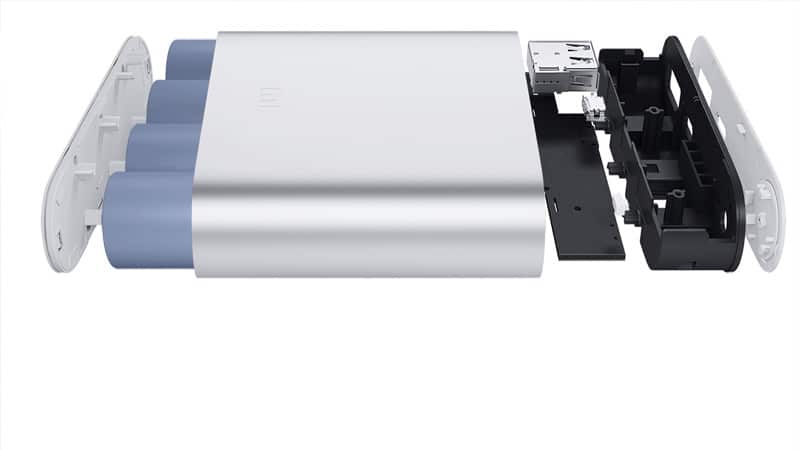
Основной проблемой современных телефонов и планшетов является малая емкость аккумулятора. Большинство смартфонов с трудом доживают до вечера или садятся в самый неподходящий момент. Большие экраны, мощные приложения 4G и 5G — все это высасывает емкость аккумулятора и разряжает телефон в самый неподходящий момент. Есть ли реальная возможность продлить срок его службы и не попасть в неприятную ситуацию? Выход прост — использовать переносные зарядные устройства для телефона, подзаряжая его при необходимости на рабочем месте, в автомобиле или в метро. В данной статье мы расскажем о том, как правильно выбрать портативную зарядку для телефона и как ей правильно пользоваться.
Содержание:
- 1 Введение
- 2 Что представляет собой Power Bank
- 3 Подробнее о емкости
- 4 Рассчитываем количество циклов зарядки
- 5 Как правильно выбрать
- 6 Токи заряда
- 7 Устройства на Li-Ion
- 8 Устройства на Li-Polymer
- 9 Выводы
Введение
Вы наверняка сталкивались с ситуацией, когда заряд у телефона заканчивается в самый неподходящий момент. Хорошо, если это происходит дома или в офисе, где его можно подзарядить. Но если вы отправились в путешествие, и используете смартфон как навигатор, если вам нужно срочно принять важный звонок или проверить почту, а до ближайшей розетки добираться несколько часов, то вам поможет только переносная зарядка или запасной аккумулятор, который придется заряжать отдельно или возить с собой.
Работать с запасным аккумулятором не всегда удобно — телефон придется разбирать, проводить замену, выключать. В некоторых моделях аккумулятор вообще не съемный, поэтому такой трюк не пройдет. Переносная зарядка для этого более предпочтительна.
Большинство зарядных устройств представляют собой аккумуляторы, заряжающиеся от USB разъема и передающие заряд через кабель телефону. Существуют и различные экзотические зарядки от солнечной батареи или костра, но они интересуют в основном туристов. В нашей статье мы сделаем акцент на так называемые Power Bank, которые в просторечии называют внешними аккумуляторами. Рассмотрим, какие бывают виды переносных аккумуляторов для зарядки телефона, чем они отличаются и какое устройство можно выбрать для перестраховки.
Переносные батареи для телефонов сейчас очень популярны на рынке.
Повер Банк, по сути, это универсальная батарея, подходящая для зарядки любых устройств через USB или mini-USB разъем. Он представляет собой массив, собранный из нескольких небольших аккумуляторов, соединенных в одно целое и запакованных в красивый корпус. От количества элементов зависит емкость батареи, в популярных моделях она варьируется от 5 mAh до 15 mAh.
Корпус Повер Банка может быть пластиковым или алюминиевым, на нем располагаются 1-2 выхода, индикаторы заряда, кнопка включения и иные дополнительные опции. К примеру, на некоторых моделях имеется встроенный светодиод, позволяющий использовать Bank как фонарик. Но основная задача устройства — зарядка телефонов, смартфонов, планшетов и иных устройств.
Подробнее о емкости
Если вы выбираете портативное зарядное устройство для мобильного телефона, то обязательно обращайте внимание на количество “махов” (mAh) или миллиампер-часов. Именно в них обозначается емкость и от этого показателя зависит, насколько зарядится ваш смартфон.
Внимание: чем больше емкость Power Bank, тем больше его вес и размеры. Не нужно покупать чересчур мощные устройства для смартфона, если вам нужно лишь изредка подзарядить телефон — это будет необоснованная трата денег, да и носить огромное и тяжелое устройство будет неудобно.
Внутри Power Bank располагаются современные литий-полимерные или литий-ионные аккумуляторы, основное достоинство которых в минимальном токе саморазряда и высокой удельной энергоемкости. Они выдерживают до 500—600 циклов зарядки/разрядки, после чего потихоньку начинают деградировать. В среднем, при зарядке телефона 2—3 раза в неделю их хватает на 5—6 лет, что является вполне достойным сроком для современных аккумуляторов.
Теперь разберемся, как правильно выбирать емкость. В продаже на данный момент имеются устройства с емкостью от 2 до 20mAh. Узнайте, какая емкость батареи на вашем телефоне. Добавьте к этому 20% и получите искомую емкость.
Пример: в вашем смартфоне установлена батарея емкостью 2200mAh. Для полной зарядки нужно использовать Power Bank емкостью 2200+2200*0,2=2640. То есть теоретически для полной зарядки вам хватит банка емкостью 2,5 маха, но лучше перестраховаться и взять на 3.
У планшетов более емкие аккумуляторы, поэтому для них подходят устройства с емкостью на 7-15 махов.
Рассчитываем количество циклов зарядки
Рассмотрим одну тонкость портативных зарядок для телефонов, которую необходимо знать в обязательном порядке и учитывать перед выбором. Многие считают, что если емкость аккумулятора 3mAh, то приобретя зарядку на 15 можно будет зарядить телефон 5 раз. Но это глубокое заблуждение. Если вы выбираете банк, который сможет заряжать батарею несколько раз, то внимательно прочтите следующую информацию.
- У аккумуляторов существует саморазряд. Если вы зарядите 15 маховое устройство на 100%, то через два дня его емкость будет равна 14, еще через 2 дня — 11 и т. д. У разных устройств разная степень саморазряда, но она присутствует везде.
- Power Bank имеет не 100% КПД. Так, аккумулятор имеет выходное напряжение в 3,7—3,5 вольта (в зависимости от степени зарядки), тогда как для USB необходимо 5 вольт. Поэтому в схему банка включен повышающий трансформатор, который также съедает часть емкости. Примечательно, что в телефоне эти 5 вольт снова преобразуются в 3,7 вольта, и потеря происходит снова.
В среднем банк способен отдать при зарядке 70—80% от своей реальной емкости. И если в городе эти потери несущественны (“накормив” телефон от Power Bank, вы сможете добраться до полноценной зарядки), то для путешественников это может стать проблемой. Поэтому обязательно приобретайте устройства с запасом на 20, а то и 30 процентов, чтобы получить нужные значения.
Пример: если емкость вашего аккумулятора в смартфоне равна 2200mAh и вы планируете заряжать его от банка минимум 5 раз, то 2200*5=11000+11000*0,3=14300. Емкости в 15 000 махов будет достаточно, чтобы зарядить устройство нужное количество раз, пока батареи внутри не начнут деградировать.
Как правильно выбрать
Теперь вы знаете, как называется переносная зарядка для телефона, как правильно рассчитывать емкость и запас. Разберем, какое же устройство подойдет именно для вашего телефона.
Ключевой совет — определитесь, в каком формате и когда вам нужна подзарядка. Если вы используете телефон по работе и его в 99% случаев из 100 хватает на весь день, а заряжаете вы его каждую ночь, то вам с головой хватит небольшого брелока емкостью на 1mAh, который можно носить на ключах. Он не будет перегружать ваш карман или мешать, а этой емкости хватит, чтобы зарядить телефон на 30—40 процентов и спокойно добраться до классической зарядки.
Рассматривая небольшие карманные зарядки для телефонов, следует остановиться на аккумуляторах, встроенных в чехлы. Это довольно интересные устройства, основным достоинством которых является компактный размер. Вы просто приобретаете удобный защитный чехол для телефона и вместе с ним получаете дополнительную батарею на 2-3 тысячи мАч, способную выполнить полноценную зарядку смартфона при необходимости.
Токи заряда
У родных телефонных зарядок есть такой параметр, как ток зарядки. Он может варьироваться от 0,5 до 1,5 Ампера (иногда даже 2 А). Чем выше ток, тем быстрее заряжается аккумулятор. У карманных зарядок этот параметр ниже, чем у проводных, и обычно составляет 0,2-1 А. Выбирая устройство, помните, что чем выше ток зарядки, тем скорее зарядится аппарат. Не покупайте недорогие устройства с минимальными показателями — очень часто они обеспечивают лишь поддержание заряда аккумулятора, при этом реально не заряжая телефон (в процессе работы смартфон потребляет столько же или даже больше, чем дает ему слабый Power Bank). Приобретайте устройства с мощностью свыше 0,5 А, а желательно 1 А, тогда ваш телефон зарядится за 3 часа вместо 5.
Устройства на Li-Ion
Самыми распространенными типами зарядок являются устройства, работающие на литий-ионных аккумуляторах типа 18650. Они похожи на обычные пальчиковые батарейки, но имеют более крупные размеры. Напряжение выхода — 3,7 вольта, стандартная емкость 2500 мАч, вес — 45 грамм. Li-Ion батареи выдерживают до 600 зарядок без деградации, к 1000 циклов зарядки теряют 20% от своей емкости. Основное достоинство элементов на литий-ионных устройствах — продолжительный срок службы, малый ток саморазряда, небольшой вес и отсутствие эффекта памяти.
Из минусов можно выделить нарушение герметичности аккумуляторов, которое проявляется при перегреве устройства — не оставляйте его на батарее, на солнце под стеклом автомобиля, в иных местах с высокой температурой. Перегрев при зарядке на современных качественных устройствах не возникает — в блок устанавливается специальная защита.
Внимание: сегодня на рынке имеется масса подделок от недобросовестных производителей, обещающих 30 000-50 000 мАч в недорогих устройствах. Приобретайте только фирменные Power Bank в проверенных местах.
Отметим примерную зависимость емкости от массы — 5 000 махов весит не менее 100 грамм. Поэтому устройство на 50 000 будет весить килограмм, а не 300 грамм, как обещают в различных интернет-магазинах. Впрочем, подобная система определения реальной емкости не является панацеей — китайцы научились подкладывать в корпус утяжелители, чтобы убедить покупателей в реальности характеристик. Проверить емкость можно при помощи мультиметра или расчетов.
Устройства на Li-Polymer
Литий-полимерные аккумуляторы считаются более продвинутыми устройствами по сравнению с литий-ионными. В роли электролита в них выступает специальный полимер с гелевым литием. Они представляют собой прямоугольные пластиковые пакеты с двумя выводами. В пакете находится электролит и рабочие элементы. Корпус Повер Банка надежно защищает нестабильный аккумулятор от повреждения. Из ключевых достоинств можно выделить малый вес, высокую плотность энергии на единицу объема, отсутствие эффекта памяти. Из минусов — сложная схема, защищающая аккумулятор от перегрева, обеспечивающая специализированный режим зарядки по току. Также нельзя допускать глубокой разрядки батареи, поскольку она может не включиться (нужно будет подавать напряжение непосредственно на контакты в обход схемы, чтобы оживить ее).
Внимание: приобретайте только сертифицированные литий-полимерные устройства, поскольку подделки часто выходят из строя. Они склонны к возгоранию с выделением огромного количества тепла и крайне вредного для здоровья газа.
Именно от этих аккумуляторов начинаются пожары и сгорают телефоны. Если произойдет замыкание во время зарядки, то устройство может вызвать серьезный пожар.

Выводы
Если вы хотите быть всегда на связи или телефон играет важную роль в вашей жизни, то портативная зарядка должна обязательно присутствовать в вашем кармане. Главное, определиться с ее емкостью и весом. Для путешественников, которые проводят неделю без розетки, подойдут мощные аккумуляторы на 15—30 тысяч махов, для офисных сотрудников небольшие 1—3 тысячные батареи. Мы рекомендуем вам приобретать оригинальные зарядки, чтобы не разочароваться в них — сегодня на рынке имеется масса подделок. Качественная вещь не будет стоить дешево. Средняя цена оригинального банка — 30—40 долларов.
Если у вас есть телефон и планшет, то можно приобрести устройство с двумя выходами — оно сможет заряжать их одновременно. На рынке присутствует множество вариантов — изучите их, прежде чем делать окончательный выбор.
Сейчас электронные гаджеты используются повсюду. Они нужны для работы, общения и развлечения. При активной работе современные мобильные телефоны и планшеты быстро разряжаются. Даже если носить всегда с собой зарядное устройство, не всегда есть возможность включить его в сеть. Не остаться в нужный момент без связи поможет переносная зарядка для телефона, которая называется Power Bank.
Содержание
- 1 Что представляет собой Power Bank?
- 2 Подробнее о ёмкости
- 3 Рассчитываем количество циклов зарядки
- 4 Токи заряда
- 5 Тип аккумулятора
- 5.1 Устройства на Li-ion
- 5.2 Устройства на Li-polymer
- 6 Как правильно выбрать?
- 7 Топ портативных зарядных устройств
Что представляет собой Power Bank?
Устройство называют по-разному — внешний аккумулятор, портативная или мобильная зарядка, переносное зарядное устройство. При этом речь идет об одном и том же — о зарядке для телефона без розетки.
Преимущество Power Bank в том, что с его помощью можно зарядить электронные гаджеты, когда другие способы недоступны. Это может произойти не только в ситуациях, когда поблизости нет розеток или они все заняты, но и во время длительных поездок, путешествий и даже туристических походов. Для любителей часто выбираться на природу есть специальные внешние аккумуляторы, оснащенные солнечной батареей.
Power Bank представляет собой аккумулятор, который нужно предварительно зарядить, а потом использовать для питания других девайсов.
Портативное зарядное устройство имеет небольшой размер и вес, поэтому его легко носить с собой в сумке. Подключение гаджетов к Power Bank осуществляется через кабель, подсоединенный к разъему USB, что делает внешний аккумулятор универсальным устройством. Его можно использовать не только для зарядки аккумулятора телефона, но и для планшетов, фотоаппаратов, ноутбуков, плееров.

Некоторые модели портативного приспособления имеют более одного разъема USB, что позволяет заряжать несколько гаджетов одновременно.
Подробнее о ёмкости
Ёмкость — это характеристика, которая указывает, как долго можно использовать переносной аккумулятор для питания других гаджетов без подзарядки. На большинстве портативных устройств есть индикатор, который начинает мигать в случае разрядки. Чтобы снова использовать PowerBank, необходимо его зарядить одним из способов — от сети, ноутбука или компьютера. Зарядка происходит через специальный разъем micro-USB на корпусе.
Большинство востребованных аккумуляторов имеет емкость в пределах 1500-20000 мАч. Какая емкость нужна, зависит от устройств, для питания которых будет использоваться PowerBank. Если нужен аккумулятор для зарядки телефона, подойдет устройство с меньшей ёмкостью, чем для подзарядки ноутбука или техники для фотографирования.
От ёмкости напрямую зависит вес переносного аккумулятора. Это следует знать, чтобы избежать покупки подделки. В интернете можно встретить предложения, в которых маленький вес и низкая цена аккумулятора не соответствуют его ёмкости. Увеличение емкости на 5000 мАч делает вес модели больше примерно на 100 г.

Рассчитываем количество циклов зарядки
PowerBank может использоваться для подзарядки электронных девайсов столько раз, во сколько его ёмкость превышает ёмкость батареи заряжающихся устройств. При выборе переносного аккумулятора советуют ориентироваться на несколько циклов зарядки. Для этого нужно емкость батареи гаджета, который вы планируете подключать к портативной зарядке, умножить на 2-2,5.
Например, если вы ищете переносную зарядку для мобильных телефонов, емкость батареи которых — 2600 мАч, не стоит покупать внешний аккумулятор менее чем на 5200 мАч.
Обратите внимание, что PowerBank не будет заряжать гаджеты, емкость батареи которых больше ёмкости внешнего аккумулятора.
Стоит понимать, что портативная батарея не сможет полностью зарядить устройство, если емкость их батарей совпадает, т. к. аккумулятор PowerBank расходуется, чтобы обеспечивать его работу.
Токи заряда
Сила тока влияет на скорость зарядки девайсов. Во внешних аккумуляторах распространены USB-порты на 1 А или 2 А. Разьем на 1 А нужен для зарядки телефонов, смартфонов, плееров, электронных книг. USB-порт на 2 А подойдет для крупной техники — планшетов, фотоаппаратов, ноутбуков.

Есть модели PowerBank с несколькими разъемами. В большинстве таких зарядок присутствуют порты с разной силой тока.
Мобильные аккумуляторы оснащены контроллерами, которые ограничивают подачу напряжения в устройства со слабой батареей, поэтому плеер или телефон не повредится, если его подключить к разъему на 2 А. В обратном случае при подключении крупной техники к разъему со слабой силой тока процесс зарядки будет происходить медленно.
Тип аккумулятора
Аккумуляторы бывают 2 видов: литий-ионные и литий-полимерные.
Устройства на Li-ion
Литий-ионные зарядки шире распространены в продаже. Такой тип аккумуляторов соответствует большинству батарей, установленных в современных мобильных телефонах.
PowerBank на Li-ion имеет невысокую цену и позволяет заряжать большинство планшетов и смартфонов.

К недостаткам данного вида батареи можно отнести риск повреждения при чрезмерной зарядке или перегреве. Есть модели PowerBank, в которых предусмотрено автоматическое выключение в подобных ситуациях.
Устройства на Li-polymer
Литий-полимерные зарядки отличаются внутренней структурой, которая позволяет получить большую ёмкость батареи при меньшем весе в сравнении с устройствами на Li-ion.
Зарядки на Li-polymer имеют более высокую цену. Это происходит из-за необходимости устанавливать специальную плату для обеспечения работы устройства, которое имеет сложную внутреннюю схему. Аккумуляторы также оснащены конструкцией, защищающей от перегрева.
Дешевые литий-полимерные зарядки могут пренебрегать установкой дополнительный элементов, из-за чего аккумуляторы могут быстро прийти в негодность.

Как правильно выбрать?
Чтобы выбрать хороший внешний аккумулятор, нужно отталкиваться от потребностей покупателя. Следует понимать, какие гаджеты планируется заряжать, в каком количестве и как часто.
Нет смысла переплачивать за PowerBank с большой емкостью, если вы выбираете внешний аккумулятор для телефона такой, какой сможет заряжаться при достаточно минимальных показателях. Для зарядки ноутбука понадобится устройство не ниже 20000 мАч, менее емкие просто не будут работать. Следует учитывать, что чем больше емкость, тем больше вес, и некоторые модели могут быть не удобными, чтобы носить их с собой ежедневно.
При использовании планшетов и фототехники лучше остановить выбор на моделях с большей силой тока, что обеспечит быструю зарядку.
Если есть необходимость в зарядке аккумулятора телефона или других гаджетов, которые не имеет порта USB, выбирайте модель, в комплект которой входят адаптеры для подключения устройств старого образца.
Портативные зарядки могут быть выполнены из пластика или металла. Во втором случае устройство для зарядки телефона будет прочнее и меньше подвержено царапинам, но его цена и вес будут выше.
Можно найти PowerBank с необычным дизайном. Они могут быть выполнены в виде различных игрушек, животных или иметь любую другую формы. Стоит иметь в виду, что подобные декоративные устройства из-за оригинального внешнего вида имеют более высокую стоимость, хотя могут не отличаться высокими характеристиками.
При необходимости использовать устройство во время путешествий стоит обратить внимание на устройства со встроенной солнечной батареей. Они дадут возможность подзарядить телефон на несколько часов даже в экстремальных условиях, где отсутствует электричество.
Иногда может возникнуть необходимость использовать устройство во время питания от PowerBank стоя или на ходу. В таком случае лучше выбрать аккумулятор небольших размеров, который позволит не отрываться от дела, — в своих руках держать подобное устройство не тяжело.
Некоторые модели оснащены дополнительными элементами, которые могут сделать работу более комфортной — светодиодными индикаторами, экраном, фонариком.

Топ портативных зарядных устройств
Востребованной моделью является Xiaomi Power Bank 2 20000 mAh. Это устройство обеспечивает оптимальное соотношение цены и качества. Имеет пластиковый корпус. Батарея на 20000 мАч и разъемы на 2,4 А позволяют его использовать не только как зарядку аккумулятора телефона, но и для планшетов и другой более емкой техники. 2 USB-порта делают возможным одновременное питание нескольких девайсов.

ASUS ZenPower 10050 mAh ABTU005 — вариант портативной зарядки для телефона, сделанный из металла и оснащенный светодиодом, который известит, когда устройство разрядится. Характеристики позволяют зарядить смартфоны, в т. ч. и новые модели iPhone, которые обладает большей емкостью.

TP-LINK TL-PB10400 — компактная модель, размеры который позволяют использовать PowerBank в пути, в дороге может выручить встроенный фонарик. Имеет 2 порта для подключения устройств на 1 и 2 А.

Один из оптимальных вариантов переносной зарядки аккумулятора телефона является SONY CP-V10. Ее преимущества в компактных размерах. Батарея на 10000 мАч и выход с силой тока на 1,5 позволяет сохранить доступную цену. Комфортности в использовании добавляет световой индикатор.

Внешний Аккумулятор – так называется переносное зарядное устройство для зарядки батареи телефона. Используются также такие варианты названий переносного блока питания:
- «Переносной аккумулятор»;
- «Портативный аккумулятор».
Power Bank – внешний аккумулятор (переносное зарядное устройство)
Power Bank (с англ. «Внешний аккумулятор») – так называется переносное зарядное устройство для телефона на английском языке, но данный термин часто используется и в русском.
Используются также такие варианты названия:
- «Повер банк»;
- «Повербанк»;
- «Пауэр банк»;
- «Пауэр бэнк»;
- И еще куча других всевозможных вариантов коверканий названия «Power Bank».
Внешний Аккумулятор — переносное зарядное устройство для телефона
Что такое Power Bank
По сути, Power Bank – это аккумулятор. Дополнительный аккумулятор, имеющий больший объем и способный накопить больше заряда. Благодаря функции раздачи заряда, он способен передавить его другим мобильным устройствам.
Внешний аккумулятор: преимущества
Power Bank – незаменимая вещь, позволяющая зарядить мобильное устройство в ситуация, когда нет доступа к стационарной зарядке от сети, компьютера или ноутбука.
Портативным зарядным устройством легко пользоваться, оно имеет небольшой размер и вес. Оно универсальное и подходит для любых мобильных устройств.
Можно быть уверенным, что благодаря этой маленькой коробочке, в долгих поездках смартфон или планшет всегда будет иметь дополнительную подзарядку. Главное – не забыть зарядить сам внешний аккумулятор и взять USB провод!
Какой Power Bank лучше купить
Где лучше купить Power Bank
Для поиска интернет-магазина, где купить портативный внешний аккумулятор (Power Bank) по хорошей цене, можно воспользоваться специализированными торговыми интернет-площадками:
- Яндекс Маркет;
- Aliexpress;
Надеюсь, данная статья была полезна и теперь вы знаете, как называется прибор-накопитель для автономной зарядки телефона.
Не нашли ответ? Тогда воспользуйтесь формой поиска:
For other senses of this term, see AC adapter.
A battery charger, recharger, or simply charger[1][2] is a device that stores energy in a battery by running an electric current through it. The charging protocol (how much voltage or current for how long, and what to do when charging is complete) depends on the size and type of the battery being charged. Some battery types have high tolerance for overcharging (i.e., continued charging after the battery has been fully charged) and can be recharged by connection to a constant voltage source or a constant current source, depending on battery type. Simple chargers of this type must be manually disconnected at the end of the charge cycle. Other battery types use a timer to cut off when charging should be complete. Other battery types cannot withstand over-charging, becoming damaged (reduced capacity, reduced lifetime), over heating or even exploding. The charger may have temperature or voltage sensing circuits and a microprocessor controller to safely adjust the charging current and voltage, determine the state of charge, and cut off at the end of charge.
Chargers may elevate the output voltage proportionally with current to compensate for impedance in the wires.[3]
A trickle charger provides a relatively small amount of current, only enough to counteract self-discharge of a battery that is idle for a long time. Some battery types cannot tolerate trickle charging; attempts to do so may result in damage. Lithium-ion batteries cannot handle indefinite trickle charging.[4]
Slow battery chargers may take several hours to complete a charge. High-rate chargers may restore most capacity much faster, but high rate chargers can be more than some battery types can tolerate. Such batteries require active monitoring of the battery to protect it from overcharging. Electric vehicles ideally need high-rate chargers. For public access, installation of such chargers and the distribution support for them is an issue in the proposed adoption of electric cars.

C-rate[edit]
Charge and discharge rates are often given as C or C-rate, which is a measure of the rate at which a battery is charged or discharged relative to its capacity. The C-rate is defined as the charge or discharge current divided by the battery’s capacity to store an electrical charge. While rarely stated explicitly, the unit of the C-rate is h−1, equivalent to stating the battery’s capacity to store an electrical charge in unit hour times current in the same unit as the charge or discharge current. The C-rate is never negative, so whether it describes a charging or discharging process depends on the context.
For example, for a battery with a capacity of 500 mAh, a discharge rate of 5000 mA (i.e., 5 A) corresponds to a C-rate of 10C, meaning that such a current can discharge 10 such batteries in one hour. Likewise, for the same battery a charge current of 250 mA corresponds to a C-rate of C/2, meaning that this current will increase the state of charge of this battery by 50% in one hour.[5]
Since the unit of the C-rate is typically implied, some care is required when using it to avoid confusing it with the battery’s capacity to store a charge, which in the SI has unit coulomb with unit symbol C.
If both the (dis)charge current and the battery capacity in the C-rate ratio is multiplied by the battery voltage, the C-rate becomes a ratio of the (dis)charge power to the battery’s energy capacity. For example, when the 100 kWh battery in a Tesla Model S P100D is undergoing supercharging at 120 kW the C-rate is 1.2C and when that battery delivers its maximum power of 451 kW, its C-rate is 4.51C.

This unit charges batteries until they reach a specific voltage, then trickle charges them until disconnected.
All charging and discharging of batteries generates internal heat, and the amount of heat generated is roughly proportional to the current involved (a battery’s current state of charge, condition / history, etc. are also factors). As some batteries reach their full charge, cooling may also be observed.[6] Battery cells which have been built to allow higher C-rates than usual must make provision for increased heating. But high C-ratings are attractive to end users because such batteries can be charged more quickly, and produce higher current output in use. High C-rates typically require the charger to carefully monitor battery parameters such as terminal voltage and temperature to prevent overcharging and so damage to the cells. Such high charging rates are possible only with some battery types. Others will be damaged or possibly overheat or catch fire. Some batteries may even explode.[citation needed] For example, an automobile SLI (starting, lighting, ignition) lead-acid battery carries several risks of explosion.

A simple charger for NiCD batteries that outputs 300mA of 12V DC.
Type[edit]
Simple charger[edit]
A simple charger works by supplying a constant DC or pulsed DC power source to a battery being charged. A simple charger typically does not alter its output based on charging time or the charge on the battery. This simplicity means that a simple charger is inexpensive, but there are tradeoffs. Typically, a carefully designed simple charger takes longer to charge a battery because it is set to use a lower (i.e., safer) charging rate. Even so, many batteries left on a simple charger for too long will be weakened or destroyed due to over-charging. These chargers also vary in that they can supply either a constant voltage or a constant current, to the battery.
Simple AC-powered battery chargers usually have much higher ripple current and ripple voltage than other kinds of battery chargers because they are inexpensively designed and built. Generally, when the ripple current is within a battery’s manufacturer recommended level, the ripple voltage will also be well within the recommended level. The maximum ripple current for a typical 12 V 100 Ah VRLA battery is 5 amps. As long as the ripple current is not excessive (more than 3 to 4 times the battery manufacturer recommended level), the expected life of a ripple-charged VRLA battery will be within 3% of the life of a constant DC-charged battery.[7]
Fast charger[edit]
Fast chargers make use of control circuitry to rapidly charge the batteries without damaging any of the cells in the battery. The control circuitry can be built into the battery (generally for each cell) or in the external charging unit, or split between both. Most such chargers have a cooling fan to help keep the temperature of the cells at safe levels. Most fast chargers are also capable of acting as standard overnight chargers if used with standard NiMH cells that do not have the special control circuitry.
Three stage charger[edit]
To accelerate the charging time and provide continuous charging, an intelligent charger attempts to detect the state of charge and condition of the battery and applies a 3-stage charging scheme. The following description assumes a sealed lead acid traction battery at 25 °C. The first stage is referred to as «bulk absorption»; the charging current will be held high and constant and is limited by the capacity of the charger. When the voltage on the battery reaches its outgassing voltage (2.22 volts per cell) the charger switches to the second stage and the voltage is held constant (2.40 volts per cell). The delivered current will decline at the maintained voltage, and when the current reaches less than 0.005C the charger enters its third stage and the charger output will be held constant at 2.25 volts per cell. In the third stage, the charging current is very small 0.005C and at this voltage the battery can be maintained at full charge and compensate for self-discharge.
Induction-powered charger[edit]
Inductive battery chargers use electromagnetic induction to charge batteries. A charging station sends electromagnetic energy through inductive coupling to an electrical device, which stores the energy in the batteries. This is achieved without the need for metal contacts between the charger and the battery. Inductive battery chargers are commonly used in electric toothbrushes and other devices used in bathrooms. Because there are no open electrical contacts, there is no risk of electrocution. Nowadays it is being used to charge wireless phones.
Smart charger[edit]

Example of a smart charger for AA and AAA batteries with integrated display for status monitoring.
A smart charger can respond to the condition of a battery and modify its charging parameters accordingly, whereas «dumb» chargers apply a steady voltage, possibly through a fixed resistance. It should not be confused with a smart battery that contains a computer chip and communicates digitally with a smart charger about battery condition. A smart battery requires a smart charger (see Smart Battery Data).
Some smart chargers can also charge «dumb» batteries, which lack any internal electronics.
The output current of a smart charger depends upon the battery’s state. An intelligent charger may monitor the battery’s voltage, temperature or charge time to determine the optimum charge current or terminate charging.
For Ni-Cd and NiMH batteries, the voltage of the battery increases slowly during the charging process, until the battery is fully charged. After that, the voltage decreases, which indicates to an intelligent charger that the battery is fully charged. Such chargers are often labeled as a ΔV, «delta-V,» or sometimes «delta peak» charger, indicating that they monitor voltage change. This can cause even an intelligent charger not to sense that the batteries are already fully charged, and continue charging. Overcharging of the batteries may result. Many intelligent chargers employ a variety of cut-off systems to prevent overcharging.
A typical smart charger fast-charges a battery up to about 85% of its maximum capacity in less than an hour, then switches to trickle charging, which takes several hours to top off the battery to its full capacity.[8]
Motion-powered charger[edit]

Several companies have begun making devices that charge batteries using energy from human motion, such as walking. An example, made by Tremont Electric, consists of a magnet held between two springs that can charge a battery as the device is moved up and down. Such products have not yet achieved significant commercial success.[9]
A pedal-powered charger for mobile phones fitted into desks has been created for installation in public spaces, such as airports, railway stations and universities. They have been installed in a number of countries on several continents.[10]
Pulse charger[edit]
Some chargers use pulse technology, in which a series of electrical pulses is fed to the battery. The DC pulses have a strictly controlled rise time, pulse width, pulse repetition rate (frequency) and amplitude. This technology works with any size and type of battery, including automotive and valve-regulated ones.[11]
With pulse charging, high instantaneous voltages are applied without overheating the battery. In a Lead–acid battery, this breaks down lead-sulfate crystals, thus greatly extending the battery service life.[12]
Several kinds of pulse chargers are patented.[13][14][15] Others are open source hardware.
Some chargers use pulses to check the current battery state when the charger is first connected, then use constant current charging during fast charge, then use pulse mode to trickle charge it.[16]
Some chargers use «negative pulse charging,» also called «reflex charging» or «burp charging.» These chargers use both positive and brief negative current pulses. There is no significant evidence that negative pulse charging is more effective than ordinary pulse charging.
Solar charger[edit]

Varta Solar Charger Model 57082 with two 2100 mAh Ni-MH rechargeable batteries
Solar chargers convert light energy into low voltage DC current. They are generally portable, but can also be fixed mounted. Fixed mount solar chargers are also known as solar panels. These are often connected to the electrical grid via control and interface circuits, whereas portable solar chargers are used off-grid (i.e. cars, boats, or RVs).
Although portable solar chargers obtain energy only from the sun, they some can charge in low light like at sunset). Portable solar chargers are often used for trickle charging, though some can completely recharge batteries.
Timer-based charger[edit]
The output of a timer charger is terminated after a predetermined time interval. Timer chargers were the most common type for high-capacity Ni-Cd cells in the late 1990s to charge low-capacity consumer Ni-Cd cells.
Often a timer charger and set of batteries could be bought as a bundle and the charger time is set for those batteries specifically. If batteries of lower capacity are charged, then they would be overcharged, and if batteries of higher capacity were timer-charged, they would not reach full capacity.
Timer based chargers also had the drawback that charging batteries that were not fully discharged would result in over-charging.
Trickle charger[edit]
A trickle charger is typically low-current (usually between 5–1,500 mA). They are generally used to charge small capacity batteries (2–30 Ah). They are also used to maintain larger capacity batteries (> 30 Ah) in cars and boats. In larger applications, the current of the battery charger is only sufficient to provide trickle current. Depending on the technology of the trickle charger, it can be left connected to the battery indefinitely. Some battery types are not suitable for trickle charging. For instance, most Li-ion batteries cannot be safely trickle charged and can cause a fire or explosion.
Universal battery charger–analyzer[edit]
The most sophisticated chargers are used in critical applications (e.g. military or aviation batteries). These heavy-duty automatic “intelligent charging” systems can be programmed with complex charging cycles specified by the battery manufacturer. The best are universal (i.e. can charge all battery types), and include automatic capacity testing and analyzing functions.
USB-based charger[edit]


Australian and New Zealand power socket with USB charger socket
Since the Universal Serial Bus specification provides five-volt power, it is possible to use a USB cable to connect a device to a power supply. Products based on this approach include chargers for cellular phones, portable digital audio players, and tablet computers. They may be fully compliant USB peripheral devices or uncontrolled, simple chargers.
Power bank[edit]
| This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (September 2020) |

Single-cell USB power bank

Power bank with digital charging state display
A power or battery bank is a portable device that can supply energy and power from its built-in battery, typically through a USB port.
Power banks have various sizes and typically contain 18650 battery cells. The smallest power banks have a single cell. Moderately sized ones for mobile phones usually have few cells in a parallel circuit, and large ones additionally in two series. The power bank’s real meaning is polymer lithium batteries as a storage unit. The power bank is a lithium battery polymer storage device, through the IC chip for voltage regulation and then by connecting the power line charging or storage and then can be stored electricity released; power bank in the market is still relatively rare more is the standby battery mix called charge bank.[17]
Power banks are popular for charging smaller battery-powered devices with USB ports such as mobile phones and tablet computers and can be used as a power supply for various USB-powered accessories such as lights, small fans and external digital camera battery chargers. They usually recharge with a USB power supply. More recent power banks use USB-C and may feature an additional USB-B micro port for backwards compatibility.
The power bank includes a control circuit that both regulates charging of the battery and converts the battery voltage to 5.0 volts for the USB port.[citation needed]
Power banks may be able to detect a connection and power on automatically. If the current load is under a model-specific threshold for a specific duration, a power bank may power down automatically.[18]
Charging state is typically indicated through four LED lamps for each quartal, whereas some higher-end models feature an exact percentage display.[19][20]
Some power banks are able to deliver power wirelessly, some are equipped with an LED flashlight for casual near-distance illumination when necessary, and some have a pass-through charging feature which allows providing power through their USB ports while being charged themselves simultaneously.[21]
Some larger power banks have DC connectors (or barrel connectors) for higher power demands such as laptop computers.
Battery cases[edit]
Battery cases are small power banks attached to the rear side of a mobile phone like a case. Power may be delivered through the USB charging ports,[22] or wirelessly.[23]
Battery cases also exist in the form of a camera grip accessory, as was for the Nokia Lumia 1020.[24]
For mobile phones with removable rear cover, extended batteries exist. These are larger internal batteries attached with a dedicated, more spacious rear cover replacing the default one. A disadvantage is incompatibility with other phone cases while attached.[25]
Applications[edit]
Since a battery charger is intended to be connected to a battery, it may not have voltage regulation or filtering of the DC voltage output; it is cheaper to make them that way. Battery chargers equipped with both voltage regulation and filtering are sometimes termed battery eliminators.
Battery charger for vehicles[edit]
There are two main types of chargers used for vehicles:
- To recharge a fuel vehicle’s starter battery, where a modular charger is used; typically an 3-stage charger.
- To recharge an electric vehicle (EV) battery pack; see Charging station.
Chargers for car batteries come in varying ratings. Chargers that are rated up to two amperes may be used to maintain charge on parked vehicle batteries or for small batteries on garden tractors or similar equipment. A motorist may keep a charger rated a few amperes to ten or fifteen amperes for maintenance of automobile batteries or to recharge a vehicle battery that has accidentally discharged. Service stations and commercial garages will have a large charger to fully charge a battery in an hour or two; often these chargers can briefly source the hundreds of amperes required to crank an internal combustion engine starter.
Electric vehicle batteries[edit]
Electric vehicle battery chargers (ECS) come in a variety of brands and characteristics. These chargers vary from 1 kW to 7.5 kW maximum charge rate. Some use algorithm charge curves, others use constant voltage, constant current. Some are programmable by the end user through a CAN port, some have dials for maximum voltage and amperage, some are preset to specified battery pack voltage, amp-hour and chemistry. Prices range from $400 to $4500.
A 10 amp-hour battery could take 15 hours to reach a fully charged state from a fully discharged condition with a 1 amp charger as it would require roughly 1.5 times the battery’s capacity.
Public EV charging stations provide 6 kW (host power of 208 to 240 VAC off a 40 amp circuit). 6 kW will recharge an EV roughly 6 times faster than 1 kW overnight charging.
Rapid charging results in even faster recharge times and is limited only by available AC power, battery type, and the type of charging system.[26]
Onboard EV chargers (change AC power to DC power to recharge the EV’s pack) can be:
- Isolated: they make no physical connection between the A/C electrical mains and the batteries being charged. These typically employ some form of inductive connection between the grid and a charging vehicle. Some isolated chargers may be used in parallel. This allows for an increased charge current and reduced charging times. The battery has a maximum current rating that cannot be exceeded
- Non-isolated: the battery charger has a direct electrical connection to the A/C outlet’s wiring. Non-isolated chargers cannot be used in parallel.
Power-factor correction (PFC) chargers can more closely approach the maximum current the plug can deliver, shortening charging time.
Charge stations[edit]
Project Better Place was deploying a network of charging stations and subsidizing vehicle battery costs through leases and credits until filing for bankruptcy in May 2013.

Auxiliary charger designed to fit a variety of proprietary devices
Induction-powered charging[edit]
Researchers at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) have developed an electric transport system, called Online Electric Vehicle (OLEV), where the vehicles get their power needs from cables underneath the surface of the road via inductive charging, a power source is placed underneath the road surface and power is wirelessly picked up on the vehicle itself.[27]
Mobile phone charger[edit]

Micro USB mobile phone charger


Mobile phone charging station

A Xiaomi MDY-11-EP1 charger with fast charging support
Most mobile phone chargers are not really chargers, only power adapters that provide a power source for the charging circuitry which is almost always contained within the mobile phone. Older ones are notoriously diverse, having a wide variety of DC connector-styles and voltages, most of which are not compatible with other manufacturers’ phones or even different models of phones from a single manufacturer. Some higher-end models feature multiple ports are equipped with a display which indicates output current.[28] Some support communication protocols for charging parameters such as Qualcomm Quick Charge or MediaTek Pump Express.
Chargers for 12V automobile auxiliary power outlets may support input voltages of up to 24 or 32V DC to ensure compatibility, and are sometimes equipped with a display to monitor current or the voltage of the vehicle’s electrical system.[29]
China, the European Union and other countries are making a national standard on mobile phone chargers using the USB standard.[30] In June 2009, 10 of the world’s largest mobile phone manufacturers signed a Memorandum of Understanding to develop specifications for and support a microUSB-equipped common external power supply (EPS) for all data-enabled mobile phones sold in the EU.[31] On October 22, 2009, the International Telecommunication Union announced that microUSB would be the standard for a universal charger for mobile handsets.[32]
Stationary battery plants[edit]
Telecommunications, electric power, and computer uninterruptible power supply facilities may have very large standby battery banks (installed in battery rooms) to maintain critical loads for several hours during interruptions of primary grid power. Such chargers are permanently installed and equipped with temperature compensation, supervisory alarms for various system faults, and often redundant independent power supplies and redundant rectifier systems. Chargers for stationary battery plants may have adequate voltage regulation and filtration and sufficient current capacity to allow the battery to be disconnected for maintenance, while the charger supplies the direct current (DC) system load. The capacity of the charger is specified to maintain the system load and recharge a completely discharged battery within, say, 8 hours or other intervals.
Prolonging battery life[edit]
A properly designed charger can allow batteries to reach their full cycle life. Excess charging current, lengthy overcharging, or cell reversal in a multiple cell pack cause damage to cells and limit the life expectancy of a battery.
Most modern cell phones, laptop and tablet computers, and most electric vehicles use Lithium-ion batteries.[33] These batteries last longest if the battery is frequently charged; fully discharging the cells will degrade their capacity relatively quickly, but most such batteries are used in equipment which can sense the approach of full discharge and discontinue equipment use.[citation needed] When stored after charging, lithium battery cells degrade more while fully charged than if they are only 40-50% charged. As with all battery types, degradation also occurs faster at higher temperatures. Degradation in lithium-ion batteries is caused by an increased internal battery resistance often due to the cell oxidation. This decreases the efficiency of the battery, resulting in less net current available to be drawn from the battery.[citation needed] However, if Li-ION cells are discharged below a certain voltage a chemical reaction occurs that make them dangerous if recharged, which is why many such batteries in consumer goods now have an «electronic fuse» that permanently disables them if the voltage falls below a set level. The electronic fuse circuitry draws a small amount of current from the battery, which means that if a laptop battery is left for a long time without charging it, and with a very low initial state of charge, the battery may be permanently destroyed.
Motor vehicles, such as boats, RVs, ATVs, motorcycles, cars, trucks, etc. have used lead–acid batteries. These batteries employ a sulfuric acid electrolyte and can generally be charged and discharged without exhibiting memory effect, though sulfation (a chemical reaction in the battery which deposits a layer of sulfates on the lead) will occur over time. Typically sulfated batteries are simply replaced with new batteries, and the old ones recycled. Lead–acid batteries will experience substantially longer life when a maintenance charger is used to «float charge» the battery. This prevents the battery from ever being below 100% charge, preventing sulfate from forming. Proper temperature compensated float voltage should be used to achieve the best results.
See also[edit]
- Automotive alternator – battery charging device in car
- Electric bus#Charging
- Battery eliminator
- Battery management system
- Charge controller
- FuelRod – a kiosk-based charging service
- Lithium-ion battery
- Rechargeable alkaline battery
- Solar energy
- Solar lamp
- State of charge (batteries)
References[edit]
- ^ «Recharger definition and meaning — Collins English Dictionary». Archived from the original on 30 November 2016. Retrieved 26 March 2017.
- ^ «recharge — definition of recharge in English — Oxford Dictionaries». Archived from the original on March 25, 2014. Retrieved 26 March 2017.
- ^ Charger with output voltage compensation – United States Patent 7602151
- ^ Phil Weicker, A Systems Approach to Lithium-Ion Battery Management, Artech House, 2013 ISBN 1608076598 page 26
- ^ «A Guide to Understanding Battery Specifications MIT Electric Vehicle Team» (PDF). web.mit.edu. December 2008. Retrieved May 10, 2017.
- ^ «LM2576,LM3420,LP2951,LP2952 Battery Charging» (PDF). www.ti.com. July 2018. Retrieved July 29, 2018.
- ^ «Effects of AC Ripple Current on VRLA Battery Life» Archived 2011-07-22 at the Wayback Machine
by Emerson Network Power - ^ Dave Etchells. «The Great Battery Shootout».
- ^ Martin LaMonica, CNET. «Motion-powered gadget charger back on track.» Jul 1, 2011. Retrieved Jul 1, 2011.
- ^ «Delayed at the station? Get pedalling to charge your phone». Connexion France. 4 April 2017.
- ^
«AN913: Switch-Mode, Linear, and Pulse Charging Techniques for Li+ Battery in Mobile Phones and PDAs». Maxim. 2001. - ^ «Lead–acid battery sulfation». Archived from the original on 2007-04-02.
- ^ ««fast pulse battery charger» patent». 2003. Archived from the original on 2011-02-28. Retrieved 2008-01-21.
- ^
«Battery charger with current pulse regulation»
patented 1981
United States Patent 4355275 - ^
«Pulse-charge battery charger»
patented 1997
United States Patent 5633574 - ^ «Pulse Maintenance charging.» Archived March 9, 2012, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Yang; Gu; Guo; Chen (2019-09-20). «Comparative Life Cycle Assessment of Mobile Power Banks with Lithium-Ion Battery and Lithium-Ion Polymer Battery». Sustainability. 11 (19): 5148. doi:10.3390/su11195148. ISSN 2071-1050.
- ^ «Port detection for power banks». Texas Instruments. April 2016. Retrieved 2021-09-13.
- ^ «INIU Portable Power Bank 20,000mAh Battery Charger». Maris Review. 10 June 2021. Retrieved 22 August 2021.
- ^ Barton, Michael (2018-10-20). «Die RealPower PB-15000C Powerbank im Test — Techtest». techtest.org/ (in German). Retrieved 22 August 2021.
- ^ «How Pass Through Tech Lets You Use Power Banks In Creative Ways». RAVPower. 2018-06-01. Retrieved 2020-09-06.
- ^ Stein, Scott. «Apple Smart Battery Case for iPhone 6S review: Addressing the iPhone’s biggest weakness». CNET.
- ^ «Galaxy Note 7 S View Standing Cover and Battery Pack hands on». Android Authority. 2 August 2016.
- ^ «IRL: Testing the Nokia Lumia 1020’s optional camera grip / battery case». Engadget. 2013-09-16.
- ^ Klug, Brian (2013-07-23). «Samsung Galaxy S 4 ZeroLemon 7500 mAh Extended Battery Review». www.anandtech.com.
- ^ Fuji Heavy Speeds Up Recharging of R1e EV. Green Car Congress (2007-09-18). Retrieved on 2011-11-11.
- ^ Korean electric vehicle solution. Gizmag.com. Retrieved on 2011-11-11.
- ^ «Index of tested and reviewed USB power supplies/chargers». lygte-info.dk. lygte-info. Retrieved 22 August 2021.
- ^
Model: YSY-C009
Qualcomm Quick Charge 3.0
Input: 12-32V
Output: 4USB 5V-7A ( 35W Max ) / 1USB 9V/12V-1.8A - ^ China to work out national standard for mobile phone chargers. English.sina.com. Retrieved on 2011-11-11.
- ^ PC World:Universal Chargers are a Good Start Jan 2009
- ^ Oct 22, 2009, ITU press release Universal charger for mobile phone handsets
- ^ Mansoori, G. Ali; Enayati, Nader; Agyarko, L. Barnie (2015-11-05). Energy: Sources, Utilization, Legislation, Sustainability, Illinois as Model State. World Scientific. ISBN 9789814704021.
For other senses of this term, see AC adapter.
A battery charger, recharger, or simply charger[1][2] is a device that stores energy in a battery by running an electric current through it. The charging protocol (how much voltage or current for how long, and what to do when charging is complete) depends on the size and type of the battery being charged. Some battery types have high tolerance for overcharging (i.e., continued charging after the battery has been fully charged) and can be recharged by connection to a constant voltage source or a constant current source, depending on battery type. Simple chargers of this type must be manually disconnected at the end of the charge cycle. Other battery types use a timer to cut off when charging should be complete. Other battery types cannot withstand over-charging, becoming damaged (reduced capacity, reduced lifetime), over heating or even exploding. The charger may have temperature or voltage sensing circuits and a microprocessor controller to safely adjust the charging current and voltage, determine the state of charge, and cut off at the end of charge.
Chargers may elevate the output voltage proportionally with current to compensate for impedance in the wires.[3]
A trickle charger provides a relatively small amount of current, only enough to counteract self-discharge of a battery that is idle for a long time. Some battery types cannot tolerate trickle charging; attempts to do so may result in damage. Lithium-ion batteries cannot handle indefinite trickle charging.[4]
Slow battery chargers may take several hours to complete a charge. High-rate chargers may restore most capacity much faster, but high rate chargers can be more than some battery types can tolerate. Such batteries require active monitoring of the battery to protect it from overcharging. Electric vehicles ideally need high-rate chargers. For public access, installation of such chargers and the distribution support for them is an issue in the proposed adoption of electric cars.

C-rate[edit]
Charge and discharge rates are often given as C or C-rate, which is a measure of the rate at which a battery is charged or discharged relative to its capacity. The C-rate is defined as the charge or discharge current divided by the battery’s capacity to store an electrical charge. While rarely stated explicitly, the unit of the C-rate is h−1, equivalent to stating the battery’s capacity to store an electrical charge in unit hour times current in the same unit as the charge or discharge current. The C-rate is never negative, so whether it describes a charging or discharging process depends on the context.
For example, for a battery with a capacity of 500 mAh, a discharge rate of 5000 mA (i.e., 5 A) corresponds to a C-rate of 10C, meaning that such a current can discharge 10 such batteries in one hour. Likewise, for the same battery a charge current of 250 mA corresponds to a C-rate of C/2, meaning that this current will increase the state of charge of this battery by 50% in one hour.[5]
Since the unit of the C-rate is typically implied, some care is required when using it to avoid confusing it with the battery’s capacity to store a charge, which in the SI has unit coulomb with unit symbol C.
If both the (dis)charge current and the battery capacity in the C-rate ratio is multiplied by the battery voltage, the C-rate becomes a ratio of the (dis)charge power to the battery’s energy capacity. For example, when the 100 kWh battery in a Tesla Model S P100D is undergoing supercharging at 120 kW the C-rate is 1.2C and when that battery delivers its maximum power of 451 kW, its C-rate is 4.51C.

This unit charges batteries until they reach a specific voltage, then trickle charges them until disconnected.
All charging and discharging of batteries generates internal heat, and the amount of heat generated is roughly proportional to the current involved (a battery’s current state of charge, condition / history, etc. are also factors). As some batteries reach their full charge, cooling may also be observed.[6] Battery cells which have been built to allow higher C-rates than usual must make provision for increased heating. But high C-ratings are attractive to end users because such batteries can be charged more quickly, and produce higher current output in use. High C-rates typically require the charger to carefully monitor battery parameters such as terminal voltage and temperature to prevent overcharging and so damage to the cells. Such high charging rates are possible only with some battery types. Others will be damaged or possibly overheat or catch fire. Some batteries may even explode.[citation needed] For example, an automobile SLI (starting, lighting, ignition) lead-acid battery carries several risks of explosion.

A simple charger for NiCD batteries that outputs 300mA of 12V DC.
Type[edit]
Simple charger[edit]
A simple charger works by supplying a constant DC or pulsed DC power source to a battery being charged. A simple charger typically does not alter its output based on charging time or the charge on the battery. This simplicity means that a simple charger is inexpensive, but there are tradeoffs. Typically, a carefully designed simple charger takes longer to charge a battery because it is set to use a lower (i.e., safer) charging rate. Even so, many batteries left on a simple charger for too long will be weakened or destroyed due to over-charging. These chargers also vary in that they can supply either a constant voltage or a constant current, to the battery.
Simple AC-powered battery chargers usually have much higher ripple current and ripple voltage than other kinds of battery chargers because they are inexpensively designed and built. Generally, when the ripple current is within a battery’s manufacturer recommended level, the ripple voltage will also be well within the recommended level. The maximum ripple current for a typical 12 V 100 Ah VRLA battery is 5 amps. As long as the ripple current is not excessive (more than 3 to 4 times the battery manufacturer recommended level), the expected life of a ripple-charged VRLA battery will be within 3% of the life of a constant DC-charged battery.[7]
Fast charger[edit]
Fast chargers make use of control circuitry to rapidly charge the batteries without damaging any of the cells in the battery. The control circuitry can be built into the battery (generally for each cell) or in the external charging unit, or split between both. Most such chargers have a cooling fan to help keep the temperature of the cells at safe levels. Most fast chargers are also capable of acting as standard overnight chargers if used with standard NiMH cells that do not have the special control circuitry.
Three stage charger[edit]
To accelerate the charging time and provide continuous charging, an intelligent charger attempts to detect the state of charge and condition of the battery and applies a 3-stage charging scheme. The following description assumes a sealed lead acid traction battery at 25 °C. The first stage is referred to as «bulk absorption»; the charging current will be held high and constant and is limited by the capacity of the charger. When the voltage on the battery reaches its outgassing voltage (2.22 volts per cell) the charger switches to the second stage and the voltage is held constant (2.40 volts per cell). The delivered current will decline at the maintained voltage, and when the current reaches less than 0.005C the charger enters its third stage and the charger output will be held constant at 2.25 volts per cell. In the third stage, the charging current is very small 0.005C and at this voltage the battery can be maintained at full charge and compensate for self-discharge.
Induction-powered charger[edit]
Inductive battery chargers use electromagnetic induction to charge batteries. A charging station sends electromagnetic energy through inductive coupling to an electrical device, which stores the energy in the batteries. This is achieved without the need for metal contacts between the charger and the battery. Inductive battery chargers are commonly used in electric toothbrushes and other devices used in bathrooms. Because there are no open electrical contacts, there is no risk of electrocution. Nowadays it is being used to charge wireless phones.
Smart charger[edit]

Example of a smart charger for AA and AAA batteries with integrated display for status monitoring.
A smart charger can respond to the condition of a battery and modify its charging parameters accordingly, whereas «dumb» chargers apply a steady voltage, possibly through a fixed resistance. It should not be confused with a smart battery that contains a computer chip and communicates digitally with a smart charger about battery condition. A smart battery requires a smart charger (see Smart Battery Data).
Some smart chargers can also charge «dumb» batteries, which lack any internal electronics.
The output current of a smart charger depends upon the battery’s state. An intelligent charger may monitor the battery’s voltage, temperature or charge time to determine the optimum charge current or terminate charging.
For Ni-Cd and NiMH batteries, the voltage of the battery increases slowly during the charging process, until the battery is fully charged. After that, the voltage decreases, which indicates to an intelligent charger that the battery is fully charged. Such chargers are often labeled as a ΔV, «delta-V,» or sometimes «delta peak» charger, indicating that they monitor voltage change. This can cause even an intelligent charger not to sense that the batteries are already fully charged, and continue charging. Overcharging of the batteries may result. Many intelligent chargers employ a variety of cut-off systems to prevent overcharging.
A typical smart charger fast-charges a battery up to about 85% of its maximum capacity in less than an hour, then switches to trickle charging, which takes several hours to top off the battery to its full capacity.[8]
Motion-powered charger[edit]

Several companies have begun making devices that charge batteries using energy from human motion, such as walking. An example, made by Tremont Electric, consists of a magnet held between two springs that can charge a battery as the device is moved up and down. Such products have not yet achieved significant commercial success.[9]
A pedal-powered charger for mobile phones fitted into desks has been created for installation in public spaces, such as airports, railway stations and universities. They have been installed in a number of countries on several continents.[10]
Pulse charger[edit]
Some chargers use pulse technology, in which a series of electrical pulses is fed to the battery. The DC pulses have a strictly controlled rise time, pulse width, pulse repetition rate (frequency) and amplitude. This technology works with any size and type of battery, including automotive and valve-regulated ones.[11]
With pulse charging, high instantaneous voltages are applied without overheating the battery. In a Lead–acid battery, this breaks down lead-sulfate crystals, thus greatly extending the battery service life.[12]
Several kinds of pulse chargers are patented.[13][14][15] Others are open source hardware.
Some chargers use pulses to check the current battery state when the charger is first connected, then use constant current charging during fast charge, then use pulse mode to trickle charge it.[16]
Some chargers use «negative pulse charging,» also called «reflex charging» or «burp charging.» These chargers use both positive and brief negative current pulses. There is no significant evidence that negative pulse charging is more effective than ordinary pulse charging.
Solar charger[edit]

Varta Solar Charger Model 57082 with two 2100 mAh Ni-MH rechargeable batteries
Solar chargers convert light energy into low voltage DC current. They are generally portable, but can also be fixed mounted. Fixed mount solar chargers are also known as solar panels. These are often connected to the electrical grid via control and interface circuits, whereas portable solar chargers are used off-grid (i.e. cars, boats, or RVs).
Although portable solar chargers obtain energy only from the sun, they some can charge in low light like at sunset). Portable solar chargers are often used for trickle charging, though some can completely recharge batteries.
Timer-based charger[edit]
The output of a timer charger is terminated after a predetermined time interval. Timer chargers were the most common type for high-capacity Ni-Cd cells in the late 1990s to charge low-capacity consumer Ni-Cd cells.
Often a timer charger and set of batteries could be bought as a bundle and the charger time is set for those batteries specifically. If batteries of lower capacity are charged, then they would be overcharged, and if batteries of higher capacity were timer-charged, they would not reach full capacity.
Timer based chargers also had the drawback that charging batteries that were not fully discharged would result in over-charging.
Trickle charger[edit]
A trickle charger is typically low-current (usually between 5–1,500 mA). They are generally used to charge small capacity batteries (2–30 Ah). They are also used to maintain larger capacity batteries (> 30 Ah) in cars and boats. In larger applications, the current of the battery charger is only sufficient to provide trickle current. Depending on the technology of the trickle charger, it can be left connected to the battery indefinitely. Some battery types are not suitable for trickle charging. For instance, most Li-ion batteries cannot be safely trickle charged and can cause a fire or explosion.
Universal battery charger–analyzer[edit]
The most sophisticated chargers are used in critical applications (e.g. military or aviation batteries). These heavy-duty automatic “intelligent charging” systems can be programmed with complex charging cycles specified by the battery manufacturer. The best are universal (i.e. can charge all battery types), and include automatic capacity testing and analyzing functions.
USB-based charger[edit]


Australian and New Zealand power socket with USB charger socket
Since the Universal Serial Bus specification provides five-volt power, it is possible to use a USB cable to connect a device to a power supply. Products based on this approach include chargers for cellular phones, portable digital audio players, and tablet computers. They may be fully compliant USB peripheral devices or uncontrolled, simple chargers.
Power bank[edit]
| This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (September 2020) |

Single-cell USB power bank

Power bank with digital charging state display
A power or battery bank is a portable device that can supply energy and power from its built-in battery, typically through a USB port.
Power banks have various sizes and typically contain 18650 battery cells. The smallest power banks have a single cell. Moderately sized ones for mobile phones usually have few cells in a parallel circuit, and large ones additionally in two series. The power bank’s real meaning is polymer lithium batteries as a storage unit. The power bank is a lithium battery polymer storage device, through the IC chip for voltage regulation and then by connecting the power line charging or storage and then can be stored electricity released; power bank in the market is still relatively rare more is the standby battery mix called charge bank.[17]
Power banks are popular for charging smaller battery-powered devices with USB ports such as mobile phones and tablet computers and can be used as a power supply for various USB-powered accessories such as lights, small fans and external digital camera battery chargers. They usually recharge with a USB power supply. More recent power banks use USB-C and may feature an additional USB-B micro port for backwards compatibility.
The power bank includes a control circuit that both regulates charging of the battery and converts the battery voltage to 5.0 volts for the USB port.[citation needed]
Power banks may be able to detect a connection and power on automatically. If the current load is under a model-specific threshold for a specific duration, a power bank may power down automatically.[18]
Charging state is typically indicated through four LED lamps for each quartal, whereas some higher-end models feature an exact percentage display.[19][20]
Some power banks are able to deliver power wirelessly, some are equipped with an LED flashlight for casual near-distance illumination when necessary, and some have a pass-through charging feature which allows providing power through their USB ports while being charged themselves simultaneously.[21]
Some larger power banks have DC connectors (or barrel connectors) for higher power demands such as laptop computers.
Battery cases[edit]
Battery cases are small power banks attached to the rear side of a mobile phone like a case. Power may be delivered through the USB charging ports,[22] or wirelessly.[23]
Battery cases also exist in the form of a camera grip accessory, as was for the Nokia Lumia 1020.[24]
For mobile phones with removable rear cover, extended batteries exist. These are larger internal batteries attached with a dedicated, more spacious rear cover replacing the default one. A disadvantage is incompatibility with other phone cases while attached.[25]
Applications[edit]
Since a battery charger is intended to be connected to a battery, it may not have voltage regulation or filtering of the DC voltage output; it is cheaper to make them that way. Battery chargers equipped with both voltage regulation and filtering are sometimes termed battery eliminators.
Battery charger for vehicles[edit]
There are two main types of chargers used for vehicles:
- To recharge a fuel vehicle’s starter battery, where a modular charger is used; typically an 3-stage charger.
- To recharge an electric vehicle (EV) battery pack; see Charging station.
Chargers for car batteries come in varying ratings. Chargers that are rated up to two amperes may be used to maintain charge on parked vehicle batteries or for small batteries on garden tractors or similar equipment. A motorist may keep a charger rated a few amperes to ten or fifteen amperes for maintenance of automobile batteries or to recharge a vehicle battery that has accidentally discharged. Service stations and commercial garages will have a large charger to fully charge a battery in an hour or two; often these chargers can briefly source the hundreds of amperes required to crank an internal combustion engine starter.
Electric vehicle batteries[edit]
Electric vehicle battery chargers (ECS) come in a variety of brands and characteristics. These chargers vary from 1 kW to 7.5 kW maximum charge rate. Some use algorithm charge curves, others use constant voltage, constant current. Some are programmable by the end user through a CAN port, some have dials for maximum voltage and amperage, some are preset to specified battery pack voltage, amp-hour and chemistry. Prices range from $400 to $4500.
A 10 amp-hour battery could take 15 hours to reach a fully charged state from a fully discharged condition with a 1 amp charger as it would require roughly 1.5 times the battery’s capacity.
Public EV charging stations provide 6 kW (host power of 208 to 240 VAC off a 40 amp circuit). 6 kW will recharge an EV roughly 6 times faster than 1 kW overnight charging.
Rapid charging results in even faster recharge times and is limited only by available AC power, battery type, and the type of charging system.[26]
Onboard EV chargers (change AC power to DC power to recharge the EV’s pack) can be:
- Isolated: they make no physical connection between the A/C electrical mains and the batteries being charged. These typically employ some form of inductive connection between the grid and a charging vehicle. Some isolated chargers may be used in parallel. This allows for an increased charge current and reduced charging times. The battery has a maximum current rating that cannot be exceeded
- Non-isolated: the battery charger has a direct electrical connection to the A/C outlet’s wiring. Non-isolated chargers cannot be used in parallel.
Power-factor correction (PFC) chargers can more closely approach the maximum current the plug can deliver, shortening charging time.
Charge stations[edit]
Project Better Place was deploying a network of charging stations and subsidizing vehicle battery costs through leases and credits until filing for bankruptcy in May 2013.

Auxiliary charger designed to fit a variety of proprietary devices
Induction-powered charging[edit]
Researchers at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) have developed an electric transport system, called Online Electric Vehicle (OLEV), where the vehicles get their power needs from cables underneath the surface of the road via inductive charging, a power source is placed underneath the road surface and power is wirelessly picked up on the vehicle itself.[27]
Mobile phone charger[edit]

Micro USB mobile phone charger


Mobile phone charging station

A Xiaomi MDY-11-EP1 charger with fast charging support
Most mobile phone chargers are not really chargers, only power adapters that provide a power source for the charging circuitry which is almost always contained within the mobile phone. Older ones are notoriously diverse, having a wide variety of DC connector-styles and voltages, most of which are not compatible with other manufacturers’ phones or even different models of phones from a single manufacturer. Some higher-end models feature multiple ports are equipped with a display which indicates output current.[28] Some support communication protocols for charging parameters such as Qualcomm Quick Charge or MediaTek Pump Express.
Chargers for 12V automobile auxiliary power outlets may support input voltages of up to 24 or 32V DC to ensure compatibility, and are sometimes equipped with a display to monitor current or the voltage of the vehicle’s electrical system.[29]
China, the European Union and other countries are making a national standard on mobile phone chargers using the USB standard.[30] In June 2009, 10 of the world’s largest mobile phone manufacturers signed a Memorandum of Understanding to develop specifications for and support a microUSB-equipped common external power supply (EPS) for all data-enabled mobile phones sold in the EU.[31] On October 22, 2009, the International Telecommunication Union announced that microUSB would be the standard for a universal charger for mobile handsets.[32]
Stationary battery plants[edit]
Telecommunications, electric power, and computer uninterruptible power supply facilities may have very large standby battery banks (installed in battery rooms) to maintain critical loads for several hours during interruptions of primary grid power. Such chargers are permanently installed and equipped with temperature compensation, supervisory alarms for various system faults, and often redundant independent power supplies and redundant rectifier systems. Chargers for stationary battery plants may have adequate voltage regulation and filtration and sufficient current capacity to allow the battery to be disconnected for maintenance, while the charger supplies the direct current (DC) system load. The capacity of the charger is specified to maintain the system load and recharge a completely discharged battery within, say, 8 hours or other intervals.
Prolonging battery life[edit]
A properly designed charger can allow batteries to reach their full cycle life. Excess charging current, lengthy overcharging, or cell reversal in a multiple cell pack cause damage to cells and limit the life expectancy of a battery.
Most modern cell phones, laptop and tablet computers, and most electric vehicles use Lithium-ion batteries.[33] These batteries last longest if the battery is frequently charged; fully discharging the cells will degrade their capacity relatively quickly, but most such batteries are used in equipment which can sense the approach of full discharge and discontinue equipment use.[citation needed] When stored after charging, lithium battery cells degrade more while fully charged than if they are only 40-50% charged. As with all battery types, degradation also occurs faster at higher temperatures. Degradation in lithium-ion batteries is caused by an increased internal battery resistance often due to the cell oxidation. This decreases the efficiency of the battery, resulting in less net current available to be drawn from the battery.[citation needed] However, if Li-ION cells are discharged below a certain voltage a chemical reaction occurs that make them dangerous if recharged, which is why many such batteries in consumer goods now have an «electronic fuse» that permanently disables them if the voltage falls below a set level. The electronic fuse circuitry draws a small amount of current from the battery, which means that if a laptop battery is left for a long time without charging it, and with a very low initial state of charge, the battery may be permanently destroyed.
Motor vehicles, such as boats, RVs, ATVs, motorcycles, cars, trucks, etc. have used lead–acid batteries. These batteries employ a sulfuric acid electrolyte and can generally be charged and discharged without exhibiting memory effect, though sulfation (a chemical reaction in the battery which deposits a layer of sulfates on the lead) will occur over time. Typically sulfated batteries are simply replaced with new batteries, and the old ones recycled. Lead–acid batteries will experience substantially longer life when a maintenance charger is used to «float charge» the battery. This prevents the battery from ever being below 100% charge, preventing sulfate from forming. Proper temperature compensated float voltage should be used to achieve the best results.
See also[edit]
- Automotive alternator – battery charging device in car
- Electric bus#Charging
- Battery eliminator
- Battery management system
- Charge controller
- FuelRod – a kiosk-based charging service
- Lithium-ion battery
- Rechargeable alkaline battery
- Solar energy
- Solar lamp
- State of charge (batteries)
References[edit]
- ^ «Recharger definition and meaning — Collins English Dictionary». Archived from the original on 30 November 2016. Retrieved 26 March 2017.
- ^ «recharge — definition of recharge in English — Oxford Dictionaries». Archived from the original on March 25, 2014. Retrieved 26 March 2017.
- ^ Charger with output voltage compensation – United States Patent 7602151
- ^ Phil Weicker, A Systems Approach to Lithium-Ion Battery Management, Artech House, 2013 ISBN 1608076598 page 26
- ^ «A Guide to Understanding Battery Specifications MIT Electric Vehicle Team» (PDF). web.mit.edu. December 2008. Retrieved May 10, 2017.
- ^ «LM2576,LM3420,LP2951,LP2952 Battery Charging» (PDF). www.ti.com. July 2018. Retrieved July 29, 2018.
- ^ «Effects of AC Ripple Current on VRLA Battery Life» Archived 2011-07-22 at the Wayback Machine
by Emerson Network Power - ^ Dave Etchells. «The Great Battery Shootout».
- ^ Martin LaMonica, CNET. «Motion-powered gadget charger back on track.» Jul 1, 2011. Retrieved Jul 1, 2011.
- ^ «Delayed at the station? Get pedalling to charge your phone». Connexion France. 4 April 2017.
- ^
«AN913: Switch-Mode, Linear, and Pulse Charging Techniques for Li+ Battery in Mobile Phones and PDAs». Maxim. 2001. - ^ «Lead–acid battery sulfation». Archived from the original on 2007-04-02.
- ^ ««fast pulse battery charger» patent». 2003. Archived from the original on 2011-02-28. Retrieved 2008-01-21.
- ^
«Battery charger with current pulse regulation»
patented 1981
United States Patent 4355275 - ^
«Pulse-charge battery charger»
patented 1997
United States Patent 5633574 - ^ «Pulse Maintenance charging.» Archived March 9, 2012, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Yang; Gu; Guo; Chen (2019-09-20). «Comparative Life Cycle Assessment of Mobile Power Banks with Lithium-Ion Battery and Lithium-Ion Polymer Battery». Sustainability. 11 (19): 5148. doi:10.3390/su11195148. ISSN 2071-1050.
- ^ «Port detection for power banks». Texas Instruments. April 2016. Retrieved 2021-09-13.
- ^ «INIU Portable Power Bank 20,000mAh Battery Charger». Maris Review. 10 June 2021. Retrieved 22 August 2021.
- ^ Barton, Michael (2018-10-20). «Die RealPower PB-15000C Powerbank im Test — Techtest». techtest.org/ (in German). Retrieved 22 August 2021.
- ^ «How Pass Through Tech Lets You Use Power Banks In Creative Ways». RAVPower. 2018-06-01. Retrieved 2020-09-06.
- ^ Stein, Scott. «Apple Smart Battery Case for iPhone 6S review: Addressing the iPhone’s biggest weakness». CNET.
- ^ «Galaxy Note 7 S View Standing Cover and Battery Pack hands on». Android Authority. 2 August 2016.
- ^ «IRL: Testing the Nokia Lumia 1020’s optional camera grip / battery case». Engadget. 2013-09-16.
- ^ Klug, Brian (2013-07-23). «Samsung Galaxy S 4 ZeroLemon 7500 mAh Extended Battery Review». www.anandtech.com.
- ^ Fuji Heavy Speeds Up Recharging of R1e EV. Green Car Congress (2007-09-18). Retrieved on 2011-11-11.
- ^ Korean electric vehicle solution. Gizmag.com. Retrieved on 2011-11-11.
- ^ «Index of tested and reviewed USB power supplies/chargers». lygte-info.dk. lygte-info. Retrieved 22 August 2021.
- ^
Model: YSY-C009
Qualcomm Quick Charge 3.0
Input: 12-32V
Output: 4USB 5V-7A ( 35W Max ) / 1USB 9V/12V-1.8A - ^ China to work out national standard for mobile phone chargers. English.sina.com. Retrieved on 2011-11-11.
- ^ PC World:Universal Chargers are a Good Start Jan 2009
- ^ Oct 22, 2009, ITU press release Universal charger for mobile phone handsets
- ^ Mansoori, G. Ali; Enayati, Nader; Agyarko, L. Barnie (2015-11-05). Energy: Sources, Utilization, Legislation, Sustainability, Illinois as Model State. World Scientific. ISBN 9789814704021.
На чтение 12 мин Просмотров 18.6к. Опубликовано 03.08.2021 Обновлено 10.02.2022
Содержание
- Выбор зарядного устройство для смартфона
- Типы зарядных устройств
- Виды разъемов для зарядки
- Lightning
- MicroUSB
- USB Type C
- Параметры тока
- Наличие быстрой зарядки
- Выбор USB провода
- Форма кабеля
- Материал оплетки
- Сила пропускного тока
- Плюсы и минусы магнитных штекеров
- Качество китайских зарядок и проводов
Каждый мобильный прибор комплектуется зарядным устройством. Но оно может выйти из строя или потеряться. Также проблема приобретения ЗУ может встать при покупке устройства с рук или если нужен адаптер для других видов работы (в автомобиле и т.п.).
Выбор зарядного устройство для смартфона
Чтобы правильно выбрать зарядное устройство, надо знать технические характеристики, определяющие потребительские свойства ЗУ. Не менее важно понимать, на что и в какую сторону влияет несоответствие параметров адаптера заданным в технических условиях на мобильный гаджет.
Типы зарядных устройств
Деление зарядок на виды можно выполнить по разным категориям — по схемотехнике, по КПД и т.п. Но для потребителя важнее, где и как он может применить ЗУ, поэтому лучше категорировать адаптеры по исполнению.
- Сетевые зарядные устройства. Включаются в бытовую сеть 220 вольт. В 99+ процентах случаев выполняются по импульсной схеме.
- Автомобильные зарядные устройства. Включаются в бортсеть автомобиля через разъем прикуривателя. Для упрощения схемотехники могут быть выполнены по линейной схеме.
- Зарядники от разъема USB. Представляют собой обычный шнур с разъемом USB A на одной стороне и соответствующим коннектором на другой.
В большинстве случаев мобильные гаджеты комплектуются штатным сетевым адаптером, а остальные виды надо покупать отдельно.

Виды разъемов для зарядки
В начале эпохи мобильных гаджетов производители устройств делали разъемы каждый под себя. Это приносило им определенную дополнительную прибыль, так как владелец был вынужден приобретать только оригинальные зарядные устройства – другие не соответствовали по форме штекера или напряжению, подобрать подходящий вариант было сложно. Неудобства приходилось терпеть пользователям. Сейчас ситуация изменилась, ведущие участники рынка мобильных гаджетов стремятся к стандартизации. В большинстве устройств используется три типа терминалов для зарядки и передачи данных.
Lightning
Этот разъем применяется в мобильных устройствах Apple. Он пришел на замену громоздкому 30-пиновому терминалу и является стандартом для гаджетов производства этой фирмы, хотя есть сведения о планах компании перейти на USB Type С. Разъем является двухсторонним – подключать можно как одной, так и другой стороной. Такое решение при разработке коннектора было применено впервые, и на тот момент это был прорыв.

Преимуществами такого разъема является прочная конструкция, а также способность очищаться от загрязнений при подключении.

Если проанализировать расположение и назначение выводов в разъеме, становится очевидно, что функционал пинов несимметричен. Направление подключения определяется в момент соединения встроенной микросхемой. Эта же микросхема служит защитой от подделок.
| Номер | Маркировка | Функциональное назначение |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Земля (0V) |
| 2 | L0p | Линия (полоса) 0 + |
| 3 | L0n | Линия (полоса) 0 — |
| 4 | ID0 | Идентификация 0 |
| 5 | PWR | Напряжение питания |
| 6 | L1n | Линия (полоса) 1 — |
| 7 | L1p | Линия (полоса) 1 + |
| 8 | ID1 | Идентификация 0 |
MicroUSB

Этот разъем пришел на смену коннектору MiniUSB. Его видимое отличие от предыдущей модификации – размеры. На самом деле у microUSB появились и другие плюсы:
- увеличенная прочность и более длительный ресурс;
- повышенная надежность соединения.
К минусам относится необходимость позиционирования при подключении (разъем не является двусторонним подобно Type С или Lightning). Это привело к сокращению сектора использования данного терминала.

На шнурах для зарядки применяется вилка типа В, так как телефон в большинстве случаев выступает в роли периферийного устройства.
| № | Обозначение | Функция | Цвет изоляции провода |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Vbus | Напряжение питания (+5 вольт) | Красный |
| 2 | D- | DATA- | Белый |
| 3 | D+ | DATA+ | Зеленый |
| 4 | ID | ON-the-GO ID | |
| 5 | GND | Общий провод (0V) | Черный |
Провод 4 определяет назначение разъема в режиме On-the-Go (когда дополнительные устройства подключаются к телефону напрямую) – соединение с общим проводом означает, что конец подключается к хосту, а если контакт ни с чем не соединен, коннектор подключается к периферийному устройству.
USB Type C

Самым распространенным и одновременно самым перспективным является разъем для мобильной техники USB Type C. Разработан для применения с гаджетами с операционной системой Андроид, но его используют и производители другой мобильной техники.

Овальная вилка содержит два ряда контактов – один ряд нумеруется от A1 до А12, другой – от B1 до B12. Контакты расположены симметрично, поэтому штекер можно вставлять любой стороной и никаких микросхем для определения положения не требуется. Контакты можно сгруппировать по функционалу.
| Номер пина | Маркировка | Назначение |
|---|---|---|
| 1,12 (A1, A12, B1, B12) | GND | 0 вольт |
| 4,9 | Vbus | + напряжения питания |
| 2,3,10,11 | TX+, TX-, RX+,RX- | Шина USB3.0 |
| 6,7 | D+, D- | Шина USB 2.0 |
| 5 | CC | Пин конфигурации |
| 8 | SBU | Дополнительный канал |
Шина питания распараллелена на два пина. Это позволяет передавать дополнительную мощность, которая у некоторых кабелей может достигать 100 ватт. Это подразумевает ток до 20 ампер при напряжении питания 5 вольт. Обычный шнур рассчитан на ток 1,5 или 3 ампера.
Выводы приемника (RX) и передатчика (TX) шины USB 3.0 в кабеле перекрещены (перекроссированы), поэтому то, что с одной стороны является входом приемника, на другой стороне подключается к выходу передатчика и наоборот. Пин конфигурации определяет:
- наличие подключенного периферийного устройства;
- потребные параметры питания периферии (ток и напряжение);
- некоторые другие функции в определенных ситуациях.
Пин SBU используется очень редко.
Разъем USB Type С обладает намного большими возможностями относительно Lightning и лучшими перспективами развития. Поэтому сведения о возможном переходе техники Apple на этот тип коннектора имеют под собой основания.
Для наглядности подкрепим видеоролик.
Параметры тока
При выборе типа зарядных устройств в первую очередь надо обратить внимание на один из самых важных параметров – наибольший ток, который может выдавать адаптер. Чем меньше ток, тем дольше будет заряжаться аккумулятор, а если ЗУ рассчитано на совсем малый ток (0,5 А и меньше), то оно может отключаться по защите от перегрузки. Такая зарядка подойдет для заряжания беспроводных наушников и других маломощных устройств.
Для смартфонов среднего класса вполне подойдет ЗУ с током 1,0..1,5 А (1000..1500 мА). Для телефонов посерьезнее и другой техники с емкими АКБ надо выбирать адаптеры с током 1,5..3 А. Если устройство поддерживает функцию быстрой зарядки, то потребуется ток не менее 5 А. Самый простой способ определить потребный ток – посмотреть параметры на корпусе родного ЗУ и приобрести зарядку с не меньшей или большей мощностью.

Наличие быстрой зарядки
Некоторые смартфоны поддерживают быструю зарядку. Она производится большим током, поэтому надо выбирать ЗУ с соответствующими параметрами (от 5 А). Производители утверждают, что такой режим не повреждает аккумулятор, но это заявление достаточно лукавое. Явно вывести из строя аккумуляторную батарею повышенный в разумных пределах зарядный ток не может, но при этом значительно (в разы) сокращается ресурс батареи. Выбор за пользователем. Кроме того, не каждый гаджет поддерживает такой режим. Поэтому, прежде чем платить за дополнительную мощность, надо выяснить, понадобится ли подобная функция вообще.
Читайте также
Заряжаем аккумулятор телефона без зарядного устройства
Выбор USB провода
Кроме сетевого адаптера, надо обратить внимание и на провод. Он выполняется съемным и продается отдельно.
Форма кабеля
Кабели чаще всего бывают плоские или круглые. На ток и время заряда форма влияния не оказывает, это просто удобство использования (большей частью, личные предпочтения):
- плоский шнур меньше склонен к запутыванию;
- круглый занимает меньше места в скрученном положении.
Большее значение имеет длина кабеля – чем он короче, тем он меньше ограничивает ток зарядки. В коротком шнуре меньше потерь, что важно при зарядке от PowerBank. Зато длинный в некоторых случаях предпочтительнее – когда надо работать и одновременно заряжать гаджет, а источник питания находится далеко. В отдельных ситуациях удобно применять шнур, завитый в форме пружины – он также не склонен к запутыванию.
Спиральный шнур можно сделать самостоятельно. Для этого его надо намотать на подходящую оправку (концы можно закрепить, например, пластиковыми хомутами) и прогреть кабель феном. После полного остывания получившийся спиральный шнур готов к применению. Если фена нет, намотанный на оправку провод можно ненадолго опустить в кипящую воду, следя, чтобы жидкость не попала в разъемы.

Материал оплетки
Большинство шнуров выпускаются в обычной ПВХ-изоляции. Она имеет отличные электрические свойства, но ее устойчивость к механическому воздействию, включая перетирание, невысока. Также у такого шнура высока вероятность перелома проводников при сгибании под малыми радиусами. Поэтому часто кабели для зарядки дополняют оплеткой, которая выполняется из различных материалов (по убыванию защитных свойств):
- металлическая – самая прочная, но наименее гибкая оплетка;
- плетеная оболочка из полимеров;
- гладкая оплетка из пластика (наиболее бюджетный вариант).
На электрические характеристики дополнительная оболочка влияния не оказывает, при ремонте кабеля ее часто просто удаляют.
Сила пропускного тока
От толщины проводника и материала зависит, будет ли он греться при достаточно большом токе зарядки. На самом деле, провода, сечением 0,75 кв. мм (диаметр без изоляции 1 мм) разумной длины хватит, чтобы без проблем работать при токах до 8 А. Этого хватит на все случаи жизни. Провода меньшего диаметра не используются по соображениям механической прочности. Да и определить даже на глаз сечение проводящей жилы непросто – она находится под изоляцией.
Но если есть подозрения, что толщина проводников все же невелика по отношению к заявленному току, лучше воздержаться от покупки такого шнура. Возможен перегрев и даже возгорание. Окончательно ток заряда определяется по меньшему из двух значений – наибольший ток адаптера или наибольший допустимый ток шнура.
Плюсы и минусы магнитных штекеров
Не так давно в продажу стали поступать магнитные разъемы для телефона, которые быстро обрели популярность. Суть такого коннектора в том, что в гнездо телефона вставляется дополнительный переходник, с одной стороны которого установлен штекер, соответствующий терминалу телефона, а с другой – две (или больше) магнитные контактные площадки.
На шнуре к зарядному устройству находится ответная часть, которая сопрягается с переходником посредством магнитного поля, создаваемого постоянными магнитами. На расстоянии порядка одного-двух сантиметров обе стороны притягиваются и становятся в рабочее положение. При этом не надо искать визуально или на ощупь точное местонахождение розетки на телефоне и не надо определять полярность подключения для разъема microUSB. Особенно это удобно при езде в автомобиле. При этом шнур лишний раз не перекручивается, что продлевает срок его службы.
Механические нагрузки на гнездо телефона сокращаются в несколько раз, что также продлевает период надежной работы. К плюсам также можно отнести защиту внутреннего разъема гаджета от попадания грязи.

Но у такого коннектора есть и недостатки. В первую очередь, это появление лишнего разъемного контакта, а значит дополнительного источника ненадежности. Кроме того, этот контакт несколько снижает зарядный ток и увеличивает время пополнения энергии. Загрязнение открытой поверхности коннектора может привести к ухудшению качества контакта и к еще большему ограничению зарядного тока, а магнит способен притягивать металлическую пыль. Твердые частицы на поверхности также мешают надежному сопряжению.
Многие магнитные разъемы имеют всего две контактные площадки, предназначенные для зарядного напряжения. Это означает, что для передачи данных в шнуре просто нет проводников, и, например, скачать файлы с компьютера с помощью такого кабеля нельзя. Для тех шнуров, что такую возможность дают, нужен специальный переходник с большими размерами. Он заметно выступает за габариты гаджета. И немаловажный факт – стоит магнитный шнур дороже, чем обычный.

Видео-обзор магнитных кабелей.
Качество китайских зарядок и проводов
Дешевые зарядные устройства и кабели от неизвестных производителей из Юго-Восточной Азии могут быть некачественными. В первую очередь это относится к применению в проводниках вместо меди сплавов неизвестного состава. Это может привести к перегреву или ограничению зарядного тока. К этому же эффекту приводят заниженное сечение проводов и некачественная пайка (а то и обжимное соединение) разъемов. Упрощенная схемотехника может привести к неоптимальным режимам зарядки, что снижает ресурс АКБ. А самое простое, но неприятное – срок жизни таких устройств, как правило, недолог, и подвести такой адаптер может в любой момент.
Выбирать зарядное устройство для мобильного гаджета надо осознанно. В противном случае не избежать не только разочарований, но и технических проблем. А в худшем случае еще и финансовых потерь.