and tail rudder (later variations on the original design would add ailerons as a means of control). One of the AEA’s inventions, a practical wingtip form of the aileron, was to become a standard component on all aircraft.[N 24] The White Wing and June Bug were to follow and by the end of 1908, over 150 flights without mishap had been accomplished. However, the AEA had depleted its initial reserves and only a $15,000 grant from Mrs. Bell allowed it to continue with experiments.[170] Lt. Selfridge had also become the first person killed in a powered heavier-than-air flight in a crash of the Wright Flyer at Fort Myer, Virginia, on September 17, 1908.
Their final aircraft design, the Silver Dart, embodied all of the advancements found in the earlier machines. On February 23, 1909, Bell was present as the Silver Dart flown by J. A. D. McCurdy from the frozen ice of Bras d’Or made the first aircraft flight in Canada.[171] Bell had worried that the flight was too dangerous and had arranged for a doctor to be on hand. With the successful flight, the AEA disbanded and the Silver Dart would revert to Baldwin and McCurdy, who began the Canadian Aerodrome Company and would later demonstrate the aircraft to the Canadian Army.[172]
Heredity and genetics
Bell, along with many members of the scientific community at the time, took an interest in the popular science of heredity which grew out of the publication of Charles Darwin’s book On the Origin of Species in 1859.[173] On his estate in Nova Scotia, Bell conducted meticulously recorded breeding experiments with rams and ewes. Over the course of more than 30 years, Bell sought to produce a breed of sheep with multiple nipples that would bear twins.[174] He specifically wanted to see if selective breeding could produce sheep with four functional nipples with enough milk for twin lambs.[175] This interest in animal breeding caught the attention of scientists focused on the study of heredity and genetics in humans.[176]
In November 1883, Bell presented a paper at a meeting of the National Academy of Sciences titled «Upon the Formation of a Deaf Variety of the Human Race».[177] The paper is a compilation of data on the hereditary aspects of deafness. Bell’s research indicated that a hereditary tendency toward deafness, as indicated by the possession of deaf relatives, was an important element in determining the production of deaf offspring. He noted that the proportion of deaf children born to deaf parents was many times greater than the proportion of deaf children born to the general population.[178] In the paper, Bell delved into social commentary and discussed hypothetical public policies to bring an end to deafness. He also criticized educational practices that segregated deaf children rather than integrated them fulling into mainstream classrooms. The paper did not propose sterilization of deaf people or prohibition on intermarriage,[179] noting that «We cannot dictate to men and women whom they should marry and natural selection no longer influences mankind to any great extent.»[177]
A review of Bell’s «Memoir upon the Formation of a Deaf Variety of the Human Race» appearing in an 1885 issue of the «American Annals of the Deaf and Dumb» states that «Dr. Bell does not advocate legislative interference with the marriages of the deaf for several reasons one of which is that the results of such marriages have not yet been sufficiently investigated.» The article goes on to say that «the editorial remarks based thereon did injustice to the author.»[180] The paper’s author concludes by saying «A wiser way to prevent the extension of hereditary deafness, it seems to us, would be to continue the investigations which Dr. Bell has so admirable begun until the laws of the transmission of the tendency to deafness are fully understood, and then by explaining those laws to the pupils of our schools to lead them to choose their partners in marriage in such a way that deaf-mute offspring will not be the result.»[180]
Historians have noted that Bell explicitly opposed laws regulating marriage, and never mentioned sterilization in any of his writings. Even after Bell agreed to engage with scientists conducting eugenic research, he consistently refused to support public policy that limited the rights or privileges of the deaf.[181]
Bell’s interest and research on heredity attracted the interest of Charles Davenport, a Harvard professor and head of the Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. In 1906, Davenport, who was also the founder of the American Breeder’s Association, approached Bell about joining a new committee on eugenics chaired by David Starr Jordan. In 1910, Davenport opened the Eugenics Records office at Cold Spring Harbor. To give the organization scientific credibility, Davenport set up a Board of Scientific Directors naming Bell as chairman.[182] Other members of the board included Luther Burbank, Roswell H. Johnson, Vernon L. Kellogg, and William E. Castle.[182]
In 1921, a Second International Congress of Eugenics was held in New York at the Museum of Natural History and chaired by Davenport. Although Bell did not present any research or speak as part of the proceedings, he was named as honorary president as a means to attract other scientists to attend the event.[183] A summary of the event notes that Bell was a «pioneering investigator in the field of human heredity».[183]
Death
Bell died of complications arising from diabetes on August 2, 1922, at his private estate in Cape Breton, Nova Scotia, at age 75.[184] Bell had also been affected by pernicious anemia.[185] His last view of the land he had inhabited was by moonlight on his mountain estate at 2:00 a.m.[N 25][188][N 26] While tending to him after his long illness, Mabel, his wife, whispered, «Don’t leave me.» By way of reply, Bell signed «no…», lost consciousness, and died shortly after.[189][190]
On learning of Bell’s death, the Canadian Prime Minister, Mackenzie King, cabled Mrs. Bell, saying:[189]
My colleagues in the Government join with me in expressing to you our sense of the world’s loss in the death of your distinguished husband. It will ever be a source of pride to our country that the great invention, with which his name is immortally associated, is a part of its history. On the behalf of the citizens of Canada, may I extend to you an expression of our combined gratitude and sympathy.
Bell’s coffin was constructed of Beinn Bhreagh pine by his laboratory staff, lined with the same red silk fabric used in his tetrahedral kite experiments. To help celebrate his life, his wife asked guests not to wear black (the traditional funeral color) while attending his service, during which soloist Jean MacDonald sang a verse of Robert Louis Stevenson’s «Requiem»:[191]
Under a wide and starry sky,
Dig the grave and let me lie.
Glad did I live and gladly die
And I laid me down with a will.
Upon the conclusion of Bell’s funeral, for one minute at 6:25 p.m. Eastern Time,[192] «every phone on the continent of North America was silenced in honor of the man who had given to mankind the means for direct communication at a distance».[146][193]
Alexander Graham Bell was buried atop Beinn Bhreagh mountain, on his estate where he had resided increasingly for the last 35 years of his life, overlooking Bras d’Or Lake.[189] He was survived by his wife Mabel, his two daughters, Elsie May and Marian, and nine of his grandchildren.[189][194]
Legacy and honors

Honors and tributes flowed to Bell in increasing numbers as his invention became ubiquitous and his personal fame grew. Bell received numerous honorary degrees from colleges and universities to the point that the requests almost became burdensome.[197] During his life, he also received dozens of major awards, medals, and other tributes. These included statuary monuments to both him and the new form of communication his telephone created, including the Bell Telephone Memorial erected in his honor in Alexander Graham Bell Gardens in Brantford, Ontario, in 1917.[198]

A quote by Alexander Graham Bell engraved in the stone wall within the Peace Chapel of the International Peace Garden (in Manitoba Canada and North Dakota, USA).
A large number of Bell’s writings, personal correspondence, notebooks, papers, and other documents reside in both the United States Library of Congress Manuscript Division (as the Alexander Graham Bell Family Papers),[197] and at the Alexander Graham Bell Institute, Cape Breton University, Nova Scotia; major portions of which are available for online viewing.
A number of historic sites and other marks commemorate Bell in North America and Europe, including the first telephone companies in the United States and Canada. Among the major sites are:
- The Alexander Graham Bell National Historic Site, maintained by Parks Canada, which incorporates the Alexander Graham Bell Museum, in Baddeck, Nova Scotia, close to the Bell estate Beinn Bhreagh[199]
- The Bell Homestead National Historic Site, includes the Bell family home, «Melville House», and farm overlooking Brantford, Ontario and the Grand River. It was their first home in North America;
- Canada’s first telephone company building, the «Henderson Home» of the late 1870s, a predecessor of the Bell Telephone Company of Canada (officially chartered in 1880). In 1969, the building was carefully moved to the historic Bell Homestead National Historic Site in Brantford, Ontario, and was refurbished to become a telephone museum. The Bell Homestead, the Henderson Home telephone museum, and the National Historic Site’s reception centre are all maintained by the Bell Homestead Society;[200]
- The Alexander Graham Bell Memorial Park, which features a broad neoclassical monument built in 1917 by public subscription. The monument depicts mankind’s ability to span the globe through telecommunications;[201]
- The Alexander Graham Bell Museum (opened in 1956), part of the Alexander Graham Bell National Historic Site which was completed in 1978 in Baddeck, Nova Scotia. Many of the museum’s artifacts were donated by Bell’s daughters;

In 1880, Bell received the Volta Prize with a purse of 50,000 French francs (approximately US$290,000 in today’s dollars[202]) for the invention of the telephone from the French government.[189][203][204][205][206][207] Among the luminaries who judged were Victor Hugo and Alexandre Dumas, fils.[208][better source needed] The Volta Prize was conceived by Napoleon III in 1852, and named in honor of Alessandro Volta, with Bell becoming the second recipient of the grand prize in its history.[209][210] Since Bell was becoming increasingly affluent, he used his prize money to create endowment funds (the ‘Volta Fund’) and institutions in and around the United States capital of Washington, D.C.. These included the prestigious ‘Volta Laboratory Association’ (1880), also known as the Volta Laboratory and as the ‘Alexander Graham Bell Laboratory’, and which eventually led to the Volta Bureau (1887) as a center for studies on deafness which is still in operation in Georgetown, Washington, D.C. The Volta Laboratory became an experimental facility devoted to scientific discovery, and the very next year it improved Edison’s phonograph by substituting wax for tinfoil as the recording medium and incising the recording rather than indenting it, key upgrades that Edison himself later adopted.[211] The laboratory was also the site where he and his associate invented his «proudest achievement», «the photophone», the «optical telephone» which presaged fibre optical telecommunications while the Volta Bureau would later evolve into the Alexander Graham Bell Association for the Deaf and Hard of Hearing (the AG Bell), a leading center for the research and pedagogy of deafness.
In partnership with Gardiner Greene Hubbard, Bell helped establish the publication Science during the early 1880s. In 1898, Bell was elected as the second president of the National Geographic Society, serving until 1903, and was primarily responsible for the extensive use of illustrations, including photography, in the magazine.[212] He also served for many years as a Regent of the Smithsonian Institution (1898–1922).[213] The French government conferred on him the decoration of the Légion d’honneur (Legion of Honor); the Royal Society of Arts in London awarded him the Albert Medal in 1902; the University of Würzburg, Bavaria, granted him a PhD, and he was awarded the Franklin Institute’s Elliott Cresson Medal in 1912. He was one of the founders of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers in 1884 and served as its president from 1891 to 1892. Bell was later awarded the AIEE’s Edison Medal in 1914 «For meritorious achievement in the invention of the telephone».[214]
The bel (B) and the smaller decibel (dB) are units of measurement of sound pressure level (SPL) invented by Bell Labs and named after him.[215] [N 28][216] Since 1976, the IEEE’s Alexander Graham Bell Medal has been awarded to honor outstanding contributions in the field of telecommunications.

In 1936, the US Patent Office declared Bell first on its list of the country’s greatest inventors,[217] leading to the US Post Office issuing a commemorative stamp honoring Bell in 1940 as part of its ‘Famous Americans Series’. The First Day of Issue ceremony was held on October 28 in Boston, Massachusetts, the city where Bell spent considerable time on research and working with the deaf. The Bell stamp became very popular and sold out in little time. The stamp became, and remains to this day, the most valuable one of the series.[218]
The 150th anniversary of Bell’s birth in 1997 was marked by a special issue of commemorative £1 banknotes from the Royal Bank of Scotland. The illustrations on the reverse of the note include Bell’s face in profile, his signature, and objects from Bell’s life and career: users of the telephone over the ages; an audio wave signal; a diagram of a telephone receiver; geometric shapes from engineering structures; representations of sign language and the phonetic alphabet; the geese which helped him to understand flight; and the sheep which he studied to understand genetics.[219] Additionally, the Government of Canada honored Bell in 1997 with a C$100 gold coin, in tribute also to the 150th anniversary of his birth, and with a silver dollar coin in 2009 in honor of the 100th anniversary of flight in Canada. That first flight was made by an airplane designed under Dr. Bell’s tutelage, named the Silver Dart.[220] Bell’s image, and also those of his many inventions have graced paper money, coinage, and postal stamps in numerous countries worldwide for many dozens of years.
Alexander Graham Bell was ranked 57th among the 100 Greatest Britons (2002) in an official BBC nationwide poll,[221] and among the Top Ten Greatest Canadians (2004), and the 100 Greatest Americans (2005). In 2006, Bell was also named as one of the 10 greatest Scottish scientists in history after having been listed in the National Library of Scotland’s ‘Scottish Science Hall of Fame’.[222] Bell’s name is still widely known and used as part of the names of dozens of educational institutes, corporate namesakes, street and place names around the world.

Bell, an alumnus of the University of Edinburgh, Scotland, receiving an honorary Doctor of Laws degree (LL.D.) at the university in 1906
Honorary degrees
Alexander Graham Bell, who could not complete the university program of his youth, received at least a dozen honorary degrees from academic institutions, including eight honorary LL.D.s (Doctorate of Laws), two Ph.D.s, a D.Sc., and an M.D.:[223]
- Gallaudet College (then named National Deaf-Mute College) in Washington, D.C. (Ph.D.) in 1880[224][225]
- University of Würzburg in Würzburg, Bavaria (Ph.D.) in 1882[224]
- Heidelberg University in Heidelberg, Germany (M.D.) in 1886[224][36]
- Harvard University in Cambridge, Massachusetts (LL.D.) in 1896[224]
- Illinois College, in Jacksonville, Illinois (LL.D.) in 1896, possibly 1881[224][226]
- Amherst College in Amherst, Massachusetts (LL.D.) in 1901[224]
- St. Andrew’s University in St Andrews, Scotland (LL.D) in 1902[224]
- University of Oxford in Oxford, England (D.Sc.) in 1906[224]
- University of Edinburgh in Edinburgh, Scotland (LL.D.) in 1906[224][227]
- George Washington University in Washington, D.C. (LL.D.) in 1913[224]
- Queen’s University at Kingston in Kingston, Ontario, Canada (LL.D.) in 1908[224][228]
- Dartmouth College in Hanover, New Hampshire (LL.D.) in 1913,[229] possibly 1914[224]
Portrayal in film and television
- The 1939 film The Story of Alexander Graham Bell was based on his life and works.[230]
- The 1992 film The Sound and the Silence was a TV film.
- Biography aired an episode Alexander Graham Bell: Voice of Invention on August 6, 1996.
- Eyewitness No. 90 A Great Inventor Is Remembered, a 1957 NFB short about Bell.
Bibliography
- Bell, Alexander Graham (October 1880). «On the Production and Reproduction of Sound by Light». American Journal of Science (Read before the American Association for the Advancement of Science, in Boston, August 27, 1880). Third. 20 (118): 305–324. Bibcode:1880AmJS…20..305B. doi:10.2475/ajs.s3-20.118.305. S2CID 130048089.
Also published as: Bell, Alexander Graham (September 23, 1880). «Selenium and the Photophone». Nature. 22 (569): 500–503. Bibcode:1880Natur..22..500.. doi:10.1038/022500a0. - Bell, Alexander Graham (1898). The Question of Sign-Language and The Utility of Signs in the Instruction of the Deaf—Two papers (PDF). Washington, D.C.: Sanders Printing Office. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 29, 2012. Retrieved January 2, 2012.
- Bell, Alexander Graham (February 1917). «Prizes for the Inventor: Some of the Problems Awaiting Solution». The National Geographic Magazine. Vol. 31, no. 2. National Geographic Society. pp. 131–146.
See also
- Alexander Graham Bell Association for the Deaf and Hard of Hearing
- Alexander Graham Bell National Historic Site
- Bell Boatyard
- Bell Homestead National Historic Site
- Bell Telephone Memorial
- Berliner, Emile
- Bourseul, Charles
- IEEE Alexander Graham Bell Medal
- John Peirce, submitted telephone ideas to Bell
- Manzetti, Innocenzo
- Meucci, Antonio
- Oriental Telephone Company
- People on Scottish banknotes
- Pioneers, a Volunteer Network
- Reis, Philipp
- The Story of Alexander Graham Bell, a 1939 movie of his life
- The Telephone Cases
- Volta Laboratory and Bureau
- William Francis Channing, submitted telephone ideas to Bell
References
Notes
- ^ Bell was a British subject for most of his early life. When he moved to Canada in 1870, Canadian and British citizenship were functionally identical, with Canadian citizenship only becoming a formal classification in 1910. He applied for American citizenship after 1877, gained it in 1882, and referred to himself as an American citizen from that point on. Quote from Bell speaking to his wife: «you are a citizen because you can’t help it – you were born one, but I chose to be one.»[5] Aside from Bell’s own view of his citizenship, many, if not most Canadians considered him also as one of theirs as evidenced in an address by the Governor General of Canada. On October 24, 1917, in Brantford, Ontario, the Governor General spoke at the unveiling of the Bell Telephone Memorial to an audience numbering in the thousands, saying: «Dr. Bell is to be congratulated upon being able to receive the recognition of his fellow citizens and fellow countrymen».[6]
- ^ From Black (1997), p. 18: «He thought he could harness the new electronic technology by creating a machine with a transmitter and receiver that would send sounds telegraphically to help people hear.»
- ^ After Bell’s death his wife Mabel wrote to John J. Carty, an AT&T vice-president, and commented on her husband’s reluctance to have a phone in his study, saying «[of the statements in the newspapers] …publishing of Mr. Bell’s dislike of the telephone. Of course, he never had one in his study. That was where he went when he wanted to be alone with his thoughts and his work. The telephone, of course, means intrusion by the outside world. And the little difficulties and delays often attending the establishment of conversation… did irritate him, so that as a rule he preferred having others send and receive messages. But all really important business over the telephone he transacted himself. There are few private houses more completely equipped with telephones than ours… and there was nothing that Mr. Bell was more particular about than our telephone service… We never could have come here [to Beinn Bhreagh] in the first place or continued here, but for the telephone which kept us in close touch with doctors and neighbors and the regular telegraph office… Mr. Bell did like to say in fun, «Why did I ever invent the Telephone,» but no one had a higher appreciation of its indispensableness or used it more freely when need was—either personally or by deputy—and he was really tremendously proud of it and all it was accomplishing.»[10]
- ^ Bell typically signed his name in full on his correspondence.
- ^ Helmholtz’s The Sensations of Tone is credited with inspiring Bell, at the age of 23, to further his studies of electricity and electromagnetism.[36]
- ^ The family pet was given to his brother’s family.
- ^ The estate, dating from 1858, is in the present day located at 94 Tutela Heights Road, Brantford, and is now known as the «Bell Homestead», and formally as the Bell Homestead National Historic Site of Canada. It received its historical designation from the Government of Canada on June 1, 1996.[49]
- ^ Bell would later write that he had come to Canada a «dying man».
- ^ Bell was thrilled at his recognition by the Six Nations Reserve and throughout his life would launch into a Mohawk war dance when he was excited.
- ^ In later years, Bell described the invention of the telephone and linked it to his «dreaming place».
- ^ Eber (1991), p. 43 claimed that Mabel had scarlet fever in New York «…shortly before her fifth birthday…«; however, Toward (1984) provided a detailed chronology of the event claiming «… shortly after their arrival in New York [in January 1863]» when Mabel would have been at least five years and five weeks of age. Mabel’s exact age when she became deaf would later play a part in the debate on the effectiveness of manual versus oral education for deaf children, as children who are older at the onset of deafness retain greater vocalization skills and are thus more successful in oral education programs. Some of the debate centred on whether Mabel had to relearn oral speech from scratch, or whether she never lost it.
- ^ From Alexander Graham Bell (1979), p. 8: «Brantford is justified in calling herself ‘The Telephone City’ because the telephone originated there. It was invented in Brantford at Tutela Heights in the summer of 1874.»
- ^ Hubbard’s financial support to the research efforts fell far short of the funds needed, necessitating Bell to continue teaching while conducting his experiments.[83] Bell was so short of funds at times that he had to borrow money from his own employee, Thomas Watson. Bell also sought an additional CAD$150 from the former Premier of Canada, George Brown, in exchange for 50% of the patent rights in the British Empire (Brown later retracted his offer to patent the telephone in the U.K. for fear of being ridiculed). The Bell Patent Association, composed of Hubbard, Sanders and Bell and which would become the precursor of the Bell Telephone Company (and later, AT&T), would later assign an approximate 10% interest of its shares to Watson,[7] in lieu of salary and for his earlier financial support to Bell while they worked together creating their first functional telephone.
- ^ A copy of a draft of the patent application is shown, described as «probably the most valuable patent ever.»
- ^ Meucci was not involved in the final trial.[clarification needed]
- ^ Tomas Farley also writes that «Nearly every scholar agrees that Bell and Watson were the first to transmit intelligible speech by electrical means. Others transmitted a sound or a click or a buzz but our boys [Bell and Watson] were the first to transmit speech one could understand.»[126]
- ^ Many of the lawsuits became rancorous, with Elisha Gray becoming particularly bitter over Bell’s ascendancy in the telephone debate, but Bell refused to launch a countersuit for libel.[citation needed]
- ^ Marian was born only days after Bell and his assistant Sumner Tainter had successfully tested their new wireless telecommunication invention at their Volta Laboratory, one which Bell would name as his greatest achievement. Bell was so ecstatic that he wanted to jointly name his new invention and his new daughter Photophone (Greek: «light–sound«),[138][139] Bell wrote: «Only think!—Two babies in one week! Mabel’s baby was light enough at birth but mine was LIGHT ITSELF! Mabel’s baby screamed inarticulately but mine spoke with distinct enunciation from the first.» Bell’s suggested scientific name for their new infant daughter did not go over well with Marian’s mother, Mabel Gardiner Hubbard Bell.[138]
- ^ Under the direction of the Boston architects, Cabot, Everett & Mead, a Nova Scotia company, Rhodes, Curry & Company, carried out the actual construction.
- ^ In one memorable incident, the newly arrived Bells were walking down one of Baddeck’s central streets when Bell peered into a storefront window and saw a frustrated shopkeeper fiddling with his problematic telephone. Bell quickly disassembled it and effected a repair, to the owner’s amazement. When asked how he was able to do so Bell only needed to introduce himself.
- ^ Bell was inspired in part by Australian aeronautical engineer Lawrence Hargrave’s work with man-carrying box kites.[165] Hargrave declined to take patents on his inventions, similar to Bell’s decision not to file patents on some of his inventions. Bell also chose maroon-colored silk as it would show up clearly against the light-colored sky in his photographic studies.
- ^ «Selfridge Aerodrome Sails Steadily for 319 feet (97 m).» The Washington Post May 13, 1908.
- ^ At 25 to 30 Miles an Hour. First Public Trip of Heavier-than-air Car in America. Professor Alexander Graham Bell’s New Machine, Built After Plans by Lieutenant Selfridge, Shown to Be Practicable by Flight Over Keuka Lake. Portion of Tail Gives Way, Bringing the Test to an End. Views of an Expert. Hammondsport, New York, March 12, 1908.
- ^ The aileron had been conceived of as early as 1868 by British inventor M.P.W. Boulton and was also created independently by Robert Esnault-Pelterie and several others.
- ^ In the last years of his life, as his final projects wound down, Bell and his wife, their extended family and friends, lived exclusively at their beloved Beinn Bhreagh.[186][187]
- ^ From Bethune (2009), p. 119: «[his end came] at 2:00 am… His wife, Mabel, daughter Daisy, and son-in-law David Fairchild had gathered around him. His last view was of the moon rising above the mountain he loved».
- ^
The Charles Fleetford Sise Chapter of the Telephone Pioneers of America commissioned and dedicated the large bronze statue of Bell in the front portico of Brantford, Ontario’s new Bell Telephone Building plant on June 17, 1949. Attending the formal ceremony were Bell’s daughter, Mrs. Gillbert Grosvenor, Frederick Johnson, President of the Bell Telephone Company of Canada, T.N. Lacy, President of the Telephone Pioneers, and Brantford Mayor Walter J. Dowden. To each side of the portico facing the monument are the engraved inscriptions «In Grateful Recognition of the Inventor of the Telephone». Its dedication was broadcast live nationally by the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation.[195][196] - ^ The decibel is defined as one tenth of a bel.
Citations
- ^ Boileau, John (2004). Fastest in the World: The Saga of Canada’s Revolutionary Hydrofoils. Halifax, Nova Scotia: Formac Publishing. p. 12. ISBN 978-0-88780-621-6.
- ^ [Is the following a quote from the source referenced?:] While Bell worked in many scientific, technical, professional and social capacities throughout his life he would remain fondest of his earliest vocation. To the end of his days, when discussing himself, Bell would always add with pride «I am a teacher of the deaf».[1]
- ^ «Particle Physics Resurrects Alexander Graham Bell’s Voice». IEEE Spectrum. April 30, 2018. Retrieved May 10, 2018.
- ^ «The Bell Family». Bell Homestead National Historic Site. Retrieved September 27, 2013.
- ^ Gray 2006, p. 228.
- ^ Reville, F. Douglas (1920). History of the County of Brant: Illustrated With Fifty Half-Tones Taken From Miniatures And Photographs (PDF). Brantford, Ontario: Brantford Historical Society & Hurley Printing. p. 319. Archived from the original (PDF) on April 19, 2012. Retrieved May 4, 2012.
- ^ a b Bruce 1990, p. 291.
- ^ Bruce, Robert V. (1990). Bell: Alexander Bell and the Conquest of Solitude. Ithaca, New York: Cornell University Press. p. 419. ISBN 978-0-8014-9691-2.
- ^ MacLeod, Elizabeth (1999). Alexander Graham Bell: An Inventive Life. Toronto, Ontario: Kids Can Press. p. 19. ISBN 978-1-55074-456-9.
- ^ Bell, Mabel (October 1922). «Dr. Bell’s Appreciation of the Telephone Service». Bell Telephone Quarterly. 1 (3): 65. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ Howley, Andrew (May 26, 2011). «NGS Celebrates 23rd Founders Day». NGS. National Geographic Society. Retrieved January 18, 2016.
Though he wasn’t one of the original 33 founders, Bell had a major influence on the Society.
- ^ Stansfield, W. D. (January 1, 2005). «The Bell Family Legacies». Journal of Heredity. 96 (1): 1–3. doi:10.1093/jhered/esi007. ISSN 0022-1503. PMID 15618310.
- ^ Petrie, A. Roy (1975). Alexander Graham Bell. Don Mills, Ontario: Fitzhenry & Whiteside. p. 4. ISBN 978-0-88902-209-6.
- ^ «Time Line of Alexander Graham Bell.» memory.loc.goiv. Retrieved: July 28, 2010. Archived October 24, 2005, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «Alexander M. Bell Dead. Father of Prof. A. G. Bell Developed Sign Language for Mutes». The New York Times. August 8, 1905. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ «Call me Alexander Graham Bell». The Franklin Institute. January 14, 2014. Archived from the original on February 24, 2015. Retrieved February 24, 2015.
- ^ Groundwater, Jennifer (2005). Alexander Graham Bell: The Spirit of Invention. Calgary, Alberta: Altitude Publishing. p. 23. ISBN 978-1-55439-006-9.
- ^ Bruce 1990, pp. 17–19.
- ^ Bruce 1990, p. 490.
- ^ a b Bruce 1990, p. 16.
- ^ a b c Gray 2006, p. 8.
- ^ Gray 2006, p. 9.
- ^ Mackay, James (1997). Sounds Out of Silence: A life of Alexander Graham Bell. Edinburgh, UK: Mainstream Publishing. p. 25. ISBN 978-1-85158-833-6.
- ^ a b Petrie 1975, p. 7.
- ^ Mackay 1997, p. 31.
- ^ Gray 2006, p. 11.
- ^ Town, Florida (1988). Alexander Graham Bell. Toronto, Ontario: Grolier. p. 7. ISBN 978-0-7172-1950-6.
- ^ Bruce 1990, p. 37.
- ^ Shulman, Seth (2008). The Telephone Gambit: Chasing Alexander Bell’s Secret. New York: Norton & Company. p. 49. ISBN 978-0-393-06206-9.
- ^ a b c Groundwater 2005, p. 25.
- ^ Petrie 1975, pp. 7–9.
- ^ Petrie 1975, p. 9.
- ^ Messenger, Stephen. «Before Inventing The Telephone, Alexander Graham Bell Tried To Teach His Dog To Talk». The Dodo. Retrieved January 30, 2021.
- ^ a b Groundwater 2005, p. 30.
- ^ Shulman 2008, p. 46.
- ^ a b c Surtees, Lawrence (2005). «BELL, ALEXANDER GRAHAM». In Cook, Ramsay; Bélanger, Réal (eds.). Dictionary of Canadian Biography. Vol. XV (1921–1930) (online ed.). University of Toronto Press. Retrieved March 6, 2009.
- ^ MacKenzie, Catherine (2003) [1928]. Alexander Graham Bell. Boston, Massachusetts: Grosset and Dunlap. p. 41. ISBN 978-0-7661-4385-2.
- ^ Groundwater 2005, p. 31.
- ^ Shulman 2008, pp. 46–48.
- ^ Micklos, John Jr. (2006). Alexander Graham Bell: Inventor of the Telephone. New York: HarperCollins. p. 8. ISBN 978-0-06-057618-9.
- ^ Bruce 1990, p. 45.
- ^ Bruce 1990, pp. 67–28.
- ^ Bruce 1990, p. 68.
- ^ Groundwater 2005, p. 33.
- ^ Mackay 1997, p. 50.
- ^ Gray 2006, p. 21.
- ^ «Reverend Thomas Henderson House». Canada’s Historic Places. Retrieved August 5, 2020.
- ^ Mackay 1997, p. 61.
- ^ Bell Homestead National Historic Site of Canada. Canadian Register of Historic Places. Retrieved September 17, 2015.
- ^ Wing, Chris (1980). Alexander Graham Bell at Baddeck. Baddeck, Nova Scotia: Christopher King. p. 10.
- ^ Groundwater 2005, p. 34.
- ^ Mackay 1997, p. 62.
- ^ Groundwater 2005, p. 35.
- ^ Wing 1980, p. 10.
- ^ Waldie, Jean H. «Historic Melodeon Is Given To Bell Museum». likely published either by the London Free Press or by the Brantford Expositor, date unknown.
- ^ Bruce 1990, p. 74.
- ^ Town 1988, p. 12.
- ^ Alexander Graham Bell ((booklet)). Halifax, Nova Scotia: Maritime Telegraph & Telephone Limited. 1979. p. 8.
- ^ a b Groundwater 2005, p. 39.
- ^ Petrie 1975, p. 14.
- ^ Petrie 1975, p. 15.
- ^ Town 1988, pp. 12–13.
- ^ Petrie 1975, p. 17.
- ^ Schoenherr, Steven E. (February 10, 2000). «Charles Sumner Tainter and the Graphophone». Recording Technology History. Audio Engineering Society. Retrieved September 19, 2015.
- ^ Hochfelder, David (July 31, 2015). «Alexander Graham Bell». Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ «Image 1 of Pamphlet by Alexander Graham Bell, 1898». Library of Congress, Washington, D.C. Retrieved June 11, 2021.
- ^ «Alexander Graham Bell and His Role in Oral Education». Disabilitymuseum.org.
- ^ Miller, Don; Branson, Jan (2002). Damned For Their Difference: The Cultural Construction Of Deaf People as Disabled: A Sociological History. Washington, D.C.: Gallaudet University Press. pp. 30–31, 152–153. ISBN 978-1-56368-121-9.
- ^ Jay, Michelle (January 2, 2020). «Alexander Graham Bell — Helpful or Harmful? | Start ASL». Retrieved March 11, 2022.
- ^ «Eugenics and Deaf People in 20th Century America». Medium. May 11, 2021. Retrieved June 28, 2022.
- ^ «A Deaf Variety Of The Human Race». Gallaudet University. Retrieved March 11, 2022.
- ^ Town 1988, p. 15.
- ^ Town 1988, p. 16.
- ^ Toward, Lilias M. (1984). Mabel Bell: Alexander’s Silent Partner. Toronto, Ontario: Methuen. p. 1. ISBN 978-0-458-98090-1.
- ^ Eber, Dorothy Harley (1991) [1982]. Genius at Work: Images of Alexander Graham Bell (reprint ed.). Toronto, Ontario: McClelland and Stewart. p. 43. ISBN 978-0-7710-3036-9.
- ^ Dunn, Andrew (1990). Alexander Graham Bell. (Pioneers of Science). East Sussex, UK: Wayland Publishers. p. 20. ISBN 978-1-85210-958-5.
- ^ «Alexander Graham Bell and Thomas Watson». CBC. July 25, 1975. Retrieved October 14, 2016.
- ^ Matthews, Tom L. (1999). Always Inventing: A Photobiography of Alexander Graham Bell. Washington, D.C.: National Geographic Society. pp. 19–21. ISBN 978-0-7922-7391-2.
- ^ Matthews 1999, p. 21.
- ^ McCormick, Blaine; Israel, Paul (January–February 2005). «Underrated entrepreneur: Thomas Edison’s overlooked business story». IEEE Power & Energy Magazine. 3 (1): 76–79. doi:10.1109/MPAE.2005.1380243. S2CID 19680450. Archived from the original on December 23, 2009.
- ^ Town 1988, p. 17.
- ^ Evenson 2000, pp. 18–25.
- ^ Fitzgerald, Brian (September 14, 2001). «Alexander Graham Bell: The BU Years». B.U. Bridge. Vol. V, no. 5. Boston University. Retrieved March 28, 2010.
- ^ Bruce 1990, pp. 158–159.
- ^ US 174465 Alexander Graham Bell: «Improvement in Telegraphy» filed on February 14, 1876, granted on March 7, 1876.
- ^ MacLeod 1999, pp. 12–13.
- ^ «Alexander Graham Bell – Lab notebook pp. 40–41 (image 22)». Quotegrab. IAP Quotegrab. August 2, 2019. Retrieved September 17, 2019.
- ^ MacLeod 1999, p. 12.
- ^ Shulman 2008, p. 211.
- ^ Evenson 2000, p. 99.
- ^ Evenson 2000, p. 98.
- ^ Evenson 2000, p. 100.
- ^ Evenson 2000, pp. 81–82.
- ^ «Mr. Wilbur «confesses»«. The Washington Post. May 22, 1886. p. 1.
- ^ Evenson, A Edward (November 10, 2000). The Telephone Patent Conspiracy of 1876: The Elisha Gray-Alexander Bell Controversy and Its Many Players. McFarland. p. 99. ISBN 0786408839.
- ^ «Alexander Graham Bell 1847–1922 Inventor of the Bell System». Telecommunications Canada. Retrieved January 14, 2020.
- ^ «Invention of the Telephone National Historic Event». Parks Canada. Retrieved January 14, 2020.
Bell made public demonstrations of his now patented invention, culminating in the world’s first long distance call, to Paris, 13 kilometres away, on 10 August
- ^ MacLeod 1999, p. 14.
- ^ Popular Mechanics Aug 1912. New York: Popular Mechanics. August 1912. p. 186.
- ^ «First Phone Call».
- ^ Fenster, Julie M. (March 7, 2006). «Inventing the Telephone—And Triggering All-Out Patent War». American Heritage. Archived from the original on March 11, 2006. Retrieved September 19, 2015.
- ^ Winfield, Richard (1987). Never the Twain Shall Meet: Bell, Gallaudet, and the Communications Debate. Washington, D.C.: Gallaudet University Press. p. 21. ISBN 978-0-913580-99-8.
- ^ Webb, Michael, ed. (1991). Alexander Graham Bell: Inventor of the Telephone. Mississauga, Ontario: Copp Clark Pitman. p. 15. ISBN 978-0-7730-5049-5.
- ^ «Bell’s centennial telephone transmitter, 1876». National Archives UK. Retrieved January 14, 2020.
- ^ «140 Years Since the First Telephone Call to Queen Victoria on the Isle of Wight». Island Echo. January 14, 2018. Retrieved January 14, 2020.
He made the UK’s first publicly-witnessed long distance calls, calling Cowes, Southampton and London. Queen Victoria liked the telephone so much she wanted to buy it.
- ^ «Alexander Graham Bell demonstrates the newly invented telephone». The Telegraph. January 13, 2017. Archived from the original on January 11, 2022. Retrieved January 14, 2020.
one of the Queen’s staff wrote to Professor Bell to inform him «how much gratified and surprised the Queen was at the exhibition of the Telephone»
- ^ «pdf, Letter from Alexander Graham Bell to Sir Thomas Biddulph, February 1, 1878». Library of Congress. Retrieved January 14, 2020.
The instruments at present in Osborne are merely those supplied for ordinary commercial purposes, and it will afford me much pleasure to be permitted to offer to the Queen a set of Telephones to be made expressly for her Majesty’s use.
- ^ Ross, Stewart (2001). Alexander Graham Bell. (Scientists who Made History). New York: Raintree Steck-Vaughn. pp. 21–22. ISBN 978-0-7398-4415-1.
- ^ «Dom Pedro II and America». The Library of Congress. Retrieved March 7, 2018.
- ^ «Phone to Pacific From the Atlantic». The New York Times. January 26, 1915. Retrieved July 21, 2007.
- ^ MacLeod 1999, p. 19.
- ^ «Who Really Invented The Telephone?». Australasian Telephone Collecting Society. Moorebank, NSW, Australia. Archived from the original on September 24, 2015. Retrieved April 22, 2011.
- ^ a b c Groundwater 2005, p. 95.
- ^ Black, Harry (1997). Canadian Scientists and Inventors: Biographies of People who made a Difference. Markham, Ontario: Pembroke. p. 19. ISBN 978-1-55138-081-0.
- ^ Mackay 1997, p. 179.
- ^ «US v. American Bell Tel Co (1897)». Findlaw. May 10, 1897. Retrieved July 28, 2010.
- ^ «United States V. American Bell Telephone Co., 128 U.S. 315 (1888)». Jusrtia US Supreme Court. November 12, 1885. Retrieved July 28, 2010.
- ^ Catania, Basilio (December 2002). «The United States Government vs. Alexander Graham Bell. An important acknowledgment for Antonio Meucci». Bulletin of Science, Technology & Society. 22 (6): 426–442. doi:10.1177/0270467602238886. S2CID 144185363.
- ^ Catania, Basilio (November 6, 2009). «Antonio Meucci – Questions and Answers: What did Meucci to bring his invention to the public?». Chezbasilio.org. Retrieved September 19, 2015.
- ^ «Our History». ADT. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ Bruce 1990, pp. 271–272.
- ^ Rory Carroll (June 17, 2002). «Bell did not invent telephone, US rules». The Guardian. Retrieved October 25, 2015.
- ^ «H.RES.269: Resolution 269.» thomas.loc.gov. Retrieved: July 28, 2010. Archived July 13, 2015, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «Congressional Record – Speech by Prof. Basillio». September 5, 2001. Archived from the original on July 17, 2011. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ «Antonio Meucci (1808–1889)». Italian Historical Society of America. Archived from the original on October 15, 2015. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ a b Bellis, Mary. «The History of the Telephone – Antonio Meucci». About.com Inventors. Retrieved December 29, 2009.
- ^ Mackay 1997, p. 178.
- ^ Parker, Steve (1995). Alexander Graham Bell and the Telephone. Scientific American. (Science Discoveries). Vol. 102. p. 23. Bibcode:1910SciAm.102..462.. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican06041910-462. ISBN 978-0-7910-3004-2.
- ^ Bruce 1990, pp. 297–299.
- ^ Eber 1991, p. 44.
- ^ Dunn 1990, p. 28.
- ^ Mackay 1997, p. 120.
- ^ «Mrs. A.G. Bell Dies. Inspired Telephone. Deaf Girl’s Romance With Distinguished Inventor Was Due to Her Affliction». The New York Times. January 4, 1923.[dead link]
- ^ «Dr. Gilbert H. Grosvenor Dies». The New York Times. Canadian Press. February 5, 1966. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
Dr. Gilbert H. Grosvenor … died on the Cape Breton Island estate once owned by his father-in-law, the inventor Alexander Graham Bell.
- ^ «Mrs. Gilbert Grosvenor Dead». The New York Times. December 27, 1964. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ Grosvenor, Edwin S.; Wesson, Morgan (1997). Alexander Graham Bell: The Life and Times of the Man Who Invented the Telephone. New York: Harry N. Abrahms. p. 104. ISBN 978-0-8109-4005-5.
- ^ «Mrs. David Fairchild, 82, Dead; Daughter of Bell, Phone Inventor». The New York Times. Canadian Press. September 25, 1962.
- ^ a b Grosvenor & Wesson 1997, p. 104.
- ^ Carson, Mary Kay (2007). Alexander Graham Bell: Giving Voice To The World. Sterling Biographies. New York: Sterling Publishing. p. 77. ISBN 978-1-4027-3230-0. OCLC 182527281.
- ^ Gray 2006, pp. 202–205.
- ^ Bruce, Robert V. (March 15, 2020). «Bell: Alexander Graham Bell and the Conquest of Solitude». Plunkett Lake Press – via Google Books.
- ^ Bruce 1990, p. 90.
- ^ Bruce 1990, pp. 471–472.
- ^ Bethune, Jocelyn (2009). Historic Baddeck. (Images of our Past). Halifax, Nova Scotia: Nimbus Publishing. p. 2. ISBN 978-1-55109-706-0.
- ^ Bethune 2009, p. 92.
- ^ a b c Bethune 2009, p. 2.
- ^ Tulloch, Judith (2006). The Bell Family in Baddeck: Alexander Graham Bell and Mabel Bell in Cape Breton. Halifax, Nova Scotia: Formac Publishing. pp. 25–27. ISBN 978-0-88780-713-8.
- ^ MacLeod 1999, p. 22.
- ^ Tulloch 2006, p. 42.
- ^ Gray 2006, p. 219.
- ^ Bruce 1990, p. 336.
- ^ Jones, Newell (July 31, 1937). «First ‘Radio’ Built by San Diego Resident Partner of Inventor of Telephone: Keeps Notebook of Experiences With Bell». Evening Tribune. San Diego, California. Archived from the original on February 19, 2002. Retrieved November 26, 2009.
- ^ Carson 2007, pp. 76–78.
- ^ Bruce 1990, p. 338.
- ^ Groth, Mike (April 1987). «Photophones Revisted». Amateur Radio: 12–17. Archived from the original on August 2, 2015. Retrieved September 19, 2015.
- ^ Mims III, Forest M. (February 10–26, 1982). «The First Century of Lightwave Communications». Fiber Optics Weekly Update: 11 of 6–23.
- ^ Phillipson, Donald J.C.; Neilson, Laura (March 4, 2015). «Alexander Graham Bell». The Canadian Encyclopedia (online ed.). Historica Canada. Archived from the original on September 25, 2015. Retrieved September 19, 2015.
- ^ Morgan, Tim J. (2011). The Fiber Optic Backbone (Report). University of North Texas. Archived from the original on September 25, 2015. Retrieved September 19, 2015.
- ^ Miller, Stewart E. (January–February 1984). «Lightwaves and Telecommunication». American Scientist. 72 (1): 66–71. JSTOR i27852430.
- ^ a b c Grosvenor & Wesson 1997, p. 107.
- ^ Bell, Alexander Graham (1882). «Upon the electrical experiments to determine the location of the bullet in the body of the late President Garfield; and upon a successful form of induction balance for the painless detection of metallic masses in the human body». American Journal of Science. 25 (145): 22–61. Bibcode:1883AmJS…25…22B. doi:10.2475/ajs.s3-25.145.22. S2CID 130896535. Retrieved April 29, 2013.
- ^ Boileau 2004, p. 18.
- ^ Boileau 2004, pp. 28–30.
- ^ Boileau 2004, p. 30.
- ^ Technical Gazette. New South Wales, Australia. 1924. p. 46.
- ^ «Nova Scotia’s Electric Scrapbook.» Archived April 17, 2009, at the Wayback Machine ns1763.ca. Retrieved: December 29, 2009.
- ^ Gillis, Rannie (September 29, 2008). «Mabel Bell Was A Focal Figure In The First Flight of the Silver Dart». Cape Breton Post. Sydney, Nova Scotia. Archived from the original on July 24, 2016. Retrieved June 12, 2010.
- ^ «Canada’s Golden Anniversary». Flight. Vol. 75, no. 2614. February 27, 1959. p. 280. Retrieved August 28, 2013.
- ^ Phillips, Allan (1977). Into the 20th Century: 1900/1910. (Canada’s Illustrated Heritage). Toronto, Ontario: Natural Science of Canada. p. 95. ISBN 978-0-919644-22-9.
- ^ Phillips 1977, p. 96.
- ^ «Link with Canadian Pioneers». Flight. Vol. 70, no. 2491. October 19, 1956. p. 642. Retrieved August 28, 2013.
- ^ Phillips 1977, pp. 96–97.
- ^ «Bell Rings for Darwin | National Center for Science Education». ncse.ngo. Retrieved March 2, 2021.
- ^ «Telephone inventor researched sheep teats». The Western Producer. October 2, 1997.
- ^ Castle, W. E. (February 1, 1924). «THE GENETICS OF MULTI-NIPPLED SHEEPAn Analysis of the Sheep-Breeding Experiments of Dr. and Mrs. Alexander Graham Bell at Beinn Bhreagh, N. S.» Journal of Heredity. 15 (2): 75–85. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a102421. ISSN 0022-1503.
- ^ Greenwald, Brian H. (2009). «The Real «Toll» of A. G. Bell: Lessons about Eugenics». Sign Language Studies. 9 (3): 258–265. ISSN 0302-1475. JSTOR 26190555.
- ^ a b Bell, Alexander Graham (1884). Upon the Formation of a Deaf Variety of the Human Race. U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ^ Memoir Upon the Formation of a Deaf Variety of the Human Race. Institute for Education Sciences. Alexander Graham Bell Association for the Deaf. 1969.
- ^ Greenwald, Brian H.; Van Cleve, John Vickrey (2015). ««A Deaf Variety of the Human Race»: Historical Memory, Alexander Graham Bell, and Eugenics». The Journal of the Gilded Age and Progressive Era. 14 (1): 28–48. doi:10.1017/S1537781414000528. ISSN 1537-7814. JSTOR 43903056. S2CID 163891681.
- ^ a b F., E. A. (1885). «Review of Memoir upon the Formation of a Deaf Variety of the Human Race». American Annals of the Deaf and Dumb. 30 (2): 155–162. ISSN 0093-1284. JSTOR 44468521.
- ^ Greenwald, Brian H.; Cleve, John Vickrey Van (January 2015). ««A Deaf Variety of the Human Race»: Historical Memory, Alexander Graham Bell, and Eugenics». The Journal of the Gilded Age and Progressive Era. 14 (1): 28–48. doi:10.1017/S1537781414000528. ISSN 1537-7814. S2CID 163891681.
- ^ a b Allen, Garland E. (1986). «The Eugenics Record Office at Cold Spring Harbor, 1910-1940: An Essay in Institutional History». Osiris. 2: 225–264. doi:10.1086/368657. ISSN 0369-7827. JSTOR 301835. PMID 11621591. S2CID 411710.
- ^ a b International Congress of Eugenics (2nd : 1921 : New York) (1923). Scientific papers of the second International Congress of Eugenics :held at American Museum of Natural History, New York, September 22-28, 1921 / (Vol. 2). The Library of Congress. Baltimore : Williams & Williams.
- ^ Gray, Charlotte (2006). Reluctant Genius: The Passionate Life and Inventive Mind of Alexander Graham Bell. New York: Arcade. p. 419. ISBN 978-1-55970-809-8.
- ^ Gray 2006, p. 418.
- ^ Bethune 2009, p. 95.
- ^ Duffy, Andrew (February 23, 2009). «The Silver Dart sputtered into history». Ottawa Citizen. Archived from the original on July 13, 2015. Retrieved September 18, 2015..
- ^ Bethune 2009, p. 119.
- ^ a b c d e «Dr. Bell, Inventor of Telephone, Dies» (PDF). The New York Times. August 3, 1922. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 9, 2022. Retrieved March 3, 2009.
- ^ Bruce 1990, p. 491.
- ^ Bethune 2009, pp. 119–120.
- ^ Pasachoff, Naomi (1996). Alexander Graham Bell: Making Connections. New York: Oxford University Press. p. 130. ISBN 978-0-19-509908-9.
- ^ Osborne 1943, pp. 18–19.
- ^ «Dr. Bell, Inventor of Telephone, Dies». The New York Times. August 3, 1922. Retrieved July 21, 2007.
Dr. Alexander Graham Bell, inventor of the telephone, died at 2 o’clock this morning at Beinn Breagh, his estate near Baddeck
- ^ Ireland, Carolyn (February 27, 2009). «The Portrait Studio House». The Globe and Mail.
- ^ «Daughter Unveils Inventor’s Statue: Bronze Figure Is Dedicated By Phone Pioneers». Brantford Expositor. June 18, 1949.
- ^ a b «About this Collection». Alexander Graham Bell Family Papers. Library of Congress. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ Osborne, Harold S. (1943). Biographical Memoir of Alexander Graham Bell 1847–1922 (PDF). Biographical Memoirs. Vol. XXIII. National Academy of Sciences. p. 18. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 9, 2022. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ «Alexander Graham Bell National Historic Site». Parks Canada. August 7, 2015. Archived from the original on October 11, 2007. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ «Pay Us a Call at Melville House!». Bell Homestead National Historic Site. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ «Alexander Graham Bell Memorial Park.» maps.google.com. Retrieved: February 14, 2012.
- ^ 1634–1699: McCusker, J. J. (1997). How Much Is That in Real Money? A Historical Price Index for Use as a Deflator of Money Values in the Economy of the United States: Addenda et Corrigenda (PDF). American Antiquarian Society. 1700–1799: McCusker, J. J. (1992). How Much Is That in Real Money? A Historical Price Index for Use as a Deflator of Money Values in the Economy of the United States (PDF). American Antiquarian Society. 1800–present: Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis. «Consumer Price Index (estimate) 1800–». Retrieved April 16, 2022.
- ^ «Honors to Professor Bell Daily Evening Traveller». Alexander Graham Bell Family Papers. Library of Congress. September 1, 1880. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ «Volta Prize of the French Academy Awarded to Prof. Alexander Graham Bell». Alexander Graham Bell Family Papers. Library of Congress. September 1, 1880. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ «Telegram from Grossman to Alexander Graham Bell». Alexander Graham Bell Family Papers. Library of Congress. August 2, 1880. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ «Telegram from Alexander Graham Bell to Count du Moncel, undated». Alexander Graham Bell Family Papers. Library of Congress. 1880. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ «Letter from Frederick T. Frelinghuysen to Alexander Graham Bell». Alexander Graham Bell Family Papers. Library of Congress. January 7, 1882. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ «The Volta Prize For Electricity» (PDF). Selected Innovation Prizes and Reward Programs (Report). Knowledge Ecology International. 2008. p. 16. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 9, 2022. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ Maindron, Ernest (1881). Gauthier-Villars (ed.). Les fondations de prix à l’Académie des sciences : les lauréats de l’Académie, 1714–1880 (in French). Vol. 1. pp. 131–133.
- ^ Davis, John L. (July 1998). «Artisans and savants: The Role of the Academy of Sciences in the Process of Electrical Innovation in France, 1850–1880». Annals of Science. 55 (3): 291–314. doi:10.1080/00033799800200211.
- ^ «Letter from Mabel Hubbard Bell». Alexander Graham Bell Family Papers. Library of Congress. February 27, 1880. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
The last line of the typed note refers to the future disposition of award funds: He intends putting the full amount into his Laboratory and Library.
- ^ «National Geographic Milestones». National Geographic Milestones. National Geographic Society. June 20, 2012. Retrieved January 18, 2016.
- ^ «Proceedings of the Board of Regents of the Smithsonian Institution at the Annual Meeting held December 14, 1922», Volume IV of the Proceedings of the Board of Regents, Dec. 9, 1920 – Dec. 10, 1931, Washington, D. C.: Smithsonian Institution, December 14, 1922, p. 547,
RESOLVED: That the Executive Committee be requested to prepare a memorial commemorative of the life and work of Dr. Alexander Graham Bell, Regent of the Smithsonian Institution from 1898 to 1922, said memorial to be presented at the next Annual Meeting of the Board.
- ^ «Alexander Graham Bell». Engineering and Technology History Wiki. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ «Decibel.» Archived August 9, 2017, at the Wayback Machine sfu.ca. Retrieved: July 28, 2010.
- ^ «bel». The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language (Fifth ed.). Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. 2011. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ Beauchamp, Christopher (October 2010). «Who Invented the Telephone?: Lawyers, Patents, and the Judgments of History». Technology and Culture. 51 (4): 854–878. doi:10.1353/tech.2010.0038. JSTOR 40928028.
- ^ Scott’s United States Stamp catalogue.
- ^ «Royal Bank Commemorative Notes». Rampant Scotland. Retrieved October 14, 2008.
- ^ «Proof Set – 100th Anniversary of Flight in Canada (2009)». Royal Canadian Mint. Archived from the original on September 9, 2017. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ «100 great British heroes». BBC News World Edition. August 21, 2002. Retrieved April 5, 2010.
- ^ «Alexander Graham Bell (1847–1922)». Scottish Science Hall of Fame. 2009.
- ^ MacDougall, D., ed. (1917). «Part V: Alexander Graham Bell». Scots and Scots Descendant in America. New York: Caledonian. p. 162. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l MacDougall 1917, p. 162.
- ^ «Honorary Degree Recipients». Gallaudet University. Washington, DC. Archived from the original on June 18, 2010. Retrieved July 28, 2010.
- ^ «Honorary Degrees Conferred». Illinois College. Archived from the original on September 24, 2015. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ «Graduations». University of Edinburgh. Archived from the original on September 1, 2015. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ «Honorary Degrees». Queen’s University. Retrieved October 14, 2020.
- ^ «Dartmouth graduates 208: Alexander Graham Bell Among Those Receiving Honorary Degrees» (PDF). The New York Times. July 26, 1913. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 9, 2022. Retrieved July 30, 2009.
- ^ «THE SCREEN; The founding of the Wrong-Number Industry WellDramatized in Roxy’s ‘Alexander Graham Bell’ At the 86th St. Garden Theatre At Three Theatres At the 86th Street Casino». The New York Times. April 1, 1939. Retrieved February 2, 2017.
Further reading
- Mullett, Mary B. The Story of A Famous Inventor. New York: Rogers and Fowle, 1921.
- Walters, Eric. The Hydrofoil Mystery. Toronto, Ontario, Canada: Puffin Books, 1999. ISBN 0-14-130220-8.
- Winzer, Margret A. The History Of Special Education: From Isolation To Integration. Washington, D.C.: Gallaudet University Press, 1993. ISBN 978-1-56368-018-2.
External links
- Alexander and Mabel Bell Legacy Foundation
- Alexander Graham Bell Institute at Cape Breton University
- Bell Telephone Memorial, Brantford, Ontario
- Bell Homestead National Historic Site, Brantford, Ontario
- Alexander Graham Bell National Historic Site of Canada, Baddeck, Nova Scotia
- Alexander Graham Bell Family Papers at the Library of Congress
- Alexander Graham Bell — Biographical Memoirs of the National Academy of Sciences
- Biography at the Dictionary of Canadian Biography Online
- Science.ca profile: Alexander Graham Bell
- Works by Alexander Graham Bell at Project Gutenberg
- Alexander Graham Bell at IMDb
- Alexander Graham Bell’s notebooks at the Internet Archive
- «Téléphone et photophone : les contributions indirectes de Graham Bell à l’idée de la vision à distance par l’électricité» at the Histoire de la télévision
- Newspaper clippings about Alexander Graham Bell in the 20th Century Press Archives of the ZBW
Multimedia
- Alexander Graham Bell at The Biography Channel
- The Story of Alexander Graham Bell (1939) at IMDb
- Alexander Graham Bell portrayed by John Bach (1992). The Sound and the Silence (Television production). Canada, New Zealand, Ireland: Atlantis Films.
- The Animated Hero Classics: Alexander Graham Bell (1995) at IMDb
- Gray, Charlotte (May 2013). «We Had No Idea What Alexander Graham Bell Sounded Like. Until Now». Smithsonian Magazine.
- Shaping The Future, from the Heritage Minutes and Radio Minutes collection at HistoricaCanada.ca (1:31 audio drama, Adobe Flash required)
| Non-profit organization positions | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded by Gardiner Greene Hubbard | President of the National Geographic Society 1897–1904 | Succeeded by William John McGee |
| Alexander Graham Bell | |
|---|---|
 Bell c. 1917 | |
| Born | Alexander Bell March 3, 1847 Edinburgh, Scotland |
| Died | August 2, 1922 (aged 75) Beinn Bhreagh, Nova Scotia, Canada |
| Citizenship | United Kingdom (1847–1922) British-subject in Canada (1870–1882) United States (1882–1922) |
| Alma mater |
|
| Occupations |
|
| Known for | Invention of the telephone b Cofounding of AT&T |
| Spouse | Mabel Gardiner Hubbard (m. 1877) |
| Children | 4 |
| Parents |
|
| Relatives |
|
| Awards |
|
| Re-identified in 2013, Bell made this wax-disc recording of his voice in 1885. | |
| Signature | |
| Notes | |
|
Alexander Graham Bell (, born Alexander Bell; March 3, 1847 – August 2, 1922)[4] was a Scottish-born[N 1] inventor, scientist and engineer who is credited with patenting the first practical telephone. He also co-founded the American Telephone and Telegraph Company (AT&T) in 1885.[7]
Bell’s father, grandfather, and brother had all been associated with work on elocution and speech, and both his mother and wife were deaf; profoundly influencing Bell’s life’s work.[8] His research on hearing and speech further led him to experiment with hearing devices which eventually culminated in Bell being awarded the first U.S. patent for the telephone, on March 7, 1876.[N 2] Bell considered his invention an intrusion on his real work as a scientist and refused to have a telephone in his study.[9][N 3]
Many other inventions marked Bell’s later life, including groundbreaking work in optical telecommunications, hydrofoils, and aeronautics. Bell also had a strong influence on the National Geographic Society[11] and its magazine while serving as the second president from January 7, 1898, until 1903.
Beyond his work in engineering, Bell had a deep interest in the emerging science of heredity.[12]
Early life
Bell was born in Edinburgh, Scotland, on March 3, 1847.[13] The family home was at South Charlotte Street, and has a stone inscription marking it as Bell’s birthplace. He had two brothers: Melville James Bell (1845–1870) and Edward Charles Bell (1848–1867), both of whom would die of tuberculosis.[14] His father was Alexander Melville Bell, a phonetician, and his mother was Eliza Grace Bell (née Symonds).[15] Born as just «Alexander Bell», at age 10, he made a plea to his father to have a middle name like his two brothers.[16][N 4] For his 11th birthday, his father acquiesced and allowed him to adopt the name «Graham», chosen out of respect for Alexander Graham, a Canadian being treated by his father who had become a family friend.[17] To close relatives and friends he remained «Aleck».[18] Bell and his siblings attended a Presbyterian Church in their youth.[19]
First invention
As a child, Bell displayed a curiosity about his world; he gathered botanical specimens and ran experiments at an early age. His best friend was Ben Herdman, a neighbour whose family operated a flour mill. At the age of 12, Bell built a homemade device that combined rotating paddles with sets of nail brushes, creating a simple dehusking machine that was put into operation at the mill and used steadily for a number of years.[20] In return, Ben’s father John Herdman gave both boys the run of a small workshop in which to «invent».[20]
From his early years, Bell showed a sensitive nature and a talent for art, poetry, and music that was encouraged by his mother. With no formal training, he mastered the piano and became the family’s pianist.[21] Despite being normally quiet and introspective, he revelled in mimicry and «voice tricks» akin to ventriloquism that continually entertained family guests during their occasional visits.[21] Bell was also deeply affected by his mother’s gradual deafness (she began to lose her hearing when he was 12), and learned a manual finger language so he could sit at her side and tap out silently the conversations swirling around the family parlour.[22] He also developed a technique of speaking in clear, modulated tones directly into his mother’s forehead wherein she would hear him with reasonable clarity.[23] Bell’s preoccupation with his mother’s deafness led him to study acoustics.
His family was long associated with the teaching of elocution: his grandfather, Alexander Bell, in London, his uncle in Dublin, and his father, in Edinburgh, were all elocutionists. His father published a variety of works on the subject, several of which are still well known, especially his The Standard Elocutionist (1860),[21] which appeared in Edinburgh in 1868. The Standard Elocutionist appeared in 168 British editions and sold over a quarter of a million copies in the United States alone. In this treatise, his father explains his methods of how to instruct deaf-mutes (as they were then known) to articulate words and read other people’s lip movements to decipher meaning. Bell’s father taught him and his brothers not only to write Visible Speech but to identify any symbol and its accompanying sound.[24] Bell became so proficient that he became a part of his father’s public demonstrations and astounded audiences with his abilities. He could decipher Visible Speech representing virtually every language, including Latin, Scottish Gaelic, and even Sanskrit, accurately reciting written tracts without any prior knowledge of their pronunciation.[24]
Education
As a young child, Bell, like his brothers, received his early schooling at home from his father. At an early age, he was enrolled at the Royal High School, Edinburgh, Scotland, which he left at the age of 15, having completed only the first four forms.[25] His school record was undistinguished, marked by absenteeism and lacklustre grades. His main interest remained in the sciences, especially biology, while he treated other school subjects with indifference, to the dismay of his father.[26] Upon leaving school, Bell travelled to London to live with his grandfather, Alexander Bell, on Harrington Square. During the year he spent with his grandfather, a love of learning was born, with long hours spent in serious discussion and study. The elder Bell took great efforts to have his young pupil learn to speak clearly and with conviction, the attributes that his pupil would need to become a teacher himself.[27] At the age of 16, Bell secured a position as a «pupil-teacher» of elocution and music, in Weston House Academy at Elgin, Moray, Scotland. Although he was enrolled as a student in Latin and Greek, he instructed classes himself in return for board and £10 per session.[28] The following year, he attended the University of Edinburgh, joining his older brother Melville who had enrolled there the previous year. In 1868, not long before he departed for Canada with his family, Bell completed his matriculation exams and was accepted for admission to University College London.[29][failed verification]
First experiments with sound
His father encouraged Bell’s interest in speech and, in 1863, took his sons to see a unique automaton developed by Sir Charles Wheatstone based on the earlier work of Baron Wolfgang von Kempelen.[30] The rudimentary «mechanical man» simulated a human voice. Bell was fascinated by the machine and after he obtained a copy of von Kempelen’s book, published in German, and had laboriously translated it, he and his older brother Melville built their own automaton head. Their father, highly interested in their project, offered to pay for any supplies and spurred the boys on with the enticement of a «big prize» if they were successful.[30] While his brother constructed the throat and larynx, Bell tackled the more difficult task of recreating a realistic skull. His efforts resulted in a remarkably lifelike head that could «speak», albeit only a few words.[30] The boys would carefully adjust the «lips» and when a bellows forced air through the windpipe, a very recognizable Mama ensued, to the delight of neighbours who came to see the Bell invention.[31]
Intrigued by the results of the automaton, Bell continued to experiment with a live subject, the family’s Skye Terrier, Trouve.[32] After he taught it to growl continuously, Bell would reach into its mouth and manipulate the dog’s lips and vocal cords to produce a crude-sounding «Ow ah oo ga ma ma». With little convincing, visitors believed his dog could articulate «How are you, grandmama?[33]» Indicative of his playful nature, his experiments convinced onlookers that they saw a «talking dog».[34] These initial forays into experimentation with sound led Bell to undertake his first serious work on the transmission of sound, using tuning forks to explore resonance.
At age 19, Bell wrote a report on his work and sent it to philologist Alexander Ellis, a colleague of his father.[34] Ellis immediately wrote back indicating that the experiments were similar to existing work in Germany, and also lent Bell a copy of Hermann von Helmholtz’s work, The Sensations of Tone as a Physiological Basis for the Theory of Music.[35]
Dismayed to find that groundbreaking work had already been undertaken by Helmholtz who had conveyed vowel sounds by means of a similar tuning fork «contraption», Bell pored over the German scientist’s book. Working from his own erroneous mistranslation of a French edition,[36] Bell fortuitously then made a deduction that would be the underpinning of all his future work on transmitting sound, reporting: «Without knowing much about the subject, it seemed to me that if vowel sounds could be produced by electrical means, so could consonants, so could articulate speech.» He also later remarked: «I thought that Helmholtz had done it … and that my failure was due only to my ignorance of electricity. It was a valuable blunder … If I had been able to read German in those days, I might never have commenced my experiments!»[37][38][39][N 5]
Family tragedy
In 1865, when the Bell family moved to London,[40] Bell returned to Weston House as an assistant master and, in his spare hours, continued experiments on sound using a minimum of laboratory equipment. Bell concentrated on experimenting with electricity to convey sound and later installed a telegraph wire from his room in Somerset College to that of a friend.[41] Throughout late 1867, his health faltered mainly through exhaustion. His younger brother, Edward «Ted,» was similarly affected by tuberculosis. While Bell recovered (by then referring to himself in correspondence as «A. G. Bell») and served the next year as an instructor at Somerset College, Bath, England, his brother’s condition deteriorated. Edward would never recover. Upon his brother’s death, Bell returned home in 1867. His older brother Melville had married and moved out. With aspirations to obtain a degree at University College London, Bell considered his next years as preparation for the degree examinations, devoting his spare time at his family’s residence to studying.
Helping his father in Visible Speech demonstrations and lectures brought Bell to Susanna E. Hull’s private school for the deaf in South Kensington, London. His first two pupils were deaf-mute girls who made remarkable progress under his tutelage. While his older brother seemed to achieve success on many fronts including opening his own elocution school, applying for a patent on an invention, and starting a family, Bell continued as a teacher. However, in May 1870, Melville died from complications due to tuberculosis, causing a family crisis. His father had also experienced a debilitating illness earlier in life and had been restored to health by a convalescence in Newfoundland. Bell’s parents embarked upon a long-planned move when they realized that their remaining son was also sickly. Acting decisively, Alexander Melville Bell asked Bell to arrange for the sale of all the family property,[42][N 6] conclude all of his brother’s affairs (Bell took over his last student, curing a pronounced lisp),[43] and join his father and mother in setting out for the «New World». Reluctantly, Bell also had to conclude a relationship with Marie Eccleston, who, as he had surmised, was not prepared to leave England with him.[44]
Canada
In 1870, 23-year-old Bell travelled with his parents and his brother’s widow, Caroline Margaret Ottaway,[45] to Paris, Ontario,[46] to stay with Thomas Henderson, a Baptist minister and family friend.[47] The Bell family soon purchased a farm of 10.5 acres (42,000 m2) at Tutelo Heights (now called Tutela Heights), near Brantford, Ontario. The property consisted of an orchard, large farmhouse, stable, pigsty, hen-house, and a carriage house, which bordered the Grand River.[48][N 7]
At the homestead, Bell set up his own workshop in the converted carriage house near to what he called his «dreaming place»,[50] a large hollow nestled in trees at the back of the property above the river.[51] Despite his frail condition upon arriving in Canada, Bell found the climate and environs to his liking, and rapidly improved.[52][N 8] He continued his interest in the study of the human voice and when he discovered the Six Nations Reserve across the river at Onondaga, he learned the Mohawk language and translated its unwritten vocabulary into Visible Speech symbols. For his work, Bell was awarded the title of Honorary Chief and participated in a ceremony where he donned a Mohawk headdress and danced traditional dances.[53][N 9]
After setting up his workshop, Bell continued experiments based on Helmholtz’s work with electricity and sound.[54] He also modified a melodeon (a type of pump organ) so that it could transmit its music electrically over a distance.[55] Once the family was settled in, both Bell and his father made plans to establish a teaching practice and in 1871, he accompanied his father to Montreal, where Melville was offered a position to teach his System of Visible Speech.
Work with the deaf

Bell, top right, providing pedagogical instruction to teachers at the Boston School for Deaf Mutes, 1871. Throughout his life, he referred to himself as «a teacher of the deaf».
Bell’s father was invited by Sarah Fuller, principal of the Boston School for Deaf Mutes (later to become the public Horace Mann School for the Deaf)[56] to introduce the Visible Speech System by providing training for Fuller’s instructors, but he declined the post in favour of his son. Travelling to Boston in April 1871, Bell proved successful in training the school’s instructors.[57] He was subsequently asked to repeat the programme at the American Asylum for Deaf-mutes in Hartford, Connecticut, and the Clarke School for the Deaf in Northampton, Massachusetts.
Returning home to Brantford after six months abroad, Bell continued his experiments with his «harmonic telegraph».[58][N 10] The basic concept behind his device was that messages could be sent through a single wire if each message was transmitted at a different pitch, but work on both the transmitter and receiver was needed.[59]
Unsure of his future, he contemplated returning to London to complete his studies, but decided to return to Boston as a teacher.[60] His father helped him set up his private practice by contacting Gardiner Greene Hubbard, the president of the Clarke School for the Deaf for a recommendation. Teaching his father’s system, in October 1872, Alexander Bell opened his «School of Vocal Physiology and Mechanics of Speech» in Boston, which attracted a large number of deaf pupils, with his first class numbering 30 students.[61][62] While he was working as a private tutor, one of his pupils was Helen Keller, who came to him as a young child unable to see, hear, or speak. She was later to say that Bell dedicated his life to the penetration of that «inhuman silence which separates and estranges».[63] In 1893, Keller performed the sod-breaking ceremony for the construction of Bell’s new Volta Bureau, dedicated to «the increase and diffusion of knowledge relating to the deaf».[64][65]
Throughout his lifetime, Bell sought to integrate the deaf and hard of hearing with the hearing world. Bell encouraged speech therapy and lip reading over sign language. He outlined this in a 1898 paper[66] detailing his belief that with resources and effort, the deaf could be taught to read lips and speak (known as oralism)[67] thus enabling their integration within the wider society.[68] Bell has been criticised by members of the Deaf community for supporting ideas that could cause the closure of dozens of deaf schools, and what some consider eugenicist ideas.[69] Bell did not support a ban on deaf people marrying each other, an idea articulated by the National Association of the Deaf (United States).[70] Although, in his memoir Memoir upon the Formation of a Deaf Variety of the Human Race, Bell observed that if deaf people tended to marry other deaf people, this could result in the emergence of a «deaf race».[71] Ultimately, in 1880, the Second International Congress on Education of the Deaf passed a resolution preferring the teaching of oral communication rather than signing in schools.
Continuing experimentation
In 1872, Bell became professor of Vocal Physiology and Elocution at the Boston University School of Oratory. During this period, he alternated between Boston and Brantford, spending summers in his Canadian home. At Boston University, Bell was «swept up» by the excitement engendered by the many scientists and inventors residing in the city. He continued his research in sound and endeavored to find a way to transmit musical notes and articulate speech, but although absorbed by his experiments, he found it difficult to devote enough time to experimentation. While days and evenings were occupied by his teaching and private classes, Bell began to stay awake late into the night, running experiment after experiment in rented facilities at his boarding house. Keeping «night owl» hours, he worried that his work would be discovered and took great pains to lock up his notebooks and laboratory equipment. Bell had a specially made table where he could place his notes and equipment inside a locking cover.[72] Worse still, his health deteriorated as he had severe headaches.[59] Returning to Boston in fall 1873, Bell made a far-reaching decision to concentrate on his experiments in sound.
Deciding to give up his lucrative private Boston practice, Bell retained only two students, six-year-old «Georgie» Sanders, deaf from birth, and 15-year-old Mabel Hubbard. Each pupil would play an important role in the next developments. George’s father, Thomas Sanders, a wealthy businessman, offered Bell a place to stay in nearby Salem with Georgie’s grandmother, complete with a room to «experiment». Although the offer was made by George’s mother and followed the year-long arrangement in 1872 where her son and his nurse had moved to quarters next to Bell’s boarding house, it was clear that Mr. Sanders was backing the proposal. The arrangement was for teacher and student to continue their work together, with free room and board thrown in.[73] Mabel was a bright, attractive girl who was ten years Bell’s junior but became the object of his affection. Having lost her hearing after a near-fatal bout of scarlet fever close to her fifth birthday,[74][75][N 11] she had learned to read lips but her father, Gardiner Greene Hubbard, Bell’s benefactor and personal friend, wanted her to work directly with her teacher.[76]
The telephone
| External audio |
|---|
By 1874, Bell’s initial work on the harmonic telegraph had entered a formative stage, with progress made both at his new Boston «laboratory» (a rented facility) and at his family home in Canada a big success.[N 12] While working that summer in Brantford, Bell experimented with a «phonautograph», a pen-like machine that could draw shapes of sound waves on smoked glass by tracing their vibrations. Bell thought it might be possible to generate undulating electrical currents that corresponded to sound waves.[78] Bell also thought that multiple metal reeds tuned to different frequencies like a harp would be able to convert the undulating currents back into sound. But he had no working model to demonstrate the feasibility of these ideas.[79]
In 1874, telegraph message traffic was rapidly expanding and in the words of Western Union President William Orton, had become «the nervous system of commerce». Orton had contracted with inventors Thomas Edison and Elisha Gray to find a way to send multiple telegraph messages on each telegraph line to avoid the great cost of constructing new lines.[80] When Bell mentioned to Gardiner Hubbard and Thomas Sanders that he was working on a method of sending multiple tones on a telegraph wire using a multi-reed device, the two wealthy patrons began to financially support Bell’s experiments.[81] Patent matters would be handled by Hubbard’s patent attorney, Anthony Pollok.[82]
In March 1875, Bell and Pollok visited the scientist Joseph Henry, who was then director of the Smithsonian Institution, and asked Henry’s advice on the electrical multi-reed apparatus that Bell hoped would transmit the human voice by telegraph. Henry replied that Bell had «the germ of a great invention». When Bell said that he did not have the necessary knowledge, Henry replied, «Get it!» That declaration greatly encouraged Bell to keep trying, even though he did not have the equipment needed to continue his experiments, nor the ability to create a working model of his ideas. However, a chance meeting in 1874 between Bell and Thomas A. Watson, an experienced electrical designer and mechanic at the electrical machine shop of Charles Williams, changed all that.
With financial support from Sanders and Hubbard, Bell hired Thomas Watson as his assistant,[N 13] and the two of them experimented with acoustic telegraphy. On June 2, 1875, Watson accidentally plucked one of the reeds and Bell, at the receiving end of the wire, heard the overtones of the reed; overtones that would be necessary for transmitting speech. That demonstrated to Bell that only one reed or armature was necessary, not multiple reeds. This led to the «gallows» sound-powered telephone, which could transmit indistinct, voice-like sounds, but not clear speech.
The race to the patent office
In 1875, Bell developed an acoustic telegraph and drew up a patent application for it. Since he had agreed to share U.S. profits with his investors Gardiner Hubbard and Thomas Sanders, Bell requested that an associate in Ontario, George Brown, attempt to patent it in Britain, instructing his lawyers to apply for a patent in the U.S. only after they received word from Britain (Britain would issue patents only for discoveries not previously patented elsewhere).[84]

Alexander Graham Bell’s telephone patent[85] drawing, March 7, 1876
Meanwhile, Elisha Gray was also experimenting with acoustic telegraphy and thought of a way to transmit speech using a water transmitter. On February 14, 1876, Gray filed a caveat with the U.S. Patent Office for a telephone design that used a water transmitter. That same morning, Bell’s lawyer filed Bell’s application with the patent office. There is considerable debate about who arrived first and Gray later challenged the primacy of Bell’s patent. Bell was in Boston on February 14 and did not arrive in Washington until February 26.[citation needed]

The master telephone patent, 174465, March 7, 1876
Bell’s patent 174,465, was issued to Bell on March 7, 1876, by the U.S. Patent Office. Bell’s patent covered «the method of, and apparatus for, transmitting vocal or other sounds telegraphically … by causing electrical undulations, similar in form to the vibrations of the air accompanying the said vocal or other sound»[86][N 14] Bell returned to Boston the same day and the next day resumed work, drawing in his notebook a diagram similar to that in Gray’s patent caveat.[citation needed]
On March 10, 1876, three days after his patent was issued, Bell succeeded in getting his telephone to work, using a liquid transmitter similar to Gray’s design. Vibration of the diaphragm caused a needle to vibrate in the water, varying the electrical resistance in the circuit. When Bell spoke the sentence «Mr. Watson—Come here—I want to see you» into the liquid transmitter,[87] Watson, listening at the receiving end in an adjoining room, heard the words clearly.[88]
Although Bell was, and still is, accused of stealing the telephone from Gray,[89] Bell used Gray’s water transmitter design only after Bell’s patent had been granted, and only as a proof of concept scientific experiment,[90] to prove to his own satisfaction that intelligible «articulate speech» (Bell’s words) could be electrically transmitted.[91] After March 1876, Bell focused on improving the electromagnetic telephone and never used Gray’s liquid transmitter in public demonstrations or commercial use.[92]
The question of priority for the variable resistance feature of the telephone was raised by the examiner before he approved Bell’s patent application. He told Bell that his claim for the variable resistance feature was also described in Gray’s caveat. Bell pointed to a variable resistance device in his previous application in which he described a cup of mercury, not water. He had filed the mercury application at the patent office a year earlier on February 25, 1875, long before Elisha Gray described the water device. In addition, Gray abandoned his caveat, and because he did not contest Bell’s priority, the examiner approved Bell’s patent on March 3, 1876. Gray had reinvented the variable resistance telephone, but Bell was the first to write down the idea and the first to test it in a telephone.[93]
The patent examiner, Zenas Fisk Wilber, later stated in an affidavit that he was an alcoholic who was much in debt to Bell’s lawyer, Marcellus Bailey, with whom he had served in the Civil War. He claimed he showed Gray’s patent caveat to Bailey. Wilber also claimed (after Bell arrived in Washington D.C. from Boston) that he showed Gray’s caveat to Bell and that Bell paid him $100 (equivalent to $2,500 in 2021). Bell claimed they discussed the patent only in general terms, although in a letter to Gray, Bell admitted that he learned some of the technical details. Bell denied in an affidavit that he ever gave Wilber any money.[94]
Later developments

On March 10, 1876, Bell used «the instrument» in Boston to call Thomas Watson who was in another room but out of earshot. He said, «Mr. Watson, come here – I want to see you» and Watson soon appeared at his side.[95]
Continuing his experiments in Brantford, Bell brought home a working model of his telephone. On August 3, 1876, from the telegraph office in Brantford, Ontario, Bell sent a tentative telegram to the village of Mount Pleasant four miles (six kilometres) distant, indicating that he was ready. He made a telephone call via telegraph wires and faint voices were heard replying. The following night, he amazed guests as well as his family with a call between the Bell Homestead and the office of the Dominion Telegraph Company in Brantford along an improvised wire strung up along telegraph lines and fences, and laid through a tunnel. This time, guests at the household distinctly heard people in Brantford reading and singing. The third test on August 10, 1876, was made via the telegraph line between Brantford and Paris, Ontario, eight miles (thirteen kilometres) distant. This test was said by many sources to be the «world’s first long-distance call».[96][97] The final test certainly proved that the telephone could work over long distances, at least as a one-way call.
[98]
The first two-way (reciprocal) conversation over a line occurred between Cambridge and Boston (roughly 2.5 miles) on October 9, 1876.[99] During that conversation, Bell was on Kilby Street in Boston and Watson was at the offices of the Walworth Manufacturing Company.[100]

Bell at the opening of the long-distance line from New York to Chicago in 1892
Bell and his partners, Hubbard and Sanders, offered to sell the patent outright to Western Union for $100,000, equal to $2,544,688 today. The president of Western Union balked, countering that the telephone was nothing but a toy. Two years later, he told colleagues that if he could get the patent for $25 million (equal to $701,982,759 today), he would consider it a bargain. By then, the Bell company no longer wanted to sell the patent.[101] Bell’s investors would become millionaires while he fared well from residuals and at one point had assets of nearly one million dollars.[102]
Bell began a series of public demonstrations and lectures to introduce the new invention to the scientific community as well as the general public. A short time later, his demonstration of an early telephone prototype at the 1876 Centennial Exposition in Philadelphia brought the telephone to international attention.[103] Influential visitors to the exhibition included Emperor Pedro II of Brazil. One of the judges at the Exhibition, Sir William Thomson (later, Lord Kelvin), a renowned Scottish scientist, described the telephone as «the greatest by far of all the marvels of the electric telegraph».[104]
On January 14, 1878, at Osborne House, on the Isle of Wight, Bell demonstrated the device to Queen Victoria,[105] placing calls to Cowes, Southampton and London. These were the first publicly witnessed long-distance telephone calls in the UK. The queen considered the process to be «quite extraordinary» although the sound was «rather faint».[106] She later asked to buy the equipment that was used, but Bell offered to make «a set of telephones» specifically for her.[107][108]
The Bell Telephone Company was created in 1877, and by 1886, more than 150,000 people in the U.S. owned telephones. Bell Company engineers made numerous other improvements to the telephone, which emerged as one of the most successful products ever. In 1879, the Bell company acquired Edison’s patents for the carbon microphone from Western Union. This made the telephone practical for longer distances, and it was no longer necessary to shout to be heard at the receiving telephone.[citation needed]
Emperor Pedro II of Brazil was the first person to buy stock in Bell’s company, the Bell Telephone Company. One of the first telephones in a private residence was installed in his palace in Petrópolis, his summer retreat forty miles (sixty-four kilometres) from Rio de Janeiro.[109]
In January 1915, Bell made the first ceremonial transcontinental telephone call. Calling from the AT&T head office at 15 Dey Street in New York City, Bell was heard by Thomas Watson at 333 Grant Avenue in San Francisco. The New York Times reported:
On October 9, 1876, Alexander Graham Bell and Thomas A. Watson talked by telephone to each other over a two-mile wire stretched between Cambridge and Boston. It was the first wire conversation ever held. Yesterday afternoon [on January 25, 1915], the same two men talked by telephone to each other over a 3,400-mile wire between New York and San Francisco. Dr. Bell, the veteran inventor of the telephone, was in New York, and Mr. Watson, his former associate, was on the other side of the continent.[110]
Competitors
As is sometimes common in scientific discoveries, simultaneous developments can occur, as evidenced by a number of inventors who were at work on the telephone.[111] Over a period of 18 years, the Bell Telephone Company faced 587 court challenges to its patents, including five that went to the U.S. Supreme Court,[112] but none was successful in establishing priority over the original Bell patent[113][114] and the Bell Telephone Company never lost a case that had proceeded to a final trial stage.[113] Bell’s laboratory notes and family letters were the key to establishing a long lineage to his experiments.[113] The Bell company lawyers successfully fought off myriad lawsuits generated initially around the challenges by Elisha Gray and Amos Dolbear. In personal correspondence to Bell, both Gray and Dolbear had acknowledged his prior work, which considerably weakened their later claims.[115]
On January 13, 1887, the U.S. Government moved to annul the patent issued to Bell on the grounds of fraud and misrepresentation. After a series of decisions and reversals, the Bell company won a decision in the Supreme Court, though a couple of the original claims from the lower court cases were left undecided.[116][117] By the time that the trial wound its way through nine years of legal battles, the U.S. prosecuting attorney had died and the two Bell patents (No. 174,465 dated March 7, 1876, and No. 186,787 dated January 30, 1877) were no longer in effect, although the presiding judges agreed to continue the proceedings due to the case’s importance as a precedent. With a change in administration and charges of conflict of interest (on both sides) arising from the original trial, the US Attorney General dropped the lawsuit on November 30, 1897, leaving several issues undecided on the merits.[118]
During a deposition filed for the 1887 trial, Italian inventor Antonio Meucci also claimed to have created the first working model of a telephone in Italy in 1834. In 1886, in the first of three cases in which he was involved,[N 15] Meucci took the stand as a witness in the hope of establishing his invention’s priority. Meucci’s testimony in this case was disputed due to a lack of material evidence for his inventions, as his working models were purportedly lost at the laboratory of American District Telegraph (ADT) of New York, which was later incorporated as a subsidiary of Western Union in 1901.[119][120] Meucci’s work, like many other inventors of the period, was based on earlier acoustic principles and despite evidence of earlier experiments, the final case involving Meucci was eventually dropped upon Meucci’s death.[121] However, due to the efforts of Congressman Vito Fossella, the U.S. House of Representatives on June 11, 2002, stated that Meucci’s «work in the invention of the telephone should be acknowledged».[122][123][124] This did not put an end to the still-contentious issue.[125] Some modern scholars do not agree with the claims that Bell’s work on the telephone was influenced by Meucci’s inventions.[126][N 16]
The value of the Bell patent was acknowledged throughout the world, and patent applications were made in most major countries, but when Bell delayed the German patent application, the electrical firm of Siemens & Halske set up a rival manufacturer of Bell telephones under their own patent. The Siemens company produced near-identical copies of the Bell telephone without having to pay royalties.[127] The establishment of the International Bell Telephone Company in Brussels, Belgium in 1880, as well as a series of agreements in other countries eventually consolidated a global telephone operation. The strain put on Bell by his constant appearances in court, necessitated by the legal battles, eventually resulted in his resignation from the company.[128][N 17]
Family life


The Brodhead–Bell mansion, the Bell family residence in Washington, D.C., from 1882 to 1889[129]
On July 11, 1877, a few days after the Bell Telephone Company was established, Bell married Mabel Hubbard (1857–1923) at the Hubbard estate in Cambridge, Massachusetts. His wedding present to his bride was to turn over 1,487 of his 1,497 shares in the newly formed Bell Telephone Company.[130] Shortly thereafter, the newlyweds embarked on a year-long honeymoon in Europe. During that excursion, Bell took a handmade model of his telephone with him, making it a «working holiday». The courtship had begun years earlier; however, Bell waited until he was more financially secure before marrying. Although the telephone appeared to be an «instant» success, it was not initially a profitable venture and Bell’s main sources of income were from lectures until after 1897.[131] One unusual request exacted by his fiancée was that he use «Alec» rather than the family’s earlier familiar name of «Aleck». From 1876, he would sign his name «Alec Bell».[132][133] They had four children:
- Elsie May Bell (1878–1964) who married Gilbert Hovey Grosvenor of National Geographic fame.[134][135]
- Marian Hubbard Bell (1880–1962) who was referred to as «Daisy». Married David Fairchild.[136][137][N 18]
- Two sons who died in infancy (Edward in 1881 and Robert in 1883).
The Bell family home was in Cambridge, Massachusetts, until 1880 when Bell’s father-in-law bought a house in Washington, D.C.; in 1882 he bought a home in the same city for Bell’s family, so they could be with him while he attended to the numerous court cases involving patent disputes.[140]
Bell was a British subject throughout his early life in Scotland and later in Canada until 1882 when he became a naturalized citizen of the United States. In 1915, he characterized his status as: «I am not one of those hyphenated Americans who claim allegiance to two countries.»[141][page needed][142] Despite this declaration, Bell has been proudly claimed as a «native son» by all three countries he resided in: the United States, Canada, and the United Kingdom.[143]
By 1885, a new summer retreat was contemplated. That summer, the Bells had a vacation on Cape Breton Island in Nova Scotia, spending time at the small village of Baddeck.[144] Returning in 1886, Bell started building an estate on a point across from Baddeck, overlooking Bras d’Or Lake.[145] By 1889, a large house, christened The Lodge was completed and two years later, a larger complex of buildings, including a new laboratory,[146] were begun that the Bells would name Beinn Bhreagh (Gaelic: Beautiful Mountain) after Bell’s ancestral Scottish highlands.[147][N 19] Bell also built the Bell Boatyard on the estate, employing up to 40 people building experimental craft as well as wartime lifeboats and workboats for the Royal Canadian Navy and pleasure craft for the Bell family. He was an enthusiastic boater, and Bell and his family sailed or rowed a long series of vessels on Bras d’Or Lake, ordering additional vessels from the H.W. Embree and Sons boatyard in Port Hawkesbury, Nova Scotia. In his final, and some of his most productive years, Bell split his residency between Washington, D.C., where he and his family initially resided for most of the year, and Beinn Bhreagh, where they spent increasing amounts of time.[148]
Until the end of his life, Bell and his family would alternate between the two homes, but Beinn Bhreagh would, over the next 30 years, become more than a summer home as Bell became so absorbed in his experiments that his annual stays lengthened. Both Mabel and Bell became immersed in the Baddeck community and were accepted by the villagers as «their own».[146][N 20] The Bells were still in residence at Beinn Bhreagh when the Halifax Explosion occurred on December 6, 1917. Mabel and Bell mobilized the community to help victims in Halifax.[149]
Later inventions

Alexander Graham Bell in his later years
Although Alexander Graham Bell is most often associated with the invention of the telephone, his interests were extremely varied. According to one of his biographers, Charlotte Gray, Bell’s work ranged «unfettered across the scientific landscape» and he often went to bed voraciously reading the Encyclopædia Britannica, scouring it for new areas of interest.[150] The range of Bell’s inventive genius is represented only in part by the 18 patents granted in his name alone and the 12 he shared with his collaborators. These included 14 for the telephone and telegraph, four for the photophone, one for the phonograph, five for aerial vehicles, four for «hydroairplanes», and two for selenium cells. Bell’s inventions spanned a wide range of interests and included a metal jacket to assist in breathing, the audiometer to detect minor hearing problems, a device to locate icebergs, investigations on how to separate salt from seawater, and work on finding alternative fuels.[citation needed]
Bell worked extensively in medical research and invented techniques for teaching speech to the deaf. During his Volta Laboratory period, Bell and his associates considered impressing a magnetic field on a record as a means of reproducing sound. Although the trio briefly experimented with the concept, they could not develop a workable prototype. They abandoned the idea, never realizing they had glimpsed a basic principle which would one day find its application in the tape recorder, the hard disc and floppy disc drive, and other magnetic media.[citation needed]
Bell’s own home used a primitive form of air conditioning, in which fans blew currents of air across great blocks of ice. He also anticipated modern concerns with fuel shortages and industrial pollution. Methane gas, he reasoned, could be produced from the waste of farms and factories. At his Canadian estate in Nova Scotia, he experimented with composting toilets and devices to capture water from the atmosphere. In a magazine interview published shortly before his death, he reflected on the possibility of using solar panels to heat houses.[citation needed]
Photophone

Bell and his assistant Charles Sumner Tainter jointly invented a wireless telephone, named a photophone, which allowed for the transmission of both sounds and normal human conversations on a beam of light.[151][152] Both men later became full associates in the Volta Laboratory Association.
On June 21, 1880, Bell’s assistant transmitted a wireless voice telephone message a considerable distance, from the roof of the Franklin School in Washington, D.C., to Bell at the window of his laboratory, some 700 feet (213 m) away, 19 years before the first voice radio transmissions.[153][154][155][156]
Bell believed the photophone’s principles were his life’s «greatest achievement», telling a reporter shortly before his death that the photophone was «the greatest invention [I have] ever made, greater than the telephone».[157] The photophone was a precursor to the fiber-optic communication systems which achieved popular worldwide usage in the 1980s.[158][159] Its master patent was issued in December 1880, many decades before the photophone’s principles came into popular use.
Metal detector
Bell’s voice, from a Volta Laboratory recording in 1885. Restored by the Smithsonian in 2013.
Bell is also credited with developing one of the early versions of a metal detector through the use of an induction balance, after the shooting of U.S. President James A. Garfield in 1881. According to some accounts, the metal detector worked flawlessly in tests but did not find Guiteau’s bullet, partly because the metal bed frame on which the President was lying disturbed the instrument, resulting in static.[160] Garfield’s surgeons, led by self-appointed chief physician Doctor Willard Bliss, were skeptical of the device, and ignored Bell’s requests to move the President to a bed not fitted with metal springs.[160] Alternatively, although Bell had detected a slight sound on his first test, the bullet may have been lodged too deeply to be detected by the crude apparatus.[160]
Bell’s own detailed account, presented to the American Association for the Advancement of Science in 1882, differs in several particulars from most of the many and varied versions now in circulation, by concluding that extraneous metal was not to blame for failure to locate the bullet. Perplexed by the peculiar results he had obtained during an examination of Garfield, Bell «proceeded to the Executive Mansion the next morning … to ascertain from the surgeons whether they were perfectly sure that all metal had been removed from the neighborhood of the bed. It was then recollected that underneath the horse-hair mattress on which the President lay was another mattress composed of steel wires. Upon obtaining a duplicate, the mattress was found to consist of a sort of net of woven steel wires, with large meshes. The extent of the [area that produced a response from the detector] having been so small, as compared with the area of the bed, it seemed reasonable to conclude that the steel mattress had produced no detrimental effect.» In a footnote, Bell adds, «The death of President Garfield and the subsequent post-mortem examination, however, proved that the bullet was at too great a distance from the surface to have affected our apparatus.»[161]
Hydrofoils
Main article: HD-4

Bell’s HD-4 on a test run ca. 1919
The March 1906 Scientific American article by American pioneer William E. Meacham explained the basic principle of hydrofoils and hydroplanes. Bell considered the invention of the hydroplane as a very significant achievement. Based on information gained from that article, he began to sketch concepts of what is now called a hydrofoil boat. Bell and assistant Frederick W. «Casey» Baldwin began hydrofoil experimentation in the summer of 1908 as a possible aid to airplane takeoff from water. Baldwin studied the work of the Italian inventor Enrico Forlanini and began testing models. This led him and Bell to the development of practical hydrofoil watercraft.
During his world tour of 1910–11, Bell and Baldwin met with Forlanini in France. They had rides in the Forlanini hydrofoil boat over Lake Maggiore. Baldwin described it as being as smooth as flying. On returning to Baddeck, a number of initial concepts were built as experimental models, including the Dhonnas Beag (Scottish Gaelic for ‘little devil’), the first self-propelled Bell-Baldwin hydrofoil.[162] The experimental boats were essentially proof-of-concept prototypes that culminated in the more substantial HD-4, powered by Renault engines. A top speed of 54 miles per hour (87 km/h) was achieved, with the hydrofoil exhibiting rapid acceleration, good stability, and steering, along with the ability to take waves without difficulty.[163] In 1913, Dr. Bell hired Walter Pinaud, a Sydney yacht designer and builder as well as the proprietor of Pinaud’s Yacht Yard in Westmount, Nova Scotia, to work on the pontoons of the HD-4. Pinaud soon took over the boatyard at Bell Laboratories on Beinn Bhreagh, Bell’s estate near Baddeck, Nova Scotia. Pinaud’s experience in boatbuilding enabled him to make useful design changes to the HD-4. After the First World War, work began again on the HD-4. Bell’s report to the U.S. Navy permitted him to obtain two 350-horsepower (260-kilowatt) engines in July 1919. On September 9, 1919, the HD-4 set a world marine speed record of 70.86 miles per hour (114.04 kilometres per hour),[164] a record which stood for ten years.
Aeronautics

In 1891, Bell had begun experiments to develop motor-powered heavier-than-air aircraft. The AEA was first formed as Bell shared the vision to fly with his wife, who advised him to seek «young» help as Bell was at the age of 60.
In 1898, Bell experimented with tetrahedral box kites and wings constructed of multiple compound tetrahedral kites covered in maroon silk.[N 21] The tetrahedral wings were named Cygnet I, II, and III, and were flown both unmanned and manned (Cygnet I crashed during a flight carrying Selfridge) in the period from 1907 to 1912. Some of Bell’s kites are on display at the Alexander Graham Bell National Historic Site.[166]
Bell was a supporter of aerospace engineering research through the Aerial Experiment Association (AEA), officially formed at Baddeck, Nova Scotia, in October 1907 at the suggestion of his wife Mabel and with her financial support after the sale of some of her real estate.[167] The AEA was headed by Bell and the founding members were four young men: American Glenn H. Curtiss, a motorcycle manufacturer at the time and who held the title «world’s fastest man», having ridden his self-constructed motor bicycle around in the shortest time, and who was later awarded the Scientific American Trophy for the first official one-kilometre flight in the Western hemisphere, and who later became a world-renowned airplane manufacturer; Lieutenant Thomas Selfridge, an official observer from the U.S. Federal government and one of the few people in the army who believed that aviation was the future; Frederick W. Baldwin, the first Canadian and first British subject to pilot a public flight in Hammondsport, New York; and J. A. D. McCurdy–Baldwin and McCurdy being new engineering graduates from the University of Toronto.[168]
The AEA’s work progressed to heavier-than-air machines, applying their knowledge of kites to gliders. Moving to Hammondsport, the group then designed and built the Red Wing, framed in bamboo and covered in red silk and powered by a small air-cooled engine.[169] On March 12, 1908, over Keuka Lake, the biplane lifted off on the first public flight in North America.[N 22][N 23] The innovations that were incorporated into this design included a cockpit enclosure and tail rudder (later variations on the original design would add ailerons as a means of control). One of the AEA’s inventions, a practical wingtip form of the aileron, was to become a standard component on all aircraft.[N 24] The White Wing and June Bug were to follow and by the end of 1908, over 150 flights without mishap had been accomplished. However, the AEA had depleted its initial reserves and only a $15,000 grant from Mrs. Bell allowed it to continue with experiments.[170] Lt. Selfridge had also become the first person killed in a powered heavier-than-air flight in a crash of the Wright Flyer at Fort Myer, Virginia, on September 17, 1908.
Their final aircraft design, the Silver Dart, embodied all of the advancements found in the earlier machines. On February 23, 1909, Bell was present as the Silver Dart flown by J. A. D. McCurdy from the frozen ice of Bras d’Or made the first aircraft flight in Canada.[171] Bell had worried that the flight was too dangerous and had arranged for a doctor to be on hand. With the successful flight, the AEA disbanded and the Silver Dart would revert to Baldwin and McCurdy, who began the Canadian Aerodrome Company and would later demonstrate the aircraft to the Canadian Army.[172]
Heredity and genetics
Bell, along with many members of the scientific community at the time, took an interest in the popular science of heredity which grew out of the publication of Charles Darwin’s book On the Origin of Species in 1859.[173] On his estate in Nova Scotia, Bell conducted meticulously recorded breeding experiments with rams and ewes. Over the course of more than 30 years, Bell sought to produce a breed of sheep with multiple nipples that would bear twins.[174] He specifically wanted to see if selective breeding could produce sheep with four functional nipples with enough milk for twin lambs.[175] This interest in animal breeding caught the attention of scientists focused on the study of heredity and genetics in humans.[176]
In November 1883, Bell presented a paper at a meeting of the National Academy of Sciences titled «Upon the Formation of a Deaf Variety of the Human Race».[177] The paper is a compilation of data on the hereditary aspects of deafness. Bell’s research indicated that a hereditary tendency toward deafness, as indicated by the possession of deaf relatives, was an important element in determining the production of deaf offspring. He noted that the proportion of deaf children born to deaf parents was many times greater than the proportion of deaf children born to the general population.[178] In the paper, Bell delved into social commentary and discussed hypothetical public policies to bring an end to deafness. He also criticized educational practices that segregated deaf children rather than integrated them fulling into mainstream classrooms. The paper did not propose sterilization of deaf people or prohibition on intermarriage,[179] noting that «We cannot dictate to men and women whom they should marry and natural selection no longer influences mankind to any great extent.»[177]
A review of Bell’s «Memoir upon the Formation of a Deaf Variety of the Human Race» appearing in an 1885 issue of the «American Annals of the Deaf and Dumb» states that «Dr. Bell does not advocate legislative interference with the marriages of the deaf for several reasons one of which is that the results of such marriages have not yet been sufficiently investigated.» The article goes on to say that «the editorial remarks based thereon did injustice to the author.»[180] The paper’s author concludes by saying «A wiser way to prevent the extension of hereditary deafness, it seems to us, would be to continue the investigations which Dr. Bell has so admirable begun until the laws of the transmission of the tendency to deafness are fully understood, and then by explaining those laws to the pupils of our schools to lead them to choose their partners in marriage in such a way that deaf-mute offspring will not be the result.»[180]
Historians have noted that Bell explicitly opposed laws regulating marriage, and never mentioned sterilization in any of his writings. Even after Bell agreed to engage with scientists conducting eugenic research, he consistently refused to support public policy that limited the rights or privileges of the deaf.[181]
Bell’s interest and research on heredity attracted the interest of Charles Davenport, a Harvard professor and head of the Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. In 1906, Davenport, who was also the founder of the American Breeder’s Association, approached Bell about joining a new committee on eugenics chaired by David Starr Jordan. In 1910, Davenport opened the Eugenics Records office at Cold Spring Harbor. To give the organization scientific credibility, Davenport set up a Board of Scientific Directors naming Bell as chairman.[182] Other members of the board included Luther Burbank, Roswell H. Johnson, Vernon L. Kellogg, and William E. Castle.[182]
In 1921, a Second International Congress of Eugenics was held in New York at the Museum of Natural History and chaired by Davenport. Although Bell did not present any research or speak as part of the proceedings, he was named as honorary president as a means to attract other scientists to attend the event.[183] A summary of the event notes that Bell was a «pioneering investigator in the field of human heredity».[183]
Death
Bell died of complications arising from diabetes on August 2, 1922, at his private estate in Cape Breton, Nova Scotia, at age 75.[184] Bell had also been affected by pernicious anemia.[185] His last view of the land he had inhabited was by moonlight on his mountain estate at 2:00 a.m.[N 25][188][N 26] While tending to him after his long illness, Mabel, his wife, whispered, «Don’t leave me.» By way of reply, Bell signed «no…», lost consciousness, and died shortly after.[189][190]
On learning of Bell’s death, the Canadian Prime Minister, Mackenzie King, cabled Mrs. Bell, saying:[189]
My colleagues in the Government join with me in expressing to you our sense of the world’s loss in the death of your distinguished husband. It will ever be a source of pride to our country that the great invention, with which his name is immortally associated, is a part of its history. On the behalf of the citizens of Canada, may I extend to you an expression of our combined gratitude and sympathy.
Bell’s coffin was constructed of Beinn Bhreagh pine by his laboratory staff, lined with the same red silk fabric used in his tetrahedral kite experiments. To help celebrate his life, his wife asked guests not to wear black (the traditional funeral color) while attending his service, during which soloist Jean MacDonald sang a verse of Robert Louis Stevenson’s «Requiem»:[191]
Under a wide and starry sky,
Dig the grave and let me lie.
Glad did I live and gladly die
And I laid me down with a will.
Upon the conclusion of Bell’s funeral, for one minute at 6:25 p.m. Eastern Time,[192] «every phone on the continent of North America was silenced in honor of the man who had given to mankind the means for direct communication at a distance».[146][193]
Alexander Graham Bell was buried atop Beinn Bhreagh mountain, on his estate where he had resided increasingly for the last 35 years of his life, overlooking Bras d’Or Lake.[189] He was survived by his wife Mabel, his two daughters, Elsie May and Marian, and nine of his grandchildren.[189][194]
Legacy and honors

Honors and tributes flowed to Bell in increasing numbers as his invention became ubiquitous and his personal fame grew. Bell received numerous honorary degrees from colleges and universities to the point that the requests almost became burdensome.[197] During his life, he also received dozens of major awards, medals, and other tributes. These included statuary monuments to both him and the new form of communication his telephone created, including the Bell Telephone Memorial erected in his honor in Alexander Graham Bell Gardens in Brantford, Ontario, in 1917.[198]

A quote by Alexander Graham Bell engraved in the stone wall within the Peace Chapel of the International Peace Garden (in Manitoba Canada and North Dakota, USA).
A large number of Bell’s writings, personal correspondence, notebooks, papers, and other documents reside in both the United States Library of Congress Manuscript Division (as the Alexander Graham Bell Family Papers),[197] and at the Alexander Graham Bell Institute, Cape Breton University, Nova Scotia; major portions of which are available for online viewing.
A number of historic sites and other marks commemorate Bell in North America and Europe, including the first telephone companies in the United States and Canada. Among the major sites are:
- The Alexander Graham Bell National Historic Site, maintained by Parks Canada, which incorporates the Alexander Graham Bell Museum, in Baddeck, Nova Scotia, close to the Bell estate Beinn Bhreagh[199]
- The Bell Homestead National Historic Site, includes the Bell family home, «Melville House», and farm overlooking Brantford, Ontario and the Grand River. It was their first home in North America;
- Canada’s first telephone company building, the «Henderson Home» of the late 1870s, a predecessor of the Bell Telephone Company of Canada (officially chartered in 1880). In 1969, the building was carefully moved to the historic Bell Homestead National Historic Site in Brantford, Ontario, and was refurbished to become a telephone museum. The Bell Homestead, the Henderson Home telephone museum, and the National Historic Site’s reception centre are all maintained by the Bell Homestead Society;[200]
- The Alexander Graham Bell Memorial Park, which features a broad neoclassical monument built in 1917 by public subscription. The monument depicts mankind’s ability to span the globe through telecommunications;[201]
- The Alexander Graham Bell Museum (opened in 1956), part of the Alexander Graham Bell National Historic Site which was completed in 1978 in Baddeck, Nova Scotia. Many of the museum’s artifacts were donated by Bell’s daughters;

In 1880, Bell received the Volta Prize with a purse of 50,000 French francs (approximately US$290,000 in today’s dollars[202]) for the invention of the telephone from the French government.[189][203][204][205][206][207] Among the luminaries who judged were Victor Hugo and Alexandre Dumas, fils.[208][better source needed] The Volta Prize was conceived by Napoleon III in 1852, and named in honor of Alessandro Volta, with Bell becoming the second recipient of the grand prize in its history.[209][210] Since Bell was becoming increasingly affluent, he used his prize money to create endowment funds (the ‘Volta Fund’) and institutions in and around the United States capital of Washington, D.C.. These included the prestigious ‘Volta Laboratory Association’ (1880), also known as the Volta Laboratory and as the ‘Alexander Graham Bell Laboratory’, and which eventually led to the Volta Bureau (1887) as a center for studies on deafness which is still in operation in Georgetown, Washington, D.C. The Volta Laboratory became an experimental facility devoted to scientific discovery, and the very next year it improved Edison’s phonograph by substituting wax for tinfoil as the recording medium and incising the recording rather than indenting it, key upgrades that Edison himself later adopted.[211] The laboratory was also the site where he and his associate invented his «proudest achievement», «the photophone», the «optical telephone» which presaged fibre optical telecommunications while the Volta Bureau would later evolve into the Alexander Graham Bell Association for the Deaf and Hard of Hearing (the AG Bell), a leading center for the research and pedagogy of deafness.
In partnership with Gardiner Greene Hubbard, Bell helped establish the publication Science during the early 1880s. In 1898, Bell was elected as the second president of the National Geographic Society, serving until 1903, and was primarily responsible for the extensive use of illustrations, including photography, in the magazine.[212] He also served for many years as a Regent of the Smithsonian Institution (1898–1922).[213] The French government conferred on him the decoration of the Légion d’honneur (Legion of Honor); the Royal Society of Arts in London awarded him the Albert Medal in 1902; the University of Würzburg, Bavaria, granted him a PhD, and he was awarded the Franklin Institute’s Elliott Cresson Medal in 1912. He was one of the founders of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers in 1884 and served as its president from 1891 to 1892. Bell was later awarded the AIEE’s Edison Medal in 1914 «For meritorious achievement in the invention of the telephone».[214]
The bel (B) and the smaller decibel (dB) are units of measurement of sound pressure level (SPL) invented by Bell Labs and named after him.[215] [N 28][216] Since 1976, the IEEE’s Alexander Graham Bell Medal has been awarded to honor outstanding contributions in the field of telecommunications.

In 1936, the US Patent Office declared Bell first on its list of the country’s greatest inventors,[217] leading to the US Post Office issuing a commemorative stamp honoring Bell in 1940 as part of its ‘Famous Americans Series’. The First Day of Issue ceremony was held on October 28 in Boston, Massachusetts, the city where Bell spent considerable time on research and working with the deaf. The Bell stamp became very popular and sold out in little time. The stamp became, and remains to this day, the most valuable one of the series.[218]
The 150th anniversary of Bell’s birth in 1997 was marked by a special issue of commemorative £1 banknotes from the Royal Bank of Scotland. The illustrations on the reverse of the note include Bell’s face in profile, his signature, and objects from Bell’s life and career: users of the telephone over the ages; an audio wave signal; a diagram of a telephone receiver; geometric shapes from engineering structures; representations of sign language and the phonetic alphabet; the geese which helped him to understand flight; and the sheep which he studied to understand genetics.[219] Additionally, the Government of Canada honored Bell in 1997 with a C$100 gold coin, in tribute also to the 150th anniversary of his birth, and with a silver dollar coin in 2009 in honor of the 100th anniversary of flight in Canada. That first flight was made by an airplane designed under Dr. Bell’s tutelage, named the Silver Dart.[220] Bell’s image, and also those of his many inventions have graced paper money, coinage, and postal stamps in numerous countries worldwide for many dozens of years.
Alexander Graham Bell was ranked 57th among the 100 Greatest Britons (2002) in an official BBC nationwide poll,[221] and among the Top Ten Greatest Canadians (2004), and the 100 Greatest Americans (2005). In 2006, Bell was also named as one of the 10 greatest Scottish scientists in history after having been listed in the National Library of Scotland’s ‘Scottish Science Hall of Fame’.[222] Bell’s name is still widely known and used as part of the names of dozens of educational institutes, corporate namesakes, street and place names around the world.

Bell, an alumnus of the University of Edinburgh, Scotland, receiving an honorary Doctor of Laws degree (LL.D.) at the university in 1906
Honorary degrees
Alexander Graham Bell, who could not complete the university program of his youth, received at least a dozen honorary degrees from academic institutions, including eight honorary LL.D.s (Doctorate of Laws), two Ph.D.s, a D.Sc., and an M.D.:[223]
- Gallaudet College (then named National Deaf-Mute College) in Washington, D.C. (Ph.D.) in 1880[224][225]
- University of Würzburg in Würzburg, Bavaria (Ph.D.) in 1882[224]
- Heidelberg University in Heidelberg, Germany (M.D.) in 1886[224][36]
- Harvard University in Cambridge, Massachusetts (LL.D.) in 1896[224]
- Illinois College, in Jacksonville, Illinois (LL.D.) in 1896, possibly 1881[224][226]
- Amherst College in Amherst, Massachusetts (LL.D.) in 1901[224]
- St. Andrew’s University in St Andrews, Scotland (LL.D) in 1902[224]
- University of Oxford in Oxford, England (D.Sc.) in 1906[224]
- University of Edinburgh in Edinburgh, Scotland (LL.D.) in 1906[224][227]
- George Washington University in Washington, D.C. (LL.D.) in 1913[224]
- Queen’s University at Kingston in Kingston, Ontario, Canada (LL.D.) in 1908[224][228]
- Dartmouth College in Hanover, New Hampshire (LL.D.) in 1913,[229] possibly 1914[224]
Portrayal in film and television
- The 1939 film The Story of Alexander Graham Bell was based on his life and works.[230]
- The 1992 film The Sound and the Silence was a TV film.
- Biography aired an episode Alexander Graham Bell: Voice of Invention on August 6, 1996.
- Eyewitness No. 90 A Great Inventor Is Remembered, a 1957 NFB short about Bell.
Bibliography
- Bell, Alexander Graham (October 1880). «On the Production and Reproduction of Sound by Light». American Journal of Science (Read before the American Association for the Advancement of Science, in Boston, August 27, 1880). Third. 20 (118): 305–324. Bibcode:1880AmJS…20..305B. doi:10.2475/ajs.s3-20.118.305. S2CID 130048089.
Also published as: Bell, Alexander Graham (September 23, 1880). «Selenium and the Photophone». Nature. 22 (569): 500–503. Bibcode:1880Natur..22..500.. doi:10.1038/022500a0. - Bell, Alexander Graham (1898). The Question of Sign-Language and The Utility of Signs in the Instruction of the Deaf—Two papers (PDF). Washington, D.C.: Sanders Printing Office. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 29, 2012. Retrieved January 2, 2012.
- Bell, Alexander Graham (February 1917). «Prizes for the Inventor: Some of the Problems Awaiting Solution». The National Geographic Magazine. Vol. 31, no. 2. National Geographic Society. pp. 131–146.
See also
- Alexander Graham Bell Association for the Deaf and Hard of Hearing
- Alexander Graham Bell National Historic Site
- Bell Boatyard
- Bell Homestead National Historic Site
- Bell Telephone Memorial
- Berliner, Emile
- Bourseul, Charles
- IEEE Alexander Graham Bell Medal
- John Peirce, submitted telephone ideas to Bell
- Manzetti, Innocenzo
- Meucci, Antonio
- Oriental Telephone Company
- People on Scottish banknotes
- Pioneers, a Volunteer Network
- Reis, Philipp
- The Story of Alexander Graham Bell, a 1939 movie of his life
- The Telephone Cases
- Volta Laboratory and Bureau
- William Francis Channing, submitted telephone ideas to Bell
References
Notes
- ^ Bell was a British subject for most of his early life. When he moved to Canada in 1870, Canadian and British citizenship were functionally identical, with Canadian citizenship only becoming a formal classification in 1910. He applied for American citizenship after 1877, gained it in 1882, and referred to himself as an American citizen from that point on. Quote from Bell speaking to his wife: «you are a citizen because you can’t help it – you were born one, but I chose to be one.»[5] Aside from Bell’s own view of his citizenship, many, if not most Canadians considered him also as one of theirs as evidenced in an address by the Governor General of Canada. On October 24, 1917, in Brantford, Ontario, the Governor General spoke at the unveiling of the Bell Telephone Memorial to an audience numbering in the thousands, saying: «Dr. Bell is to be congratulated upon being able to receive the recognition of his fellow citizens and fellow countrymen».[6]
- ^ From Black (1997), p. 18: «He thought he could harness the new electronic technology by creating a machine with a transmitter and receiver that would send sounds telegraphically to help people hear.»
- ^ After Bell’s death his wife Mabel wrote to John J. Carty, an AT&T vice-president, and commented on her husband’s reluctance to have a phone in his study, saying «[of the statements in the newspapers] …publishing of Mr. Bell’s dislike of the telephone. Of course, he never had one in his study. That was where he went when he wanted to be alone with his thoughts and his work. The telephone, of course, means intrusion by the outside world. And the little difficulties and delays often attending the establishment of conversation… did irritate him, so that as a rule he preferred having others send and receive messages. But all really important business over the telephone he transacted himself. There are few private houses more completely equipped with telephones than ours… and there was nothing that Mr. Bell was more particular about than our telephone service… We never could have come here [to Beinn Bhreagh] in the first place or continued here, but for the telephone which kept us in close touch with doctors and neighbors and the regular telegraph office… Mr. Bell did like to say in fun, «Why did I ever invent the Telephone,» but no one had a higher appreciation of its indispensableness or used it more freely when need was—either personally or by deputy—and he was really tremendously proud of it and all it was accomplishing.»[10]
- ^ Bell typically signed his name in full on his correspondence.
- ^ Helmholtz’s The Sensations of Tone is credited with inspiring Bell, at the age of 23, to further his studies of electricity and electromagnetism.[36]
- ^ The family pet was given to his brother’s family.
- ^ The estate, dating from 1858, is in the present day located at 94 Tutela Heights Road, Brantford, and is now known as the «Bell Homestead», and formally as the Bell Homestead National Historic Site of Canada. It received its historical designation from the Government of Canada on June 1, 1996.[49]
- ^ Bell would later write that he had come to Canada a «dying man».
- ^ Bell was thrilled at his recognition by the Six Nations Reserve and throughout his life would launch into a Mohawk war dance when he was excited.
- ^ In later years, Bell described the invention of the telephone and linked it to his «dreaming place».
- ^ Eber (1991), p. 43 claimed that Mabel had scarlet fever in New York «…shortly before her fifth birthday…«; however, Toward (1984) provided a detailed chronology of the event claiming «… shortly after their arrival in New York [in January 1863]» when Mabel would have been at least five years and five weeks of age. Mabel’s exact age when she became deaf would later play a part in the debate on the effectiveness of manual versus oral education for deaf children, as children who are older at the onset of deafness retain greater vocalization skills and are thus more successful in oral education programs. Some of the debate centred on whether Mabel had to relearn oral speech from scratch, or whether she never lost it.
- ^ From Alexander Graham Bell (1979), p. 8: «Brantford is justified in calling herself ‘The Telephone City’ because the telephone originated there. It was invented in Brantford at Tutela Heights in the summer of 1874.»
- ^ Hubbard’s financial support to the research efforts fell far short of the funds needed, necessitating Bell to continue teaching while conducting his experiments.[83] Bell was so short of funds at times that he had to borrow money from his own employee, Thomas Watson. Bell also sought an additional CAD$150 from the former Premier of Canada, George Brown, in exchange for 50% of the patent rights in the British Empire (Brown later retracted his offer to patent the telephone in the U.K. for fear of being ridiculed). The Bell Patent Association, composed of Hubbard, Sanders and Bell and which would become the precursor of the Bell Telephone Company (and later, AT&T), would later assign an approximate 10% interest of its shares to Watson,[7] in lieu of salary and for his earlier financial support to Bell while they worked together creating their first functional telephone.
- ^ A copy of a draft of the patent application is shown, described as «probably the most valuable patent ever.»
- ^ Meucci was not involved in the final trial.[clarification needed]
- ^ Tomas Farley also writes that «Nearly every scholar agrees that Bell and Watson were the first to transmit intelligible speech by electrical means. Others transmitted a sound or a click or a buzz but our boys [Bell and Watson] were the first to transmit speech one could understand.»[126]
- ^ Many of the lawsuits became rancorous, with Elisha Gray becoming particularly bitter over Bell’s ascendancy in the telephone debate, but Bell refused to launch a countersuit for libel.[citation needed]
- ^ Marian was born only days after Bell and his assistant Sumner Tainter had successfully tested their new wireless telecommunication invention at their Volta Laboratory, one which Bell would name as his greatest achievement. Bell was so ecstatic that he wanted to jointly name his new invention and his new daughter Photophone (Greek: «light–sound«),[138][139] Bell wrote: «Only think!—Two babies in one week! Mabel’s baby was light enough at birth but mine was LIGHT ITSELF! Mabel’s baby screamed inarticulately but mine spoke with distinct enunciation from the first.» Bell’s suggested scientific name for their new infant daughter did not go over well with Marian’s mother, Mabel Gardiner Hubbard Bell.[138]
- ^ Under the direction of the Boston architects, Cabot, Everett & Mead, a Nova Scotia company, Rhodes, Curry & Company, carried out the actual construction.
- ^ In one memorable incident, the newly arrived Bells were walking down one of Baddeck’s central streets when Bell peered into a storefront window and saw a frustrated shopkeeper fiddling with his problematic telephone. Bell quickly disassembled it and effected a repair, to the owner’s amazement. When asked how he was able to do so Bell only needed to introduce himself.
- ^ Bell was inspired in part by Australian aeronautical engineer Lawrence Hargrave’s work with man-carrying box kites.[165] Hargrave declined to take patents on his inventions, similar to Bell’s decision not to file patents on some of his inventions. Bell also chose maroon-colored silk as it would show up clearly against the light-colored sky in his photographic studies.
- ^ «Selfridge Aerodrome Sails Steadily for 319 feet (97 m).» The Washington Post May 13, 1908.
- ^ At 25 to 30 Miles an Hour. First Public Trip of Heavier-than-air Car in America. Professor Alexander Graham Bell’s New Machine, Built After Plans by Lieutenant Selfridge, Shown to Be Practicable by Flight Over Keuka Lake. Portion of Tail Gives Way, Bringing the Test to an End. Views of an Expert. Hammondsport, New York, March 12, 1908.
- ^ The aileron had been conceived of as early as 1868 by British inventor M.P.W. Boulton and was also created independently by Robert Esnault-Pelterie and several others.
- ^ In the last years of his life, as his final projects wound down, Bell and his wife, their extended family and friends, lived exclusively at their beloved Beinn Bhreagh.[186][187]
- ^ From Bethune (2009), p. 119: «[his end came] at 2:00 am… His wife, Mabel, daughter Daisy, and son-in-law David Fairchild had gathered around him. His last view was of the moon rising above the mountain he loved».
- ^
The Charles Fleetford Sise Chapter of the Telephone Pioneers of America commissioned and dedicated the large bronze statue of Bell in the front portico of Brantford, Ontario’s new Bell Telephone Building plant on June 17, 1949. Attending the formal ceremony were Bell’s daughter, Mrs. Gillbert Grosvenor, Frederick Johnson, President of the Bell Telephone Company of Canada, T.N. Lacy, President of the Telephone Pioneers, and Brantford Mayor Walter J. Dowden. To each side of the portico facing the monument are the engraved inscriptions «In Grateful Recognition of the Inventor of the Telephone». Its dedication was broadcast live nationally by the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation.[195][196] - ^ The decibel is defined as one tenth of a bel.
Citations
- ^ Boileau, John (2004). Fastest in the World: The Saga of Canada’s Revolutionary Hydrofoils. Halifax, Nova Scotia: Formac Publishing. p. 12. ISBN 978-0-88780-621-6.
- ^ [Is the following a quote from the source referenced?:] While Bell worked in many scientific, technical, professional and social capacities throughout his life he would remain fondest of his earliest vocation. To the end of his days, when discussing himself, Bell would always add with pride «I am a teacher of the deaf».[1]
- ^ «Particle Physics Resurrects Alexander Graham Bell’s Voice». IEEE Spectrum. April 30, 2018. Retrieved May 10, 2018.
- ^ «The Bell Family». Bell Homestead National Historic Site. Retrieved September 27, 2013.
- ^ Gray 2006, p. 228.
- ^ Reville, F. Douglas (1920). History of the County of Brant: Illustrated With Fifty Half-Tones Taken From Miniatures And Photographs (PDF). Brantford, Ontario: Brantford Historical Society & Hurley Printing. p. 319. Archived from the original (PDF) on April 19, 2012. Retrieved May 4, 2012.
- ^ a b Bruce 1990, p. 291.
- ^ Bruce, Robert V. (1990). Bell: Alexander Bell and the Conquest of Solitude. Ithaca, New York: Cornell University Press. p. 419. ISBN 978-0-8014-9691-2.
- ^ MacLeod, Elizabeth (1999). Alexander Graham Bell: An Inventive Life. Toronto, Ontario: Kids Can Press. p. 19. ISBN 978-1-55074-456-9.
- ^ Bell, Mabel (October 1922). «Dr. Bell’s Appreciation of the Telephone Service». Bell Telephone Quarterly. 1 (3): 65. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ Howley, Andrew (May 26, 2011). «NGS Celebrates 23rd Founders Day». NGS. National Geographic Society. Retrieved January 18, 2016.
Though he wasn’t one of the original 33 founders, Bell had a major influence on the Society.
- ^ Stansfield, W. D. (January 1, 2005). «The Bell Family Legacies». Journal of Heredity. 96 (1): 1–3. doi:10.1093/jhered/esi007. ISSN 0022-1503. PMID 15618310.
- ^ Petrie, A. Roy (1975). Alexander Graham Bell. Don Mills, Ontario: Fitzhenry & Whiteside. p. 4. ISBN 978-0-88902-209-6.
- ^ «Time Line of Alexander Graham Bell.» memory.loc.goiv. Retrieved: July 28, 2010. Archived October 24, 2005, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «Alexander M. Bell Dead. Father of Prof. A. G. Bell Developed Sign Language for Mutes». The New York Times. August 8, 1905. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ «Call me Alexander Graham Bell». The Franklin Institute. January 14, 2014. Archived from the original on February 24, 2015. Retrieved February 24, 2015.
- ^ Groundwater, Jennifer (2005). Alexander Graham Bell: The Spirit of Invention. Calgary, Alberta: Altitude Publishing. p. 23. ISBN 978-1-55439-006-9.
- ^ Bruce 1990, pp. 17–19.
- ^ Bruce 1990, p. 490.
- ^ a b Bruce 1990, p. 16.
- ^ a b c Gray 2006, p. 8.
- ^ Gray 2006, p. 9.
- ^ Mackay, James (1997). Sounds Out of Silence: A life of Alexander Graham Bell. Edinburgh, UK: Mainstream Publishing. p. 25. ISBN 978-1-85158-833-6.
- ^ a b Petrie 1975, p. 7.
- ^ Mackay 1997, p. 31.
- ^ Gray 2006, p. 11.
- ^ Town, Florida (1988). Alexander Graham Bell. Toronto, Ontario: Grolier. p. 7. ISBN 978-0-7172-1950-6.
- ^ Bruce 1990, p. 37.
- ^ Shulman, Seth (2008). The Telephone Gambit: Chasing Alexander Bell’s Secret. New York: Norton & Company. p. 49. ISBN 978-0-393-06206-9.
- ^ a b c Groundwater 2005, p. 25.
- ^ Petrie 1975, pp. 7–9.
- ^ Petrie 1975, p. 9.
- ^ Messenger, Stephen. «Before Inventing The Telephone, Alexander Graham Bell Tried To Teach His Dog To Talk». The Dodo. Retrieved January 30, 2021.
- ^ a b Groundwater 2005, p. 30.
- ^ Shulman 2008, p. 46.
- ^ a b c Surtees, Lawrence (2005). «BELL, ALEXANDER GRAHAM». In Cook, Ramsay; Bélanger, Réal (eds.). Dictionary of Canadian Biography. Vol. XV (1921–1930) (online ed.). University of Toronto Press. Retrieved March 6, 2009.
- ^ MacKenzie, Catherine (2003) [1928]. Alexander Graham Bell. Boston, Massachusetts: Grosset and Dunlap. p. 41. ISBN 978-0-7661-4385-2.
- ^ Groundwater 2005, p. 31.
- ^ Shulman 2008, pp. 46–48.
- ^ Micklos, John Jr. (2006). Alexander Graham Bell: Inventor of the Telephone. New York: HarperCollins. p. 8. ISBN 978-0-06-057618-9.
- ^ Bruce 1990, p. 45.
- ^ Bruce 1990, pp. 67–28.
- ^ Bruce 1990, p. 68.
- ^ Groundwater 2005, p. 33.
- ^ Mackay 1997, p. 50.
- ^ Gray 2006, p. 21.
- ^ «Reverend Thomas Henderson House». Canada’s Historic Places. Retrieved August 5, 2020.
- ^ Mackay 1997, p. 61.
- ^ Bell Homestead National Historic Site of Canada. Canadian Register of Historic Places. Retrieved September 17, 2015.
- ^ Wing, Chris (1980). Alexander Graham Bell at Baddeck. Baddeck, Nova Scotia: Christopher King. p. 10.
- ^ Groundwater 2005, p. 34.
- ^ Mackay 1997, p. 62.
- ^ Groundwater 2005, p. 35.
- ^ Wing 1980, p. 10.
- ^ Waldie, Jean H. «Historic Melodeon Is Given To Bell Museum». likely published either by the London Free Press or by the Brantford Expositor, date unknown.
- ^ Bruce 1990, p. 74.
- ^ Town 1988, p. 12.
- ^ Alexander Graham Bell ((booklet)). Halifax, Nova Scotia: Maritime Telegraph & Telephone Limited. 1979. p. 8.
- ^ a b Groundwater 2005, p. 39.
- ^ Petrie 1975, p. 14.
- ^ Petrie 1975, p. 15.
- ^ Town 1988, pp. 12–13.
- ^ Petrie 1975, p. 17.
- ^ Schoenherr, Steven E. (February 10, 2000). «Charles Sumner Tainter and the Graphophone». Recording Technology History. Audio Engineering Society. Retrieved September 19, 2015.
- ^ Hochfelder, David (July 31, 2015). «Alexander Graham Bell». Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ «Image 1 of Pamphlet by Alexander Graham Bell, 1898». Library of Congress, Washington, D.C. Retrieved June 11, 2021.
- ^ «Alexander Graham Bell and His Role in Oral Education». Disabilitymuseum.org.
- ^ Miller, Don; Branson, Jan (2002). Damned For Their Difference: The Cultural Construction Of Deaf People as Disabled: A Sociological History. Washington, D.C.: Gallaudet University Press. pp. 30–31, 152–153. ISBN 978-1-56368-121-9.
- ^ Jay, Michelle (January 2, 2020). «Alexander Graham Bell — Helpful or Harmful? | Start ASL». Retrieved March 11, 2022.
- ^ «Eugenics and Deaf People in 20th Century America». Medium. May 11, 2021. Retrieved June 28, 2022.
- ^ «A Deaf Variety Of The Human Race». Gallaudet University. Retrieved March 11, 2022.
- ^ Town 1988, p. 15.
- ^ Town 1988, p. 16.
- ^ Toward, Lilias M. (1984). Mabel Bell: Alexander’s Silent Partner. Toronto, Ontario: Methuen. p. 1. ISBN 978-0-458-98090-1.
- ^ Eber, Dorothy Harley (1991) [1982]. Genius at Work: Images of Alexander Graham Bell (reprint ed.). Toronto, Ontario: McClelland and Stewart. p. 43. ISBN 978-0-7710-3036-9.
- ^ Dunn, Andrew (1990). Alexander Graham Bell. (Pioneers of Science). East Sussex, UK: Wayland Publishers. p. 20. ISBN 978-1-85210-958-5.
- ^ «Alexander Graham Bell and Thomas Watson». CBC. July 25, 1975. Retrieved October 14, 2016.
- ^ Matthews, Tom L. (1999). Always Inventing: A Photobiography of Alexander Graham Bell. Washington, D.C.: National Geographic Society. pp. 19–21. ISBN 978-0-7922-7391-2.
- ^ Matthews 1999, p. 21.
- ^ McCormick, Blaine; Israel, Paul (January–February 2005). «Underrated entrepreneur: Thomas Edison’s overlooked business story». IEEE Power & Energy Magazine. 3 (1): 76–79. doi:10.1109/MPAE.2005.1380243. S2CID 19680450. Archived from the original on December 23, 2009.
- ^ Town 1988, p. 17.
- ^ Evenson 2000, pp. 18–25.
- ^ Fitzgerald, Brian (September 14, 2001). «Alexander Graham Bell: The BU Years». B.U. Bridge. Vol. V, no. 5. Boston University. Retrieved March 28, 2010.
- ^ Bruce 1990, pp. 158–159.
- ^ US 174465 Alexander Graham Bell: «Improvement in Telegraphy» filed on February 14, 1876, granted on March 7, 1876.
- ^ MacLeod 1999, pp. 12–13.
- ^ «Alexander Graham Bell – Lab notebook pp. 40–41 (image 22)». Quotegrab. IAP Quotegrab. August 2, 2019. Retrieved September 17, 2019.
- ^ MacLeod 1999, p. 12.
- ^ Shulman 2008, p. 211.
- ^ Evenson 2000, p. 99.
- ^ Evenson 2000, p. 98.
- ^ Evenson 2000, p. 100.
- ^ Evenson 2000, pp. 81–82.
- ^ «Mr. Wilbur «confesses»«. The Washington Post. May 22, 1886. p. 1.
- ^ Evenson, A Edward (November 10, 2000). The Telephone Patent Conspiracy of 1876: The Elisha Gray-Alexander Bell Controversy and Its Many Players. McFarland. p. 99. ISBN 0786408839.
- ^ «Alexander Graham Bell 1847–1922 Inventor of the Bell System». Telecommunications Canada. Retrieved January 14, 2020.
- ^ «Invention of the Telephone National Historic Event». Parks Canada. Retrieved January 14, 2020.
Bell made public demonstrations of his now patented invention, culminating in the world’s first long distance call, to Paris, 13 kilometres away, on 10 August
- ^ MacLeod 1999, p. 14.
- ^ Popular Mechanics Aug 1912. New York: Popular Mechanics. August 1912. p. 186.
- ^ «First Phone Call».
- ^ Fenster, Julie M. (March 7, 2006). «Inventing the Telephone—And Triggering All-Out Patent War». American Heritage. Archived from the original on March 11, 2006. Retrieved September 19, 2015.
- ^ Winfield, Richard (1987). Never the Twain Shall Meet: Bell, Gallaudet, and the Communications Debate. Washington, D.C.: Gallaudet University Press. p. 21. ISBN 978-0-913580-99-8.
- ^ Webb, Michael, ed. (1991). Alexander Graham Bell: Inventor of the Telephone. Mississauga, Ontario: Copp Clark Pitman. p. 15. ISBN 978-0-7730-5049-5.
- ^ «Bell’s centennial telephone transmitter, 1876». National Archives UK. Retrieved January 14, 2020.
- ^ «140 Years Since the First Telephone Call to Queen Victoria on the Isle of Wight». Island Echo. January 14, 2018. Retrieved January 14, 2020.
He made the UK’s first publicly-witnessed long distance calls, calling Cowes, Southampton and London. Queen Victoria liked the telephone so much she wanted to buy it.
- ^ «Alexander Graham Bell demonstrates the newly invented telephone». The Telegraph. January 13, 2017. Archived from the original on January 11, 2022. Retrieved January 14, 2020.
one of the Queen’s staff wrote to Professor Bell to inform him «how much gratified and surprised the Queen was at the exhibition of the Telephone»
- ^ «pdf, Letter from Alexander Graham Bell to Sir Thomas Biddulph, February 1, 1878». Library of Congress. Retrieved January 14, 2020.
The instruments at present in Osborne are merely those supplied for ordinary commercial purposes, and it will afford me much pleasure to be permitted to offer to the Queen a set of Telephones to be made expressly for her Majesty’s use.
- ^ Ross, Stewart (2001). Alexander Graham Bell. (Scientists who Made History). New York: Raintree Steck-Vaughn. pp. 21–22. ISBN 978-0-7398-4415-1.
- ^ «Dom Pedro II and America». The Library of Congress. Retrieved March 7, 2018.
- ^ «Phone to Pacific From the Atlantic». The New York Times. January 26, 1915. Retrieved July 21, 2007.
- ^ MacLeod 1999, p. 19.
- ^ «Who Really Invented The Telephone?». Australasian Telephone Collecting Society. Moorebank, NSW, Australia. Archived from the original on September 24, 2015. Retrieved April 22, 2011.
- ^ a b c Groundwater 2005, p. 95.
- ^ Black, Harry (1997). Canadian Scientists and Inventors: Biographies of People who made a Difference. Markham, Ontario: Pembroke. p. 19. ISBN 978-1-55138-081-0.
- ^ Mackay 1997, p. 179.
- ^ «US v. American Bell Tel Co (1897)». Findlaw. May 10, 1897. Retrieved July 28, 2010.
- ^ «United States V. American Bell Telephone Co., 128 U.S. 315 (1888)». Jusrtia US Supreme Court. November 12, 1885. Retrieved July 28, 2010.
- ^ Catania, Basilio (December 2002). «The United States Government vs. Alexander Graham Bell. An important acknowledgment for Antonio Meucci». Bulletin of Science, Technology & Society. 22 (6): 426–442. doi:10.1177/0270467602238886. S2CID 144185363.
- ^ Catania, Basilio (November 6, 2009). «Antonio Meucci – Questions and Answers: What did Meucci to bring his invention to the public?». Chezbasilio.org. Retrieved September 19, 2015.
- ^ «Our History». ADT. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ Bruce 1990, pp. 271–272.
- ^ Rory Carroll (June 17, 2002). «Bell did not invent telephone, US rules». The Guardian. Retrieved October 25, 2015.
- ^ «H.RES.269: Resolution 269.» thomas.loc.gov. Retrieved: July 28, 2010. Archived July 13, 2015, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «Congressional Record – Speech by Prof. Basillio». September 5, 2001. Archived from the original on July 17, 2011. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ «Antonio Meucci (1808–1889)». Italian Historical Society of America. Archived from the original on October 15, 2015. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ a b Bellis, Mary. «The History of the Telephone – Antonio Meucci». About.com Inventors. Retrieved December 29, 2009.
- ^ Mackay 1997, p. 178.
- ^ Parker, Steve (1995). Alexander Graham Bell and the Telephone. Scientific American. (Science Discoveries). Vol. 102. p. 23. Bibcode:1910SciAm.102..462.. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican06041910-462. ISBN 978-0-7910-3004-2.
- ^ Bruce 1990, pp. 297–299.
- ^ Eber 1991, p. 44.
- ^ Dunn 1990, p. 28.
- ^ Mackay 1997, p. 120.
- ^ «Mrs. A.G. Bell Dies. Inspired Telephone. Deaf Girl’s Romance With Distinguished Inventor Was Due to Her Affliction». The New York Times. January 4, 1923.[dead link]
- ^ «Dr. Gilbert H. Grosvenor Dies». The New York Times. Canadian Press. February 5, 1966. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
Dr. Gilbert H. Grosvenor … died on the Cape Breton Island estate once owned by his father-in-law, the inventor Alexander Graham Bell.
- ^ «Mrs. Gilbert Grosvenor Dead». The New York Times. December 27, 1964. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ Grosvenor, Edwin S.; Wesson, Morgan (1997). Alexander Graham Bell: The Life and Times of the Man Who Invented the Telephone. New York: Harry N. Abrahms. p. 104. ISBN 978-0-8109-4005-5.
- ^ «Mrs. David Fairchild, 82, Dead; Daughter of Bell, Phone Inventor». The New York Times. Canadian Press. September 25, 1962.
- ^ a b Grosvenor & Wesson 1997, p. 104.
- ^ Carson, Mary Kay (2007). Alexander Graham Bell: Giving Voice To The World. Sterling Biographies. New York: Sterling Publishing. p. 77. ISBN 978-1-4027-3230-0. OCLC 182527281.
- ^ Gray 2006, pp. 202–205.
- ^ Bruce, Robert V. (March 15, 2020). «Bell: Alexander Graham Bell and the Conquest of Solitude». Plunkett Lake Press – via Google Books.
- ^ Bruce 1990, p. 90.
- ^ Bruce 1990, pp. 471–472.
- ^ Bethune, Jocelyn (2009). Historic Baddeck. (Images of our Past). Halifax, Nova Scotia: Nimbus Publishing. p. 2. ISBN 978-1-55109-706-0.
- ^ Bethune 2009, p. 92.
- ^ a b c Bethune 2009, p. 2.
- ^ Tulloch, Judith (2006). The Bell Family in Baddeck: Alexander Graham Bell and Mabel Bell in Cape Breton. Halifax, Nova Scotia: Formac Publishing. pp. 25–27. ISBN 978-0-88780-713-8.
- ^ MacLeod 1999, p. 22.
- ^ Tulloch 2006, p. 42.
- ^ Gray 2006, p. 219.
- ^ Bruce 1990, p. 336.
- ^ Jones, Newell (July 31, 1937). «First ‘Radio’ Built by San Diego Resident Partner of Inventor of Telephone: Keeps Notebook of Experiences With Bell». Evening Tribune. San Diego, California. Archived from the original on February 19, 2002. Retrieved November 26, 2009.
- ^ Carson 2007, pp. 76–78.
- ^ Bruce 1990, p. 338.
- ^ Groth, Mike (April 1987). «Photophones Revisted». Amateur Radio: 12–17. Archived from the original on August 2, 2015. Retrieved September 19, 2015.
- ^ Mims III, Forest M. (February 10–26, 1982). «The First Century of Lightwave Communications». Fiber Optics Weekly Update: 11 of 6–23.
- ^ Phillipson, Donald J.C.; Neilson, Laura (March 4, 2015). «Alexander Graham Bell». The Canadian Encyclopedia (online ed.). Historica Canada. Archived from the original on September 25, 2015. Retrieved September 19, 2015.
- ^ Morgan, Tim J. (2011). The Fiber Optic Backbone (Report). University of North Texas. Archived from the original on September 25, 2015. Retrieved September 19, 2015.
- ^ Miller, Stewart E. (January–February 1984). «Lightwaves and Telecommunication». American Scientist. 72 (1): 66–71. JSTOR i27852430.
- ^ a b c Grosvenor & Wesson 1997, p. 107.
- ^ Bell, Alexander Graham (1882). «Upon the electrical experiments to determine the location of the bullet in the body of the late President Garfield; and upon a successful form of induction balance for the painless detection of metallic masses in the human body». American Journal of Science. 25 (145): 22–61. Bibcode:1883AmJS…25…22B. doi:10.2475/ajs.s3-25.145.22. S2CID 130896535. Retrieved April 29, 2013.
- ^ Boileau 2004, p. 18.
- ^ Boileau 2004, pp. 28–30.
- ^ Boileau 2004, p. 30.
- ^ Technical Gazette. New South Wales, Australia. 1924. p. 46.
- ^ «Nova Scotia’s Electric Scrapbook.» Archived April 17, 2009, at the Wayback Machine ns1763.ca. Retrieved: December 29, 2009.
- ^ Gillis, Rannie (September 29, 2008). «Mabel Bell Was A Focal Figure In The First Flight of the Silver Dart». Cape Breton Post. Sydney, Nova Scotia. Archived from the original on July 24, 2016. Retrieved June 12, 2010.
- ^ «Canada’s Golden Anniversary». Flight. Vol. 75, no. 2614. February 27, 1959. p. 280. Retrieved August 28, 2013.
- ^ Phillips, Allan (1977). Into the 20th Century: 1900/1910. (Canada’s Illustrated Heritage). Toronto, Ontario: Natural Science of Canada. p. 95. ISBN 978-0-919644-22-9.
- ^ Phillips 1977, p. 96.
- ^ «Link with Canadian Pioneers». Flight. Vol. 70, no. 2491. October 19, 1956. p. 642. Retrieved August 28, 2013.
- ^ Phillips 1977, pp. 96–97.
- ^ «Bell Rings for Darwin | National Center for Science Education». ncse.ngo. Retrieved March 2, 2021.
- ^ «Telephone inventor researched sheep teats». The Western Producer. October 2, 1997.
- ^ Castle, W. E. (February 1, 1924). «THE GENETICS OF MULTI-NIPPLED SHEEPAn Analysis of the Sheep-Breeding Experiments of Dr. and Mrs. Alexander Graham Bell at Beinn Bhreagh, N. S.» Journal of Heredity. 15 (2): 75–85. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a102421. ISSN 0022-1503.
- ^ Greenwald, Brian H. (2009). «The Real «Toll» of A. G. Bell: Lessons about Eugenics». Sign Language Studies. 9 (3): 258–265. ISSN 0302-1475. JSTOR 26190555.
- ^ a b Bell, Alexander Graham (1884). Upon the Formation of a Deaf Variety of the Human Race. U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ^ Memoir Upon the Formation of a Deaf Variety of the Human Race. Institute for Education Sciences. Alexander Graham Bell Association for the Deaf. 1969.
- ^ Greenwald, Brian H.; Van Cleve, John Vickrey (2015). ««A Deaf Variety of the Human Race»: Historical Memory, Alexander Graham Bell, and Eugenics». The Journal of the Gilded Age and Progressive Era. 14 (1): 28–48. doi:10.1017/S1537781414000528. ISSN 1537-7814. JSTOR 43903056. S2CID 163891681.
- ^ a b F., E. A. (1885). «Review of Memoir upon the Formation of a Deaf Variety of the Human Race». American Annals of the Deaf and Dumb. 30 (2): 155–162. ISSN 0093-1284. JSTOR 44468521.
- ^ Greenwald, Brian H.; Cleve, John Vickrey Van (January 2015). ««A Deaf Variety of the Human Race»: Historical Memory, Alexander Graham Bell, and Eugenics». The Journal of the Gilded Age and Progressive Era. 14 (1): 28–48. doi:10.1017/S1537781414000528. ISSN 1537-7814. S2CID 163891681.
- ^ a b Allen, Garland E. (1986). «The Eugenics Record Office at Cold Spring Harbor, 1910-1940: An Essay in Institutional History». Osiris. 2: 225–264. doi:10.1086/368657. ISSN 0369-7827. JSTOR 301835. PMID 11621591. S2CID 411710.
- ^ a b International Congress of Eugenics (2nd : 1921 : New York) (1923). Scientific papers of the second International Congress of Eugenics :held at American Museum of Natural History, New York, September 22-28, 1921 / (Vol. 2). The Library of Congress. Baltimore : Williams & Williams.
- ^ Gray, Charlotte (2006). Reluctant Genius: The Passionate Life and Inventive Mind of Alexander Graham Bell. New York: Arcade. p. 419. ISBN 978-1-55970-809-8.
- ^ Gray 2006, p. 418.
- ^ Bethune 2009, p. 95.
- ^ Duffy, Andrew (February 23, 2009). «The Silver Dart sputtered into history». Ottawa Citizen. Archived from the original on July 13, 2015. Retrieved September 18, 2015..
- ^ Bethune 2009, p. 119.
- ^ a b c d e «Dr. Bell, Inventor of Telephone, Dies» (PDF). The New York Times. August 3, 1922. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 9, 2022. Retrieved March 3, 2009.
- ^ Bruce 1990, p. 491.
- ^ Bethune 2009, pp. 119–120.
- ^ Pasachoff, Naomi (1996). Alexander Graham Bell: Making Connections. New York: Oxford University Press. p. 130. ISBN 978-0-19-509908-9.
- ^ Osborne 1943, pp. 18–19.
- ^ «Dr. Bell, Inventor of Telephone, Dies». The New York Times. August 3, 1922. Retrieved July 21, 2007.
Dr. Alexander Graham Bell, inventor of the telephone, died at 2 o’clock this morning at Beinn Breagh, his estate near Baddeck
- ^ Ireland, Carolyn (February 27, 2009). «The Portrait Studio House». The Globe and Mail.
- ^ «Daughter Unveils Inventor’s Statue: Bronze Figure Is Dedicated By Phone Pioneers». Brantford Expositor. June 18, 1949.
- ^ a b «About this Collection». Alexander Graham Bell Family Papers. Library of Congress. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ Osborne, Harold S. (1943). Biographical Memoir of Alexander Graham Bell 1847–1922 (PDF). Biographical Memoirs. Vol. XXIII. National Academy of Sciences. p. 18. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 9, 2022. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ «Alexander Graham Bell National Historic Site». Parks Canada. August 7, 2015. Archived from the original on October 11, 2007. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ «Pay Us a Call at Melville House!». Bell Homestead National Historic Site. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ «Alexander Graham Bell Memorial Park.» maps.google.com. Retrieved: February 14, 2012.
- ^ 1634–1699: McCusker, J. J. (1997). How Much Is That in Real Money? A Historical Price Index for Use as a Deflator of Money Values in the Economy of the United States: Addenda et Corrigenda (PDF). American Antiquarian Society. 1700–1799: McCusker, J. J. (1992). How Much Is That in Real Money? A Historical Price Index for Use as a Deflator of Money Values in the Economy of the United States (PDF). American Antiquarian Society. 1800–present: Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis. «Consumer Price Index (estimate) 1800–». Retrieved April 16, 2022.
- ^ «Honors to Professor Bell Daily Evening Traveller». Alexander Graham Bell Family Papers. Library of Congress. September 1, 1880. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ «Volta Prize of the French Academy Awarded to Prof. Alexander Graham Bell». Alexander Graham Bell Family Papers. Library of Congress. September 1, 1880. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ «Telegram from Grossman to Alexander Graham Bell». Alexander Graham Bell Family Papers. Library of Congress. August 2, 1880. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ «Telegram from Alexander Graham Bell to Count du Moncel, undated». Alexander Graham Bell Family Papers. Library of Congress. 1880. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ «Letter from Frederick T. Frelinghuysen to Alexander Graham Bell». Alexander Graham Bell Family Papers. Library of Congress. January 7, 1882. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ «The Volta Prize For Electricity» (PDF). Selected Innovation Prizes and Reward Programs (Report). Knowledge Ecology International. 2008. p. 16. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 9, 2022. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ Maindron, Ernest (1881). Gauthier-Villars (ed.). Les fondations de prix à l’Académie des sciences : les lauréats de l’Académie, 1714–1880 (in French). Vol. 1. pp. 131–133.
- ^ Davis, John L. (July 1998). «Artisans and savants: The Role of the Academy of Sciences in the Process of Electrical Innovation in France, 1850–1880». Annals of Science. 55 (3): 291–314. doi:10.1080/00033799800200211.
- ^ «Letter from Mabel Hubbard Bell». Alexander Graham Bell Family Papers. Library of Congress. February 27, 1880. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
The last line of the typed note refers to the future disposition of award funds: He intends putting the full amount into his Laboratory and Library.
- ^ «National Geographic Milestones». National Geographic Milestones. National Geographic Society. June 20, 2012. Retrieved January 18, 2016.
- ^ «Proceedings of the Board of Regents of the Smithsonian Institution at the Annual Meeting held December 14, 1922», Volume IV of the Proceedings of the Board of Regents, Dec. 9, 1920 – Dec. 10, 1931, Washington, D. C.: Smithsonian Institution, December 14, 1922, p. 547,
RESOLVED: That the Executive Committee be requested to prepare a memorial commemorative of the life and work of Dr. Alexander Graham Bell, Regent of the Smithsonian Institution from 1898 to 1922, said memorial to be presented at the next Annual Meeting of the Board.
- ^ «Alexander Graham Bell». Engineering and Technology History Wiki. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ «Decibel.» Archived August 9, 2017, at the Wayback Machine sfu.ca. Retrieved: July 28, 2010.
- ^ «bel». The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language (Fifth ed.). Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. 2011. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ Beauchamp, Christopher (October 2010). «Who Invented the Telephone?: Lawyers, Patents, and the Judgments of History». Technology and Culture. 51 (4): 854–878. doi:10.1353/tech.2010.0038. JSTOR 40928028.
- ^ Scott’s United States Stamp catalogue.
- ^ «Royal Bank Commemorative Notes». Rampant Scotland. Retrieved October 14, 2008.
- ^ «Proof Set – 100th Anniversary of Flight in Canada (2009)». Royal Canadian Mint. Archived from the original on September 9, 2017. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ «100 great British heroes». BBC News World Edition. August 21, 2002. Retrieved April 5, 2010.
- ^ «Alexander Graham Bell (1847–1922)». Scottish Science Hall of Fame. 2009.
- ^ MacDougall, D., ed. (1917). «Part V: Alexander Graham Bell». Scots and Scots Descendant in America. New York: Caledonian. p. 162. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l MacDougall 1917, p. 162.
- ^ «Honorary Degree Recipients». Gallaudet University. Washington, DC. Archived from the original on June 18, 2010. Retrieved July 28, 2010.
- ^ «Honorary Degrees Conferred». Illinois College. Archived from the original on September 24, 2015. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ «Graduations». University of Edinburgh. Archived from the original on September 1, 2015. Retrieved September 18, 2015.
- ^ «Honorary Degrees». Queen’s University. Retrieved October 14, 2020.
- ^ «Dartmouth graduates 208: Alexander Graham Bell Among Those Receiving Honorary Degrees» (PDF). The New York Times. July 26, 1913. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 9, 2022. Retrieved July 30, 2009.
- ^ «THE SCREEN; The founding of the Wrong-Number Industry WellDramatized in Roxy’s ‘Alexander Graham Bell’ At the 86th St. Garden Theatre At Three Theatres At the 86th Street Casino». The New York Times. April 1, 1939. Retrieved February 2, 2017.
Further reading
- Mullett, Mary B. The Story of A Famous Inventor. New York: Rogers and Fowle, 1921.
- Walters, Eric. The Hydrofoil Mystery. Toronto, Ontario, Canada: Puffin Books, 1999. ISBN 0-14-130220-8.
- Winzer, Margret A. The History Of Special Education: From Isolation To Integration. Washington, D.C.: Gallaudet University Press, 1993. ISBN 978-1-56368-018-2.
External links
- Alexander and Mabel Bell Legacy Foundation
- Alexander Graham Bell Institute at Cape Breton University
- Bell Telephone Memorial, Brantford, Ontario
- Bell Homestead National Historic Site, Brantford, Ontario
- Alexander Graham Bell National Historic Site of Canada, Baddeck, Nova Scotia
- Alexander Graham Bell Family Papers at the Library of Congress
- Alexander Graham Bell — Biographical Memoirs of the National Academy of Sciences
- Biography at the Dictionary of Canadian Biography Online
- Science.ca profile: Alexander Graham Bell
- Works by Alexander Graham Bell at Project Gutenberg
- Alexander Graham Bell at IMDb
- Alexander Graham Bell’s notebooks at the Internet Archive
- «Téléphone et photophone : les contributions indirectes de Graham Bell à l’idée de la vision à distance par l’électricité» at the Histoire de la télévision
- Newspaper clippings about Alexander Graham Bell in the 20th Century Press Archives of the ZBW
Multimedia
- Alexander Graham Bell at The Biography Channel
- The Story of Alexander Graham Bell (1939) at IMDb
- Alexander Graham Bell portrayed by John Bach (1992). The Sound and the Silence (Television production). Canada, New Zealand, Ireland: Atlantis Films.
- The Animated Hero Classics: Alexander Graham Bell (1995) at IMDb
- Gray, Charlotte (May 2013). «We Had No Idea What Alexander Graham Bell Sounded Like. Until Now». Smithsonian Magazine.
- Shaping The Future, from the Heritage Minutes and Radio Minutes collection at HistoricaCanada.ca (1:31 audio drama, Adobe Flash required)
| Non-profit organization positions | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded by Gardiner Greene Hubbard | President of the National Geographic Society 1897–1904 | Succeeded by William John McGee |
Александр Белл — биография
Александр Белл – ученый изобретатель шотландского происхождения, ставший основателем телекоммуникационной сети в Соединенных Штатах и Канаде.
Современного человека едва ли получится удивить даже самой крутой научной разработкой, а ведь каких-то 150 лет назад появление телефона, гидросамолета и металлоискателя воспринималось, как невероятная сенсация. Автором этих изобретений стал шотландец Александр Белл, задавший вектор развития телекоммуникаций как в Соединенных Штатах, так и во всем мире.
Детство и юность
Полное имя ученого – Александр Грайам Белл. Он родился 3 марта 1847 года в шотландском городе Эдинбург, в семье учителей красноречия и логопедов. Его дед, тоже Александр, в молодости подрабатывал театральным суфлером, а потом начал давать уроки ораторского искусства. Дело оказалось успешным, и впоследствии мужчина смог открыть собственную школу дикции в Лондоне. С тех пор преподавательская деятельность стала неотъемлемой частью семейства Беллов. Отец изобретателя телефона даже выпустил трактат, посвященный мастерству красноречия.

Белл-младший с детства был окружен музыкой, в доме часто обсуждали вопросы культуры и искусства. В подростковом возрасте Александр и два его брата перебрались к деду в столицу, где стали изучать философию и медицину. После окончания Эдинбургской Королевской Высшей школы будущий ученый начал жить самостоятельно, устроившись преподавателем ораторского искусства и музыки в академию Уэстон-Хаус.
Получив экспертные знания в области физики человеческой речи и акустики, Александр начал ассистировать своему отцу, работавшему в то время над собственной методикой по совершенствованию произношения.
У матери изобретателя были проблемы со слухом, и все разработки супруга были направлены на помощь ей. Белл-старший создал уникальную систему «Визуальная речь», где звуки заменялись картинками и символами, помогающими слабослышащему человеку определять мимику речевого аппарата. Для людей, испытывавших проблемы с восприятием звуков, это была серьезная помощь.
В результате вспышки туберкулеза скончались оба брата ученого, после чего в 1870 году семья перебралась в Канаду, а после в США. В Штатах они продолжили преподавать ораторское мастерство и заниматься изобретением полезных приспособлений для слабослышащих. Вскоре Александр основал свою школу, где преподавал коллегам семейную методику развития дикции.

Став самостоятельным в финансовом плане, Белл продолжил эксперименты по передаче звуков посредством электрического провода. Эти опыты он начал ставить еще в Англии, но полноценно погрузиться в работу смог только здесь. Он открыл небольшую лабораторию, где в свободное от лекций часы проводил исследования, результаты которых стали настоящим прорывом в науке.
Среди добровольцев, участвовавших в экспериментах отца и сына, была будущая супруга Александра – Мейбл Хаббард, а также маленький слабослышащий мальчик по фамилии Сандерс.
Научная деятельность
Изобретение с названием «телефон» Александр Белл впервые показал в 1876 году, в рамках Всемирной научной выставки в штате Филадельфия. В том же году новинка была запатентована, но всерьез ее тогда еще никто не воспринимал. Участники выставки сочли телефон забавной, но непрактичной игрушкой.

К тому времени Александр накопил немало долгов, и, чтобы покончить с безденежьем, решил продать свое детище за 100 тысяч долларов. С предложением он обратился в компанию «Вестерн Юнион», но руководство сочло такую покупку бессмысленной тратой денег. Впоследствии бизнесмены признали свою ошибку и предложили изобретателю выгодный контракт.

Первая модель телефона была далека от совершенства: звук получался искаженным, а дальность действия устройства не превышала 250 метров. Создатель постоянно дорабатывал свое изобретение, добиваясь хорошего качества звука и возможности передавать его на большие расстояния. Зимой 1880-го ученый вместе с ассистенткой создали новый аппарат – фотофон – способный передавать звуки посредством света.

В следующем году Белл представил усовершенствованный металлоискатель, разработку которого начал еще несколько лет назад. В начале 20-го века изобретатель явил миру еще одно свое детище – пирамидального воздушного змея, который мог выдержать вес человека.

В 1907 году была основана «Ассоциация экспериментальной аэронавтики», во главе которой стояли Александр и его супруга Мейбл. Вскоре научный деятель построил аэроплан «Серебряный дротик», который взмыл в небо 23 февраля 1909 года. В Канаде эту дату принято считать днем основания авиации.

В начале 20-го века Белл работал над чертежами лодки HD-4, которая впоследствии побила все скоростные рекорды на воде. Подлодка, оснащенная подводными крыльями, могла развивать скорость более 110 км/час.
Могут быть знакомы
Предпринимательство
В конце 1870-х Белл возобновил переговоры с «Western Union», и вскоре он с компаньонами стал владельцем объединенной компании «Bell Company». Ключевая часть пакета ценных бумаг досталась Александру Беллу, при этом стоимость одной акции составляла 1 тысячу долларов. Благодаря деятельности новой компании было положено начало телефонизации и появлению других телекоммуникационных организаций. В начале века в Америке было установлено 1,5 миллиона телефонных аппаратов, а всего через два года их количество выросло до 13 миллионов.

Ученый понимал, что будущее – за энергичными, квалифицированными людьми, поэтому оказывал серьезную помощь перспективным специалистам. Он способствовал получению патентов на новые изобретения в области телефонии, а на вырученные средства смог открыть институт для обучения кадров. Это учебное заведение Белл назвал в честь знаменитого итальянца Алессандро Вольта.
Помимо научной деятельности, Александр занимался общественной работой и много сил отдавал благотворительности. Хорошо известен факт о том, что изобретатель стоял у истоков Национального географического общества, а также был инициатором создания научно-популярного журнала «National Geographic», выпускаемого по сей день.

Со временем вклад Белла в развитие науки был высоко оценен во всем мире, а его компания разрослась до гиганта в области телекоммуникаций, электронных систем и компьютерных технологий. Однажды гений заявил, что когда-нибудь люди смогут видеть друг друга при телефонном разговоре. Тогда слова ученого вызвали улыбку, но сейчас уже никто не сомневается в его прозорливости.
Основанная ученым компания продолжает работать и активно развиваться, оставаясь верной принципам своего гениального создателя. Здесь по-прежнему изобретают новинки в сфере телекоммуникаций, а в последнее время активно развивают такие прогрессивные направления, как изучение ДНК, космических технологий и современных языков программирования.
Заслуги в медицине
В начале июля 1881 года было совершено покушение на 20-го президента США Джеймса Гарфилда, но умер он не сразу. Одна из пуль пронзила руку главы государства, вторая застряла в спине. Последние дни президент провел в страшных мучениях, и даже лучшие доктора не смогли облегчить его страдания.

Узнав о случившемся, Белл немедленно отправился в Бостон, где в срочном порядке продолжил совершенствовать свой металлодетектор. Изначально прибор создавался для обнаружения редкоземельных металлов, теперь же с его помощью ученый намеревался разыскать пулю в теле Гарфилда. Прибыв с устройством в Белый дом, Александр изрядно напугал раненого, который до ужаса боялся электрического тока. Пулю обнаружить не удалось – аппарат выдавал равномерный пищащий звук по всей поверхности тела. Как выяснилось позже, доктора пренебрегли просьбой положить президента на матрас без металлических пружин. Металлоискатель попросту отреагировал на металлический каркас кровати.
Джеймс Гарфилд начал было идти на поправку, но 19 сентября вдруг внезапно скончался. Застрявшая пуля была ни при чем: он умер от занесенной врачами инфекции. Не имея рентгеновского аппарата, медики исследовали раны руками, отсюда и столь печальный итог.

Как это ни трагично, но смерть президента дала толчок к усовершенствованию металлодетектора, который впоследствии широко применялся как в горнодобывающей промышленности, так и в медицине. После нью-йоркской конференции врачей 1881 года многие хирурги заинтересовались прибором и стали использовать его при проведении операций. До изобретения рентгена металлоискатель стал отличным подспорьем, когда речь шла об извлечении пуль и осколков гранат из тел раненых солдат.

Один из сыновей Белла скончался от легочной недостаточности, и эта трагедия подтолкнула ученого к изобретению, ставшему прототипом аппарата искусственной вентиляции легких.
Личная жизнь
Биография Александра Белла была тесно связана с преподавательской деятельностью, даже когда он стал состоятельным бизнесменом. Большое внимание ученый уделял слабослышащим ученикам, среди которых однажды встретил свою будущую жену Мейбл.

Их знакомство состоялось, когда девушке было всего 15 лет. Дождавшись ее совершеннолетия, влюбленные организовали помолвку, но о свадьбе речи пока не шло. В течение следующих двух лет Белл копил деньги, чтобы родители невесты убедились в его состоятельности. Оценив целеустремленность потенциального зятя, отец с матерью благословили дочь на брак с ученым.
Судя по сохранившимся дневникам и письмам, личная жизнь супругов была счастливой. Своей матери Мейбл писала, что каждый день супруг открывается ей с новой стороны. Девушка неустанно заботилась о муже, старалась как можно вкуснее его накормить. Связано это или нет, но через несколько лет после свадьбы ученый стал весить почти 100 килограмм, что на 40 кг больше его обычного веса.

Медовый месяц счастливые влюбленные провели в Канаде, в живописном местечке Ниагара Фоллз. Александру приходилось часто уезжать в командировки, и разлука с женой наводила на него сильнейшую тоску. В конце концов изобретатель решил не терзать ни себя, ни любимую женщину, начав брать ее с собой во все деловые поездки.
Единственной претензией Мейбл к мужу было то, что все свои исследования он проводил исключительно по ночам. До четырех часов утра супруга ждала его в спальне, не смыкая глаз. Изменить свое рабочее расписание гений пытался, но всякий раз безуспешно.

В семье родилось четверо детей – два мальчика и две девочки, но оба сына умерли еще в младенчестве. Чета переживала эту утрату очень тяжело, но мудрая Мейбл старалась относиться к горю философски. Она говорила, что мальчики навсегда останутся в их сердцах, пытаясь успокоить этим и супруга.
Брак преподавателя и его подопечной был долгим: в горе и в радости они прожили практически половину века.
Смерть
В последние годы ученого изматывал сахарный диабет, и к концу жизни он оказался прикованным к постели. Дни перед смертью изобретатель провел в беспамятстве, придя в сознание только на несколько минут. Открыв глаза, Белл увидел возле себя любимую жену, улыбнулся, вновь закрыл глаза и отошел в мир иной. Это произошло 2 августа 1922 года, когда 75-летний Александр находился в своем поместье в Новой Шотландии, Канада.
Чтобы отдать дань памяти великому ученому, 4 августа того же года по всей территории Соединенных Штатов были ровно на одну минуту отключены телефоны. Этот жест поддержали миллионы граждан, которые благодаря Александру Беллу получили уникальную возможность разговаривать друг с другом на любом расстоянии.



В память о гениальном американце шотландского происхождения были сняты документальные картины, а его имя увековечено в десятках новых разработок. Малоизвестный факт: в 2002-м решением американского конгресса изобретателем телефона был признан итальянский ученый Антонио Меуччи, который по утверждению некоторых исследователей придумал аппарат за два года до Белла. Не получив патента, Меуччи умер в полной нищете и безызвестности, а слава досталась более предприимчивому Александру.
Интересные факты
- Когда телефонные разговоры стали более-менее привычным делом, Белл предложил использовать слово «Ahoy» в качестве приветствия. Позже оно трансформировалось в «Hello», которое в русском варианте звучит как привычное нам «Алло!».
- Создатель таких серьезных изобретений, как телефон, аэроплан и подводная лодка, на полном серьезе пытался обучить своего пса человеческой речи.
- Белл был истинно верующим человеком, поэтому считал, что когда-нибудь с помощью телефона люди смогут общаться с умершими близкими.
- Основатель телекоммуникационной империи так и не смог поговорить по телефону ни с женой, ни с матерью. Обе женщины были слабослышащими.
Известные изобретения
- Машина для обработки зерна (1858);
- Телефон (1876);
- Аудиометр (1879);
- Фотофон (1880);
- Металлоискатель (1881);
- Вакуумный насос (1881);
- Пирамидальный воздушный змей (1901);
- Аэроплан (1909);
- Подводная лодка HD-4 (1919).
Ссылки
- Страница в Википедии
Для нас важна актуальность и достоверность информации. Если вы обнаружили ошибку или неточность, пожалуйста, сообщите нам. Выделите ошибку и нажмите сочетание клавиш Ctrl+Enter.
Александр Грейам Белл
Александр Грейам
Белл (Alexander Graham Bell)
Родословная
Дед
великого изобретателя телефона, которого тоже звали Александр Белл, родился в
1790-м году в Эдинбурге, в Шотландии. Он стал башмачником, как и все его
предки.

Александр Белл, дед изобретателя
В
1814 году он женился на Элизабет Колвилль (Elizabet Colville) и решил сменить
профессию. Быть может, повлиял его тесть, который был очень предприимчивым
человеком: он и плотничал, и изготавливал волынки, и даже лечил пациентов. Те, которые
выживали, не жаловались. Александр стал актером и начал с комедийных ролей, но
большую популярность ему принесли роли шотландских горцев. Театральные обзоры
того времени с восторгом отзывались о его выступлении в пьесе «Роб Рой».
Но
одних гонораров на жизнь не хватало, и он вместе с женой содержал таверну, а в
театре ему еще приходилось быть суфлером. В 1817 у него родился сын Дэвид, в
1819 году родился сын Мелвилл (Melville
Bell),
в 1822 году родилась дочь Элизабет. Семейство Александра Белла росло, а доходы
падали.
В
1822 году глава семьи решил переехать в Сэнт-Эндрюс (St. Andrews), где Александр стал
давать уроки красноречия. Там он даже стал учителем в местной школе (St. Andrews Grammar School), так как местные жители считали,
что у столичного жителя и джентльмена (по их меркам) есть чему поучиться.
В
1826 году Александр переехал в Данди (Dundee), и там его налаженная жизнь дала трещину. Его жена
Элизабет завела роман с ректором местной академии (Dundee Academy), и эта интрижка стала
достоянием всего городка. В 1831 году Александр развелся со своей женой и
потерял почти все имущество в судебных процессах. Ему пришлось начать все с
нуля в Лондоне.
В
1836 году Александр Белл выпустил книгу «Заикание и другие нарушения речи» («Stammering and Other Impediments of Speech») и некоторые газеты стали его
называть Профессором Красноречия («Professor of Elocution»). Он женился второй
раз, на вдове своего издателя.
Детские годы
изобретателя
У
Мелвилла в Лондоне испортилось здоровье, да и работа подмастерьем драпировщика
не приносила ему радости. Отец отправил его в Канаду, на остров Ньюфаундленд (Newfoundland), дабы местный климат
поправил ему самочувствие. Там Мелвилл трудился клерком в торговой компании и
наслаждался жизнью, играл в любительских спектаклях и зачитывался трудами
Шекспира в местном литературном салоне. В 1842-м он решил вернуться обратно на
Британские острова и продолжить дело своего отца. Его брат Дэвид женился и стал
учителем красноречия в Дублине, а Мелвилл отправился в Эдинбург. В 1843-м он
повстречал Элайзу Грэйс Саймондс (Eliza Grace Symonds), дочь корабельного хирурга, которая рисовала картины
на заказ. Она была на 10 лет старше своего будущего супруга, и у нее был
ужасный слух, до такой степени, что ей постоянно приходилось пользоваться
специальной слуховой трубой. Тем не менее, они поженились, и в этом браке
родился гениальный изобретатель, ныне известный всему миру.

Слева — Мелвилл Белл (отец
изобретателя); Справа — Элайза Белл (мать изобретателя)
В
1845 году у них родился сын Мэлвилл Джеймс (Mellville James). Александр Белл (Alexander Graham Bell) родился 3 марта 1847 года. В 1848
году родился третий сын, Эдвард (Edward Charles).
Все
три брата первое время учились на дому, но примерно в 10 лет они отправлялись в
частную школу мистера Макларена (Maclaren’s Hamilton Place Academy). В 11 им уже следовало
продолжать обучение, и отец смог отправить своих сыновей в лучшую школу в
Шотландии, Эдинбургскую Королевскую Высшую Школу (Edinburgh’s Royal High School). Эту школу называли «Северными
Афинами» за прекрасное преподавание античных языков, но Александр Белл
ненавидел латынь и греческий. Его старший брат получил первый приз за
декламацию стихов в 1858 году, еще один приз в 1860-м, а в 1862-м он взял приз
за успехи во французском языке. Александр Белл никогда не был отмечен в школе.

Семья Мелвилла Белла
Александр
Белл, помимо прочего, учился у пианиста Аугусто Бенуа Бертини (Auguste Benoit Bertini) игре на рояле. В
школьные годы он играл в крикет, как и все ученики Эдинбургской Школы, но без
всякого увлечения.
Но
он всегда был любопытным и затейливым, и уже в юные годы основал «Общество
Развития Наук Среди Мальчиков». В этом обществе всякий сорванец имел титул
«профессора» и выступал с научными докладами. Однажды Общество решило провести
вскрытие туши свиньи. Александр Белл стал делать надрез, и вдруг из туши пошли
газы, издавая страшный звук, напоминающий звериный рык. В итоге «Профессура» в
ужасе разбежалась.
Старший
брат Александра Белла закончил шестилетний курс Эдинбургской Высшей Школы, в то
время как Александр проучился там всего 4 года. В возрасте 15 лет отец отправил
его в Лондон, чтобы дед научил его ремеслу и уму-разуму. Тот взялся за учебу
своего внука, и внук старался оправдать его надежды. Позже в своих дневниках
Александр Белл писал, что они с дедом прекрасно подружились.
Мелвилл
Белл сознательно готовил своего сына к ремеслу учителя красноречия. Сам он
изрядно много работал над этой темой, и в 1849-м году выпустил книгу «Новое
разъяснение принципов речи и красноречия» (A New Elucidation Of The Principles Of
Speech And Elocution). В этой книге он выразил мысль, что следует создать
«научный алфавит, который бы мог выразить все возможные способы выражения
разных звуков». В 1860-м году он выпустил книгу «Ораторский Стандарт» (The Standard Elocutionist), которая имела
грандиозный успех. К концу XIX
века
она выдержала 168 (!) изданий в одной только Великобритании, а в Соединенных
Штатах продали более 250 тысяч копий этой книги. Эта книга обогащала ее
издателей, в то время как автору доставались очень маленькие отчисления. Но эти
научные труды прославили Мелвилла Белла и сделали его признанным экспертом в
области произношения. В 1853 году он уже давал лекции в Эдинбургском Университете,
а так же выступал с публичными чтениями по всей стране. Мелвилл годами собирал
все возможные звуки человеческой речи, тщательно записывал способы их
воспроизведения, и все его труды были обобщены в книге «Видимая Речь» (Visible Speech: The Science Of Universal Alphabetics), которая была
отпечатана в 1867-м году. Мелвилл утверждал, что всякий, следующий инструкциям,
изложенным в книге «Видимая Речь», сможет воспроизвести любой звук и любое
слово даже из чужеродного наречия. Во время демонстрации своей системы в
Лондоне Мелвилл Белл просил публику озадачить его чем-нибудь, и, столичные
профессора лингвистики, знающие самые диковинные языки Британской Империи,
брали самые заковыристые слова из Урду, Хинди и Санскрита. Но, на удивление
всех зрителей, ученики и последователи системы Мелвилла Белла легко справлялись
со всеми заданиями.
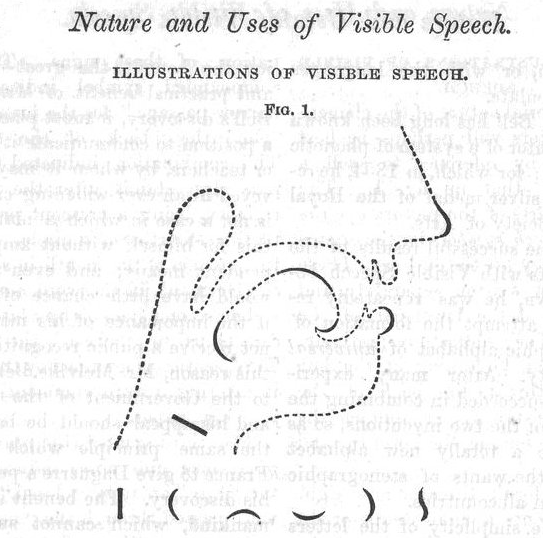
Иллюстрация из учебного пособия
«Видимая Речь»
Учительская
карьера
Александр
Белл помогал своему отцу в его экспериментах, а вскоре и сам стал работать
учителем красноречия. В 1863 году он приехал в Элгин (Elgin), маленький город на северном
побережье Шотландии, чтобы стать учителем в местной частной школе Вэстон Хауз (Weston House). Там он стал преподавателем музыки
и красноречия за 10 фунтов в год. Самому Александру Беллу было тогда только 16,
и несколько учеников были старше его, но столичный лоск выгодно отличал
молодого учителя от местных учеников.

Александр Белл в Элгине, в возрасте
16 лет
В
1864-м году Александр Белл начал учиться в Эдинбургском Университете. Он
приступил к изучению античных языков, но долго там не проучился. На следующий
год он вернулся преподавать в Вэстон Хауз, а семейство пережило тяжелую утрату:
в 1865 году умер его дед. Мелвилл Белл отправился в Лондон, чтобы продолжить
его дело. Ему долго пришлось уговаривать своего сына последовать за ним.
Александр Белл считал, что сможет одновременно преподавать и сдавать все
экзамены в Эдинбургском Университете. Мелвилл утверждал, что он не сможет
совмещать работу с учебой да и самостоятельно преподавать, и что ему надо
отучиться в Лондонском Университете, прежде чем заявлять о своих притязаниях.
В
1866-м году Мелвилл смог раздобыть для своего сына вакансию учителя в городе Бэф,
в Сомерсетширском колледже (Somersetshire
College,
Bath).
Это заведение, хоть и называлось колледжем, было по сути частной школой и
готовило отпрысков джентльменов к университетам.
Там
Александр Белл познакомился с работами Гельмгольца по теории звука, и сам стал
ставить эксперименты с передачей звука на расстояние. В его жилище часто
наблюдали электрические батареи, магниты и сосуды с разными реактивами. Из его
окна тянулись провода в помещение кампуса, и Александр любил общаться со своими
друзьями при помощи телеграфа Чарльза Уитстона. Пребывание Александра в Бэф продолжалось
весь учебный год 1866-1867 гг., но оно было омрачено смертью его младшего
брата, который умер весной 1867 года от туберкулеза.
Летом
1867 Александр Белл переехал в Лондон, чтобы помогать своему отцу в его научных
и педагогических занятиях. Там он познакомился с мистером Мюрреем (Murray), будущим автором Оксфордского
Словаря Английского Языка (Oxford
English
Dictionary),
да и вообще наслаждался жизнью. Он стал ухаживать за учительницей Мэри Экклстон
(Marie Ecclston), которая часто бывала в
доме Белла на званых ужинах. В 1868-м году Александр Белл сдал вступительные
экзамены и был зачислен в Лондонский Университет. В этом же году он впервые стал
сурдопедагогом, впервые стал учить глухих детей. К Мелвиллу обратилась Сьюзан
Халл (Susanna
E.
Hull),
с просьбой использовать его систему «Видимой Речи» для ее частной школы для
глухих детей в Южном Кенсингтоне (South Kensington). Мелвилл отправил Александра на это
задание, и впоследствии сурдопедагогика стала одним из главных занятий в его
жизни.
В
1868 году у Александра Белла родился еще один брат, но в 1870-м он умер. В том
же году от туберкулеза умер его старший брат, Мелвилл. Горе и уныние постигло
Александра Белла, но, что еще хуже, у него самого стало портиться здоровье. В
этой ужасной ситуации Мелвилл Белл решился на отчаянный шаг: он решил оставить
свою карьеру, налаженный быт и обширные знакомства в Лондоне, чтобы не потерять
последнего сына. Он вспомнил, как в свое время климат Ньюфаундленда помог
поправить его расшатанное здоровье, и решил переехать в Канаду.
Все,
что Александр Белл знал о Канаде, умещалось в приключенческих книгах про жизнь
в глуши среди дикарей, и уезжать он никуда не стремился. Но все время усиливался
его чахоточный кашель, цвет лица становился серым, и совершенно пропал аппетит,
поэтому медлить было нельзя. 21 июля 1870 года семейство Белл село на корабль и
отправилось в Новый Свет. Когда Александр Белл рассказывал об этом своим
друзьям и родным, то говорил, что «я уехал в Канаду, чтобы умереть».
Первые шаги в
Новом Свете
Жизнь
в глухой провинции Британской Империи была не столь насыщенной, как в Лондоне.
Семейство Белл остановилось в Брэнтфорде, Онтарио. Там не было вакансий для
учителя красноречия, разве что Мелвилл Белл изумлял своими декламациями
Шекспира местных жителей на публичных чтениях. Александр обнаружил в нескольких
милях от дома резервацию индейцев разных племен: Могавк, Тускарора, Онейда,
Онондага, Каюга и Сенека (Mohawk,
Tuscarora,
Oneida,
Onondaga,
Cayuga and Seneca). Индейцы этих племен обогатили
словарный и звуковой запас Александра Белла и предоставили обширный материал
для его исследований. Говорят, что сам вождь племени Могавк научил Александра
Белла танцу войны. Потом Александр Белл любил отплясывать этот танец во время
своих триумфов, что всегда повергало в шок окружающих.
Мелвилл
Белл пытался найти любые занятия для себя и Александра, но сделать это было не
так просто. Долгие месяцы он писал прошения во все окрестные учебные заведения,
пока в марте 1871 года не пришел ответ из Бостонской школы для глухих, которая
предлагала вакансию учителя с жалованьем 500 долларов в год.

Бостонская
школа для глухих, 1871 год. Вверху справа – Александр Белл
Система
«Видимой Речи» дала свои плоды, и уже в ноябре 1871 года бостонские газеты
стали писать об успехах Александра Белла в сурдопедагогике. В 1872 году он стал
профессором «голосовой физиологии и красноречия» в Ораторской Школе Бостонского
Университета (professor
of Vocal Physiology and Elocution, Oratory School), что было довольно высоким титулом для
26-летнего молодого человека без университетского диплома. Его успехи были
замечены президентом Школы Кларка для Глухих в Нортгэмптоне (Clarke School for
the Deaf, Northampton, Massachusetts), мистером Гардинером Хаббардом (Gardiner
Greene Hubbard). В апреле 1872 года он вернулся из двухлетней поездки по Европе,
в ходе которой изучал разные школы и методы преподавания для глухих детей. Его
интерес был обусловлен тем, что его дочь, Мэйбел Хаббард (Mabel Gardiner
Hubbard), в пять лет осталась глухой после перенесенной скарлатины. Он не
собирался оставлять ее в закрытой лечебнице, где бы она научилась языку жестов
и проводила свое время с такими же больными, навсегда удаленная от мира
слышащих. Поэтому он был одним из главных спонсоров Школы Кларка, первой школы
в США, где практиковалось чтение по губам.

Гардинер Грин Хаббард
Будущие соратники
Сам
Гардинер Хаббард родился в 1822 году, в семье Верховного Судьи. Он окончил
Дартмутский колледж (Dartmouth College) и занялся адвокатской практикой. Он
поселился в Кэмбридже, рядом с Бостоном, и помимо судебных дел занимался
коммерческими проектами. При активном участии Гардинера была основана Конная
Железная дорога (Cambridge
Horse Railroad Company) и газовое освещение в
Кэмбридже (Cambridge
Gas Light Company). У мистера Хаббарда
были интересы в продвижении разных продуктов, разных механизмов и устройств,
поэтому он часто бывал в Патентном Бюро и даже состоял в переписке с Джозефом
Генри (Joseph Henry), великим физиком, который в своих научных работах шел вровень
с Фарадеем и открыл явление самоиндукции. Его фамилия известна каждому
человеку, изучающему физику, ведь именно в Генри измеряется индуктивность.
Но
все эти коммерческие проекты не мешали ему заниматься благотворительностью.
Школа Кларка была основана в 1867 году при активном участии Гардинера Хаббарда,
и всю свою жизнь он привлекал к ней спонсоров.
Сама
Мэйбел Хаббард училась у лучших преподавателей и даже 2 года провела в Европе,
где с ней занимались лучшие учителя Старого Света. Она прекрасно научилась
скрывать свою глухоту и общаться на нескольких языках (если сохранялся
зрительный контакт). Но все же над ее речью стоило работать, и Гардинер Хаббард
решил, что ей стоит подучиться у Александра Белла по его системе «Видимой
Речи». Мэйбел поступила к Александру на учебу, когда ей было уже 15 лет, и в
своих дневниках признавалась, что при первой встрече он ей совсем не понравился.
Но все же они приступили к учебе, и Александр Белл говорил, что у него еще не
было такой усердной и такой быстро прогрессирующей ученицы.
Система
«Видимой Речи» удостоилась оваций на заседании Массачусетского Медицинского
Общества (Massachusetts
Medical
Society),
а в 1874-м году Александр Белл уже проводил самостоятельно конвенцию
преподавателей «Видимой Речи», на которой собралось 60 делегатов.
Для
своих научных изысканий и демонстраций Александру Беллу требовались наглядные
учебные пособия. В конце 1873 года он уже пытался проводить опыты с
акустическим телеграфом. Затем он рассказал своему знакомому доктору-ауристу
Кларенсу Блэйку (Clarence
Blake),
что собирается создать механическое устройство, имитирующее работу
человеческого уха. Тот со смехом сказал ему, что нет смысла изобретать колесо,
и можно взять настоящее ухо. Через несколько дней Александру Беллу пришла
посылка с разными частями человеческого уха: молоточком, наковальней и
мембраной, взятых от мертвого пациента. Из этих подарков и подручных средств
Александр соорудил фонаутограф, который должен был демонстрировать студентам
работу человеческого слуха. Все звуки, попадавшие на мембрану, приводили в
движение стилус, рисующий узоры.

Фонаутограф
Когда
летом 1874-го года Александр Белл приехал к родителям в Канаду, он долго
пытался объяснить своему отцу, в чем же состоит его затея. В дневнике Мелвилла
Белла появилась короткая, полная сомнения заметка: «Электрическая речь?».
Так
бы и занимался Александр Белл фонетикой и сурдопедагогикой, но одна затея
Гардинера Хаббарда заставила его пересмотреть свои планы. Еще с 1860-х гг.
Хаббард пытался протолкнуть в Конгрессе проект устройства телеграфной
корпорации, которая бы упростила и удешевила телеграфное сообщение в США. Он
утверждал, что монополия телеграфной компании Вестерн Юнион (Western Union) сдерживает прогресс телеграфии, что
ее телеграммы дороже чем в Великобритании, которая национализировала телеграф в
1868 году. Правительство США, по его мнению, не должно было пускать ситуацию на
самотек, оно должно было создать «Американскую Почтовую Телеграфную Компанию» (United States Postal Telegraph Company), которая строила бы
телеграфные линии у почтовых трактов и отправляла бы телеграммы вдвое дешевле,
чем Вестерн Юнион. Хаббард утверждал, что новые технологии позволят удешевить
процесс, и что новая компания должна управляться таким энергичным человеком,
как Гардинер Хаббард.

Уильям Ортон, руководитель компании
Вестерн Юнион
Президент
Вестерн Юнион мистер Уильям Ортон (William Orton) был совершенно не согласен с таким предложением. По
его мнению, такой шаг явился бы грубым вмешательством государства в
экономическую жизнь, нарушил бы свободу частного предпринимательства. Хоть Хаббард
проводил целые месяцы в Вашингтоне, проталкивая свой проект, но и у Ортона было
кому защищать его интересы. В результате расходы Хаббарда росли, он занимал
деньги у родственников своей жены, а результата не было никакого.
Гардинер
пытался придумать обходной вариант. Он слышал о научных работах в области
мультиплексного телеграфа, с помощью которого можно было бы отправлять
несколько телеграфных сообщений по одному проводу одновременно. Гардинер
посчитал, что если у него будет такое устройство, то он сможет привлечь
инвесторов в свою новую компанию. И как-то раз к нему на чай зашел Александр
Белл, учитель его дочери. Он был прекрасным пианистом, и развлекал гостей своей
музыкой. После чего он показал гостям трюк с акустическим резонансом. Он
напевал различные ноты внутрь корпуса пианино, а в ответ звучали различные
струны.

Александр Белл демонстрирует явление
акустического резонанса гостям (кадр из фильма «The Story of Alexander Graham Bell» 1939 года)
Гардинер
Хаббард спросил, можно ли таким образом передавать телеграфные сообщения, на
что Александр Белл ответил, что как разные ноты можно передавать в одном
воздушном пространстве, так и разные сообщения можно передавать по одному
проводу. После этого Александр Белл занялся мультиплексным телеграфом.
Но
в этом направлении Вестерн Юнион оказалась намного продуктивнее. В 1872-м году
компания приобрела права на дуплексный телеграф Джозефа Стернса (Joseph Stearns),
который мог посылать встречные сообщения по одному проводу одновременно. В
1874-м году она приобрела квадруплексный телеграф Томаса Эдисона (Thomas Edison),
который удвоил этот показатель.
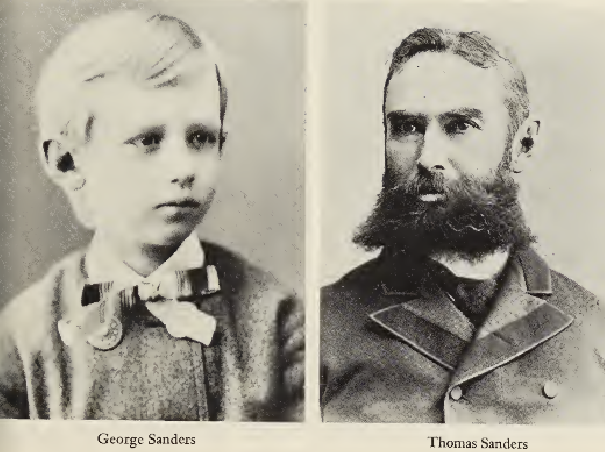
Слева – Джордж Сандерс, ученик
Александра Белла; Справа – Томас Сандерс, его отец и спонсор предприятий
Александра Белла
Другой
спонсор Александра Белла, Томас Сандерс (Thomas Sanders) владел прибыльными
конюшнями и кожевенным бизнесом. Его сын Джордж был глухим с рождения, и он
тоже попал на учебу к профессору Беллу. Для занятий с ним Александр разработал
особую систему общения. Указывая пальцем на разные участки своей руки, он
обозначал разные буквы. Для тренировки этой методики он создал специальную
перчатку, которая была изрисована разными буквами. Сначала Александр указывал
Джорджу на перчатку, но вскоре совсем избавился от нее. Александр мог общаться
с Джорджем на виду у людей, и никто даже не подозревал, что мальчик был глухой.

Перчатка Александра Белла для общения
с глухими учениками
Александр
Белл оставался далеко позади в своих изысканиях, но все же продолжал опыты с
телеграфом, и пытался настроить его на одновременную передачу шести сообщений.
Очень часто Александр Белл заказывал инструменты и материалы для своих опытов в
мастерской Чарльза Вильямса (Charles
Williams)
в Бостоне. Телеграф никак не хотел работать должным образом, разные детали
ломались, и от заказчика не было отбоя, он приходил снова и снова. По правилам
мастерской, клиент должен был оставлять заказ у клерка, а тот распределял их
среди мастеровых.


Слева – Чарльз Вильямс, владелец
мастерской, справа – Томас Ватсон, мастеровой, ставший помощником Александра
Белла
Но
однажды сотрудник мастерской Томас Ватсон (Thomas Watson) увидел, как к его столу устремился
некий клиент, который свалил ему на стол телеграфную аппаратуру, и стал
объяснять, как нужно сделать телеграф, рассчитанный на передачу шести
сообщений.
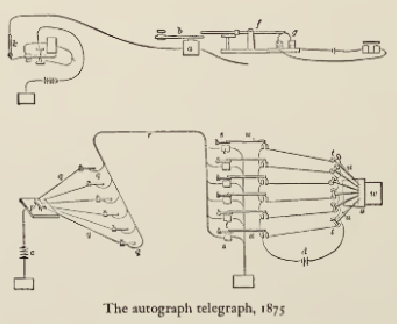
Эскизы мультиплексного телеграфа
Александра Белла
Александр
показал Томасу телеграфный приемник и передатчик, которые, по его замыслу,
должны были передавать 6 телеграмм одновременно по одному проводу. Томас
сконструировал преемник и передатчик, настроенные на одну частоту, и они
прекрасно работали. Восхищенный прекрасной работой Ватсона, Александр Белл
заказал еще 6 пар устройств, настроенных на разные частоты, и способные
отделять свои сигналы среди множества других, идущих по одному проводу. Правда,
когда все эти аппараты испытали на чердаке мастерской Вильямса, опыты были
неудачными. Александр Белл не отчаивался, и заказывал новые опытные образцы у
Ватсона. Несколько месяцев они ставили опыты, пытаясь сконструировать
«гармонический телеграф», передающий несколько сигналов одновременно, но
безуспешно.
Мультиплексный
телеграф никак не хотел работать. Зачастую половина сообщения, отправленная
передатчиком, приходила на специально настроенный приемник, а остальные части
приходили на разные приемники, никак не предназначенные для этого. Как ни
переделывали устройства, ничего не выходило.
Конкуренты
тоже давали о себе знать. Этой же проблемой занимался Элиша Грей (Elisha Grey)
из компании Вестерн Электрик (Western Electric). Велика была вероятность
остаться позади. Томас Ватсон вспоминает, что всякий раз, когда к ним в
мастерскую попадали изделия Вестерн Электрик, все механики приходили любоваться
на эти шедевры и изучать их детали, а все инструменты из мастерской Вильямса казались
грубыми и неотесанными на их фоне.

Элиша Грей
Александр
Белл все же пытался продать свою идею, но покупателей не находил. В январе 1874
года он написал письмо британскому Суперинтенданту Телеграфов с прошением
оценить его изобретение. Ответ был не очень обнадеживающий: королевское
почтовое ведомство оставляло за собой право использовать его изобретение, но не
обещало хранить тайну его конструкции, и даже в случае успешного использования
«вопрос о награждении решался бы по усмотрению королевского ведомства».
Зимой
1875 года Александр Белл приехал в Вашингтон, чтобы запатентовать устройство
своего телеграфа. В ходе этой поездки он получил американский патент № 161739
за 6 апреля 1875 года (оформлен он был на Белла, Хаббарда и Сандерса), но
никакой пользы от него не получил.

Джозеф Генри
Однако
в столицу он съездил не зря, ведь в ходе поездки он удостоился приема у
великого физика Джозефа Генри. Мистер Хаббард написал ему рекомендательное
письмо, но оно ему не требовалось, ведь дочь мистера Генри зачитывалась книгами
о «Видимой Речи». В ходе насыщенных бесед Александр Белл рассказал ему о своих
идеях о передаче звука при помощи электричества, и даже продемонстрировал
эксперимент. Мистер Генри поведал ему о научных работах в этой области, и даже
о телефонном аппарате немца Филиппа Рейса. Восхищенный ученый муж спросил его,
стоит ли публиковать его открытия в печати Смитсоновского Института, или же
Александр сможет довести свои эксперименты до логического завершения. Александр
Белл ответил, что он не обладает познаниями в сфере электромагнетизма и
сомневается в своем успехе. К слову, у мистера Генри был свой печальный опыт по
этой части. В свое время Майкл Фарадей опубликовал свои работы по физике раньше
него, и прославился открытиями, о которых мог бы заявить и Джозеф Генри. В
другой раз он опубликовал свои научные изыскания о передаче сигнала при помощи
электричества, но не стал работать над устройством, в итоге Сэмюель Морзе
получил все богатство и славу, которые принес телеграф. Мистер Генри
строго-настрого приказал Александру Беллу не публиковать своих работ, а
работать до получения работающего аппарата, который можно выгодно продать.
«Берись за дело!» — рявкнул он. Белл признавался, что эти слова вдохновили его
лучше всех других.
Когда
Александр Белл приехал в Бостон, то поделился со своим компаньоном идеей,
которая изумила Томаса Ватсона. Тот предположил, что если бы он смог создать
устройство, варьирующее электрический ток точно так же, как варьируется
плотность воздуха во время передачи звуков, то он смог бы говорить по
телеграфу.
Но
главные спонсоры Белла, Гардинер Хаббард и Томас Сандерс, не были довольны этим
полетом фантазии. Они требовали, чтобы он закончил работу с мультиплексным
телеграфом, после чего он смог бы заниматься другими затеями.
Изобретение
телефона
Но
эксперименты с телеграфом проходили безуспешно. А 2 июня 1875 года опыты все же
дали результаты. Когда Александр и Томас настраивали телеграфные аппараты, они
замкнули контакты, и Александр услышал у своего приемника слабое эхо. Как
только он услыхал этот звук, тут же ринулся к Ватсону, который в это время
настраивал телеграфный ключ, и вся его возня отзывалась эхом на приемнике. К
слову, подобные события случались и раньше, но никто не придавал им значения, а
вот Александр Белл увидел в этом подтверждение своим догадкам, что звук можно
передавать по проводам. После этого они весь день ставили опыты, полностью
замыкая контакт на передатчике и используя различные камертоны вместо
телеграфного ключа и приемника.

Первая передача звука по проводам в практике
Александра Белла
В
тот день Александр Белл сделал набросок телефонного аппарата, который Ватсон
изготовил уже на следующий день, 3 июня 1875 года. Телефон этот по своей форме
напоминал виселицу, и таковым остался в памяти историков связи. В этот раз они
разошлись по разным комнатам и звук был еле слышен, даже хуже, чем в предыдущий
день. Сам Ватсон назвал этот телефон «горьким разочарованием», но вешаться от
этой виселицы экспериментаторы не стали, а продолжили свои опыты. Они шли не
так интенсивно, потому что Томас Ватсон вскоре заболел тифом.

Так называемый телефон – «виселица»
1875 года (копия и чертеж)
В
ходе опытов Александр Белл продолжал преподавать, но с одной ученицей отношения
зашли очень далеко. Летом 1875 года Мэйбел Хаббард уехала в Нэнтакет (Nantucket, столица китобойного
промысла, о которой можно прочесть в романе «Моби Дик») на несколько месяцев, и
Александр решил, что такой долгой разлуки он может не пережить. 24 июня того же
года он написал письмо маме Мэйбел, Гертруде Хаббард, в котором рассказал «что
его интерес к ученице перерос в более высокие чувства… что он научился любить
ее… и что он очень сожалеет о том, что вынужден разлучиться с ней».

Мэйбел Хаббард в возрасте 20 лет
Для
Гертруды это был большой сюрприз, мягко говоря. При встрече она сказала
Александру, что девушке было только 17 лет, что ей нужно было еще увидеть свет,
а учителю стоило подождать хотя бы годик, прежде чем заявлять о своих чувствах.
Но чувства были настолько сильны, что сдержать их было невозможно. Александр
стал писать письма Мэйбел в Нэнтакет, а вскоре и сам отправился туда. Несмотря
на обоюдные симпатии, родители Мэйбел сошлись на том, что о свадьбе говорить
еще рано.
Телефон
не интересовал мистера Хаббарда, поэтому Белл решил уступить часть прав на него
своему канадскому соседу, мистеру Джорджу Брауну (George Brown) за 500 долларов. По соглашению, тот
должен был подать заявку в британское патентное бюро во время своего визита в
Лондон. Но лондонский приятель сказал ему, что эта глупая затея ничего не
стоит.
Следующие
месяцы были очень тревожными для Александра Белла. Он ждал известий от мистера
Брауна, который плюнул на его затею. Гардинер Хаббард требовал результатов и
был не очень доволен тем, что какой-то проходимец, который не может доделать
телеграф, добивается руки его дочери. Его конкуренты тоже занимались
устройством для передачи звука и вплотную подбирались к результатам. Нужно было
делать хоть что-то, но Александр Белл был связан своим соглашением с мистером
Брауном. Тогда мистер Хаббард решил взять дело в свои руки.
14
февраля 1876 года один из коллег Хаббарда, мистер Энтони Поллок (Anthony Pollok), представляющий адвокатскую контору
«Бэйли и Поллок» (Bailey
& Pollok),
подал заявку на патент «Усовершенствования в телеграфии» от имени Александра
Белла. В тот же самый день в Бюро Патентов в Вашингтоне пришел мистер Уильям
Болдвин (William
D.
Baldwin)
и подал заявку на патент на жидкостный передатчик от имени Элиша Грея. Оба этих
чертежа были очень похожи друг на друга. В этот день влюбленных разгорелась
страшная вражда, ознаменованная судами, подлогами и трупами.
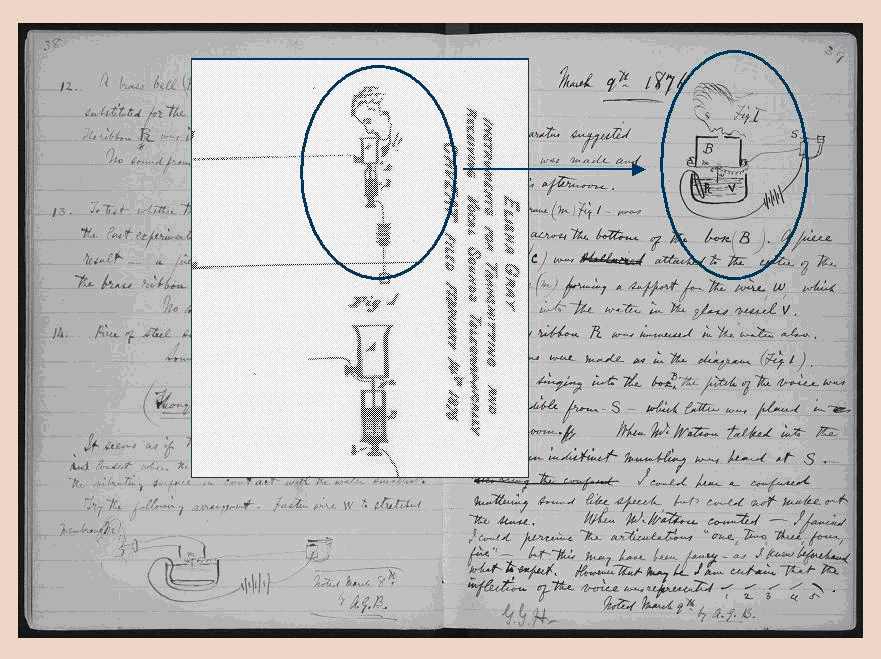
В
центре – вырезка из заявки Элиша Грея, на фоне дневников Александра Белла
Обе
заявки принял мистер Зенас Фиск Уилбер (Zenas Fisk Wilber). 19 февраля он написал мистеру
Поллоку, что заявка Белла копирует конструкцию мистера Грея. Тогда Поллок и
Бэйли решили обратиться к его начальнику, мистеру Эллису Спеару (Acting Comissioner of Patents, Ellis Spear). 24 февраля они написали ему, что
провели анализ заявок за тот день, и выяснили, что заявка Белла была подана на
несколько часов раньше. Мистер Спеар отменил решение Фиска Уилбера, и 25
февраля обе стороны были уведомлены, что конфликт исчерпан. Но он еще не
начинался.
В
1886 году Фиск Уилбер будет клясться под присягой, что он был алкоголиком, что
служил с мистером Бэйли в одном полку и что постоянно занимал у него деньги, в
том числе на выпивку. Он так же будет говорить о том, что получал деньги от
Александра Белла и давал ему заявку Грея для ознакомления. В том же году его
привезут в Денвер на судебные слушания, Фиска Вилбера поместят в отель,
принадлежащий будущему мэру Денвера, Мариону ван Хорну (Marion DeKalb Van Horn).
Постояльцы говорили, что все это время он был «чудовищно пьяным» и утверждал,
что его держат там как заложника. Марион ван Хорн оплачивал все его счета. Через
некоторое время обнаружат мертвое тело Фиска Вилбера, а после этого Марион ван
Хорн возьмет на себя все расходы по его похоронам. В 1895 году Марион ван Хорн упадет
с третьего этажа своего отеля и разобьется насмерть. Как много трупов и
странных совпадений вокруг.
Самый дорогой
патент
7 марта 1876 года был
оформлен патент Александра Белла. Если сейчас, в 2020 году, вы спросите у Google, какой патент был самым дорогим в
истории, то первой же строчкой будет указан «US patent №
174465, patented
March
7, 1876», или же просто «патент на телефон».
10
марта 1876 года Александр Белл и Томас Ватсон проводил опыты с этим
устройством, с жидкостным передатчиком. По легенде, как только они стали
расходиться по разным комнатам, Александр Белл случайно пролил кислоту из
батареи себе на брюки, и громко крикнул «Ватсон, идите сюда, вы мне нужны!».
Тот не услышал его крика, поскольку был в другой комнате, но впервые услышал
слова из приемника. Он тут же вбежал в комнату Белла и крикнул «Я слышал каждое
слово!». Александр сначала не понял произошедшего и говорил о своем ожоге, но
когда узнал об успехе опыта, тут же позабыл о своей травме. Весь день и всю ночь
они менялись местами за приемником и передатчиком, и чего только не говорили
друг другу, в том числе и «Боже, храни королеву!». Потом многие люди задавались
вопросом, почему же они провели первый разговор по телефону только через месяц
после заявки на патент, но потом вопросов появилось еще больше.

Жидкостный передатчик Александра
Белла, март 1876 (копия)
Своим
открытием Александр Белл желал поделиться с публикой и еще он хотел найти
инвесторов. 10 мая 1876 года он провел демонстрацию телефона перед Американской
Академией Искусств и Наук (American
Academy
of Arts and Sciences). После того, как
зрители услышали напевы из коробки, зал неистово зааплодировал. Тут же
посыпались запросы на лекции Александра Белла. 25 мая 1876 года он показал свое
изобретение Массачусетскому Технологическому Институту (Massachusetts Institute
of Technology), и там успех был потрясающий.
Но
у Александра Белла были и другие занятия. Он готовил своих учеников к
экзаменам, Бостонскую школу для глухих посетил бразильский император Дом Педро
и познакомился с «Видимой Речью». Гардинер Хаббард настаивал, что в этом году
Александр должен принять участие в Промышленной Выставке в Филадельфии,
посвященной столетию независимости США. В программе выставки были все
достижения американской индустрии и научной мысли, и это была прекрасная
возможность заявить о своем изобретении.

Иллюстрация, посвященная выставке в
Филадельфии
Но
беда заключалась в том, что Александр Белл ехать на выставку не хотел, как не
убеждал его Гардинер Хаббард. Тогда он решил прибегнуть к крайним мерам.
Гардинер отправил телеграмму Гертруде и Мэйбел и приказал им вытащить
Александра во что бы то ни стало. Тогда Мэйбел наняла экипаж и поехала к
съемной квартире Александра. Сказала ему, что ей требуется компаньон для
поездки, и затолкала в экипаж. Затем велела кучеру ехать на вокзал, и высадила
там Александра с билетом в Филадельфию.
25
июня 1876 года Александр стоял со своим стендом в Машиностроительном зале в
ожидании Комиссии по Электротехнике. День выдался жаркий, и Комиссия объявила,
что завершит свой осмотр еще до стенда Александра Белла. Но вдруг в зал вошел
бразильский император Дом Педро и увидел своего знакомого учителя. Когда тот
стал объяснять ему принцип работы телефона, тот все время приговаривал «Это
невозможно!». Император привлек внимание великого английского физика Лорда
Кельвина (William Thomson (с 1892 Lord Kelvin of Largs)), и вскоре вся комиссия
оказалась у стенда Александра Белла. Он решил продемонстрировать свое
устройство, и выдал Дому Педро приемник. Когда император услышал слова,
доносящиеся из него, то с удивлением воскликнул: «Он говорит!». После этого вся
комиссия целый час испытывала устройство Белла, пробуя его возможности и
выискивая подвох, но с каждым опытом восхищение росло. Вердикт комиссии был
единогласный: Александр Белл заслужил золотую медаль выставки. В тот же день он
узнал, что и «Видимая Речь» удостоилась золотой медали.
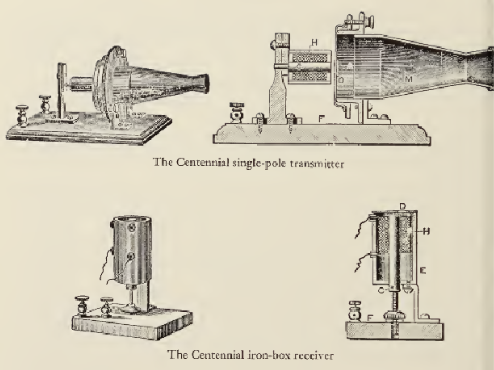
Аппараты, продемонстрированные на
выставке в Филадельфии. Сверху – передатчик; снизу – приемник
После
этого даже главный конкурент Александра, Элиша Грей, пришел поздравить своего
оппонента с успехом и поболтать о возможной пользе их сотрудничества, ведь два
таких ума смогли бы принести большую пользу Вестерн Юнион, а эта корпорация
всегда щедро платила своим сотрудникам. К сожалению или к счастью, этим планам
не суждено было сбыться.
В
газетах 1876 года никак не был отражен успех Александра Белла, быть может,
потому что тексты июльских выпусков были готовы еще до описываемых событий. Но
Александр продолжал свои опыты, ведь телефон еще нужно было совершенствовать. В
ноябре 1876 года удалось поговорить по телефону между Бостоном и Сейлемом, на
расстоянии примерно 15 миль (~ 25 км). 3 декабря 1876 года Восточная Железная
Дорога (Eastern Railroad) предоставила свои телеграфные провода для испытания
телефонов на длинной дистанции. В тот день прошел телефонный разговор между
Бостоном и Северным Конвеем (North Conway) на расстоянии примерно 140 миль (~
225 км). Хоть качество было далеко не лучшим, связь была установлена и сигналы
переданы. Человечеству еще предстояло использовать витую пару вместо
телеграфного провода с заземлением, использовать индукционные катушки на линиях
(«катушки Пупина»), но первый шаг был сделан.
На
свой первый судебный процесс по «телефонному делу» Александр Белл приехал в
декабре 1876 года. Тогда представители Вестерн Юнион утверждали, что аппараты
Александра копируют конструкцию гармонического телеграфа Томаса Эдисона. Потом
Александр, его компаньоны и коллеги пройдут через сотни таких процессов.

Эймос Эмерсон Долбеар
Конструкцию
телефонного аппарата нужно было совершенствовать, и на этом пути Александр Белл
обзавелся еще одним врагом. На промышленной выставке в Филадельфии в 1876 году,
где телефон Белла удостоился высочайших похвал, Эмерсон Долбеар (Amos Emerson
Dolbear) демонстрировал камертоны Лиссажу, опейдоскоп и электрический гироскоп.
После выставки мистер Персиваль Ричардс (Percival D. Richards), который работал
на выставке в отделе образования, обратился к Эмерсону и спросил, есть ли у
него идеи для бизнеса. Тот ответил, что раз телефон уже запатентован, то ему не
стоит и пытаться. Тогда Персиваль попросил Эмерсона поучаствовать в опытах
Белла. В августе 1876 года профессор Долбеар проводил опыты с передачей звука
на расстояние, хотя тогда он не был знаком ни с опытами Рейса, ни с устройством
Александра Белла. Уже тогда он использовал постоянные магниты в своих
устройствах. Что же касается Белла, то его жидкостный передатчик 1876 года мог
служить лишь для потехи, ведь даже на небольшом расстоянии он передавал лишь
едва уловимые звуки.
Когда
Эмерсон приехал в Гарвардскую обсерваторию на испытания устройства Белла, он
уговорил добавить электромагнит для усиления вибрации мембраны. Профессор
Долбеар писал в дневнике, что до этого в аппарате Белла была батарея из 15 элементов
Грове, и Александр Белл стал убирать один элемент за другим. Устройство
продолжало свою работу, и когда оно продолжило работу с питанием только от
одного элемента, Александр Белл пустился в пляс, заявив, что теперь он знает,
как нужно делать телефоны.
15
января 1877 года представитель Александра Белла подал заявку на патент нового
телефона, который мог работать и без батареи, и 30 января 1877 года был выдан
американский патент № 186787. Эмерсон был возмущен тем, что его устройство было
запатентовано без его уведомления и требовал объяснений. На что Белл в своих
письмах отвечал, что собирается в Европу на медовый месяц, и что профессор
Долбеар может обсудить все вопросы с его многочисленными адвокатами.
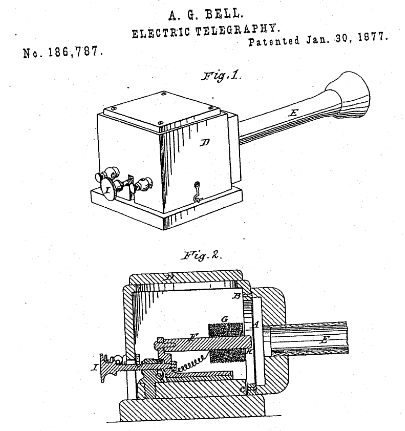
Американский патент на телефон №
186787 от 30 января 1877 года
Биографы
Александра Белла, которые работали с его наследниками, тактично обходили
участие Долбеара в истории Александра Белла. В их трудах патент № 186787 был
представлен как результат опытов Томаса Ватсона. Потом Эмерсон Долбеар в своих притязаниях
дойдет до Верховного Суда. Там он будет демонстрировать смонтированный им
аппарат Филиппа Рейса, сделанный по чертежам 1860-х гг., утверждая, что Белл
был далеко не первым изобретателем телефона. Но все его иски будут отвергнуты.
Между
тем телефон стал обретать популярность. Александр Белл давал публичные лекции в
различных городах с наглядной демонстрацией телефона. Для привлечения внимания
он арендовал на полчаса телеграфную линию и передавал из Бостона в Нью-Йорк
песню «Yankee Doodle», в Нью-Хэйвене (New Haven) речь передавали не по проводу, а через 16 Йельских
профессоров, взявшихся за руки. В марте 1877 в Провиденс (Providence) более 2000 человек
вломились на его лекцию, несмотря на снежный шторм, а после этого почти все
зрители захотели получить автограф Белла. При этом зрители платили иногда по
два доллара за билет, и Александр стал получать хорошие деньги по тем временам.

Рисунок с изображением публичной
лекции, посвященной телефону
Помимо
развлечений, телефон стали использовать по прямому назначению. В апреле 1877
года установили телефонную линию, ведущую из дома Чарльза Вильямса до его
мастерской, протяженностью около 5 км. И как-то в мае 1877 сын Эдвина Холмса,
«отца охранной сигнализации», заехал по делам в мастерскую Вильямса и увидел,
как тот, сгорбившись над какой-то коробкой на столе, что-то старательно
выкрикивал.

Эдвин Томас Холмс увидел, как Чарльз
Вильямс пользуется телефоном. 1877
— Ради всего святого, что у вас там в
коробке? — спросил Холмс.
— Эту штуку приятель Ватсона называет
телефоном, по нему можно говорить друг с другом, — таков был ответ.
Как
только Вильямс объяснил принцип этого устройства, Эдвин Томас Холмс тут же
понял его выгоды и основал собственную телефонную компанию (Telephone Despatch
Company). Тут же он разыскал Гардинера Хаббарда, и поделился с ним своей идеей:
— Мистер Хаббард, если вы дадите мне два
или три рабочих телефона, то я покажу их всему Бостону.
— Покажете всему Бостону? Что вы имеете
ввиду?
— У меня есть офис в Бостоне, откуда
отходят провода ко многим клиентам. К примеру, я могу поставить телефон в
Обменном Банке (Exchange Bank) и дозвониться до него с телефона из моего офиса,
а третий поставить в Кожевенном Банке (Hide & Leather Bank). Затем я могу позвонить
в Кожевенный Банк и сказать, что директор Обменного Банка желает с ним
поговорить, и соединить их между собой.
Это
предложение понравилось мистеру Хаббарду, и опыт был проведен. Многие клиенты
Холмса оценили новинку и пожелали поставить ее в своих офисах, а Хаббард стал
сдавать ему в аренду телефоны. В офисе Холмса были сконструированы
переключатели, через которые абоненты соединялись между собой. В августе 1877
года компания Белла установила 778 телефонов, и более 700 из них были соединены
через офис Холмса.
Эдвин
Холмс Младший создал первую конструкцию телефонного коммутатора еще в мае 1877
года, и многие вещи ему пришлось делать впервые. Компания Холмса стала
устанавливать телефоны с рычагом-переключателем еще до того, как Томас Ватсон и
Гилборн Рузвельт (Hilborne Lewis Roosevelt) заявили свои права на изобретение.
До этого пользователи забывали нажимать кнопки отключения, и десятки телефонов
оставались включенными в сеть, что затрудняло работу на коммутаторе.
Первые
разговоры приходилось соединять сыну Эдвина Холмса, а первым человеком,
специально нанятым для этой работы, стал Фрэнк Мур (Frank M. Moore). Потом на
эту должность стали нанимать девиц, и Эдвин Холмс с гордостью отмечал, что его
фирма первая сделала этот шаг на пути к женскому равноправию.
В
мае 1877 года на телефонных аппаратах появился удобный приемник, который стали
называть «Трубкой Белла» или «масляной печатью». Это устройство разработали
Александр и Уильям Ченнинг (William
Channing),
выпускник Пенсильванского Университета (University of Pennsylvania), который
устанавливал системы пожарной сигнализации в Бостоне. Конечно же, в его
альма-матер Ченнинга считают первым и единственным изобретателем телефонной
трубки, но есть и другие мнения.

Чертежи приемника «масляная печать»
Телефонная
сеть росла, а Гардинер Хаббард не спешил продавать телефоны. Он только сдавал
их в аренду, чтобы сохранять монополию на телефонную сеть, и чтобы никто не
смог скопировать конструкцию телефона. Но со временем желающих устанавливать
свои сети и изготавливать свои аппараты становилось все больше и больше,
поскольку все поняли выгоды телефонии. Согласно патенту № 174465, Александр
Белл и его компаньоны получали исключительное право на производство телефонов
на 17 лет, с 1876 по 1893 год. Но только за это время в США появилось более
1500 компаний, предлагающих услуги связи и торговавших аппаратами! А через 10
лет после истечения срока патента их появилось еще более 6000! Гардинеру
Хаббарду пришлось использовать весь свой юридический опыт и задействовать все
связи в судебной системе, чтобы сокрушить оппонентов.
После
успехов публичных лекций и заказов на телефонную связь, родители Мэйбел решили,
что молодой человек все же встал на ноги. 9 июля 1877 года он основал свою
компанию (Bell Telephone Company of Massachusetts (BTC)), а 11 июля женился на
Мэйбел Хаббард.
5000 акций компании были распределены следующим
образом:
1. Александр
Белл – 10 акций
2.
Мэйбел Белл
– 1497 акций
3.
Гардинер Хаббард
– 1387 акций
4. Жена
Гардинера Хаббарда, Гертруда Хаббард – 100 акций
5. Томас
Сандерс – 1497 акций (инвестировал в дело 110 тысяч долларов);
6. Томас
Ватсон – 499 акций
7. Брат
Гардинера Хаббарда (C.
E.
Hubbard)
– 10 акций
Первоначально
Александр Белл получил 1500 акций, но он словно чувствовал, что у его жены было
больше умения распоряжаться деньгами, поэтому он подарил ей весь свой капитал. Такой
шаг удивил родителей Мэйбел, но с этим пришлось жить.
Медовый месяц
Летом
1877 года Александр с молодой женой отправился в свадебное путешествие, оставив
все хлопоты по продвижению телефона на рынке своим друзьям и компаньонам. В
августе он уже был в порту Глазго, в Шотландии, и остановился в одном из лучших
отелей.
Мы
знаем об этой поездке довольно много благодаря дневникам Мэйбел, которая писала
о своем мечтательном и непрактичном супруге. То он собирался жить в домике у
моря и питаться только той рыбой, что удалось поймать самостоятельно, но вскоре
нанял домработницу, которая закупалась провизией в городе. Александр постоянно
исследовал окружающий мир, ставил невообразимые опыты и вынашивал грандиозные
гипотезы. То он собирал различные виды камней и минералов; то стрелял местную
живность, то следил за ее повадками. Мэйбел составила небольшой список идей,
над которыми работал Александр в то время: это и летательные аппараты с
торпедами на борту, и возможные конструкции телефонов, то он принимался
измерять преломление луча света, проходящего через желе, а иногда он принимался
анализировать скалистый рельеф и размышлять о его происхождении… Еще Мэйбел
отметила, что Александр не сдерживал свои аппетиты: за время их поездки
располнел с 75 кг до 92 кг, но торжественно клялся приобрести книгу о похудении
(они издавались уже в те годы).
Его
телефон очень понравился английской королеве Виктории. Во время демонстрации
она ненадолго отвернулась, и Александр, привыкший к общению со своей глухой
женой, взял ее за руку и вложил туда приемник. Это было очень грубым нарушением
этикета, о котором еще долго помнили в британских светских кругах, но ее
королевское высочество осталось довольно новым устройством.
Что
же касается продвижения своих интересов в Европе, то здесь дела обстояли не
лучшим образом. Беллу не хватало опыта и связей Хаббарда. Его английские
патенты долго не находили применения и инвесторов, и вскоре стали появляться
другие изобретатели, которые чуть-чуть дорабатывали конструкцию Белла и
заявляли о своем гениальном прорыве.
В
Германии статс-секретарь Имперского почтового управления Генрих фон Стефан (Heinrich
von Stephan) узнал об изобретении Белла и скомандовал немецким компаниям
производить собственные телефоны. Уже в ноябре 1877 компания «Сименс и Гальске»
(Siemens & Halske) стала производить по 200 телефонных аппаратов в день, за
ней подключилась Микс и Дженест (Mix & Genest). Разрозненные германские
земли объединились совсем недавно, и в Германской Империи патентное бюро (Patentgesetz)
появилось только в мае 1877 года. Александр Белл и его сотрудники не успели
среагировать, а Вернер Сименс тут же закрепил свои права телефон. На все письма
Белла он отвечал, что «раз вы не запатентовали изобретение в Германии, я
продолжу производство».
Во
Франции немедленно появились представители Эдисона, которые продвигали его
конструкцию телефона. В отсутствие Белла лекции с демонстрацией телефона стал
проводить репортер Фред Гауэр (Fred Gower). Мистер Хаббард дал ему контракт на
установку телефонов по всей Новой Англии, но не был доволен результатами, поэтому
он так и остался на должности лектора. Затем он отправился в Европу помогать
Беллу в поисках инвесторов. Он нашел инвесторов в Англии, немного дополнил
конструкцию, и стал продавать телефоны без всяких выплат Александру Беллу и
мистеру Хаббарду, в то время как Белл ничего не мог поделать со своими
английскими патентами. Гауэр сколотил приличное состояние, женился на
популярной певице Лилиэн Нордика (Lillian Nordica), но счастье было недолгим.
Однажды он отправился в путешествие на воздушном шаре. Французский рыбак его
окликнул и спросил, куда полетит шар. Гауэр ответил «В Лондон!» и воспарил в
небеса. Больше его никто не видел.
Битва за телефон
В
США компания Вестерн Юнион взялась за производство собственных телефонов и
подключение абонентов, и Александр получал телеграммы о том, что его
присутствие необходимо на судебных заседаниях. Он же говорил Мэйбел, что ему
надоел телефон, и что он желает продолжить преподавание. Когда ему пришло
письмо из шотландского городка Гринок (Greenock) с просьбой подыскать учителя
«Видимой Речи» для глухих детей, всемирно известный изобретатель ринулся занять
эту вакансию. Мэйбел все же удалось его уговорить отправиться в США. Александр
сел на корабль, отправляющийся в канадский порт Квебек, чтобы остановиться в
родительском доме, не заезжая в Бостон. Но когда в ноябре 1878 он сходил с
трапа корабля, его лично встретил Томас Ватсон. Пришлось Александру опять
заняться телефонией.
Дела
телефонной компании были довольно плохи. Сотрудники не получали жалованье
месяцами, поставщики отказывались работать с компанией. Даже Томас Сандерс,
богатейший из спонсоров, стал терять терпение. В письме Хаббарду он написал,
что не может погасить чек на 200 долларов, имея пустую казну и 30 тысяч
задолженности. Сандерс уже вложил 110 тысяч долларов, но не получил ни цента. На
фоне всех этих финансовых затруднений появились слухи о том, что Хаббард
предлагал компании Вестерн Юнион компанию и все патенты Белла за 100 тысяч
долларов, но предложение было отвергнуто.
Телефонная
компания Белла подала иск против Вестерн Юнион, обвиняя его в нарушении своей
привилегии. Одним из козырей Белла было письмо, написанное мистером Греем в
марте 1877 года, где он поздравлял своего оппонента с его достижением, и
говорил, что «даже не требует себе права на его изобретение». Уже в сентябре
1879 года юристы Вестерн Юнион стали выходить на компанию Белла с предложениями
о досудебном решении вопроса. Неожиданно для всех, компания Вестерн Юнион согласилась
на компромисс с компанией Белла. 10 ноября 1879 года было достигнуто
соглашение:
1.
Александр Белл признавался изобретателем
телефона
2.
«Western Union» передает свою телефонную сеть
(55 тысяч абонентов в 17 городах) компании Белла (NBTC), та обязывается платить
20 % ее доходов в течение 17 лет, пока патент Белла еще действителен
3.
NBTC обязывается никогда не строить
телеграфных сетей
Александр
Белл и не собирался строить телеграфные сети, теперь у него был собственный
доходный бизнес. В марте 1879 года его акции продавались по 65 $, в сентябре их
цена достигла 337 $, в октябре уже 525 $, а после известия о соглашении с
Вестерн Юнион цена взлетела до 1000 долларов!
Что
же касается Элиша Грея, то после его смерти среди его бумаг нашли черновик с
записью:
«Историю
телефона никогда не напишут полностью. Она скрыта за 30 тысячами страниц
свидетельских показаний, а еще она лежит на совести людей, чьи уста навеки
ЗАКРЫТЫ. Кому-то их закрыла сама смерть, кому-то золото, что еще надежнее».
А
судебные заседания продолжались, появлялись новые претенденты. 24 января 1887
года начался процесс в Верховном Суде США. 19 марта 1888 года было оглашено
решение: «…Всякий человек, взирающий на ночное небо, мог бы увидеть планету
Нептун, но только расчеты Леверье и наблюдения Адамса смогли доказать ее
существование и указать ее позицию в Солнечной системе. Так же обстоят дела с
Беллом… Белл сконструировал телефон и научно обосновал основу своего
изобретения, а так же запатентовал его…». 4 верховных судьи были за, 3 против.
В ходе процесса, один из судей умер. Судья Вэйт (Chief Justice Waite), который
написал это решение, не мог его прочесть из-за болезни, и доверил это своему
коллеге. Судья Вэйт умер через 4 дня после оглашения приговора. Таким образом,
Белл выиграл с преимуществом только в 1 голос!
Споры
продолжаются до сих пор. В Германии вам скажут, что телефон изобрел немец
Филипп Рейс, на целых 15 лет раньше Белла. В Италии вам скажут, что флорентиец
Антонио Меуччи ставил опыты с телефоном, когда Беллу было только 2 года. Да и в
некоторых штатах есть свои герои.
Дальний предок
оптоволокна
В
1879 году Александр приобрел Британскую Энциклопедию, которую читал вдоль и
поперек в поисках новых идей. Ведь он не собирался останавливаться на телефоне.
В
1870-х в Англии стали узнавать об уникальных свойствах селена. У этого элемента
менялось сопротивление и электропроводимость при попадании на него солнечного
луча. Когда Александр приехал на медовый месяц в Великобританию, все местные
научные журналы пестрели статьями об этом. В 1878 году, на докладе перед
Королевской академией наук, он заявил, что «если вы поместите селен в батарею
телефона и направите на него солнечный луч, то сможете его услышать, так же как
услышать тень». Из этого можно представить возможности для применения селена
для сигнализации и для передачи данных.
В
1879-м он взялся за это дело основательно. В этом деле Александру помогал
Чарльз Самнер Тэйнтер (Charles
Sumner Tainter), к нему он часто
заходил в магазин-мастерскую в Кэмбриджпорте (Cambridgeport) за инструментами и
реактивами для своих опытов. В январе 1880 года Александр поставил цель –
воспроизведение речи при помощи света, о чем написал в своих лабораторных
записках. 19 февраля 1880 года он сделал запись о том, что эта проблема была
успешно решена.
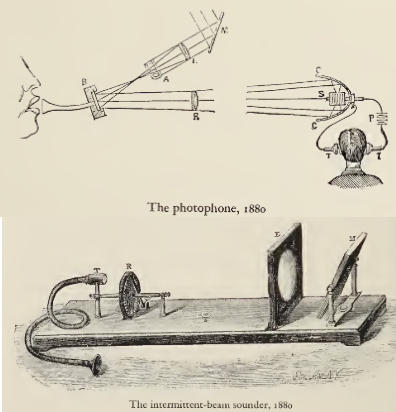
Эскизы фотофона
Весной
начались опыты по увеличению дальности передачи. В марте можно было услышать
отчетливую речь по фотофону на расстоянии 82 метров, в апреле дальность
перешагнула за 200 метров. Но практическое применение фотофона ограничивалось
рельефом, погодными условиями и другими факторами.
Все
же Александр Белл считал это изобретение одним из самых величайших своих
творений. Передача информации при помощи света стала рентабельной только с
внедрением оптоволоконного кабеля, но это произошло через 100 с лишним лет
после изобретения Белла.
Достижения в
медицине
2
июля 1881 года президент США Джеймс Гарфилд (James A. Garfield) был застрелен,
но мучиться ему предстояло еще долго. Две пули попали в президента: одна попала
в руку, другая угодила ему в спину и осталась там. Эта трагедия потрясла всю
страну, но все еще теплились надежды на его скорейшее выздоровление, и к
больничной койке с президентом потянулись самые лучшие врачи.
Как
только Александр Белл узнал об этом, тут же заказал себе экипаж и поехал в
Бостон, в мастерскую Вильямса. Там он стал работать над своим
металлодетектором, изначально созданным для обнаружения металлов в земле. К
нему он присоединил телефонный приемник, который сигнализировал о наличии
металлов.

Александр Белл пытается найти пулю у
раненого президента Гарфилда
26
июля Александр Белл и Самнер Тэйнтер пришли в Белый Дом со своим устройством.
Они увидели страшную картину: мистер Гарфилд, всегда славившийся бодростью
духа, лежал неподвижно на кровати, а его лицо было серого цвета. Вокруг было
несколько докторов, которые ждали чуда. Но мистер Гарфилд боялся удара током, и
вид батарей и проводов привел его в ужас. Александр и врачи стали осторожно
водить металлодетектором, пытаясь обнаружить пулю, но прибор выдавал только
равномерный писк, и невозможно было определить, где именно она находилась.
Опыты закончились безрезультатно, Александр стал дорабатывать устройство.
Газеты
стали писать о том, что Александр Белл был очередной шарлатан, жадный до славы.
Как же он разозлился, когда узнал, что врачи отвергли все его просьбы и не
поместили Гарфилда на постель без матраса с металлическими пружинами. Не
удивительно, что прибор выдавал равномерный писк, он точно диагностировал
металлический каркас матраса!
Однако
президент пошел на поправку, и в августе уже мог садиться на кровати и
принимать пищу без посторонней помощи. Но 19 сентября он уже умер. Умер он не
от пули, которая застряла в мягких тканях и не угрожала жизни, а от инфекции,
которую туда занесли врачи. Доктора того времени, не имея ни рентгена, ни
металлодетектора, засовывали руки в рану для осмотра. Что же касается
антисептиков, то они еще не закрепились в медицине тех лет.
В
октябре 1881 года Александр Белл демонстрировал свой металлодетектор врачам в
Нью-Йорке. Один из зрителей, доктор Джон Гирднер (John H. Girdner), стал использовать этот
прибор в своих операциях. Когда он писал об этом в научных журналах, то всегда
указывал на «превосходное изобретение профессора Белла», и говорил, что «его
имя следует записать рядом с великими целителями, благодетелями страждущего
человечества». Но потом он стал продавать «Телефонический детектор пуль доктора
Гирднера», а в его некрологе газеты написали, что детектор мистера Гирднера
служил для выявления и извлечения тысяч пуль из пациентов до изобретения
рентгена.
Белл
прекрасно знал о деятельности Гирднера, но не придавал ей большого значения. В
1886 году Гейдельбергский университет даровал Александру почетную степень
доктора медицины за изобретение этого чудесного прибора. Это устройство спасло
тысячи жизней до открытия рентгеновских лучей, и даже служило в Первую Мировую
войну, когда рентгенография была еще не всем доступна, особенно на фронте.
Летом
1881 года у Александра Белла умер новорожденный сын из-за нарушения функций
дыхательных путей. Иной человек был бы убит горем, но для Александра это
послужило стимулом к новому изобретению, спасающему жизни людей. Он тут же
начал работу над аппаратом для искусственного дыхания, который назвал «Вакуумной
курткой». Она окутывала торс пациента и была абсолютно герметичной. Убирая
давление воздуха с тела пациента, она позволяла подавать воздух в легкие через
ротовое отверстие, словом, проводила искусственное дыхание пациента. Александр
соорудил рабочую модель устройства в Англии в 1882-м году и демонстрировал его
Британскому Физиологическому Обществу. После этого медики продолжили работу в
данном направлении, в результате появилось устройство, которое назвали
«железные легкие». Сейчас такое устройство принято называть «аппаратом
искусственной вентиляции легких», и оно жизненно необходимо больным, страдающим
от тяжелой формы коронавируса.
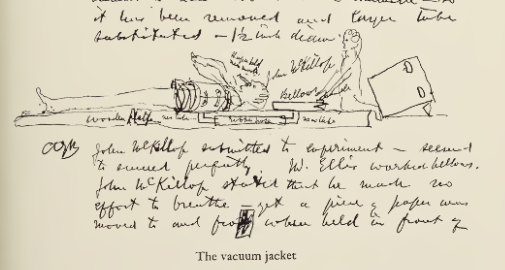
Эскиз аппарата «вакуумная куртка»
Александра Белла
Графофон
В
1880 году Александр Белл приехал в Париж, чтобы получить премию имени Вольта в
размере 50 тысяч франков. Это была очень редкая и престижная награда, которую
Александр получил за изобретение телефона. Но он не стал почивать на лаврах и
продолжил свои эксперименты. На вырученные деньги он организовал лабораторию
имени Вольта, в которой ставили опыты над звуком. Среди прочих экспериментов
там стали ставить опыты с записью звука.
В
этом деле Александру помогал его кузен, Чичестер Белл (Chichester Bell). Был он человеком разносторонним,
умел играть и в хоккей, и на пианино, от боксерских матчей остался у него
переломанный нос. Он учился химии в Тринити Колледж (Trinity College), в
Дублинском университете. Чичестер Белл вращался в высоких кругах, он учил
итальянский язык вместе с писателем Бернардом Шоу (позже тот признался, что
ничему итальянскому не научился, но много узнал о физиологии и патологии), и
был персональным учителем химии герцога Мальборо. Он был профессором химии, и когда
американский кузен попросил его принять участие в научной работе, тот просто не
смог отказать. Одним из первых плодов их совместной работы стал Спектрофон,
устройство для спектрального анализа.

Чичестер Белл
В
ходе дальнейших опытов в лаборатории Вольта Белл и Тэйнтер создавали новые
конструкции телефонных приемников и передатчиков. Но главным их триумфом стало
создание графофона, устройства для записи звука, которое превосходило фонограф
Эдисона по всем параметрам. В нем звук фиксировался резцом на картонном
цилиндре с вощеной поверхностью. В 1886 году была основана Графофонная компания
имени Вольта (The Volta Graphophone Company). Предприятие нашло инвесторов и
обеспечило своих основателей богатством и славой. Самнер Тэйнтер работал с
записью звука до конца своих дней, за свои труды получил медаль Джона Скотта (John
Scott Medal) и золотые медали различных промышленных выставок. Когда Чичестер
Белл уехал в Англию, он уже ни в чем не нуждался, и продолжал свою научную
работу.
Патент на графофон
Полет мысли и
механизма
Разум
Александра Белла искал себе применения, и в своих научных поисках он стремился
воспарить в небеса. Это стремление разделял его коллега Сэмюель Лэнгли (Samuel P. Langley), который уже в 1891
году он писал в вестнике Смитсоновского Института (Smithsonian Contributions to Knowledge) о своих экспериментах в
сфере аэродинамики о том, что передвижение тяжелых тел по воздуху с большой
скоростью не только возможно, но и вполне достижимо с имеющимися механизмами.
Александр
проводил эксперименты и с ракетами с пороховым зарядом, и с пропеллерами, и с
воздушными змеями различных конструкций. Как правило, эти опыты изумляли
окрестных жителей, но до полноценного полета было еще очень далеко.

Такие конструкции парили в небесах у канадского поместья Александра
Белла, которое он назвал Беин Бреа (Beinn Bhreagh, «Красивая гора» — гаэльский)

Множество ученых и конструкторов
пробовали воспарить в небеса, и Александру Беллу пришлось включиться в гонку с
лучшими умами современности. Ему явно не хватало помощников, таких как Томас
Ватсон или Самнер Тэйнтер. Первым стал лейтенант Томас Сэлфридж (Thomas E. Selfridge), выпускник военной академии Вэст
Поинт (West Point), которого военное ведомство
направило наблюдателем за опытами Александра Белла (по его настойчивой
просьбе). Вторым стал Глен Кёртис (Glenn Curtis), победитель мотогонок и
гениальный механик, у которого Александр заказывал двигатели для своих
аппаратов. Третьим стал Дуглас Маккёрди (Douglas McCurdy), и он привел с собой университетского приятеля, Кейси Болдвина (Frederick
Walker «Casey» Baldwin), внука канадского премьера. Финансирование
для этой компании обеспечила верная жена Александра Мэйбел, которая
пожертвовала 20 тысяч долларов на занятие для своего супруга. В 1907 году была торжественно
основана Ассоциация Авиационных Экспериментов (Aerial Experiment Association).
Перед ними стояла цель –
пролететь более одного километра. В 1907 году Американский Аэроклуб и журнал «Сайентифик
Америкэн» (Aero Club of America and Scientific American) учредил приз за
достижения в авиации. Первым его бы взял тот авиатор, который бы преодолел
дистанцию в один километр. Компания Белла соорудила аэроплан «Июньский Жук» (June Bug), который первое время трудно
было поднять в воздух. Пришлось ему мазать крылья парафином для улучшения
аэродинамических показателей. В июне 1908 года он мог держаться в воздухе по
900 метров, 4 июля совершил свой великий полет, в ходе которого преодолел 1634 метров
и провел в воздухе 1 минуту и 40 секунд. Авиаторы Белла заслужили свою награду.

Приз Сайентифик Америкэн за 1908 год
Конечно, не все обрадовались
этому достижению. Братья Райт написали Глену Кёртису, что всегда делились
своими разработками с Ассоциацией Белла, и он использовал их устройство для
управления аэропланом, но не уведомил их об этом. Странным образом, 17 сентября
1908 года Томас Сэлфридж принял участие в полете Орвила Райта (Orville Wright)
в качестве пассажира, и этот этот полет закончился плачевно. Орвил был серьезно
искалечен, а Томас умер от полученных травм.
На тот момент у Ассоциации
заканчивались деньги, и Мэйбел пожертвовала еще 10 тысяч долларов на 6 месяцев
полетов. Последний аэроплан Александра Белла, «Серебрянный Дротик» (Silver Dart) летал уже по 12 миль в марте 1909
года. 31 марта 1909 года состоялось последнее заседание Ассоциации Авиационных
Экспериментов. Потом Глен Кёртис серьезно занялся авиационным бизнесом, и в
начале своей карьеры стал заимствовать патенты Белла. Александр уже не
собирался тратить время на суды в свои преклонные годы, и договорился о продаже
патентов Ассоциации Авиационных Экспериментов компании Кёртиса за 5900 долларов
и акций компании Кёртиса на сумму 50 тысяч долларов в 1917 году.
В конечном итоге братья Райт
смогли построить надежные, управляемые аэропланы, а за ними последовали и
другие конструкторы.
На крыльях по
водной глади
Другим занятием Александра Белла
стали гидродромы. В своем поместье Беин Бреа (Beinn Bhreagh) он стал
изготавливать водный транспорт на крыльях, с пропеллером позади. Эту
конструкцию Александр назвал гидродром (hydrodrome), и первый гидродром был спущен
на воду в 1911 году. Он назывался HD-1, за ним последовал HD-2 (как-то в ходе заплывов он
чуть не затонул, и его назвали «Иона», в честь библейского пророка, побывавшего
во чреве кита). Следующий гидродром, HD-3, в 1913 году разгонялся до 50
миль в час (80 км/ч).
Но все эти опыты были прекращены
в 1914 году, когда Германия объявила войну Великобритании, и поместье Белла
тоже оказалось под угрозой, ведь оно располагалось на британской территории.
Тем не менее, в 1915 году Александр Белл убеждал военно-морское ведомство США в
том, что его гидродром может преследовать немецкие подводные лодки. Но не было
желающих отправиться на британскую территорию и подвергать себя опасности ради
какой-то сомнительной инновации. Но в 1917 году Александр получил заказ от
британского правительства на изготовление спасательных шлюпок. С этой задачей
он прекрасно справился, и они были доставлены раньше указанного срока.
Следующий гидродром, HD-4, разгонялся до 70 миль в час
(110 км/ч). Александр Белл убеждал военных моряков, что HD-4 будет идеальным патрульным или
спасательным судном. В Вашингтоне и Лондоне заинтересовались этим изобретением.
Но интерес быстро угас по разным причинам. Кто-то считал, что это судно больше
напоминает забаву богатея, кто-то волновался о безопасности, кто-то еще о чем.
В 1923 году все эксперименты с гидродромами были прекращены. Но прав был
Александр Белл, и эту правоту осознали только в 1950-е гг., когда судна на
подводных крыльях стали использоваться в коммерческих целях.

Гидродром HD-4 на плаву
Наследие
Хоть
и не все заслуги Александра Белла оценили по достоинству, но список полученных
им наград впечатляет. Он был почетным доктором Гарвардского, Эдинбургского,
Оксфордского и других университетов. Он получил Премию имени Вольта, золотую
медаль имени Эдисона и другие награды. Уже при жизни Александра Белла их трудно
было сосчитать. В 1899 году Александр Белл получил чек на оплату членских
взносов от Американской Ассоциации Лесного Хозяйства (American Forestry Association), то написал своему секретарю:
«Не знал я, что был членом этой организации. Вычеркни меня из ее списков! Что
же касается остальных обществ, узнай у Мэйбел, стоит ли мне в них состоять».
За
этим сверкающим величием стоял человек, который порой ставил эксперименты с
кошками, считавший, сколько раз она приземлиться на лапы, падая с различной
высоты. На старости лет жена ловила его на кухне за трапезой, хоть и пыталась
ограничить его диету. Изобретатель телефона запретил его использовать в
собственном доме, чтобы его не беспокоили по пустякам. Очень часто он играл на
пианино по ночам, потому что не мог заснуть (об этом мы знаем из записок его
дочерей; к счастью для Александра, его жена была глухая, и не слышала всего
этого). Словом, ничего человеческое ему не было чуждо.
2
августа 1922 года этот человек умер, и на его могиле было установлено довольно
скромное надгробие. Потом ему стали ставить грандиозные памятники, писать книги
о нем и снимать про него кино, а еще его именем названы школы. И весь мир будет
помнить его как изобретателя телефона.

Могила Александра Белла
Список
использованной литературы:
1.
A
History of Engineering and Science in the Bell System. The Early Years
(1875-1925). Bell Telephone laboratories, Inc. 1975 USA.
2.
Bruce,
Robert V. Alexander Graham Bell and the Conquest of Solitude. Little, Brown and
Company. Boston Toronto. 1973.
3.
Dolbear,
Inza S. Amos Emerson Dolbear: A Biography. 1963.
4.
Gray,
Charlotte. Reluctant genius. Alexander Graham Bell and the passion for
invention. Arcade Publishing. New York. 2011.
5.
Grosvenor,
Edwin S. and Wesson, Morgan. Alexander Graham Bell. The life and times of the
man who invented the telephone. Harry N. Abrams, Inc. New York. 1997.
6.
Holmes,
Edwin Thomas. A Wonderful Fifty Years. Published by Andersite Press.
7.
Huurdeman,
Anton A. The worldwide history of telecommunications. 2003.
8.
Pizer,
Russell A. The Tangled Web Of Patent #174465. AuthorHouse. Bloomington. 2009
9.
Watson,
Thomas A. Exploring Life: The Autobiography of Thomas A. Watson. D. Appleton
and Company. New York. London. 1926.
10. The June Bug. http://www.wright-brothers.org. http://www.wright-brothers.org/History_Wing/Wright_Story/Showing_the_World/June_Bug/June_Bug.htm
Александр Иванов
экскурсовод Музея истории телефона

